Abstract
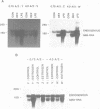
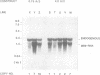
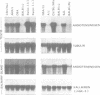
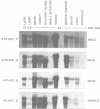
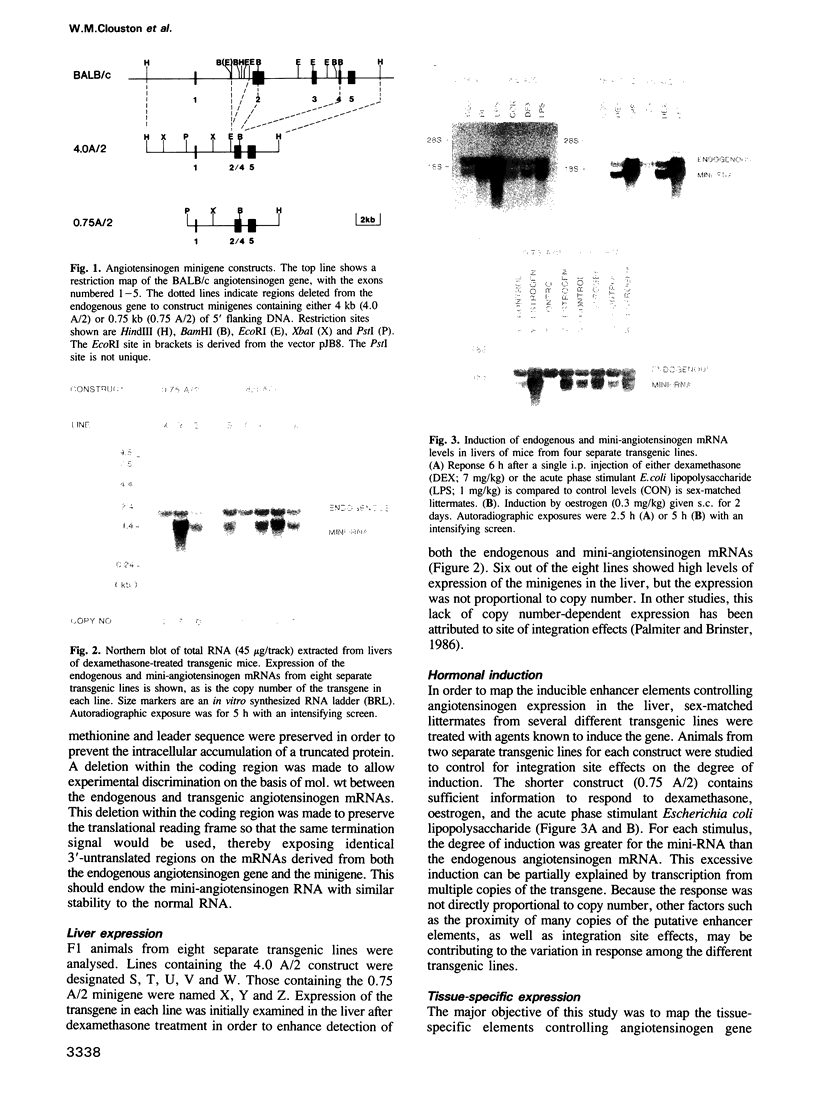
Angiotensinogen is the precursor of the potent vasoactive peptide angiotensin II, and is therefore an important determinant of blood pressure and electrolyte homeostasis. In order to map the tissue-specific and inducible enhancer elements governing angiotensinogen gene expression in transgenic mice, we constructed minigenes containing either 0.75 kb or 4 kb or 5' flanking DNA from the BALB/c angiotensinogen gene. Sequences necessary and sufficient to mediate induction by glucocorticoids, oestrogen and bacterial endotoxin were contained on the minigene bearing 0.75 kb of DNA upstream of the capsite. This construct was also able to confer tissue specificity in the majority of organs producing angiotensinogen. In the testis and salivary gland, differences between the donor (BALB/c) and recipient (Swiss) strains were responsible for the apparently aberrant expression of the minigene constructs. The genetic lesion responsible for these expression polymorphisms has been characterized using recombinant inbred mice. An EcoRI restriction fragment length polymorphism which co-segregates with the angiotensinogen expression phenotypes into many inbred mouse strains is also described.
Full text
PDF
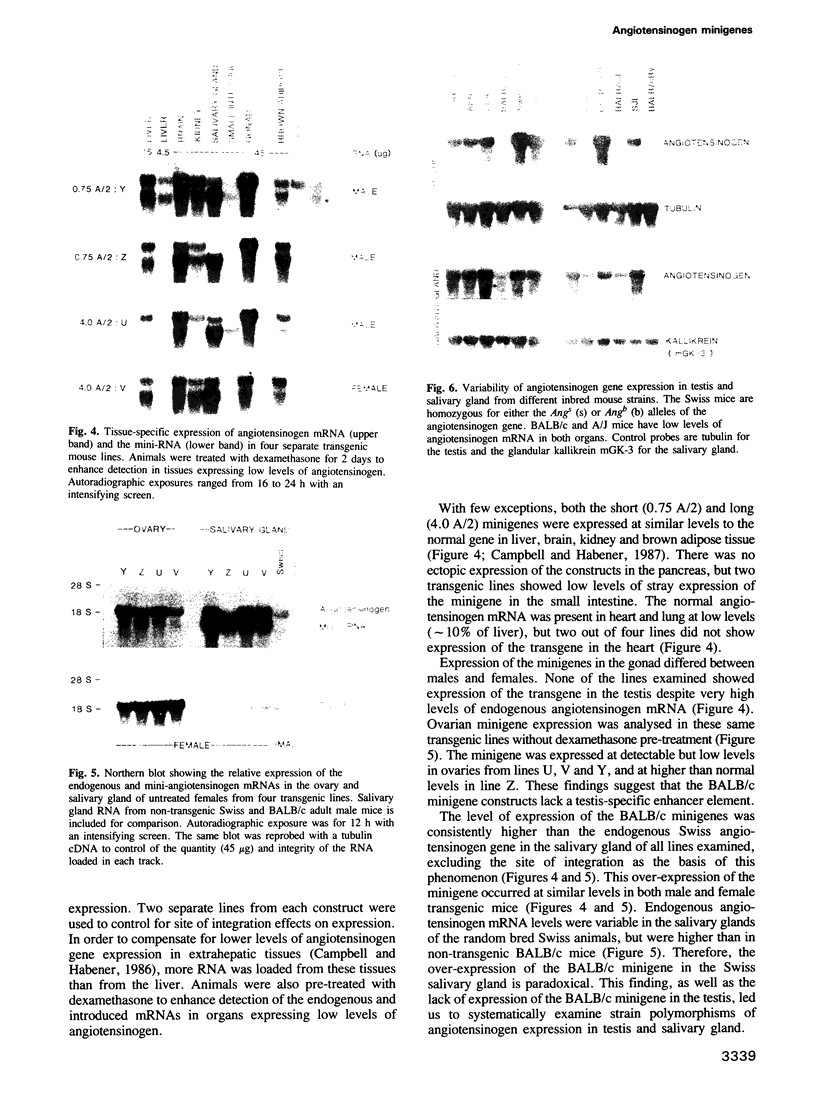




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blom van Assendelft G., Hanscombe O., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. The beta-globin dominant control region activates homologous and heterologous promoters in a tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90630-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Philippe J., Campbell D. J., Habener J. F. Novel expression of the angiotensinogen gene in a rat pancreatic islet cell line. Transcriptional regulation by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16148–16154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Nadal-Ginard B. Developmentally induced, muscle-specific trans factors control the differential splicing of alternative and constitutive troponin T exons. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):793–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90617-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. J., Bouhnik J., Coezy E., Pinet F., Clauser E., Menard J., Corvol P. Characterization of precursor and secreted forms of rat angiotensinogen. Endocrinology. 1984 Mar;114(3):776–785. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-3-776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. J. Circulating and tissue angiotensin systems. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI112768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. J., Habener J. F. Angiotensinogen gene is expressed and differentially regulated in multiple tissues of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):31–39. doi: 10.1172/JCI112566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. J., Habener J. F. Cellular localization of angiotensinogen gene expression in brown adipose tissue and mesentery: quantification of messenger ribonucleic acid abundance using hybridization in situ. Endocrinology. 1987 Nov;121(5):1616–1626. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-5-1616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clauser E., Bouhnik J., Coezy E., Corvol P., Menard J. Synthesis and release of immunoreactive angiotensinogen by rat liver slices. Endocrinology. 1983 Apr;112(4):1188–1193. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-4-1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouston W. M., Evans B. A., Haralambidis J., Richards R. I. Molecular cloning of the mouse angiotensinogen gene. Genomics. 1988 Apr;2(3):240–248. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouston W. M., Richards R. I. An allelic polymorphism of the angiotensinogen gene in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):822–822. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Stivaletta L. A., Smith M. L. Analysis of gene expression using episomal mouse dihydrofolate reductase minigenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7025–7042. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner M. E., Leonard C. M., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Developmental regulation of constitutive and inducible expression of hepatocyte-specific genes in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3049–3051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Matthai R., Huppi K., Roderick T., Potter M. Genes that modify expression of major urinary proteins in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2705–2712. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J. Circulating versus local renin-angiotensin system in cardiovascular homeostasis. Circulation. 1988 Jun;77(6 Pt 2):I4–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Ellison K. E., Brody T., Ingelfinger J., Pratt R. E. A comparative study of the distributions of renin and angiotensinogen messenger ribonucleic acids in rat and mouse tissues. Endocrinology. 1987 Jun;120(6):2334–2338. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-6-2334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. J. Atrial natriuretic factor-SV40 T antigen transgenes produce tumors and cardiac arrhythmias in mice. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1029–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.2964082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. J., Gross K. W. Ren-1 and Ren-2 loci are expressed in mouse kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard I., Clauser E., Corvol P. Structure of human angiotensinogen gene. DNA. 1989 Mar;8(2):87–99. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Wilson F. D., Lang G., Kioussis D. Human CD2 3'-flanking sequences confer high-level, T cell-specific, position-independent gene expression in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90631-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Krumlauf R., Camper S. A., Brinster R. L., Tilghman S. M. Diversity of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in mice is generated by a combination of separate enhancer elements. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.2432657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard J. M., Herbomel P., Ott M. O., Mottura-Rollier A., Weiss M., Yaniv M. Determinants of rat albumin promoter tissue specificity analyzed by an improved transient expression system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2425–2434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Induction of rat liver angiotensinogen mRNA following acute inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):826–832. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91966-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klett C., Hellmann W., Suzuki F., Nakanishi S., Ohkubo H., Ganten D., Hackenthal E. Induction of angiotensinogen mRNA in hepatocytes by angiotensin II and glucocorticoids. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1988;10(6):1009–1022. doi: 10.1080/07300077.1988.11878797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loreni F., Stavenhagen J., Kalff M., Robins D. M. A complex androgen-responsive enhancer resides 2 kilobases upstream of the mouse Slp gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2350–2360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. R., Simnad V. I., Ben-Ari E. T., Garrison J. C. Localization of preangiotensinogen messenger RNA sequences in the rat brain. Hypertension. 1986 Jun;8(6):540–543. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.8.6.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. J., Sigmund C. D., Kane-Haas C., Wu C. Z., Pacholec F., Zeng Q., Gross K. W. Studies on the regulation of renin genes using transgenic mice. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1988;10(6):1157–1167. doi: 10.1080/07300077.1988.11878808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura N., Burt D. W., Paul M., Dzau V. J. Negative control elements and cAMP responsive sequences in the tissue-specific expression of mouse renin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):56–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Kimura H., Yeul Y. D., Yokoyama S., Nakayama K., Takahashi M. Identification of the 5'-flanking regulatory region responsible for the difference in transcriptional control between mouse complement C4 and Slp genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7883–7887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo H., Nakayama K., Tanaka T., Nakanishi S. Tissue distribution of rat angiotensinogen mRNA and structural analysis of its heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):319–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Palmiter R. D., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Swift G. H., MacDonald R. J. Specific expression of an elastase-human growth hormone fusion gene in pancreatic acinar cells of transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):600–602. doi: 10.1038/313600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccini N., Knopf J. L., Gross K. W. A DNA polymorphism, consistent with gene duplication, correlates with high renin levels in the mouse submaxillary gland. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Ornitz D. M., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. An albumin enhancer located 10 kb upstream functions along with its promoter to direct efficient, liver-specific expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):268–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. Transcriptional interference and termination between duplicated alpha-globin gene constructs suggests a novel mechanism for gene regulation. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):562–565. doi: 10.1038/322562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richoux J. P., Cordonnier J. L., Bouhnik J., Clauser E., Corvol P., Menard J., Grignon G. Immunocytochemical localization of angiotensinogen in rat liver and kidney. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;233(2):439–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00238309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Fenner S., Greenoak G. E., Moran C., Coffin J. M. Role of endogenous retroviruses as mutagens: the hairless mutation of mice. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Common structural organization of the angiotensinogen and the alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8063–8065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Quiroga M., Zaldivar J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W., Cleveland D. W. Nucleotide and corresponding amino acid sequences encoded by alpha and beta tubulin mRNAs. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):650–655. doi: 10.1038/289650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Erdös E. G., Wilson J. D., Taylor B. A. Location on chromosome 1 of Rnr, a gene that regulates renin in the submaxillary gland of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5623–5626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen B. H., Evans B. A., Tregear G. W., Richards R. I. Mouse glandular kallikrein genes. Identification, structure, and expression of the renal kallikrein gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5529–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]