Abstract
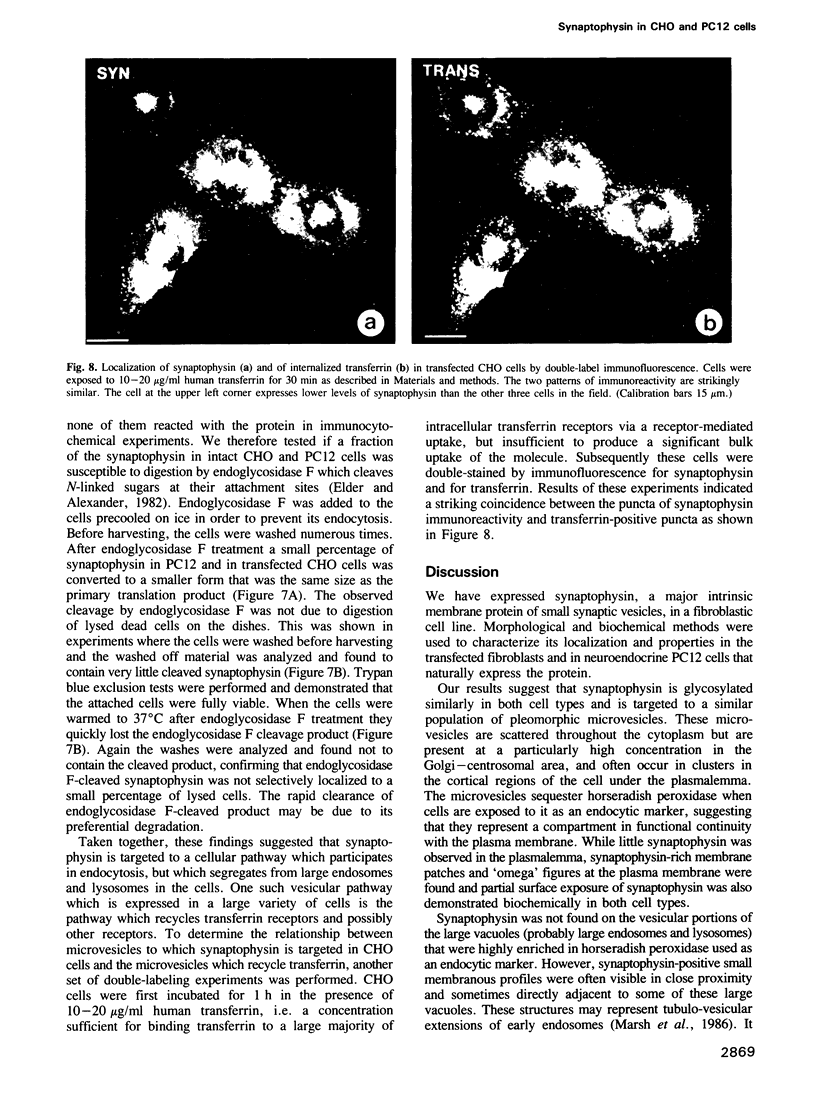
Synaptophysin, an integral membrane protein of small synaptic vesicles, was expressed by transfection in fibroblastic CHO-K1 cells. The properties and localization of synaptophysin were compared between transfected CHO-K1 cells and native neuroendocrine PC12 cells. Both cell types similarly glycosylate synaptophysin and sort it into indistinguishable microvesicles. These become labeled by endocytic markers and are primarily concentrated below the plasmalemma and at the area of the Golgi complex and the centrosomes. A small pool of synaptophysin is transiently found on the plasma membrane. In CHO-K1 cells synaptophysin co-localizes with transferrin that has been internalized by receptor-mediated endocytosis. These findings suggest that synaptophysin in transfected CHO-K1 cells and neuroendocrine PC12 cells is directed into a pathway of recycling microvesicles which, in CHO cells, is shown to coincide with that of the transferrin receptor. They further indicate that fibroblasts have the ability to sort a synaptic vesicle membrane protein. Our results suggest a pathway for the evolution of small synaptic vesicles from a constitutively recycling organelle which is normally present in all cells.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Falck J. R., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Visualization of acidic organelles in intact cells by electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4838–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G., Orci L., Brown M. S., Garcia-Segura L. M., Goldstein J. L. Ultrastructural analysis of crystalloid endoplasmic reticulum in UT-1 cells and its disappearance in response to cholesterol. J Cell Sci. 1983 Sep;63:1–20. doi: 10.1242/jcs.63.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates G. W., Schlabach M. R. The reaction of ferric salts with transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3228–3232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley K. M., Floor E., Kelly R. B. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding p38, a major synaptic vesicle protein. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2447–2456. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Moretti M., Donini S. D., Walter U., Lohmann S. M. Heterogeneous distribution of the cAMP receptor protein RII in the nervous system: evidence for its intracellular accumulation on microtubules, microtubule-organizing centers, and in the area of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):189–203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Alexander S. endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F: endoglycosidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that cleaves both high-mannose and complex glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4540–4544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann U., Bause E., Legler G., Ploegh H. Novel mannosidase inhibitor blocking conversion of high mannose to complex oligosaccharides. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):755–758. doi: 10.1038/307755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze H. J., Slot J. W., Schwartz A. L. Membranes of sorting organelles display lateral heterogeneity in receptor distribution. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1715–1723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: concepts emerging from the LDL receptor system. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Ouimet C., Greengard P. A 38,000-dalton membrane protein (p38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Transmembrane topography and evolutionary conservation of synaptophysin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1268–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. A., Tokuyasu K. T., Dutton A. H., Singer S. J. An improved procedure for immunoelectron microscopy: ultrathin plastic embedding of immunolabeled ultrathin frozen sections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5744–5747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. The cell biology of the nerve terminal. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90174-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leube R. E., Kaiser P., Seiter A., Zimbelmann R., Franke W. W., Rehm H., Knaus P., Prior P., Betz H., Reinke H. Synaptophysin: molecular organization and mRNA expression as determined from cloned cDNA. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3261–3268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe A. W., Madeddu L., Kelly R. B. Endocrine secretory granules and neuronal synaptic vesicles have three integral membrane proteins in common. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):51–59. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Griffiths G., Dean G. E., Mellman I., Helenius A. Three-dimensional structure of endosomes in BHK-21 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2899–2903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I in nerve terminals: selective association with small synaptic vesicles. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1209–1211. doi: 10.1126/science.6438799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Jahn R., Di Gioia G., Stukenbrok H., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Protein p38: an integral membrane protein specific for small vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2511–2527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Hille A., Lee R. W., Zanini A., De Camilli P., Huttner W. B. Secretogranins I and II: two tyrosine-sulfated secretory proteins common to a variety of cells secreting peptides by the regulated pathway. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1999–2011. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W. The LDL receptor gene: a mosaic of exons shared with different proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):815–822. doi: 10.1126/science.2988123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Lottspeich F., Greengard P., Mehl E., Jahn R. A synaptic vesicle protein with a novel cytoplasmic domain and four transmembrane regions. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1142–1144. doi: 10.1126/science.3120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Lottspeich F., Greengard P., Mehl E., Jahn R. The cDNA and derived amino acid sequences for rat and human synaptophysin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9607–9607. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Russell D. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. 42 bp element from LDL receptor gene confers end-product repression by sterols when inserted into viral TK promoter. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1061–1069. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90713-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M., Vassalli P. Lectin-binding sites as markers of Golgi subcompartments: proximal-to-distal maturation of oligosaccharides. J Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;97(4):1243–1248. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.4.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Application of cryoultramicrotomy to immunocytochemistry. J Microsc. 1986 Aug;143(Pt 2):139–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb02772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble W. S., Scheller R. H. Molecular biology of synaptic vesicle-associated proteins. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jun;11(6):241–242. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Identification and localization of synaptophysin, an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000 characteristic of presynaptic vesicles. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro D. J., Tycko B., Fluss S. R., Maxfield F. R. Segregation of transferrin to a mildly acidic (pH 6.5) para-Golgi compartment in the recycling pathway. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):789–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Camilli P., Navone F. Regulated secretory pathways of neurons and their relation to the regulated secretory pathway of endocrine cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:461–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]