Abstract
A diuretic hormone of unusual structure was isolated from extracts of whole heads of the mealworm Tenebrio molitor. The hormone is a 37-aa peptide of 4371 Da, with the sequence SPTISITAPIDVLRKTWEQERARKQMVKNREFLNSLN. This peptide increases cAMP production in Malpighian tubules of T. molitor. The amino acid sequence reveals that this peptide is a member of the family of sauvagine/corticotropin-releasing factor/urotensin I-related insect diuretic hormones. The C-terminal sequence of this peptide is quite different from other members of this family, which have a hydrophobic C terminus (isoleucinamide or valinamide). When aligned comparably, T. molitor diuretic hormone has a more hydrophilic C terminus, leucylasparagine (free acid). In contrast to all other known diuretic hormones of this family, this peptide has exceptionally low stimulatory activity on cAMP production in Malpighian tubules of Manduca sexta. However, at nanomolar concentrations it stimulates cAMP production in Malpighian tubules of T. molitor. Diuretic hormones of this family have been isolated previously from Lepidoptera, Orthoptera, Dictyoptera, and Diptera. This appears to be the first diuretic hormone isolated from a coleopteran insect.
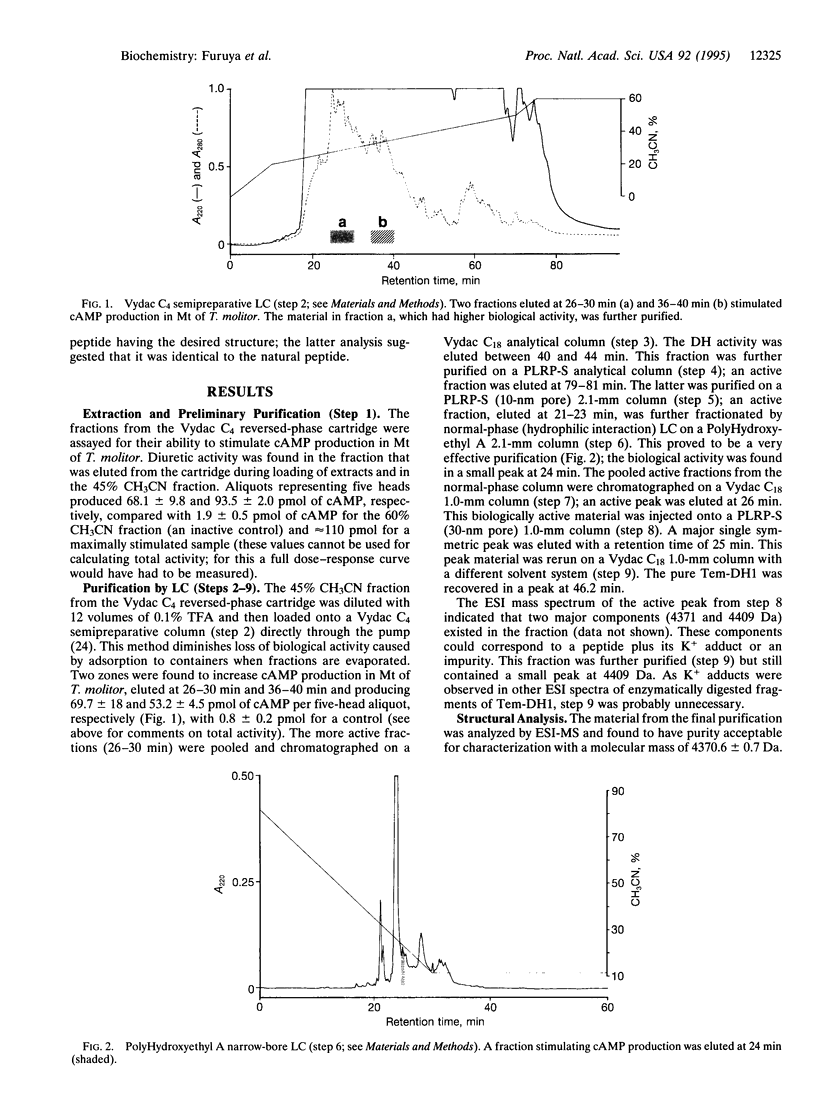
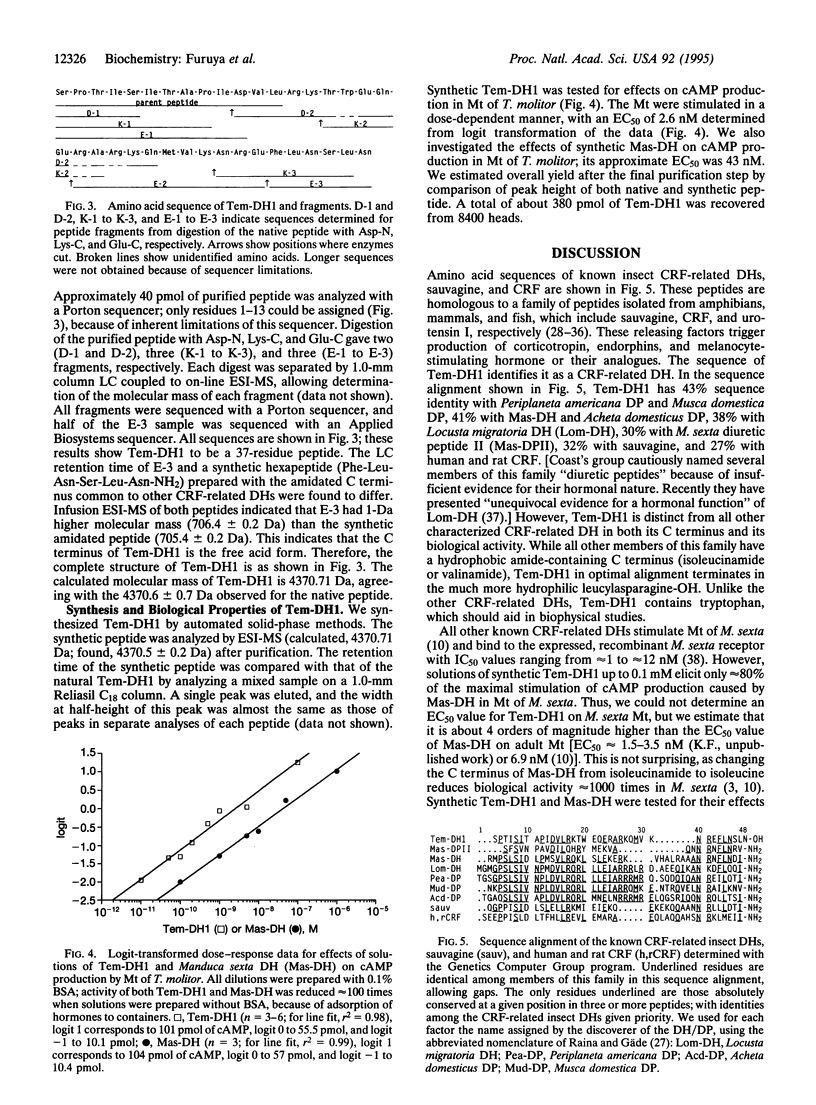
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Audsley N., Kay I., Hayes T. K., Coast G. M. Cross reactivity studies of CRF-related peptides on insect Malpighian tubules. Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol. 1995 Jan;110(1):87–93. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(94)00132-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn M. B., Kingan T. G., Bodnar W., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Kempe T., Wagner R. M., Raina A. K., Schnee M. E., Ma M. C. Isolation and identification of a new diuretic peptide from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):927–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92025-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clottens F. L., Holman G. M., Coast G. M., Totty N. F., Hayes T. K., Kay I., Mallet A. I., Wright M. S., Chung J. S., Truong O. Isolation and characterization of a diuretic peptide common to the house fly and stable fly. Peptides. 1994;15(6):971–979. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. A., Michaud D. P. Synthesis of a fluorescent derivatizing reagent, 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate, and its application for the analysis of hydrolysate amino acids via high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1993 Jun;211(2):279–287. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F., Ling N., Bohlen P., Baird A., Benoit R., Guillemin R. Isolation and characterization of the bovine hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):899–905. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. Protein binding assays for cyclic nucleotides. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;2:9–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. K., Pannabecker T. L., Hinckley D. J., Holman G. M., Nachman R. J., Petzel D. H., Beyenbach K. W. Leucokinins, a new family of ion transport stimulators and inhibitors in insect Malpighian tubules. Life Sci. 1989;44(18):1259–1266. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa T., McMaster D., Lederis K., Kobayashi H. Isolation and amino acid sequence of urotensin I, a vasoactive and ACTH-releasing neuropeptide, from the carp (Cyprinus carpio) urophysis. Peptides. 1982 Sep-Oct;3(5):859–867. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(82)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka H., Troetschler R. G., Li J. P., Kramer S. J., Carney R. L., Schooley D. A. Isolation and identification of a diuretic hormone from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2976–2980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay I., Coast G. M., Cusinato O., Wheeler C. H., Totty N. F., Goldsworthy G. J. Isolation and characterization of a diuretic peptide from Acheta domesticus. Evidence for a family of insect diuretic peptides. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 Jul;372(7):505–512. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1991.372.2.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay I., Patel M., Coast G. M., Totty N. F., Mallet A. I., Goldsworthy G. J. Isolation, characterization and biological activity of a CRF-related diuretic peptide from Periplaneta americana L. Regul Pept. 1992 Dec 11;42(3):111–122. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(92)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay I., Wheeler C. H., Coast G. M., Totty N. F., Cusinato O., Patel M., Goldsworthy G. J. Characterization of a diuretic peptide from Locusta migratoria. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 Oct;372(10):929–934. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1991.372.2.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. S., Fields C. G., Fields G. B. A cleavage method which minimizes side reactions following Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1990 Sep;36(3):255–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1990.tb00976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederis K., Letter A., McMaster D., Moore G., Schlesinger D. Complete amino acid sequence of urotensin I, a hypotensive and corticotropin-releasing neuropeptide from Catostomus. Science. 1982 Oct 8;218(4568):162–165. doi: 10.1126/science.6981844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmberg E., Ota R. B., Furuya K., King D. S., Applebaum S. W., Ferenz H. J., Schooley D. A. Identification of a diuretic hormone of Locusta migratoria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 16;179(2):1036–1041. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91923-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N., Esch F., Böhlen P., Baird A., Guillemin R. Isolation and characterization of caprine corticotropin-releasing factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1218–1224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddrell S. H., Herman W. S., Mooney R. L., Overton J. A. 5-Hydroxytryptamine: a second diuretic hormone in Rhodnius prolixus. J Exp Biol. 1991 Mar;156:557–566. doi: 10.1242/jeb.156.1.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montecucchi P. C., Anastasi A., de Castiglione R., Erspamer V. Isolation and amino acid composition of sauvagine. An active polypeptide from methanol extracts of the skin of the South American frog Phyllomedusa sauvagei. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1980 Sep;16(3):191–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montecucchi P. C., Henschen A. Amino acid composition and sequence analysis of sauvagine, a new active peptide from the skin of Phyllomedusa sauvagei. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1981 Aug;18(2):113–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1981.tb02047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montoreano R., Triana F., Abate T., Rangel-Aldao R. Cyclic AMP in the Malpighian tubule fluid and in the urine of Rhodnius prolixus. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1990 Jan;77(1):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(90)90214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan P. J., Mordue W. 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulates fluid secretion in locust malpighian tubules independently of cAMP. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1984;79(2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(84)90205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M, Hayes T, Coast G. Evidence for the hormonal function of a CRF-related diuretic peptide (Locusta-DP) in Locusta migratoria. J Exp Biol. 1995;198(Pt 3):793–804. doi: 10.1242/jeb.198.3.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reagan J. D. Expression cloning of an insect diuretic hormone receptor. A member of the calcitonin/secretin receptor family. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier J., Spiess J., Vale W. Characterization of rat hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4851–4855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibahara S., Morimoto Y., Furutani Y., Notake M., Takahashi H., Shimizu S., Horikawa S., Numa S. Isolation and sequence analysis of the human corticotropin-releasing factor precursor gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):775–779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Spiess J., Rivier C., Rivier J. Characterization of a 41-residue ovine hypothalamic peptide that stimulates secretion of corticotropin and beta-endorphin. Science. 1981 Sep 18;213(4514):1394–1397. doi: 10.1126/science.6267699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




