Abstract
Conjugative transfer of the plasmid pCF10 by Enterococcus faecalis donor cells occurs in response to a peptide sex pheromone, cCF10, secreted by recipients. The plasmid-encoded cCF10 binding protein, PrgZ, is similar in sequence to binding proteins (OppAs) encoded by oligopeptide permease (opp) operons. Mutation of prgZ decreased the sensitivity of donor cells to pheromone, whereas inactivation of the chromosomal E. faecalis opp operon abolished response at physiological concentrations of pheromone. Affinity chromatography experiments demonstrated the interaction of the pheromone with several putative intracellular regulatory molecules, including an RNA molecule required for positive regulation of conjugation functions. These data suggest that processing of the pheromone signal involves recruitment of a chromosomal Opp system by PrgZ and that signaling occurs by direct interaction of internalized pheromone with intracellular effectors.
Full text
PDF

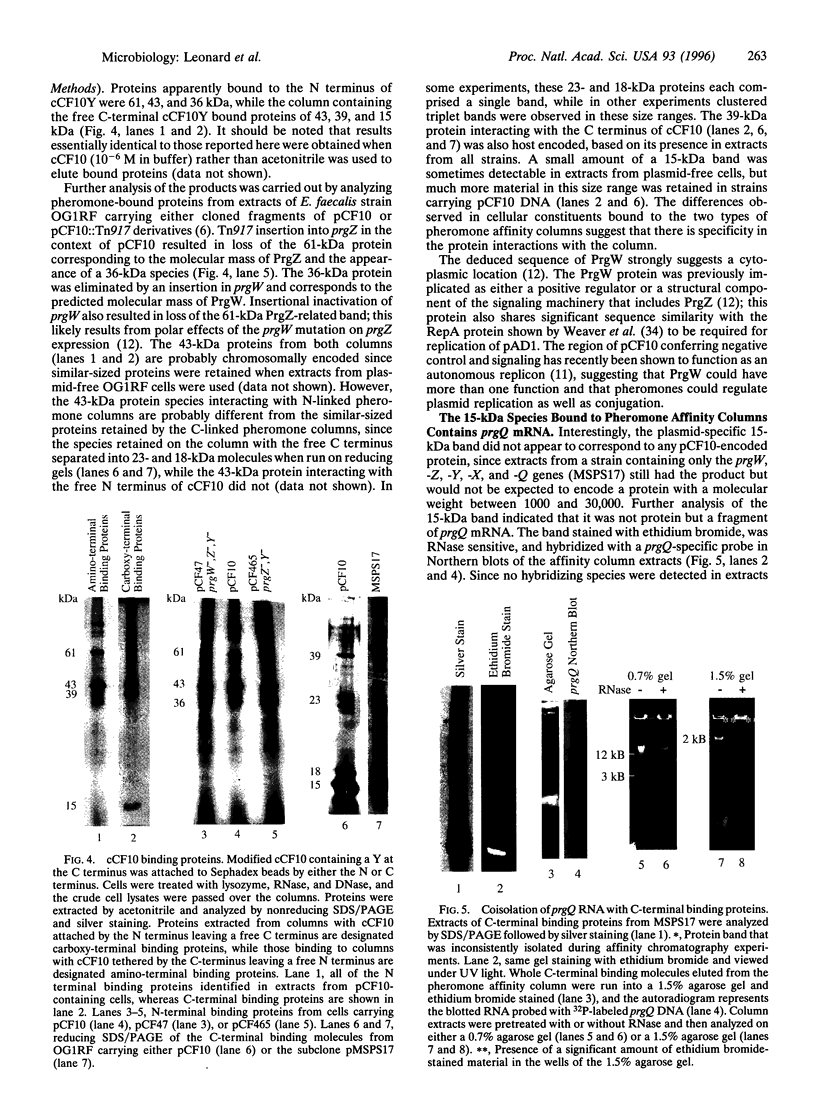

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alloing G., Trombe M. C., Claverys J. P. The ami locus of the gram-positive bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae is similar to binding protein-dependent transport operons of gram-negative bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):633–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas I., Gruss A., Ehrlich S. D., Maguin E. High-efficiency gene inactivation and replacement system for gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3628–3635. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3628-3635.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi S. H., Greenberg E. P. Genetic dissection of DNA binding and luminescence gene activation by the Vibrio fischeri LuxR protein. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):4064–4069. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.4064-4069.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie P. J., Dunny G. M. Identification of regions of the Streptococcus faecalis plasmid pCF-10 that encode antibiotic resistance and pheromone response functions. Plasmid. 1986 May;15(3):230–241. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie P. J., Kao S. M., Adsit J. C., Dunny G. M. Cloning and expression of genes encoding pheromone-inducible antigens of Enterococcus (Streptococcus) faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5161–5168. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5161-5168.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J. W., Bensing B. A., Dunny G. M. Genetic analysis of a region of the Enterococcus faecalis plasmid pCF10 involved in positive regulation of conjugative transfer functions. J Bacteriol. 1995 Apr;177(8):2107–2117. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.8.2107-2117.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J. W., Dunny G. M. Cis-acting, orientation-dependent, positive control system activates pheromone-inducible conjugation functions at distances greater than 10 kilobases upstream from its target in Enterococcus faecalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9020–9024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J. W., Dunny G. M. Transcriptional analysis of a region of the Enterococcus faecalis plasmid pCF10 involved in positive regulation of conjugative transfer functions. J Bacteriol. 1995 Apr;177(8):2118–2124. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.8.2118-2124.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Bacterial sex pheromone-induced plasmid transfer. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90153-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Craig R. A., Carron R. L., Clewell D. B. Plasmid transfer in Streptococcus faecalis: production of multiple sex pheromones by recipients. Plasmid. 1979 Jul;2(3):454–465. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Leonard B. A., Hedberg P. J. Pheromone-inducible conjugation in Enterococcus faecalis: interbacterial and host-parasite chemical communication. J Bacteriol. 1995 Feb;177(4):871–876. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.4.871-876.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui F. M., Zhou L., Morrison D. A. Competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae: organization of a regulatory locus with homology to two lactococcin A secretion genes. Gene. 1995 Feb 3;153(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)00841-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. M., Olmsted S. B., Viksnins A. S., Gallo J. C., Dunny G. M. Molecular and genetic analysis of a region of plasmid pCF10 containing positive control genes and structural genes encoding surface proteins involved in pheromone-inducible conjugation in Enterococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7650–7664. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7650-7664.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. B., Greenberg E. P. Diffusion of autoinducer is involved in regulation of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence system. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1210–1214. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1210-1214.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Lee L. N., Inamine J. M. Cloning and nucleotide base sequence analysis of a spectinomycin adenyltransferase AAD(9) determinant from Enterococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Sep;35(9):1804–1810. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.9.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S. Nascent peptide regulation of translation. J Bacteriol. 1994 Nov;176(21):6415–6417. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.21.6415-6417.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson R., Solomon J., Grossman A. D. Biochemical and genetic characterization of a competence pheromone from B. subtilis. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Sakagami Y., Ishii Y., Isogai A., Kitada C., Fujino M., Adsit J. C., Dunny G. M., Suzuki A. Structure of cCF10, a peptide sex pheromone which induces conjugative transfer of the Streptococcus faecalis tetracycline resistance plasmid, pCF10. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14574–14578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama J., Ruhfel R. E., Dunny G. M., Isogai A., Suzuki A. The prgQ gene of the Enterococcus faecalis tetracycline resistance plasmid pCF10 encodes a peptide inhibitor, iCF10. J Bacteriol. 1994 Dec;176(23):7405–7408. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.23.7405-7408.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted S. B., Kao S. M., van Putte L. J., Gallo J. C., Dunny G. M. Role of the pheromone-inducible surface protein Asc10 in mating aggregate formation and conjugal transfer of the Enterococcus faecalis plasmid pCF10. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7665–7672. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7665-7672.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce B. J., Naughton A. M., Masure H. R. Peptide permeases modulate transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jun;12(6):881–892. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Higgins C. F., Pearce S. R., Gallagher M. P., Hoch J. A. The oligopeptide transport system of Bacillus subtilis plays a role in the initiation of sporulation. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):173–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner D. Z., LeDeaux J. R., Ireton K., Grossman A. D. The spo0K locus of Bacillus subtilis is homologous to the oligopeptide permease locus and is required for sporulation and competence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1388-1398.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhfel R. E., Manias D. A., Dunny G. M. Cloning and characterization of a region of the Enterococcus faecalis conjugative plasmid, pCF10, encoding a sex pheromone-binding function. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(16):5253–5259. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.16.5253-5259.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon J. M., Magnuson R., Srivastava A., Grossman A. D. Convergent sensing pathways mediate response to two extracellular competence factors in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1995 Mar 1;9(5):547–558. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.5.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam R., Saier M. H., Jr Structural, functional, and evolutionary relationships among extracellular solute-binding receptors of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Jun;57(2):320–346. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.2.320-346.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tame J. R., Murshudov G. N., Dodson E. J., Neil T. K., Dodson G. G., Higgins C. F., Wilkinson A. J. The structural basis of sequence-independent peptide binding by OppA protein. Science. 1994 Jun 10;264(5165):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.8202710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto K., An F. Y., Clewell D. B. Characterization of the traC determinant of the Enterococcus faecalis hemolysin-bacteriocin plasmid pAD1: binding of sex pheromone. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(16):5260–5264. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.16.5260-5264.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L. Gene regulation by phosphate in enteric bacteria. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Jan;51(1):47–54. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240510110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver K. E., Clewell D. B., An F. Identification, characterization, and nucleotide sequence of a region of Enterococcus faecalis pheromone-responsive plasmid pAD1 capable of autonomous replication. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(7):1900–1909. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.7.1900-1909.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver K. E., Clewell D. B. Regulation of the pAD1 sex pheromone response in Enterococcus faecalis: effects of host strain and traA, traB, and C region mutants on expression of an E region pheromone-inducible lacZ fusion. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2633–2641. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2633-2641.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C. Two-way chemical signaling in Agrobacterium-plant interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):12–31. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.12-31.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth R. The sex pheromone system of Enterococcus faecalis. More than just a plasmid-collection mechanism? Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jun 1;222(2):235–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]