Abstract
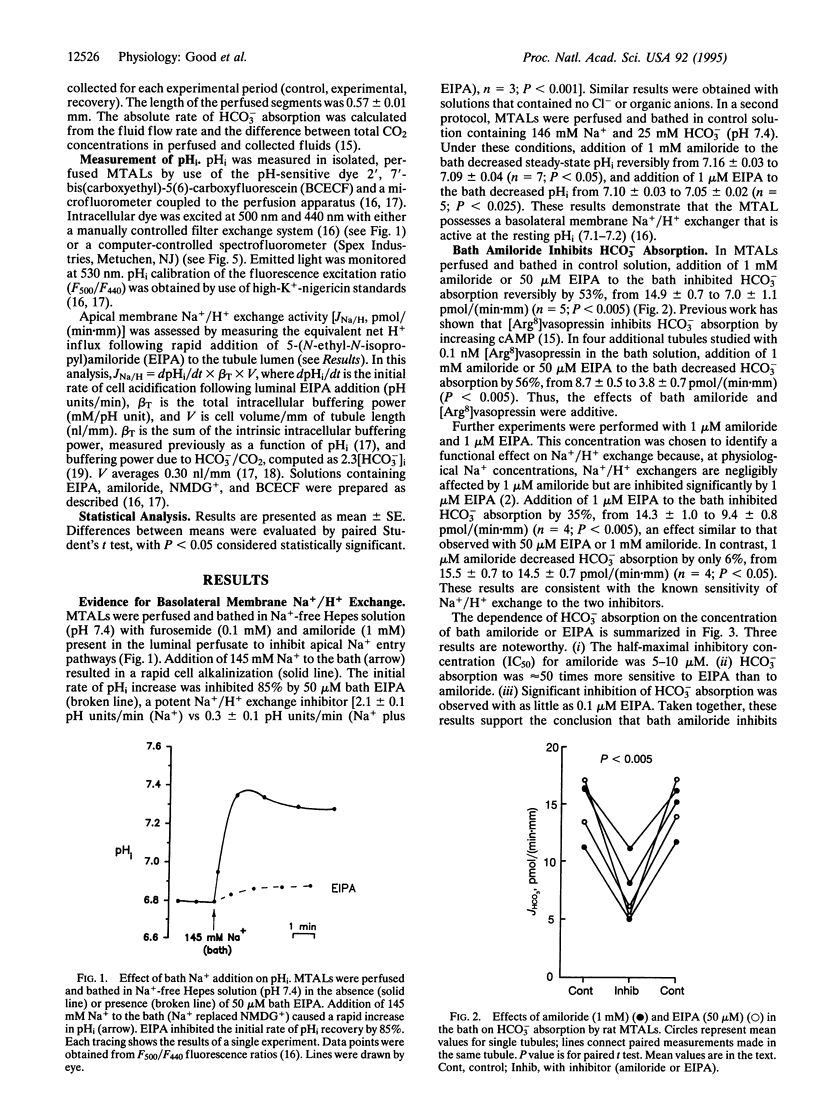
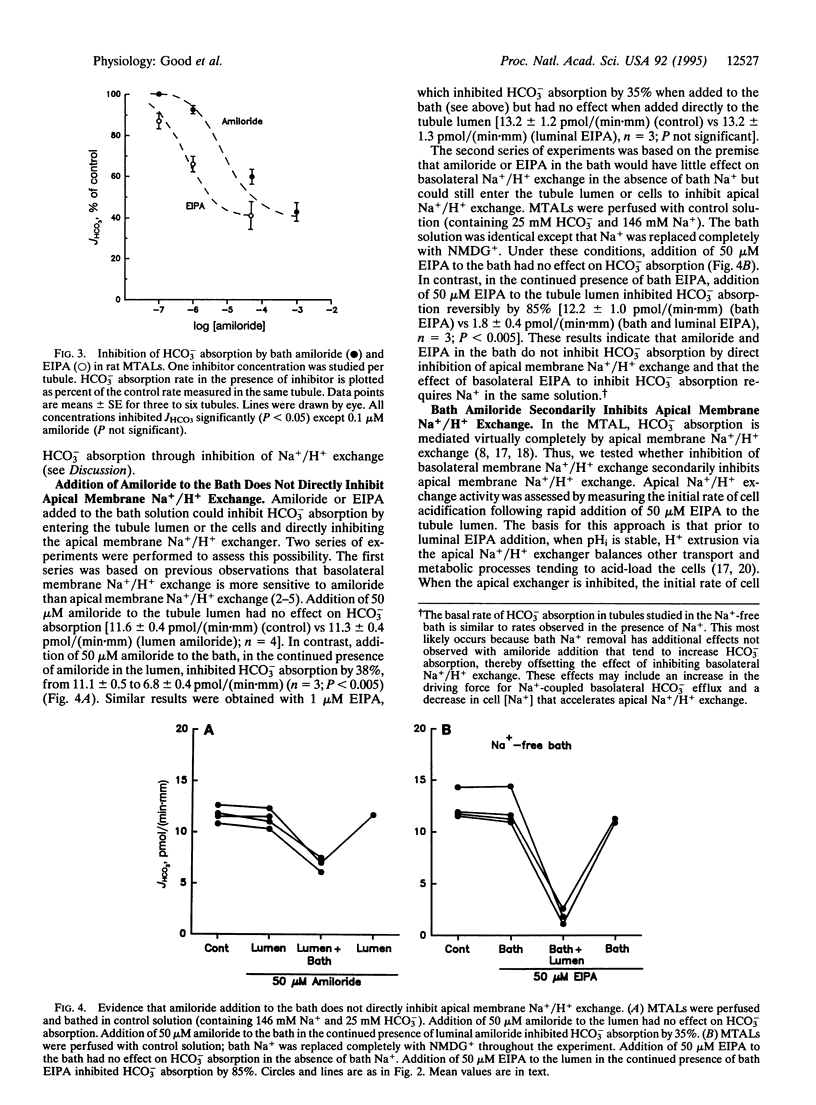
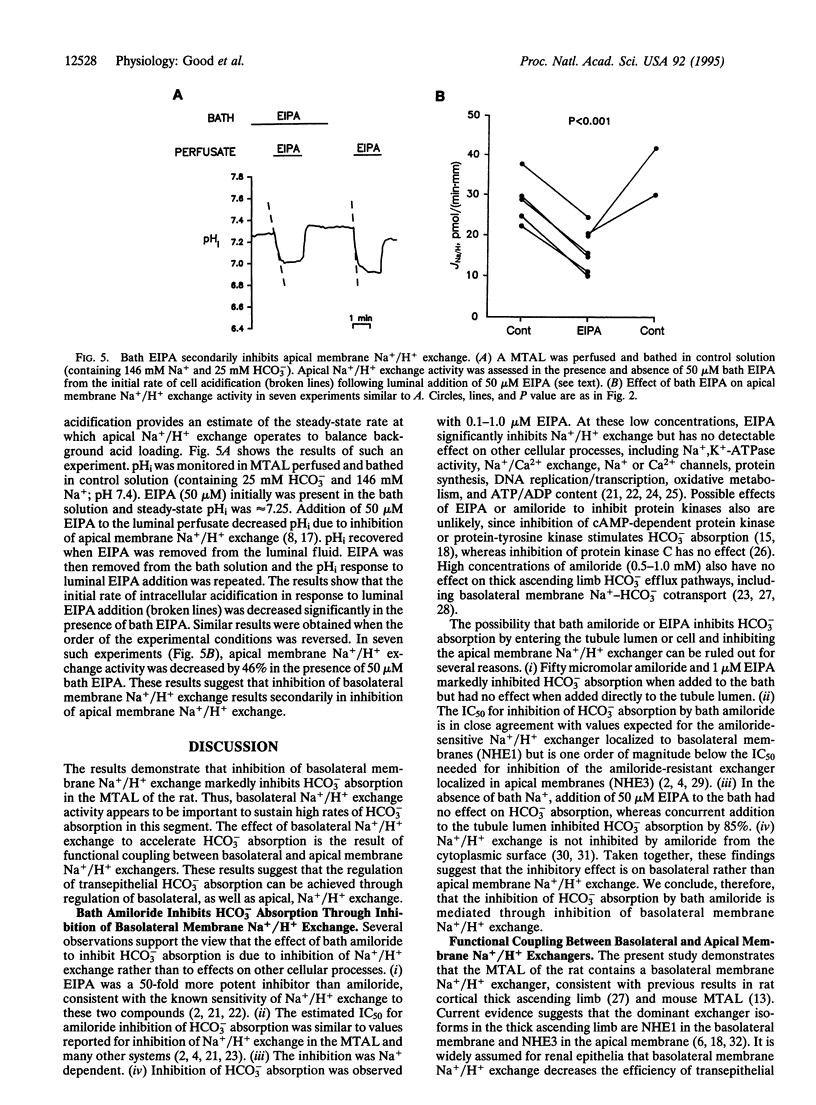
The role of basolateral membrane Na+/H+ exchange in transepithelial HCO3- absorption (JHCO3) was examined in the isolated, perfused medullary thick ascending limb (MTAL) of the rat. In Na(+)-free solutions, addition of Na+ to the bath resulted in a rapid, amiloride-sensitive increase in intracellular pH. In MTALs perfused and bathed with solutions containing 146 mM Na+ and 25 mM HCO3-, bath addition of amiloride (1 mM) or 5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl) amiloride (EIPA, 50 microM) reversibly inhibited JHCO3 by 50%. Evidence that the inhibition of JHCO3 by bath amiloride was the result of inhibition of Na+/H+ exchange included the following: (i) the IC50 for amiloride was 5-10 microM, (ii) EIPA was a 50-fold more potent inhibitor than amiloride, (iii) the inhibition by bath amiloride was Na+ dependent, and (iv) significant inhibition was observed with EIPA as low as 0.1 microM. Fifty micromolar amiloride or 1 microM EIPA inhibited JHCO3 by 35% when added to the bath but had no effect when added to the tubule lumen, indicating that addition of amiloride to the bath did not directly inhibit apical membrane Na+/H+ exchange. In experiments in which apical Na+/H+ exchange was assessed from the initial rate of cell acidification following luminal EIPA addition, bath EIPA secondarily inhibited apical Na+/H+ exchange activity by 46%. These results demonstrate basolateral membrane Na+/H+ exchange enhances transepithelial HCO3- absorption in the MTAL. This effect appears to be the result of cross-talk in which an increase in basolateral membrane Na+/H+ exchange activity secondarily increases apical membrane Na+/H+ exchange activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biemesderfer D., Pizzonia J., Abu-Alfa A., Exner M., Reilly R., Igarashi P., Aronson P. S. NHE3: a Na+/H+ exchanger isoform of renal brush border. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 2):F736–F742. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.5.F736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biemesderfer D., Reilly R. F., Exner M., Igarashi P., Aronson P. S. Immunocytochemical characterization of Na(+)-H+ exchanger isoform NHE-1 in rabbit kidney. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 2):F833–F840. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.5.F833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein C., DePaoli A. M., Xie Y., Niu P., Musch M. W., Rao M. C., Chang E. B. Na+/H+ exchangers, NHE-1 and NHE-3, of rat intestine. Expression and localization. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):106–113. doi: 10.1172/JCI116933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztein P., Froissart M., Laghmani K., Bichara M., Paillard M. RT-PCR analysis of Na+/H+ exchanger mRNAs in rat medullary thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol. 1995 Jun;268(6 Pt 2):F1224–F1228. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1995.268.6.F1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Na-H exchange. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):29–52. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyarsky G., Ganz M. B., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Boron W. F. Intracellular-pH dependence of Na-H exchange and acid loading in quiescent and arginine vasopressin-activated mesangial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5921–5924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casavola V., Reshkin S. J., Murer H., Helmle-Kolb C. Polarized expression of Na+/H+ exchange activity in LLC-PK1/PKE20 cells: II. Hormonal regulation. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Mar;420(3-4):282–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00374460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desir G. V., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Aronson P. S. High affinity binding of amiloride analogs at an internal site in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2267–2271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W. Hyperosmolality inhibits bicarbonate absorption in rat medullary thick ascending limb via a protein-tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 28;270(17):9883–9889. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.17.9883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W. Inhibition of bicarbonate absorption by peptide hormones and cyclic adenosine monophosphate in rat medullary thick ascending limb. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1006–1013. doi: 10.1172/JCI114530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W., Knepper M. A., Burg M. B. Ammonia and bicarbonate transport by thick ascending limb of rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 2):F35–F44. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.1.F35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W. The thick ascending limb as a site of renal bicarbonate reabsorption. Semin Nephrol. 1993 Mar;13(2):225–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rotin D., Mason M. J. Na+/H+ exchange and growth factor-induced cytosolic pH changes. Role in cellular proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):73–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Smith J. D. Asymmetry of the Na+/H+ antiport of dog red cell ghosts. Sidedness of inhibition by amiloride. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9088–9092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Agarwal N., Reilly R. F., Adelberg E. A., Slayman C. W. Pharmacologically different Na/H antiporters on the apical and basolateral surfaces of cultured porcine kidney cells (LLC-PK1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6797–6801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert S. C. Hypertonic cell volume regulation in mouse thick limbs. II. Na+-H+ and Cl(-)-HCO3- exchange in basolateral membranes. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):C920–C931. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.6.C920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Battilana C. A., Lacy F. B., Jamison R. L. Evidence for a concentration gradient favoring outward movement of sodium from the thin loop of Henle. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):234–240. doi: 10.1172/JCI108633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Slaughter R. S., King V. F., Garcia M. L. Inhibitors of sodium-calcium exchange: identification and development of probes of transport activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 9;988(2):287–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikeri D., Azar S., Sun A., Zeidel M. L., Hebert S. C. Na(+)-H+ antiporter and Na(+)-(HCO3-)n symporter regulate intracellular pH in mouse medullary thick limbs of Henle. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):F445–F456. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.3.F445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyman T. R., Cragoe E. J., Jr Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J Membr Biol. 1988 Oct;105(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01871102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knickelbein R. G., Aronson P. S., Dobbins J. W. Characterization of Na(+)-H+ exchangers on villus cells in rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 1):G802–G806. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.5.G802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R. Basolateral membrane H/OH/HCO3 transport in the rat cortical thick ascending limb. Evidence for an electrogenic Na/HCO3 cotransporter in parallel with a Na/H antiporter. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):234–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI113576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leviel F., Borensztein P., Houillier P., Paillard M., Bichara M. Electroneutral K+/HCO3- cotransport in cells of medullary thick ascending limb of rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):869–878. doi: 10.1172/JCI115962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackovic-Basic M., Kurtz I. H+/base transport in the proximal straight tubule and thin descending limb of Henle. Semin Nephrol. 1990 Mar;10(2):122–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mrkic B., Forgo J., Murer H., Helmle-Kolb C. Apical and basolateral Na/H exchange in cultured murine proximal tubule cells (MCT): effect of parathyroid hormone (PTH). J Membr Biol. 1992 Dec;130(3):205–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00240478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noël J., Pouysségur J. Hormonal regulation, pharmacology, and membrane sorting of vertebrate Na+/H+ exchanger isoforms. Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 1):C283–C296. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.2.C283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig P. A., Alpern R. J. Basolateral membrane H/HCO3 transport in renal tubules. Kidney Int. 1991 Jun;39(6):1077–1086. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani M., Bookstein C., McAteer J. A., Hattabaugh Y. J., Bizal G. L., Musch M. W., Villereal M., Rao M. C., Howard R. L., Chang E. B. Effect of high osmolality on Na+/H+ exchange in renal proximal tubule cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15613–15618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Mandel L. J. Amiloride analogues inhibit proximal tubule metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 1):C744–C747. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.5.C744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun A. M., Kikeri D., Hebert S. C. Vasopressin regulates apical and basolateral Na(+)-H+ antiporters in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 2):F241–F247. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.2.F241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts B. A., 3rd, Good D. W. Apical membrane Na+/H+ exchange in rat medullary thick ascending limb. pH-dependence and inhibition by hyperosmolality. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20250–20255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts B. A., 3rd, Good D. W. Effects of ammonium on intracellular pH in rat medullary thick ascending limb: mechanisms of apical membrane NH4+ transport. J Gen Physiol. 1994 May;103(5):917–936. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.5.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


