Abstract
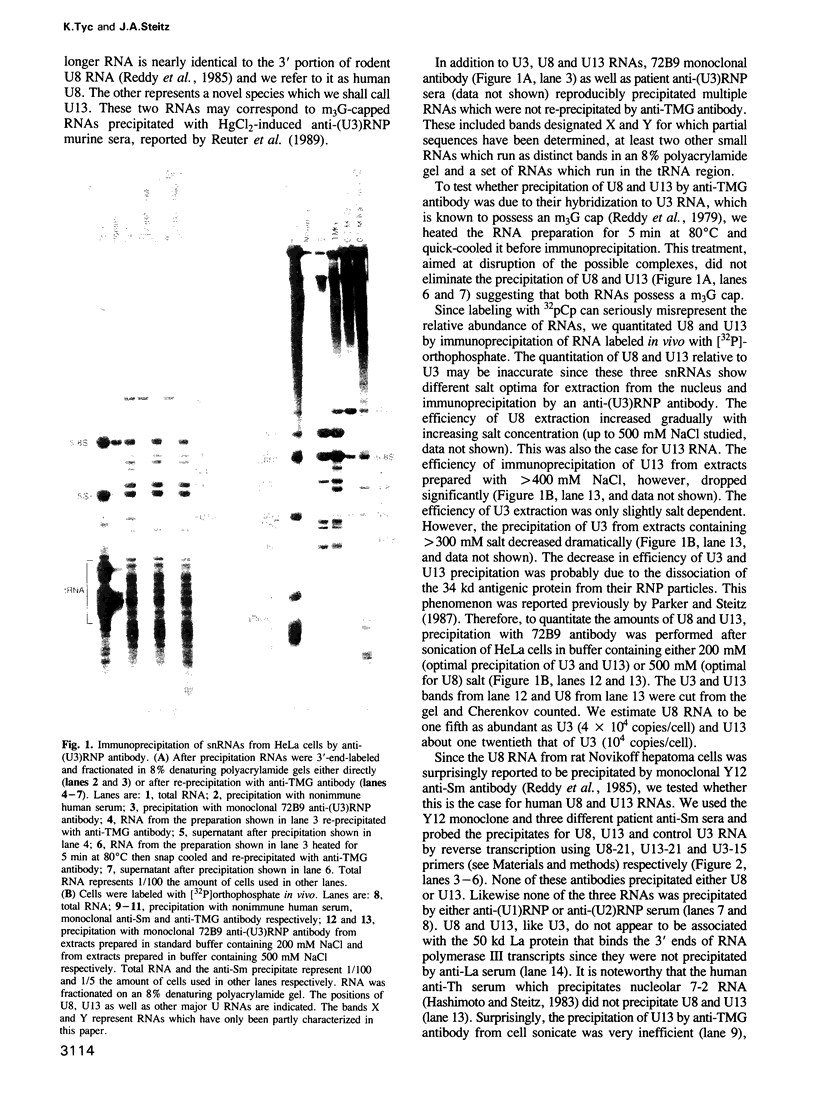
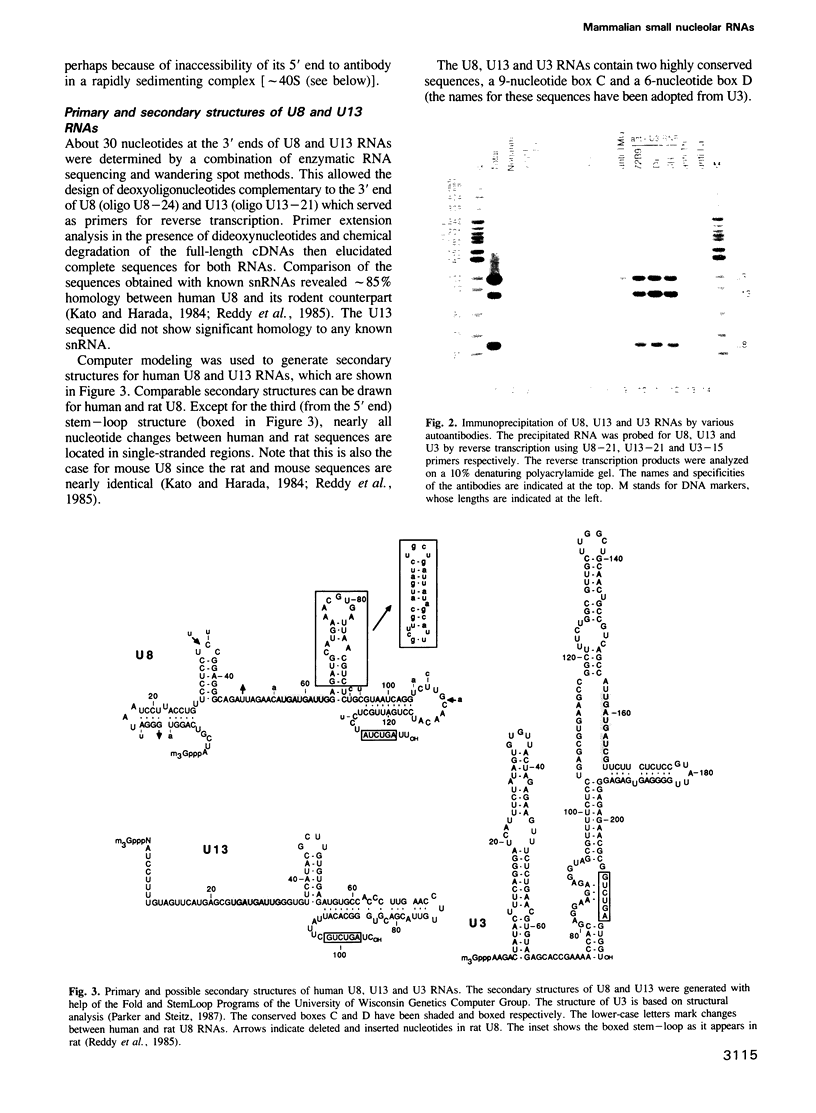
Using anti-(U3)RNP autoantibodies, we have isolated and characterized two additional small nucleolar RNAs from HeLa cells, which are less abundant than U3 RNA. Both RNAs possess a trimethylguanosine cap as judged by precipitation with anti-TMG antibody, but are not precipitated by either anti-Sm or anti-La antibodies. In addition, both RNAs are not precipitable by anti-Th serum, which recognizes another nucleolar RNP autoantigen. Sequence analysis revealed that one of these RNAs, 136 nucleotides long, is the human U8 homolog; while the other, 105 nucleotides long, represents a novel species which we designate U13. Both RNAs share with U3 two conserved sequences (boxes C and D). The role of one or both of these boxes in binding the common 34 kd antigenic protein, otherwise known as fibrillarin, is discussed. Fractionation of HeLa cells revealed that U8 and U13, like U3, reside in the nucleolus. In glycerol gradients both RNAs cosediment with larger structures possibly representing ribosomal precursors. We propose that U3, U8 and U13 comprise a new subset of mammalian snRNPs whose roles in ribosome biogenesis are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. S., Herrera R. J., Luhrmann R., Lizardi P. M. Isolation and partial characterization of U1-U6 small RNAs from Bombyx mori. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):117–125. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachellerie J. P., Michot B., Raynal F. Recognition signals for mouse pre-rRNA processing. A potential role for U3 nucleolar RNA. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 May;9(1-2):79–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00777477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzik J. P., Van Doren K., Hirsh D., Steitz J. A. Trans splicing involves a novel form of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):559–562. doi: 10.1038/335559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch H., Reddy R., Rothblum L., Choi Y. C. SnRNAs, SnRNPs, and RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:617–654. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvet J. P., Pederson T. Base-pairing interactions between small nuclear RNAs and nuclear RNA precursors as revealed by psoralen cross-linking in vivo. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Keller W. 3' cleavage and polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in vitro requires a poly(A) polymerase, a cleavage factor, and a snRNP. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):875–889. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch R. J., Kanaya S., Earl P. L. A model for the involvement of the small nucleolar RNA (U3) in processing eukaryotic ribosomal RNA. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 May;9(1-2):75–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00777476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Phy M: an RNase activity specific for U and A residues useful in RNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3133–3142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P., Reddy R., Busch H. Multiple states of U3 RNA in Novikoff hepatoma nucleoli. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5421–5425. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P., Reddy R., Henning D., Busch H. The nucleotide sequence of nuclear U6 (4.7 S) RNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8901–8906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. Sequential association of nucleolar 7-2 RNA with two different autoantigens. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1379–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Wolin S. L., Rinke J., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins are a subclass of La ribonucleoproteins: further characterization of the Ro and La small ribonucleoproteins from uninfected mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1138–1149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Konings D. A., Cesareni G. The yeast homologue of U3 snRNA. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2145–2155. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen C., Stebbins-Boaz B., Gerbi S. A. Nucleotide sequence determination and secondary structure of Xenopus U3 snRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2127–2148. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass S., Craig N., Sollner-Webb B. Primary processing of mammalian rRNA involves two adjacent cleavages and is not species specific. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2891–2898. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Harada F. Nucleotide sequence of nuclear 5.4 S RNA of mouse cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 16;782(2):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss T., Tóth M., Solymosy F. Plant small nuclear RNAs. Nucleolar U3 snRNA is present in plants: partial characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):259–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R. Pre-mRNA splicing by complementation with purified human U1, U2, U4/U6 and U5 snRNPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9415–9429. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A. Fractionation of HeLa cell nuclear extracts reveals minor small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8408–8412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. A., Lerner M. R., Janeway C. A., Jr, Steitz J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to nucleic acid-containing cellular constituents: probes for molecular biology and autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2737–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Hardin J. A., Steitz J. A. Two novel classes of small ribonucleoproteins detected by antibodies associated with lupus erythematosus. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.6164096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Ochs R. L., Reddy R., Cook R. G., Yeoman L. C., Tan E. M., Reichlin M., Busch H. Purification and partial characterization of a nucleolar scleroderma antigen (Mr = 34,000; pI, 8.5) rich in NG,NG-dimethylarginine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14304–14310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. Cap trimethylation of U snRNA is cytoplasmic and dependent on U snRNP protein binding. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):905–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., De Robertis E. M. Nuclear segregation of U2 snRNA requires binding of specific snRNP proteins. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell E. S., Martin T. E. A low-molecular-weight RNA from mouse ascites cells that hybridizes to both 18S rRNA and mRNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7261–7265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Hinterberger M., Pettersson I., Steitz J. A. Autoantibodies to the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein in a patient with scleroderma-polymyositis overlap syndrome. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):560–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montzka K. A., Steitz J. A. Additional low-abundance human small nuclear ribonucleoproteins: U11, U12, etc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8885–8889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowry K. L., Steitz J. A. snRNP mediators of 3' end processing: functional fossils? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Nov;13(11):447–451. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs R. L., Lischwe M. A., Spohn W. H., Busch H. Fibrillarin: a new protein of the nucleolus identified by autoimmune sera. Biol Cell. 1985;54(2):123–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1985.tb00387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. A., Bruzik J. P., Steitz J. A. An in vitro interaction between the human U3 snRNP and 28S rRNA sequences near the alpha-sarcin site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10493–10509. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. A., Steitz J. A. Structural analysis of the human U3 ribonucleoprotein particle reveal a conserved sequence available for base pairing with pre-rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2899–2913. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Simmons T., Shuster E. O., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Genetic analysis of small nuclear RNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: viable sextuple mutant. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3150–3159. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Mimori T., Gottlieb E., Steitz J. A. The structure of mammalian small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Identification of multiple protein components reactive with anti-(U1)ribonucleoprotein and anti-Sm autoantibodies. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5907–5914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter G. L., Brennwald P. J., Holm K. A., Wise J. A. The sequence of U3 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe suggests structural divergence of this snRNA between metazoans and unicellular eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10131–10152. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R. Compilation of small RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16 (Suppl):r71–r85. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.suppl.r71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Busch H. Nucleotide sequence of nucleolar U3B RNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11097–11105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Busch H. Primary and secondary structure of U8 small nuclear RNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):10930–10935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Li W. Y., Henning D., Choi Y. C., Nohga K., Busch H. Characterization and subcellular localization of 7-8 S RNAs of Novikoff hepatoma. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8452–8457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer G., Pollard K. M., Penning C. A., Ochs R. L., Lischwe M. A., Busch H., Tan E. M. Monoclonal autoantibody from a (New Zealand black x New Zealand white)F1 mouse and some human scleroderma sera target an Mr 34,000 nucleolar protein of the U3 RNP particle. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jul;30(7):793–800. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter R., Tessars G., Vohr H. W., Gleichmann E., Lührmann R. Mercuric chloride induces autoantibodies against U3 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein in susceptible mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):237–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Wise J. A., Swerdlow H., Mak A., Guthrie C. Small nuclear RNAs from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: unexpected diversity in abundance, size, and molecular complexity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8097–8101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroke I. L., Weiner A. M. Genes and pseudogenes for rat U3A and U3B small nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 20;184(2):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90372-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Galli G., Busslinger M., Birnstiel M. L. The cDNA sequences of the sea urchin U7 small nuclear RNA suggest specific contacts between histone mRNA precursor and U7 RNA during RNA processing. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2801–2807. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh D., Busch H., Reddy R. Isolation and characterization of a human U3 small nucleolar RNA gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 30;137(3):1133–1140. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tague B. W., Gerbi S. A. Processing of the large rRNA precursor: two proposed categories of RNA-RNA interactions in eukaryotes. J Mol Evol. 1984;20(3-4):362–367. doi: 10.1007/BF02104742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey D. A yeast small nuclear RNA is required for normal processing of pre-ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4169–4175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02763.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey D., Guthrie C. Deletion of a yeast small nuclear RNA gene impairs growth. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3873–3878. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinh-Rohlik Q., Maxwell E. S. Homologous genes for mouse 4.5S hybRNA are found in all eukaryotes and their low molecular weight RNA transcripts intermolecularly hybridize with eukaryotic 18S ribosomal RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6041–6056. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. Distribution of newly formed ribosomal proteins in HeLa cell fractions. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):767–772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. A., Weiner A. M. Dictyostelium small nuclear RNA D2 is homologous to rat nucleolar RNA U3 and is encoded by a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagorski J., Tollervey D., Fournier M. J. Characterization of an SNR gene locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae that specifies both dispensible and essential small nuclear RNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3282–3290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G., Penman S. Small RNA species of the HeLa cell: metabolism and subcellular localization. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]