Abstract
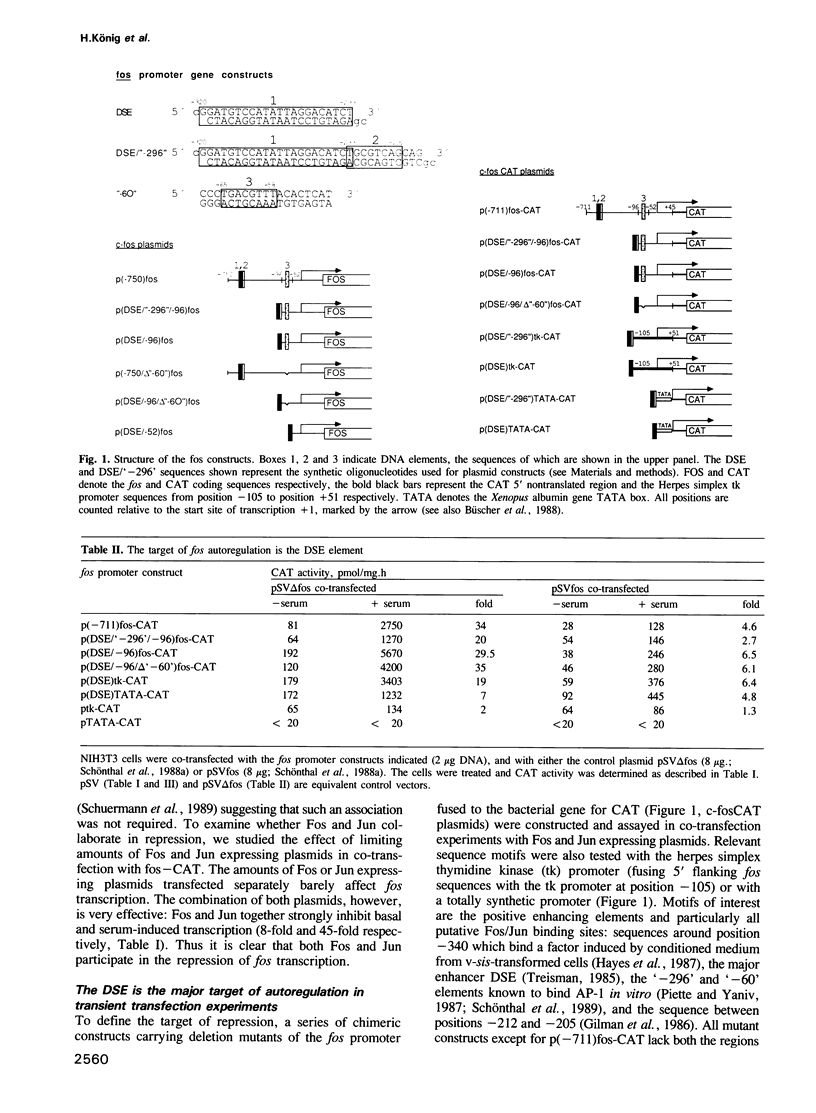
Fos and Jun co-operatively repress the fos promoter. Removal of all putative Fos/Jun binding sites from the fos promoter neither obliterates the repression by Fos/Jun in transient cotransfection experiments in NIH3T3 cells nor the turn-off kinetics of serum-induced fos expression in stably transfected NIH3T3 cells. The dyad symmetry element (DSE) suffices to subject a promoter to this type of repression. However, one of the putative Fos/Jun binding sites (-292 to -299 and thus located immediately adjacent to the DSE), determines the very low level of basal expression.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher M., Rahmsdorf H. J., Litfin M., Karin M., Herrlich P. Activation of the c-fos gene by UV and phorbol ester: different signal transduction pathways converge to the same enhancer element. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):301–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Janssen-Timmen U., Mattéi M. G., Zerial M., Bravo R., Charnay P. Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the mouse zinc finger gene Krox-20: multiple gene products and coregulation with the proto-oncogene c-fos. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):787–797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., MacConnell W. P., van Straaten F., Verma I. M. Structure of the FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus genome: molecular cloning of its associated helper virus and the cellular homolog of the v-fos gene from mouse and human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):914–921. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erba H. P., Eddy R., Shows T., Kedes L., Gunning P. Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the human gamma-actin gene: differential evolution, location, and expression of the cytoskeletal beta- and gamma-actin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1775–1789. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. An AP1-binding site in the c-fos gene can mediate induction by epidermal growth factor and 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1327–1331. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. c-fos sequence necessary for basal expression and induction by epidermal growth factor, 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate and the calcium ionophore. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3490–3502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Simon M. C., Roeder R. G. Multiple sequence elements in the c-fos promoter mediate induction by cAMP. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):198–211. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
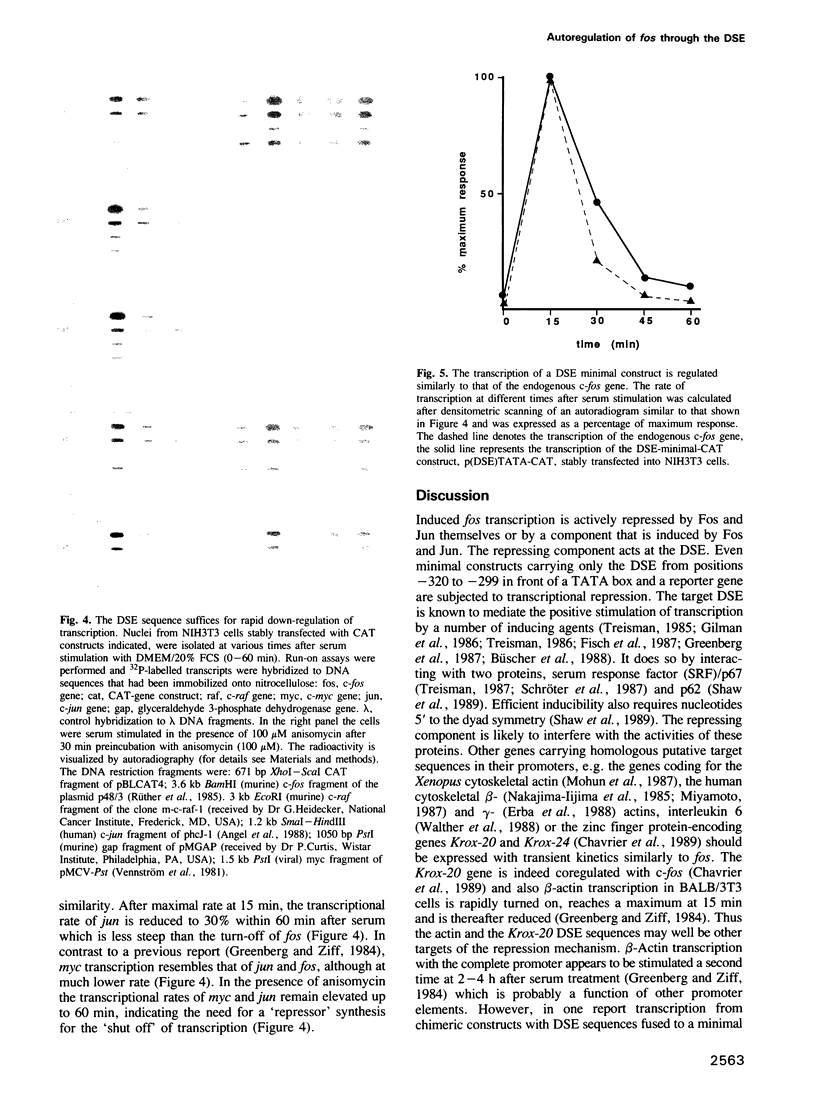
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Siegfried Z., Ziff E. B. Mutation of the c-fos gene dyad symmetry element inhibits serum inducibility of transcription in vivo and the nuclear regulatory factor binding in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1217–1225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Allegretto E. A., Karin M., Green M. R. A family of immunologically related transcription factors that includes multiple forms of ATF and AP-1. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1216–1226. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Kitchen A. M., Cochran B. H. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos regulatory region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1272–1276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlich P., Ponta H. 'Nuclear' oncogenes convert extracellular stimuli into changes in the genetic program. Trends Genet. 1989 Apr;5(4):112–115. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Jones N. C. Identification of factors that interact with the E1A-inducible adenovirus E3 promoter. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1132–1146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G. Nucleotide sequence of the human beta-actin promoter 5' flanking region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):9095–9095. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.9095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T., Garrett N., Treisman R. Xenopus cytoskeletal actin and human c-fos gene promoters share a conserved protein-binding site. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):667–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima-Iijima S., Hamada H., Reddy P., Kakunaga T. Molecular structure of the human cytoplasmic beta-actin gene: interspecies homology of sequences in the introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6133–6137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Yaniv M. Two different factors bind to the alpha-domain of the polyoma virus enhancer, one of which also interacts with the SV40 and c-fos enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1331–1337. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Schönthal A., Angel P., Litfin M., Rüther U., Herrlich P. Posttranscriptional regulation of c-fos mRNA expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1643–1659. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Wagner E. F., Müller R. Analysis of the differentiation-promoting potential of inducible c-fos genes introduced into embryonal carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1775–1781. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Sisson J. C., Verma I. M. Transcriptional autoregulation of the proto-oncogene fos. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):314–319. doi: 10.1038/334314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorpp M., Kugler W., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. Hepatocyte-specific promoter element HP1 of the Xenopus albumin gene interacts with transcriptional factors of mammalian hepatocytes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Purification of intercalator-released p67, a polypeptide that interacts specifically with the c-fos serum response element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10145–10158. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuermann M., Neuberg M., Hunter J. B., Jenuwein T., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Müller R. The leucine repeat motif in Fos protein mediates complex formation with Jun/AP-1 and is required for transformation. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Büscher M., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H., Hattori K., Chiu R., Karin M., Herrlich P. The Fos and Jun/AP-1 proteins are involved in the downregulation of Fos transcription. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):629–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Herrlich P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H. Requirement for fos gene expression in the transcriptional activation of collagenase by other oncogenes and phorbol esters. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Schröter H., Nordheim A. The ability of a ternary complex to form over the serum response element correlates with serum inducibility of the human c-fos promoter. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification and purification of a polypeptide that binds to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2711–2717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Moscovici C., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning of the avian myelocytomatosis virus genome and recovery of infectious virus by transfection of chicken cells. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):625–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.625-631.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Graham W. R. The fos oncogene. Adv Cancer Res. 1987;49:29–52. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60793-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther Z., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Transcriptional regulation of the interferon-beta 2/B cell differentiation factor BSF-2/hepatocyte-stimulating factor gene in human fibroblasts by other cytokines. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):974–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Fos C-terminal mutations block down-regulation of c-fos transcription following serum stimulation. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4193–4202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





