Abstract
CD40-induced signalling through ligation with its natural ligand (CD40L/CD154) is dependent on recruitment of TRAF molecules to the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor. Here, we applied the yeast two-hybrid system to examine whether other proteins can interact with CD40. Fas-Associated Factor 1(FAF1) was isolated from a HeLa cDNA library using the CD40 cytoplasmic tail (216–278 aa) as a bait construct. FAF1 was able to interact with CD40 both in vitro and in vivo. The FAF1 N-terminal domain was sufficient to bind CD40 and required the TRAF6-binding domain within the cytoplasmic tail of CD40 for binding. CD40 ligation induced FAF1 expression in an NFκB-dependent manner. Knockdown of FAF1 prolonged CD40-induced NFκB, whereas overexpression of FAF1 suppressed CD40-induced NFκB activity and this required interaction of FAF1 with the CD40 receptor via its FID domain. Thus, we report a novel role for FAF1in regulating CD40-induced NFκB activation via a negative feedback loop. Loss of FAF1 function in certain human malignancies may contribute to oncogenesis through unchecked NFκB activation, and further understanding of this process may provide a biomarker of NFκB-targeted therapies for such malignancies.
Keywords: CD40, FAF1, NFκB
CD40, a member of the tumour necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily, and its ligand (CD40L/CD154) have a central role in coordinating immune responses and can mediate antiviral and antitumour effects.1 CD40 is expressed in normal B cells and malignant haemopoietic cells. Although CD40 ligation induces the survival and proliferation of normal B cells and of low-grade B-cell malignancies, the activation of CD40 in Burkitt lymphoma cells results in growth inhibition and apoptosis.2, 3, 4 CD40 expression is also upregulated in a number of carcinomas. It is assumed that CD40 expression in the context of malignant epithelium confers a growth/survival advantage via signalling pathways such as NFκB and PI3Kinase/Akt and/or via modulation of antitumour immune responses, although its precise contribution to malignancy remains unclear. As CD40 lacks intrinsic kinase activity, signalling depends on the recruitment of adapter proteins known as TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs) to mediate signal transduction initiated by CD40 ligation. Two domains in the cytoplasmic tail of CD40 are critical for TRAF association and signal activation: a membrane-proximal region containing amino acids Gln234Glu235 responsible for TRAF6 binding and a Pro250XGln252XThr254 motif that is critical for interactions with TRAF2 and TRAF3 and indirectly with TRAF5.5, 6, 7 The ligand-dependent recruitment of these adaptor molecules triggers the activation of multiple signalling pathways, including the JNK, ERK and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), the transcription factors NFκB, STAT and the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K) cascade, which act in concert to regulate many of the pleiotropic activities of CD40 in a cell type-dependent manner.7, 8, 9 Previous studies have shown that stimulation of Hela cells expressing a CD40 mutant (CD40AmT6; the amino acids T254, Q234, E235 within the CD40 cytoplasmic tail were replaced by A residues), which does not bind TRAF2,3,5 and 6,6, 7, 10 induced robust ERK and JNK phosphorylation, detectable phosphorylation of p38 and significant IκBα degradation, suggesting that other signalling motifs within CD40 or other proteins may still be involved in CD40-induced signalling pathways. Therefore, identification of other proteins that directly interact with the CD40 receptor may provide better understanding of CD40-induced signalling pathways. In this study, we attempted to identify other CD40-interacting proteins by utilising the yeast two-hybrid analysis technique (YTH) using the CD40 cytoplasmic tail as the bait construct. Fas-Associated Factor 1 (FAF1) was isolated as a novel CD40-interacting partner, and we report a novel function for FAF1 regulation of CD40-induced NFκB.
Results
Identification of FAF1 as a novel CD40 interactor by YTH analysis
Before screening the Hela cDNA library, the inability of CD40 to activate the transcription of the reporter markers was confirmed as EGY48 yeast cells harbouring the pEG202/LexA-CD40 bait construct were unable to grow on Glu/CM-H,L plate. In the primary screening of the HeLa cDNA library, several clones were selected and seven of these were found to interact specifically with the CD40 bait construct. On sequencing, one clone was found to code a partial cDNA of FAF1 (50–602 aa) and the other six clones were partial cDNAs of the TRAF3 molecule.
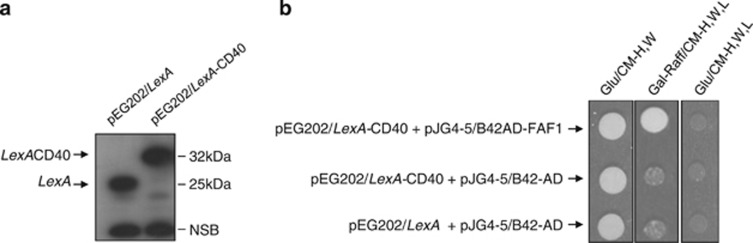
To verify this putative interaction between FAF1 and CD40, EGY48 yeast cells harbouring the pEG202/LexA-CD40 (bait) or pEG202/LexA construct were grown in Glu/CM-H liquid medium, and LexA-CD40 fusion expression was then confirmed by immunoblotting analysis using a specific anti-LexA antibody (Figure 1a). To test the CD40–FAF1 interaction, EGY48 cells harbouring the CD40 bait construct were co-transformed with the isolated pJG4-5/FAF1-HA.tag (prey) or the empty pJG/4-5 vector. An interaction between CD40 and FAF1 proteins was confirmed as yeast cells were able to grow and form single colonies on the selective Gal-Raff/CM-H,W,L but not on the Glu/CM-H,W.L (Figure 1b). The inability of yeast cells harbouring either pEG202/LexA-CD40 or the pJG4-5/FAF1-HA.tag alone or the empty vectors to grow on the selective Gal-Raff/CM-H,W,L medium further indicates the specificity of CD40-FAF1 interaction in the two-hybrid system.
Figure 1.
CD40–FAF1 interaction in yeast two-hybrid system. (a) EGY48 yeast strain cells harbouring the pEG202/LexA empty plasmid or the pEG202/LexA-CD40 bait construct were grown under glucose inducible media. Protein lysates were prepared, and expression of the CD40 bait construct was then confirmed by western blot analysis using the anti-LexA antibody. (b) EGY48 yeast strain cells harbouring pEG202/LexA+pJG4-5/B42-AD, or pEG202/LexA-CD40+pJG4-5/B42-AD or pEG202/LexA-CD40+pJG4-5/B42-AD-FAF1 were plated on the selective media indicated above. EGY48 cells that harbour pEG202/LexA-CD40+pJG4-5/B42-AD-FAF1 were only able to grow on Gal-Raff/CM agar media lacking the amino acids histidine (H), tryptophan (W) and leucine (L) but not on the Glu/CM-H,W.L medium. EGY48 yeast cells transformed with empty plasmids of pEG202/LexA (202) and pJG4-5/B42-AD (4-5) were used as negative controls
FAF1 interacts with the TRAF6-binding domain of CD40 via its Fas-interacting domain
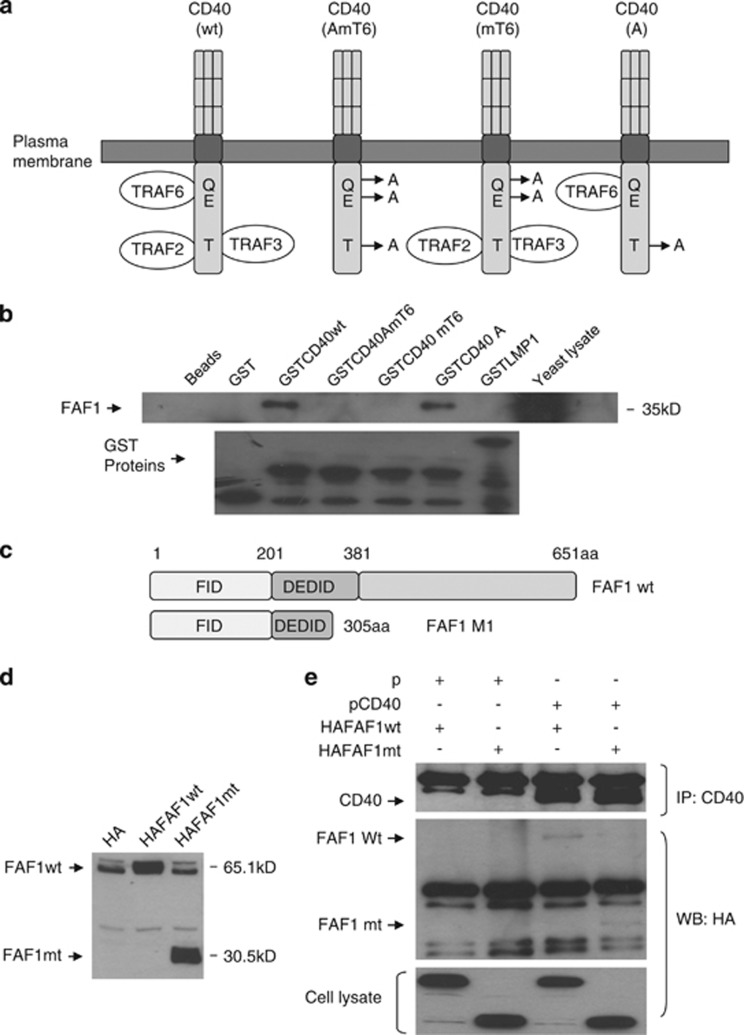
To confirm CD40–FAF1 interaction in vitro and to determine which domain of CD40 was requisite for this, we investigated whether a series GST-CD40 fusions incorporating wild-type CD40 or mutants lacking specific TRAF-binding domains could pull down FAF1 protein in a GST pull-down assay. Thus, GST-CD40 fusions including wild-type CD40, CD40mT6 (which does not bind TRAF6), CD40A (which does not bind TRAF2/3) and CD40AmT6 (which does not bind any of TRAF6, TRAF2 or TRAF3) mutants were expressed and purified from E.coli BL21 bacterial cells for GST pull-down assays (Figure 2a). In addition, a GST-LMP1 fusion protein was used as a negative control as an LMP1 protein does not possess a TRAF6-binding domain; instead, TRAF6 is recruited to LMP1 indirectly via TRADD molecules in the LMP1-induced signalling complex.11 An overexpressed FAF1 protein from the pJG4-5/FAF1-HA.tag construct in yeast cells was specifically detected using an anti-HA specific antibody with GST-CD40wt and A mutant but not with the CD40mT6 or CD40AmT6 or the LMP1 control, indicating the requirement of the TRAF6-binding domain of CD40 for its interaction with FAF1 (Figure 2b).
Figure 2.
CD40–FAF1 interaction in vitro. (a) Schematic diagram of the different point mutations within the GST-CD40 (wt) construct. A T254→A mutation (CD40A) abolishes TRAF2 and TRAF3 binding to CD40 but does not affect interaction with TRAF6, while Q234E235→AA (CD40mT6) double mutation disrupts interaction only with TRAF6. Finally, a CD40AmT6 mutant is unable to bind TRAF2, TRAF3 or TRAF6. (b) GST pull-down of FAF1 by CD40 protein was performed as previously described. Denaturated samples were analysed by western blotting using anti-HA and anti-GST specific antibodies. GST-LMP1 and GST proteins were used as negative controls. Protein lysate from EGY48 yeast cells harbouring the pJG4-5/B42-AD Hela cDNA FAF1 clone growing in Gal-Raff/CM-W liquid medium was used as a positive control. (c) Schematic representation of FAF1 domain structure, highlighting the Fas-interacting domain (FID) and the death-effector domain interacting domain (DEDID). (d) HEK293 cells were transected with 0.5 μg of empty pMCV/HA (HA) vector or pMCV/HA-FAF1wild-type (HA-FAF1wt) or pMCV/HA-FAF1mutant (FAF1mt; 1-305aa) (HAFAF1mt) for 36 h. HA-tagged FAF1 proteins were then examined by immunoblotting using an anti-HA specific antibody. (e) HEK293 cells were co-transfected with 2 μg of either empty pcDNA3.1 (pcD) and pMCV/HA-FAF1wt (HA-FAF1wt) or empty pcDNA3.1 (P) and pMCV/HA-FAF1mutant (HAFAF1mt) or pcDNA3.1/CD40 (pCD40) and pMCV/HA-FAF1wt, or pcDNA3.1/CD40 and pMCV/HA-FAF1mt for 36h. Protein lysates were prepared and co-immunoprecipitation was performed as previously described. Denaturated samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting using anti-HA and anti-CD40 specific antibodies. Protein lysates were used as a positive control
To determine which domain of FAF1 mediates its interaction with CD40, full-length FAF1 and truncated N-terminal domain, which contains the Fas-interacting domain (FID) required for FAF1–Fas interaction, (FAF1mt; 1-305aa) were cloned as HA-tagged fusions in pMCV/HA vectors (Figure 2c). Expression of full-length FAF1 and FAF1mt in HEK293 cells was confirmed by immunoblotting analysis using an anti-HA specific antibody (Figure 2d). FAF1wt and FAF1mt were transiently co-expressed with CD40 in HEK293 cells, and lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) using a monoclonal anti-CD40 antibody. Both full-length FAF1 and FAF1mt co-immunopreciptated specifically with CD40, but not with the empty pcDNA3.1 vector control, indicating that the FAF1 N-terminal domain (1–305 aa) is sufficient for CD40-FAF1 interaction (Figure 2e).
Endogenous interaction of FAF1 with CD40 in CD40-expressing carcinoma cells was also demonstrated by co-immunoprecipitation in EJ cells, confirming the physiological relevance of this interaction (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Endogenous FAF1–CD40 interaction in EJ and AGS cells. Total protein lysates (1.5 mg/ml) of either EJ or AGS cells in co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) lysis buffer were prepared and precleared for 1 h at 4 oC with 30 μl Protein G sepharose beads (Amersham) (1:1 slurry, prewashed in co-immunoprecipitation lysis buffer), and 40 μg of each precleared total protein lysate was tested for FAF1 and CD40 expression to ensure equal input of total protein lysate in each tube. Lysates were then incubated with either 4 μg of purified mouse IgG1K isotype control (ebioscience cat, 14-4714-82) (Isotype ab) or mouse monoclonal anti-CD40 antibody (MABTECH) (CD40 ab) overnight at 4 oC. Immunoprecipitation was then performed as previously described. Denaturated samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting using anti-FAF1and anti-CD40 specific antibodies
CD40 ligation induces FAF1 in an NFκB-dependent manner
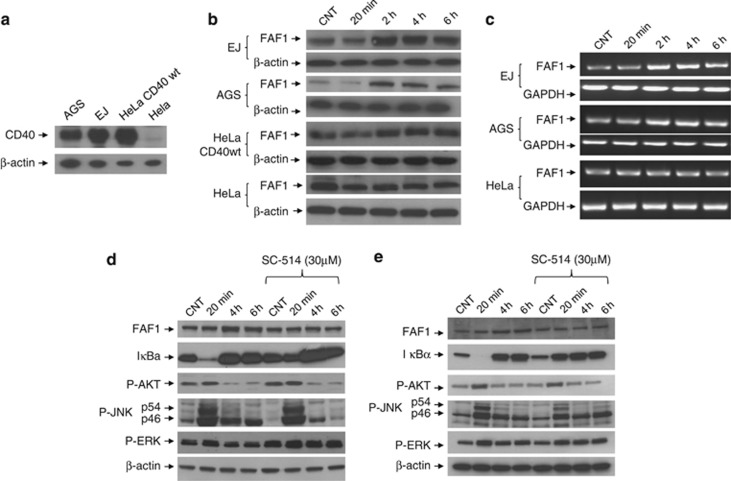
We next sought to investigate the functional significance of CD40-FAF1 interaction. To examine the effect of CD40 ligation on FAF1 expression, CD40-positive carcinomas (EJ, AGS, Hela cells stably expressing CD40) and CD40-negative Hela cells (Figure 4a) were each treated with recombinant soluble CD40L (1 μg/ml) for 20 min, 2 h, 4 h and 6 h or left untreated as a negative control. Cells were collected for protein lysate preparation and total RNA extraction for cDNA synthesis and subsequent RT-PCR reaction. FAF1 protein expression was upregulated following CD40 ligation in CD40-positive carcinomas but not in the CD40-negative Hela control (Figure 4b). Next RT-PCR was performed to quantify the level of FAF1 mRNA expression. FAF1 mRNA was upregulated following CD40 ligation in CD40-positive cells but not in CD40-negative cells in a time-dependent manner, confirming that FAF1 upregulation was due to increased transcription rather than protein stabilisation (Figure 4c).
Figure 4.
CD40 ligation induces FAF1 upregulation in an NFκB-dependent manner. (a) CD40-positive carcinomas (EJ, AGS, Hela cells stably expressing CD40) and CD40-negative carcinoma Hela cells were plated for 24 h in 60 mm tissue culture-treated dishes. Protein lysates were then prepared and analysed for CD40 expression and β-actin using specific antibodies against CD40 and β-actin. (b) Cells were plated for 24 h in 60 mm tissue culture-treated dishes, then treated with 1 μg/ml rsCD40L for 20 min, 2, 4 and 6 h or left untreated as a negative control. Cells were washed with PBS then lysed in situ for protein lysate preparation. FAF1 expression was examined by western blot analysis. (c) Total RNA was extracted from EJ, AGS and HeLa cells at the indicated time points, and 2 μg RNA was reverse transcribed for cDNA synthesis. RT-PCR using 1 μl cDNA was performed utilizing specific primers for FAF1 and GAPDH as a loading control. RT-PCR products were resolved by 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis. (d) EJ cells and (e) AGS cells were pretreated with the NFκB inhibitor, SC-514 (30 μM) for 6 h. Culture media were then replaced with fresh media containing rsCD40L (1 μg/ml) and NFκB inhibitor SC-514 (30 μM) for 20 min, 4 h or 6 h or left untreated with rsCD40L as a negative control, then lysed in situ. Protein extracts were examined by western blotting for FAF1, IκBα, P-AKT, P-JNK, P-ERK expression. β-Actin was used as loading control
As CD40 ligation activates the transcription factor, NFκB, we investigated whether CD40-induced FAF1 expression is regulated by NFκB. CD40-positive EJ cells and AGS cells were treated with rsCD40L (1 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of the NFκB inhibitor, SC-514 (30 μM). FAF1 upregulation was suppressed in cells pretreated with the NFκB inhibitor (Figures 4d and e). To ensure that SC514 was functioning specifically through NFκB inhibition and not through interference with other CD40-induced signalling molecules, total IκBα, P-AKT, P-ERK and P-JNK were examined by western blot analysis. SC-514 successfully inhibited NFκB activity, evidenced by increased IκBα levels, but had no effect on CD40-induced activation of the AKT, ERK or JNK pathways (Figures 4d and e).
FAF1 inhibits CD40-induced NFκB activation
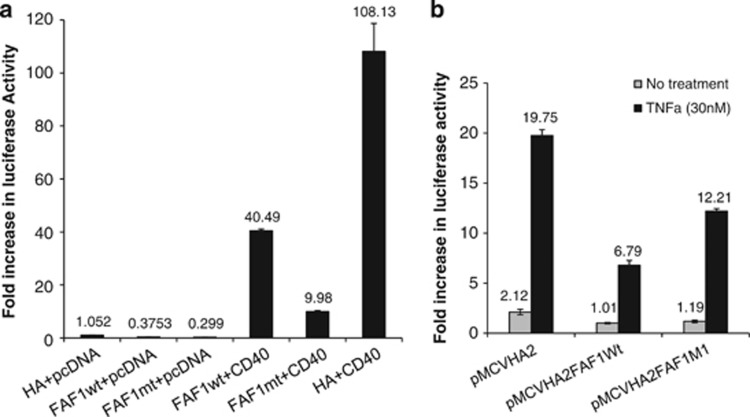
FAF1 has been reported to regulate NFκB when induced by a variety of stimuli including TNF-α, IL-1β and LPS in a HEK293 cell transfection system.12 To test the effect of FAF1 on CD40-induced NFκB activation, HEK293 cells transfected with the luciferase reporter plasmids pNFκB-Luc firefly reporter (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA), the pRL-TK renilla reporter (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) and the pCDNA3.1/CD40wt construct were co-transfected with either GFP-expressing pEGFPC1 vector or pEGFPC1/FAF1 construct. CD40-induced NFκB activation was significantly reduced when FAF1 was co-expressed with CD40 in an FAF1 concentration-dependent manner (Figure 5a). To confirm that this effect was not due to FAF1 overexpression negatively affecting the concomitant expression of CD40, the level of CD40 expression in the presence or absence of FAF1 was examined by western blotting using anti-CD40 and GFP specific antibodies for detection of CD40 and GFP-FAF1 fusions. FAF1 expression did not alter the level of CD40 expression (Figure 5b).
Figure 5.
FAF1 inhibits CD40-induced NFκB and FAF1 knockdown results in prolonged NFκB activation. (a) HEK293 cells transiently transfected with 100 ng of the reporter plasmids were co-transfected with the empty pEGFPC1 (GFP, 500 ng) and empty pcDNA3.1 (P, 500 ng) or the empty pcDNA3.1 (500 ng) and pEGFPC1/FAF1 (GFP-FAF1, 50 ng or 500 ng) or empty pEGFPC1 (GFP, 500 ng) and the pcDNA3.1/CD40 (pCD40, 500 ng) or pcDNA3.1/CD40 (500 ng) and pEGFPC1/FAF1 (50 ng or 500 ng). Twenty-four hours later, NFκB activity was measured by luciferase reporter assay. Results are a mean of three triplicate samples±S.D. (b) Protein lysates were probed with anti-CD40 and anti-GFP antibodies to examine the expression of CD40 and GFP-FAF1 protein fusion, respectively. (c) EJ and (d) AGS cells were transfected with either control siRNA or FAF1 siRNA (50 pM) for 48 h then treated with rsCD40 (1 μg/ml) for 20 min, 2 h and 4 h or left untreated as a negative control and then lysed in situ. Protein extracts were then examined by western blotting for FAF1, IκBα, P- IκBα, using specific antibodies. β-Actin was used as a loading control
To examine the effect of FAF1 downregulation on CD40-induced NFκB activity, CD40-positive EJ cells and AGS cells were transfected with FAF1 siRNA (SC-37520) or scrambled siRNA as a control (SC-37007) for 48 h then treated with rsCD40L (1 μg/ml) for 20 min, 2 h and 4 h or left untreated as a negative control. Cells were then lysed in situ and the levels of FAF1, total IκBα, phospho-IκBα were analysed by western blotting. FAF1 knockdown resulted in lower IκBα protein levels and higher levels of phospho-IκBα, indicating that FAF1 downregulation allowed a more robust and prolonged activation of NFκB and further indicating its regulatory role in CD40-induced NFκB activation (Figures 5c and d).
Inhibition of CD40-induced NFκB by FAF1 requires FAF1–CD40 interaction
FAF1 has previously been reported to regulate TNFα-induced NFκB via direct interaction with RelA, IKKβ or CK2, and these require the active ubiquitin-like C-terminal domain of the protein. However, as we have shown here that FAF1 interacts with CD40 and that this interaction requires the TRAF6-binding domain of CD40 and the N-terminal FID domain of FAF1, we postulated that FAF1 regulation of CD40-induced NFκB activation may be via an alternative mechanism requiring this interaction, perhaps through competition with TRAF6 for occupancy of this binding site on the CD40 receptor. If this were the case, then it would be anticipated that the CD40-binding FID domain of FAF1 would be sufficient to inhibit CD40-induced NFκB even in the absence of the active C-terminal domain of FAF1. This was investigated by examining the effect of truncated FAF1 (FAF1mt: 1–305 aa) compared with full-length FAF1 on CD40-induced NFκB activation. HEK293 cells transfected with NFκB reporters as above were co-transfected with CD40 and either wt or truncated mt FAF1 (or the relevant empty vector controls) as described in Figure 5a.
Similar to wild-type full-length FAF1, the truncated mutant FAF1 retained the capacity to inhibit CD40-induced NFκB activation (Figure 6a).
Figure 6.
The FAF1 N-terminal domain is sufficient to inhibit CD40-induced NFκB activity. HEK293 cells transiently transfected with reporter plasmids (100 ng) were (a) co-transfected with the empty pMCV/HA (HA) and empty pcDNA3.1 (pcDNA) or the empty pcDNA3.1 and pMCV/HA-FAF1wt (FAF1wt) or empty pcDNA3.1 and pMCV/HA-FAF1mt, or pcDNA3.1/CD40 (CD40) and pMCV/HA-FAF1wt, or pcDNA3.1/CD40 and pMCV/HA-FAF1mt or pcDNA3.1/CD40 and pMCV/HA empty vector for 24 h, or (b) transfected with the 0.5 μg of empty pMCV/HA or pMCVHA/FAF1wt or pMCV/HAFAF1mt (1–305 aa) for 24 h then treated with TNFα (30 nM) for 6 h. NFκB activity was measured by luciferase reporter assay. Results are a mean of three triplicate samples±S.D.
To further confirm that the mechanism of this inhibition is dependent on direct FAF1–CD40 interaction, we investigated the effect of wt and mt FAF1 on NFκB activated by a CD40-independent stimulus, TNFα. Thus, HEK293 cells transiently transfected with the reporter plasmids were again co-transfected with either wt or mt FAF1 plasmids before treatment with TNFα (30 nM). Although expression of FAF1mt resulted in modest inhibition of TNFα-induced NFκB activation, inhibition was more profound with full-length FAF1, suggesting that, unlike CD40, FAF1-mediated inhibition of TNF-induced NFκB activation requires the full-length protein with its C-terminal ubiquitin-related functions (Figure 6b).
FAF1 regulates TRAF6-mediated CD40 signalling through competition for CD40 receptor binding
Activation of NFκB by CD40 is, to a large extent, dependent upon TRAF6 binding to the CD40 receptor upon its ligation. We have shown above that FAF1 can regulate CD40-induced NFκB activation and that this requires interaction of FAF1 with the CD40 receptor. Furthermore, we have shown that FAF1 interaction with CD40 is via the TRAF6-binding domain. Thus, we hypothesise that FAF1-mediated regulation of NFκB is through competition with TRAF6 for CD40 binding.
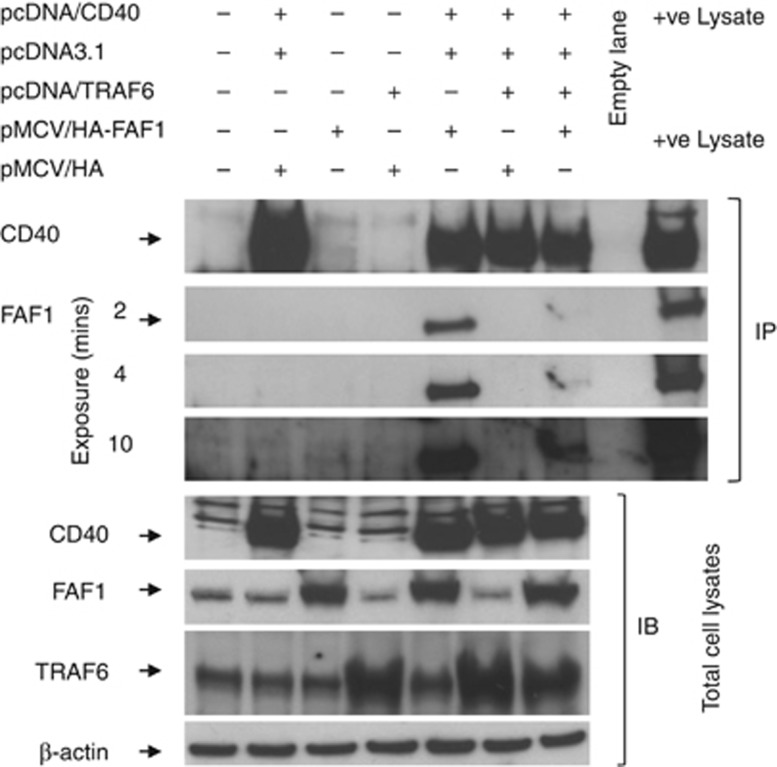
To investigate this, HEK293 cells were co-transfected with permutations of plasmids expressing CD40, TRAF6, HA-tagged FAF1 or control plasmids as indicated in Figure 7 and then subjected to co-immunoblotting using specific antibodies against CD40, HA-tagged FAF1 and TRAF6.
Figure 7.
TRAF6 overexpression abrogates CD40–FAF1 interaction. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with 2 μg of each plasmid as indicated or left untransfected as a negative control. Thirty hours later, cells were lysed in situ in co-immunoprecipitation buffer (1% NP-40/PBS, 1 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM CaCl2, 20 mM Hepes pH 7.4, 1 mM Na3VO4, 50 mM NaF, 5 mg/ml leupeptin, 1 mg/ml aprotinin, and 1mg/ml pepstatin) for 1 h on ice. Protein lysates were prepared, and co-immunoprecipitation was performed as previously described. Denaturated samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting using specific antibodies against CD40, Haemagglutinin (HA) tag and TRAF6. Total protein lysates were used as a positive control in the immunoprecipitation (IP) blots. β-Actin was used as a loading control
As expected, co-transfection with CD40 and HA-FAF1 resulted in co-immunoprecipitation of FAF1 with CD40 (Figure 7, lane 5). However, the additional transfection of TRAF6 resulted in a significant reduction in FAF1 co-IP with CD40 (Figure 7, lane 7). Blotting of total cell lysates indicated that this reduction was not due to an effect of TRAF6 transfection on the level of HA-FAF1 expression as cells transfected with CD40, HA-FAF1 and TRAF6 satisfactorily expressed all three proteins (Figure 7, lower panel). As TRAF6 and FAF1 do not directly interact with each other, these data suggest that FAF1 and TRAF6 are competing for the TRAF6-binding site of CD40.
Discussion
Although the interaction between CD40 and members of the TRAF family is well characterised, this is the first study to show an interaction between CD40 and Fas-associated factor 1 (FAF1). FAF1 was first identified as a partner of the Fas receptor using yeast two-hybrid analysis13 and has recently been reported as a component of the death-inducing signalling complex (DISC) in Fas-mediated apoptosis.14 Although structurally FAF1 does not contain any typical death motifs such as a death domain (DD), death effector domain (DED) or caspase recruitment domain, FAF1 overexpression can initiate apoptosis in the absence of any extrinsic death signals.15 FAF1 is a 74-kDa protein with an N-terminal domain that mediates its interaction with Fas, the Fas-interacting domain (FID), and a functional ubiquitin-like C-terminal domain that is required for its pro-apoptotic activity. FAF1 is also involved in the ubiquitination pathway and interacts with ubiquitin and valosin-containing protein, a multiubiquitin chain-targeting factor, stabilising the protein, which may activate survival pathways including Akt and NFκB.16 In addition, FAF1 inhibits the chaperone activities of the heat-shock proteins Hsc70 and Hsp70.17
Here we report for the first time the finding that FAF1 is also a novel interactor with the CD40 receptor. We further demonstrate that the CD40–FAF1interaction requires the TRAF6-binding domain in CD40 and the FID of FAF1, as CD40 mutants lacking the TRAF6-binding domain failed to bind to FAF1, although the N-terminal domain of FAF1 (FAF1mt; 1-305aa) was sufficient to bind to CD40 in the co-immunoprecipitation analysis.
Although in the yeast two-hybrid experiments CD40 could not pull down full-length FAF1, this may be attributable to the high proteolytic activity associated with protein purification in yeast. Indeed, a 40-kDa degradation product of FAF1 has been found in various human cell lines.18 Moreover, 40-kDa FAF1 fragments (spanning 1–313 and 1–315 aa) have been identified with ectopic expression of recombinant FAF1 in Escherichia coli (E-coli).19 In addition, it is possible that steric hindrance caused by the large GST tag (26 kDa) to the FAF1-binding site within the relatively small CD40 cytoplasmic domain (6.3 kDa) might prevent interaction of the full-length FAF1 protein with CD40 but allow smaller fragments that contain the crucial CD40-binding site to bind. In support of this, HA-tagged FAF1 fusions, including the full-length FAF1 (FAF1wt) and its N-terminal domain (FAF1mt; 1–305 aa), were co-immunoprecipitated and detected with CD40 in the in vitro co-immunoprecipitation experiments.
An additional novel finding reported here is that FAF1 is upregulated in response to CD40 ligation and this is a result of transcriptional activity as increased levels of FAF1 mRNA were also detected. Furthermore, this appears to be mediated by CD40-induced NFκB activation, as inhibition of NFκB blocked the upregulation of FAF1. This is of particular interest as FAF1 has been reported to inhibit NFκB activation by various stimuli including TNFα.12 In agreement with this, here we report that CD40-induced NFκB activation was inhibited by ectopic expression of FAF1 in HEK293 cells and that more prolonged activation of NFκB by CD40 ligation was observed following FAF1 knockdown. Thus, as FAF1 expression is induced by CD40-mediated NFκB activation and as FAF1 then suppresses CD40-induced NFκB, we postulate a regulatory role for FAF1 in CD40-induced NFκB signalling via a negative feedback loop. This is further supported by the kinetics of NFκB and FAF1 activation in response to CD40 ligation with a rapid, yet transient induction of NFκB followed temporally by increased FAF1 expression and then rapid downregulation of NFκB.
FAF1 is reported to regulate TNF-induced NFκB activity via direct interaction with RelA, preventing its translocation to the nucleus or through interaction with IKKβ to suppress IKK activity or by binding to and blocking the protein kinase CK2.12, 20, 21, 22 Functional CK2 is a key NFκB regulator that can phosphorylates IκB and activate the IKKα kinase, leading to NFκB activation.23, 24, 25 However, here we report a novel mechanism by which FAF1 regulates NFκB induced by CD40 ligation. We have demonstrated for the first time that FAF1 interacts directly with CD40 via the TRAF6-binding domain of the receptor. As TRAF6 binding in response to CD40 ligation is, at least in part, responsible for CD40-mediated NFκB activation, we propose that FAF1 regulates NFκB in the context of CD40 signalling through competition with TRAF6 for its CD40-binding domain (Figure 7). Thus, CD40 ligation recruits TRAF6 to the receptor, which, in turn, stimulates NFκB activation. Among other things, this results in transcriptional activation of the FAF1 gene and the increased FAF1 protein then competes with, and displaces, TRAF6 from the CD40 receptor, thus terminating NFκB activation via a negative feedback loop (Figure 8). This is supported by our observation that a truncated FAF1, lacking the functional C-terminal domain but retaining the capacity to bind to CD40, is still able to inhibit CD40-induced NFκB activation. Indeed, NFκB inhibition was more pronounced with the mutant compared with wtFAF1 perhaps due to the stoichiometry of the shorter mutant protein allowing it to access the TRAF6-binding site of the CD40 receptor more readily (Figure 6a).
Figure 8.
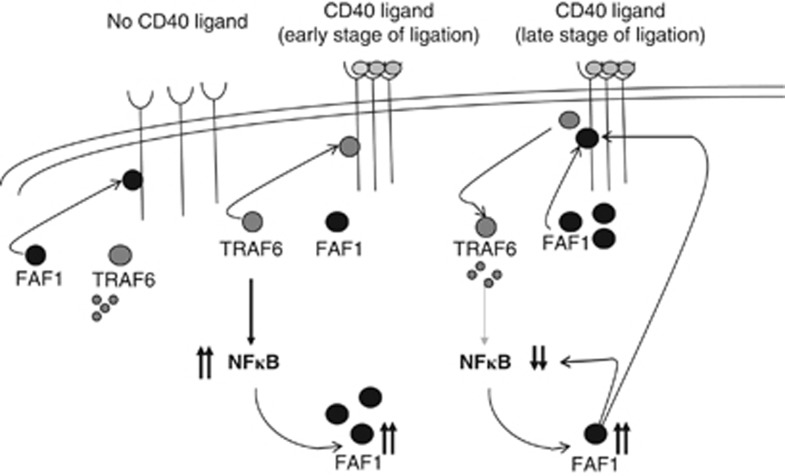
Proposed mechanism of FAF1 regulation of CD40 ligand-induced NFκB activity. In the absence of CD40 ligand, the conformation of the CD40 receptor favours FAF1 binding. In this conformation, TRAF6 is not bound to the receptor and is therefore degraded resulting in low NFκB activity. In the early stage of CD40 ligation, receptor trimerisation promotes recruitment of TRAF6. This results in NFκB induction, which, in turn, upregulates FAF1 expression. Higher FAF1 protein levels result in NFκB inhibition by direct inhibition of the assembly of the IKK complex and, indirectly, by competing with the CD40-TRAF6 binding through the TRAF6-binding domain
As well as having an important homeostatic role in regulating CD40 signalling, it is likely that aberrant FAF1 function has a pathological role in cancer. For example, it has been reported that FAF1 function is downregulated in mantle cell lymphoma,26 gastric cancer27 and mesothelioma.28 Thus, loss of regulatory function of FAF1 may permit constitutive NFκB signalling, which then contributes to the malignant phenotype. Perturbation of FAF1 function may therefore serve as a predictive biomarker for sensitivity to therapeutic inhibition of NFκB-dependent cancers. Further studies to characterise loss of FAF1 in solid tumours, particularly those associated with CD40 expression and their potential sensitivity to NFκB inhibition, are warranted and are currently underway in our laboratory.
Materials and Methods
Maintenance of cell lines
Bladder carcinoma EJ cells, gastric carcinoma AGS cells, cervical carcinoma HeLa cells, Hela cells stably expressing wild-type CD40 and embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells were maintained in either RPMI 1640 or DMEM supplemented with 2 mM glutamine, 10% FCS.
Plasmids
A cDNA encoding wild-type CD40 cytoplasmic tail (216–278 aa) was amplified by PCR (Table 1) from the pCDNA3.1/CD40 construct and cloned into the LexA-based pEG202 yeast two-hybrid plasmid between EcoRI and XhoI restriction sites. FAF1 wild-type and its FID-containing mutant (1–305 aa) were amplified by PCR and engineered with a XhoI-EcoRI artificial sites and cloned as GFP fusions into the pEGFPC1 vector (Clontech, Mountain View, CA, USA). To clone the FAF1 wild-type and its FID mutant as HA-tagged fusions, they were released from the pEGFPC1 vector by XhoI-KpnI restriction and cloned into a home-modified pMCV/HA expression vector.
Table 1. Oligonucleotides used in this study.
| Name | Primer (5′-3′) | Restriction sites | Construct | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD40EcoR-F | GAATTCAAAAAGGTGGCCAAGAAG | EcoR1 | pEG202/CD40 | Yeast two hybrid |
| CD40Xho-R | CTCGAGTCACTGTCTCTCCTGC | Xho1 | pEG202/CD40 | Yeast two hybrid |
| FAFXho-F1 | CTCGAGTGGCGTCCAACATGGA C | Xho1 | pEGFPC1/FAF1wt&mt | Protein expression |
| FAFEcoR-R915 | CTTAAGTTAATCCACCCCAAATTCTGTAG C | EcoR1 | pEGFPC1/FAF1mt | Protein expression |
| FAFEcoR-R1953 | CTTAAGTTACTCTTTTGCTTCAAGGAAAAGG | EcoR1 | pEGFPC1/FAF1wt | Protein expression |
| GAPDHF244 | CCTCCAAAATCAAGTGGGGCG | NA | NA | RT-PCR |
| GAPDHR845 | ACCACCAGGTGCTCAGTGTAG | NA | NA | RT-PCR |
| FAF1F | GCCACCAAT TATGGGAGG G | NA | NA | RT-PCR |
| FAF1R | CAG ATC CCA AGC CCA GGT | NA | NA | RT-PCR |
Yeast two-hybrid screening
A LexA-based yeast two-hybrid screen was performed as described previously by Golemis et al.29 In brief, the Hela cDNA library, cloned into the pJG4-5 vector, was used to screen for CD40 cytoplasmic domain interacting proteins. The cDNAs were expressed as fusions to a nuclear localisation sequence, transcriptional activation domain (the acid blob B42AD) and a haemagglutinin (HA) epitope under the control of the GAL1 promoter.30 The LexA DNA-binding domain fusion in the pEG202 vector was the screen ‘bait'. To construct the pEG202/CD40 plasmid, the CD40 cytoplasmic domain (646–834 bp) coding sequence was PCR amplified from the pcDNA3.1/CD40 construct using CD40EcoR-F and CD40Xho-R primers (Table 1), cloned into the TOPO2.1 vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and subcloned into pEG202 via the EcoR1-XhoI sites, expressing a LexA-CD40 fusion under the control of the alcohol dehydrogenase 1 (ADH1) promoter. The pEG202/CD40 construct was transformed into the yeast reporter Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain EGY48 (Matα, ura3 trp1 his3 3LexA-operator) in a lithium acetate-mediated transformation method31 and tested for the inability to self-activate by growing on glucose/complete medium lacking histidine and leucine. Co-transformed EGY48 cells with pEG202/CD40 bait and pJG4-5/HeLa cDNA library were plated into glucose/complete medium lacking histidine and tryptophan (Glu/CM-H,W) and allowed to grow. Aliquots of the library primary transformants were diluted (1:10) in galactose-raffinose/CM lacking histidine, and tryptophan (Gal-Raff/CM-H,W) liquid medium, allowed to grow (induction of the expression of the library proteins under the control of GAL1 promoter) and plated on selective Gal-Raff/CM lacking histidine, tryptophan and leucine (Gal-Raff/CM-H,W,L) dropout plates. To confirm positive interactions, individual colonies from Gal-Raff/CM-H,W,L plates were re-plated on Glu/CM-H,W and replica-plated on Glu/CM lacking histidine, tryptophan and leucine (Glu/CM-H,W,L) and Gal-Raff/CM-H,W,L plates. The putative positive library plasmids were extracted, reproduced in TOPO 10F Escherichia coli (E-coli) (Invitrogen) and reintroduced back into the EGY48 reporter strain in the presence or absence of pEG202/CD40 and were tested for reproducibility of the interactions. The final isolated positive clones were identified by sequencing.
GST pull-down, immunoprecipitation and western blotting
For preparation of protein extract from yeast cells, EGY48 cells transformed with the isolated pJG4-5/HeLa cDNA clone coding the FAF1 sequence obtained from 5 ml overnight cultures grown in Glu/CM-W medium were switched into Gal-Raff/CM-W for at least 8 h with vigorous shaking for induction of HA-FAF1 protein fusion under the GAL1 promoter. Cells were spun down and resuspended in 1ml of GST pull-down lysis buffer (20 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM Na3VO4, 50 mM NaF, 2.5 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 1 mM β-glycerophosphate, 1 μg/ml leupeptin and 1 μg/ml aprotinin). An equal volume of acid washed glass beads (Sigma UK) was added and vortexed for 60 s then immediately placed on ice for 1 min, 8–10 times. The supernatant was collected and the protein concentration was assessed. For preparation of GST-CD40 fusion protein (Figure 2a) extract, E.coli BL21 cells (Invitrogen) were transformed with pGEX-5X-1/CD40 constructs and grown up to an OD600 ∼0.4 before supplementing the bacterial culture with isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) at a final concentration of 0.1 mM for 5 h. Cells were spun down and resuspended in 1 ml of GST pull-down lysis buffer and lysed on ice by pulse sonication. Lysates were then clarified by centrifugation at 13 000 r.p.m. at 4 oC for 15 min. Soluble GST-CD40 proteins were purified by incubating overnight at 4 °C with lysis buffer-prewashed GST Sephrose 4B beads (Amersham, Amersham, UK). Sepharose bead/GST-CD40 complexes were obtained by centrifugation at 3000 r.p.m. at 4 oC for 5 min. Following three washes with lysis buffer; the resultant Sepharose bead/GST-CD40 complexes were resuspened in a volume of lysis buffer to obtain 1:4 slurry. For the GST pull-down, 1 mg of precleared total yeast protein lysate was incubated with 20 μl of Sepharose/GST-CD40 beads for 2 h at 4 °C. The GST-CD40-FAF1 bead complexes were pelletted down by slow-spin centrifugation (3000 r.p.m., 5 min, 4 oC) then washed three times with 1 ml of lysis buffer. The GST-CD40-FAF1 bead complexes were resuspended in 50 μl 2 × concentrated GSB buffer and boiled for 5 min. Thirty microlitres of the total volume of the samples was examined by western blot analysis for HA-FAF1 fusion protein using an anti-HA antibody, and the remaining volumes were immunoblotted for GST fusion proteins using an anti-GST antibody.
For the co-immunoprecepitation studies, 293 cells co-transfected with 2 μg empty pcDNA and pMCV/HA-FAF1wt or empty pcDNA3.1 and pMCV/HA-FAF1mt mutant or pcDNA/CD40 and pMCV/HA-FAF1wt, or pcDNA3.1/CD40 and pMCV/HA-FAF1mt mutant were lysed in situ with co-immunoprecipitation lysis buffer (1% Brij-98/PBS, 1 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM CaCl2, 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM Hepes pH 7.4, 1 mM Na3VO4, 50 mM NaF, 5 μg/ml leupeptin, 1 μg/ml aprotinin, and 1 μg/ml pepstatin), allowed to lyse on ice for 20 min and clarified by centrifugation for 5 min at 13 000 r.p.m. at 4 oC. One milligram of total protein/ml co-immunoprecipitation lysis buffer was precleared for 1 h at 4 oC with 30 μl Protein G sepharose beads (Amersham) (1:1 slurry, prewashed in co-immunoprecipitation lysis buffer). CD40 immunocomplexes were then prepared by incubating the pre-cleared lysate with 4 μg mouse monoclonal anti-CD40 antibody (MABTECH) overnight at 4oC then precipitated by incubating for 2 h at 4 oC with 20 μl protein G-Sepharose beads prewashed three times in co-immunoprecipitation lysis buffer. The CD40-sepharose bead complexes were subjected to slow-spin centrifugation (3000 r.p.m., 5 min at 4 oC) and then washed three times with 1 ml co-immunoprecipitation lysis buffer using slow-spin centrifugation to pellet the beads. Beads were drained with a Hamilton glass syringe and resuspended in 35 μl 2 × concentrated GSB. Samples were denatured by boiling for 5 min and examined by western blotting.
RNA extraction and RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted using the RNAzol reagent (Biogenesis Ltd, Poole, UK), and cDNA synthesis was performed using the RETROscript RNase reverse transcription kit (Ambion Europe, Huntingdon, UK) according to the manufacturer's instructions. RT-PCR was performed using PLATINUM Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen) utilizing the human FAF1-specific primers: FAF1: forward 5′-GCCACCAATTATGGGAGGG-3′ and reverse 5′CAGATCCCAAGCCCAGGT3′. The amount of cDNA template used for the RT-PCR was adjusted on the basis of amplification with primers specific for human GAPDH: forward 5′-CCTCCAAAATCAAGTGGGGCG-3′ and reverse 5′-ACCACCAGGTGCTCAGTGTAG-3′.
RNA interference studies
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) directed to FAF1 (SC-37520) and a control siRNA-A (SC-37007), which does not lead to specific degradation of any known cellular mRNA, were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Cells were transfected with 50 pM of either siRNA according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Reporter gene assay
HEK293 cells growing in 48-well plates were transfected with pNF-κB-Luc firefly reporter (Stratagene), pRL-TK renilla reporter (Promega) and the indicated expression plasmids. After 24 h, cell lysates were prepared and the firefly and renilla luciferase activities were measured using the dual-luciferase reporter assay system (Promega). The relative luciferase activity (RLA) was calculated as follows: RLA=firefly luciferase activity/renilla luciferase activity.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funding from a Cancer Research UK Clinician Scientist Fellowship (DHP) and from the Northwest Cancer Research Fund. The Hela cDNA library was the kind gift of Dr Antonios M Makris, Department of Natural Products and Biotechnology, Mediterranean Agronomic Institute of Chania, PO Box 85, Chania 73100, Greece.
Glossary
- bp
base pair
- DD
death domain
- DED
death effector domain
- DEDID
death-effector domain-interacting domain
- DISC
death-inducing signalling complex
- E coli
Escherichia coli
- FAF1
Fas-associated factor 1
- FID
Fas-interacting domain
- GFP
Green fluorescent protein
- Gln
Glycine
- GLU
Glutamine
- HA
haemagglutinin
- IL-1β
interleukin-1β
- IP
immunoprecipitation
- LMP1
latent membrane protein 1
- LPS
lipopolysaccharide
- MAPK
mitogen-activated protein kinases
- Mt
mutant
- NFκB
nuclear factor κB
- PI3Kinase
phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase
- Pro
proline
- rsCD40L
recombinant soluble CD40 ligand
- siRNA
small interfering RNA
- Thr
threonine
- TNF-α
tumour necrosis factorα
- TRADD
TNF receptor-associated death domain
- TRAF
TNF receptor-associated factor
- Wt
wild type
- YTH
yeast two-hybrid
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Edited by G Raschellà
References
- van Kooten C, Banchereau J. CD40-CD40 ligand. J Leukoc Biol. 2000;67:2–17. doi: 10.1002/jlb.67.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos AG, Young LS. The role of the CD40 pathway in the pathogenesis and treatment of cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004;4:360–367. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2004.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planken EV, Dijkstra NH, Willemze R, Kluin-Nelemans JC. Proliferation of B cell malignancies in all stages of differentiation upon stimulation in the CD40 system. Leukemia. 1996;10:488–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funakoshi S, Longo DL, Beckwith M, Conley DK, Tsarfaty G, Tsarfaty I, et al. Inhibition of human B-cell lymphoma growth by CD40 stimulation. Blood. 1994;83:2787–2794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies CC, Mak TW, Young LS, Eliopoulos AG. TRAF6 is required for TRAF2 dependant CD40 signal transduction in nonhemopoietic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:9806–9819. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.22.9806-9819.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu HM, O'Rourke K, Boguski MS, Dixit VM. A novel RING finger protein interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of CD40. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:30069–30072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto N, Kobayashi N, Azuma S, Yamamoto T, Inoue J. Two differently regulated nuclear factor kappaB activation pathways triggered by the cytoplasmic tail of CD40. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:1234–1239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.4.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanissian SH, Geha RS. Jak3 is associated with CD40 and is critical for CD40 induction of gene expression in B cells. Immunity1997. 6:379–387. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies CC, Mason J, Wakelam MJ, Young LS, Eliopoulos AG. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase- and ERK MAPK-regulated protein synthesis reveals the pro- apoptotic properties of CD40 ligation in carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:1010–1019. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303820200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen SS, Miller HG, Everdeen DS, Dang TT, Crute JJ, Kehry MR. CD40-tumor necrosis factor receptor rassociated factor (TRAF) interactions: regulation of CD40 signaling through multiple TRAF binding sites and TRAF hetero-oligomerization. Biochemistry. 1998;37:11836–11845. doi: 10.1021/bi981067q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultheiss Ute, Püschner Stephanie, Kremmer Elisabeth, Tak WM, Engelmann Hartmut. Wolfgang Hammerschmidt and Arnd Kieser. TRAF6 is a critical mediator of signal transduction by the viral oncogene latent membrane protein 1. EMBO J. 2001;20:5678–5691. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.20.5678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park MY, Jang HD, et al. Fas-associated factor-1 inhibits nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) activity by interfering with nuclear translocation of the RelA (p65) subunit of NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:2544–2549. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304565200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu SW, Chae SK, Lee KJ, Kim E. Identification and characterization of human Fas associated factor 1, hFAF1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;262:388–394. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu SW, Lee SJ, Park MY, Jun JI, Jung YK, Kim E. Fas-associated factor 1, FAF1, is a member of Fas death inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:24003–24010. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302200200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu SW, Kim E. Apoptosis induced by human Fas-associated factor 1, hFAF1, requires its ubiquitin homologous domain, but not the Fas-binding domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;286:1027–1032. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song HY, Régnier CH, Kirschning CJ, Goeddel DV, Rothe M. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated Kinase cascades: bifurcation of nuclear factor-kappaB and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK/SAPK) pathways at TNF receptor-associated factor 2. Proc Nat1 Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:9792–9796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.18.9792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim HJ, Song EJ. Human Fas-associated factor 1 interacts with heat shock protein 70and negatively regulates chaperone activity. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:8125–8133. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406297200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu SW, Chae SK, Lee KJ, Kim E. Identification and characterization of human Fas associated factor 1, hFAF1. Biochem Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999;262:388–394. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen HH, Hjerrild M, Guerra B, Larsen MR, HØjrup P, Boldyre B. Phosphorylation of the Fas associated factor FAF1 by protein kinase CK2 and identification of serines 289 and 291 as the in vitro phosphorylation site. Int J Biochem. 2001;33:577–589. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(01)00039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park MY, Moon JH, et al. FAF1 suppresses IkappaB kinase (IKK) activation by disrupting the IKK complex assembly. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:27572–27577. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C700106200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litchfield DW, Luscher B. Casein kinase II in signal transduction and cell cycle regulation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993;127-128:187–199. doi: 10.1007/BF01076770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerra B, Boldyreff B, Issinger OG. FAS-associated factor 1 interacts with protein kinase CK2 in vivo upon apoptosis induction. Int J Oncol. 2001;19:1117–1126. doi: 10.3892/ijo.19.6.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu ZL, McKinsey TA, Liu L, Qi X, Ballard DW. Basal phosphorylation of the PEST domain in the I(kappa)B(beta) regulates its functional interaction with the crel proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:5974–5984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.11.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElhinny JA, Trushin SA, Bren GD, Chester N, Paya CV. Casein kinase II phosphorylates I kappa B alpha at S-283, S-289, S-293, and T-291 and is required for its degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:899–906. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.3.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy SF, Guo S, Demicco EG, Romieu-Mourez R, Landesman-Bollag E, Seldin DC, et al. Inducible IkappaB kinase/IkappaB kinase epsilon expression is induced by CK2 and promotes aberrant nuclear factor-kappaB activation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:11375–11383. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beà S, Salaverria I, Armengol L, Pinyol M, Fernández V, Hartmann EM, et al. Uniparental disomies, homozygous deletions, amplifications and target genes in mantle cell lymphoma revealed by integrative high-resolution whole-genome profiling. Blood. 2009;113:3059–3069. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-170183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjørling-Poulsen M, Seitz G, Guerra B, Issinger OG. The pro-apoptotic FAS-associated factor1 is specifically reduced in human gastric carcinomas. Int J Oncol. 2003;23:1015–1023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altomare DA, Menges CW, Pei J, Zhang L, Skele-Stump KL, Carbone M, et al. Activated TNFalpha/NFkappaB signaling via downregulation of Fas-associated factor 1in asbestos-induced mesotheliomas from Arf knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:3420–3425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808816106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golemis EA, Khazak V. Alternative yeast two-hybrid systems.The interaction trap and interaction mating. Methods Mol Biol. 1997;63:197–218. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-481-X:197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyuris JE, Golemis H, Cherikov R. Brent. CDI1 a human G1-phase and S phase protein phosphate that associates with CDK2. Cell. 1993;75:791–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90498-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker L, Becker DM, Lundblad V.Introduction of DNA into yeast cells Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, et al (eds).Current Protocols in Molecular Biology John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York; 200113.7.1–13.7.10. [Google Scholar]