Abstract
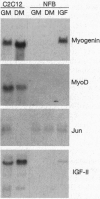
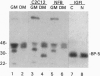
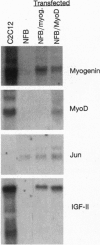
In the present study we used the mutant muscle cell line NFB4 to study the balance between proliferation and myogenic differentiation. We show that removal of serum, which induced the parental C2C12 cells to withdraw from the cell cycle and differentiate, had little effect on NFB4 cells. Gene products characteristic of the proliferation state, such as c-Jun, continued to accumulate in the mutant cells in low serum, whereas those involved in differentiation, like myogenin, insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II), and IGF-binding protein 5 (IGFBP-5) were undetectable. Moreover, NFB4 cells displayed a unique pattern of tyrosine phosphorylated proteins, especially in low serum, suggesting that the signal transduction pathway(s) that controls differentiation is not properly regulated in these cells. Treatment of NFB4 cells with exogenous IGF-I or IGF-II at concentrations shown to promote myogenic differentiation in wild-type cells resulted in activation of myogenin but not MyoD gene expression, secretion of IG-FBP-5, changes in tyrosine phosphorylation, and enhanced myogenic differentiation. Similarly, transfection of myogenin expression constructs also enhanced differentiation and resulted in activation of IGF-II expression, showing that myogenin and IGF-II cross-activate each other's expression. However, in both cases, the expression of Jun mRNA remained elevated, suggesting that IGFs and myogenin cannot overcome all aspects of the block to differentiation in NFB4 cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. E., Boxhorn L. K. Regulation of skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by transforming growth factor-beta, insulin-like growth factor I, and fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Feb;138(2):311–315. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Tjian R. Control of c-Jun activity by interaction of a cell-specific inhibitor with regulatory domain delta: differences between v- and c-Jun. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Ransone L., Scharfmann R., Dwarki V. J., Tapscott S. J., Weintraub H., Verma I. M. Functional antagonism between c-Jun and MyoD proteins: a direct physical association. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):507–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90187-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T. J., Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. Aberrant regulation of MyoD1 contributes to the partially defective myogenic phenotype of BC3H1 cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):929–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Hsiao D., Rosenthal S. M. Induction and peak gene expression of insulin-like growth factor II follow that of myogenin during differentiation of BC3H-1 muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 31;183(3):1084–1089. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80301-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. S., Wenderoth M. P., Hauschka S. D., Krebs E. G. Differential activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in response to basic fibroblast growth factor in skeletal muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 31;92(3):870–874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.3.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casella S. J., Smith E. P., van Wyk J. J., Joseph D. R., Hynes M. A., Hoyt E. C., Lund P. K. Isolation of rat testis cDNAs encoding an insulin-like growth factor I precursor. DNA. 1987 Aug;6(4):325–330. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Jones J. I., Busby W. H., Wright G. Role of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in modifying IGF actions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Aug 27;692:10–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb26201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Falen S. L., Florini J. R. The type II insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor has low affinity for IGF-I analogs: pleiotypic actions of IGFs on myoblasts are apparently mediated by the type I receptor. Endocrinology. 1987 Jan;120(1):115–123. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Florini J. R. Effects of the somatomedins and insulin on myoblast differentiation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1981 Aug;86(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90312-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Roof S. L., Magri K. A., McWade F. J., Florini J. R. IGF-II is more active than IGF-I in stimulating L6A1 myogenesis: greater mitogenic actions of IGF-I delay differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Nov;161(2):277–284. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041610212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Ewton D. Z., Falen S. L., Van Wyk J. J. Biphasic concentration dependency of stimulation of myoblast differentiation by somatomedins. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 1):C771–C778. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.5.C771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Ewton D. Z. Highly specific inhibition of IGF-I-stimulated differentiation by an antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotide to myogenin mRNA. No effects on other actions of IGF-T. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13435–13437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Ewton D. Z. Induction of gene expression in muscle by the IGFs. Growth Regul. 1992 Mar;2(1):23–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Ewton D. Z., Magri K. A. Hormones, growth factors, and myogenic differentiation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:201–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Ewton D. Z., Roof S. L. Insulin-like growth factor-I stimulates terminal myogenic differentiation by induction of myogenin gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 May;5(5):718–724. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-5-718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Magri K. A., Ewton D. Z., James P. L., Grindstaff K., Rotwein P. S. "Spontaneous" differentiation of skeletal myoblasts is dependent upon autocrine secretion of insulin-like growth factor-II. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15917–15923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev V. G., Moerman E. J., Goldstein S. Senescence and cell density of human diploid fibroblasts influence metabolism of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Jul;160(1):203–211. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041600123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Lee J. D., Bibbs L., Ulevitch R. J. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):808–811. doi: 10.1126/science.7914033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irminger J. C., Rosen K. M., Humbel R. E., Villa-Komaroff L. Tissue-specific expression of insulin-like growth factor II mRNAs with distinct 5' untranslated regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6330–6334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P. L., Jones S. B., Busby W. H., Jr, Clemmons D. R., Rotwein P. A highly conserved insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP-5) is expressed during myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22305–22312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konigsberg I. R. Diffusion-mediated control of myoblast fusion. Dev Biol. 1971 Sep;26(1):133–152. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Chambard J. C., Karin M., Olson E. N. Fos and Jun repress transcriptional activation by myogenin and MyoD: the amino terminus of Jun can mediate repression. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):676–689. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCusker R. H., Camacho-Hübner C., Clemmons D. R. Identification of the types of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins that are secreted by muscle cells in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7795–7800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. J. c-myc inhibition of MyoD and myogenin-initiated myogenic differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2842–2851. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Klein W. H. bHLH factors in muscle development: dead lines and commitments, what to leave in and what to leave out. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):1–8. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlath G. K., Rich K., Webster S. G., Blau H. M. Localization of muscle gene products in nuclear domains. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):570–573. doi: 10.1038/337570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. A., Gordon H., Hall Z. W., Paterson B. M., Blau H. M. Negative control of the helix-loop-helix family of myogenic regulators in the NFB mutant. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Brown A. L. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins: gene structure and expression. Growth Regul. 1992 Jun;2(2):55–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen K. M., Wentworth B. M., Rosenthal N., Villa-Komaroff L. Specific, temporally regulated expression of the insulin-like growth factor II gene during muscle cell differentiation. Endocrinology. 1993 Aug;133(2):474–481. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.2.8393762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal S. M., Brown E. J., Brunetti A., Goldfine I. D. Fibroblast growth factor inhibits insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) gene expression and increases IGF-I receptor abundance in BC3H-1 muscle cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 May;5(5):678–684. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-5-678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Keath E. J., Piccoli S. P., Cole M. D. Novel myc oncogene RNA from abortive immunoglobulin-gene recombination in mouse plasmacytomas. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szebenyi G., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors and their receptors in muscle development. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;293:289–295. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5949-4_26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
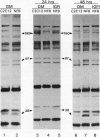
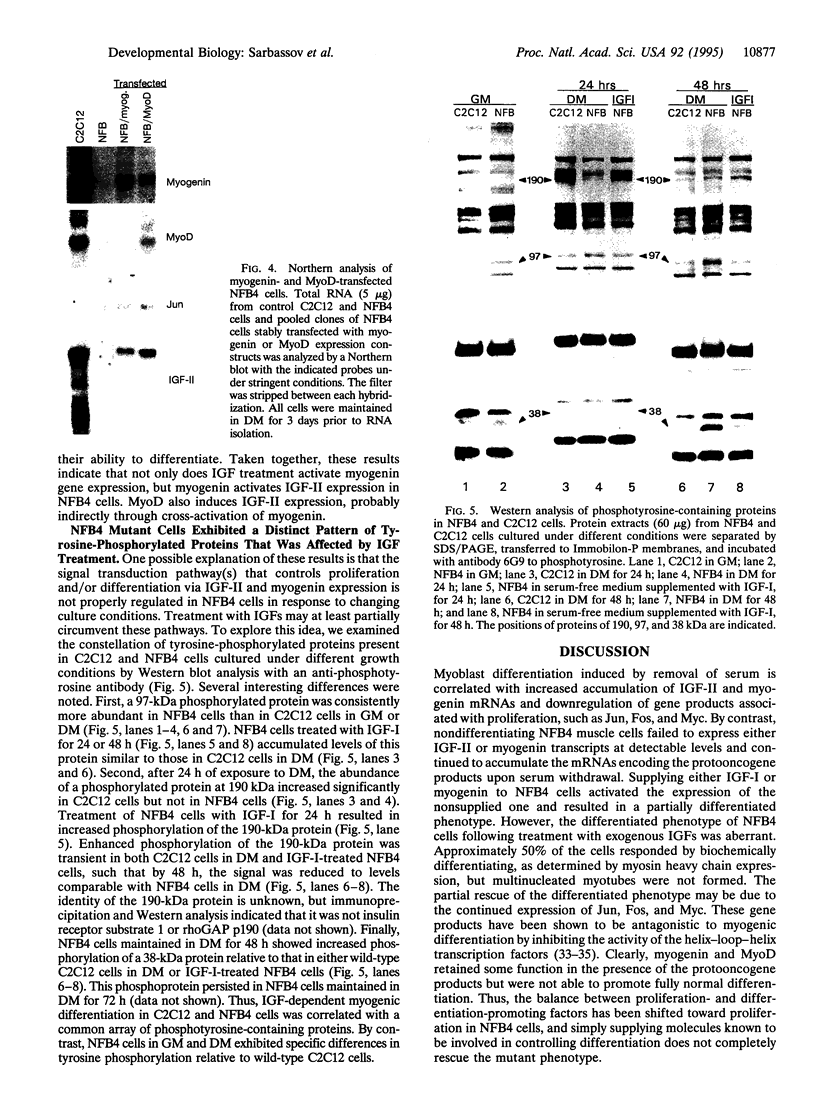
- Tobe K., Tamemoto H., Yamauchi T., Aizawa S., Yazaki Y., Kadowaki T. Identification of a 190-kDa protein as a novel substrate for the insulin receptor kinase functionally similar to insulin receptor substrate-1. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 17;270(11):5698–5701. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.11.5698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Lajara R., McCusker R. H., Clemmons D. R., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in muscle development. Expression of IGF-I, the IGF-I receptor, and an IGF binding protein during myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13810–13817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Sadow J. L., Rotwein P. Coordinate expression of insulin-like growth factor II and its receptor during muscle differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1543–1547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou G., Bao Z. Q., Dixon J. E. Components of a new human protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 26;270(21):12665–12669. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.21.12665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu A. X., Zhao Y., Moller D. E., Flier J. S. Cloning and characterization of p97MAPK, a novel human homolog of rat ERK-3. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8202–8211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]