Abstract
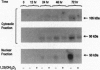
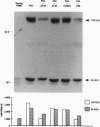
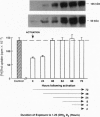
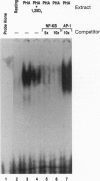
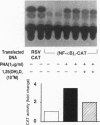
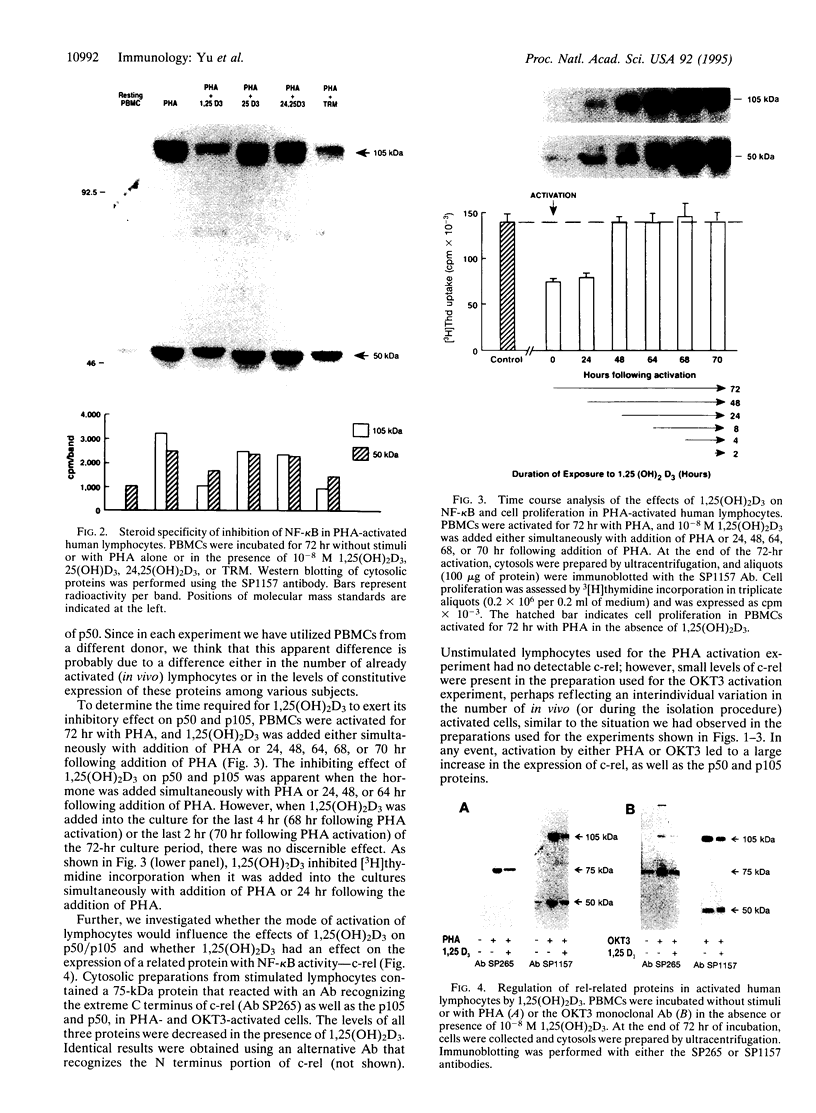
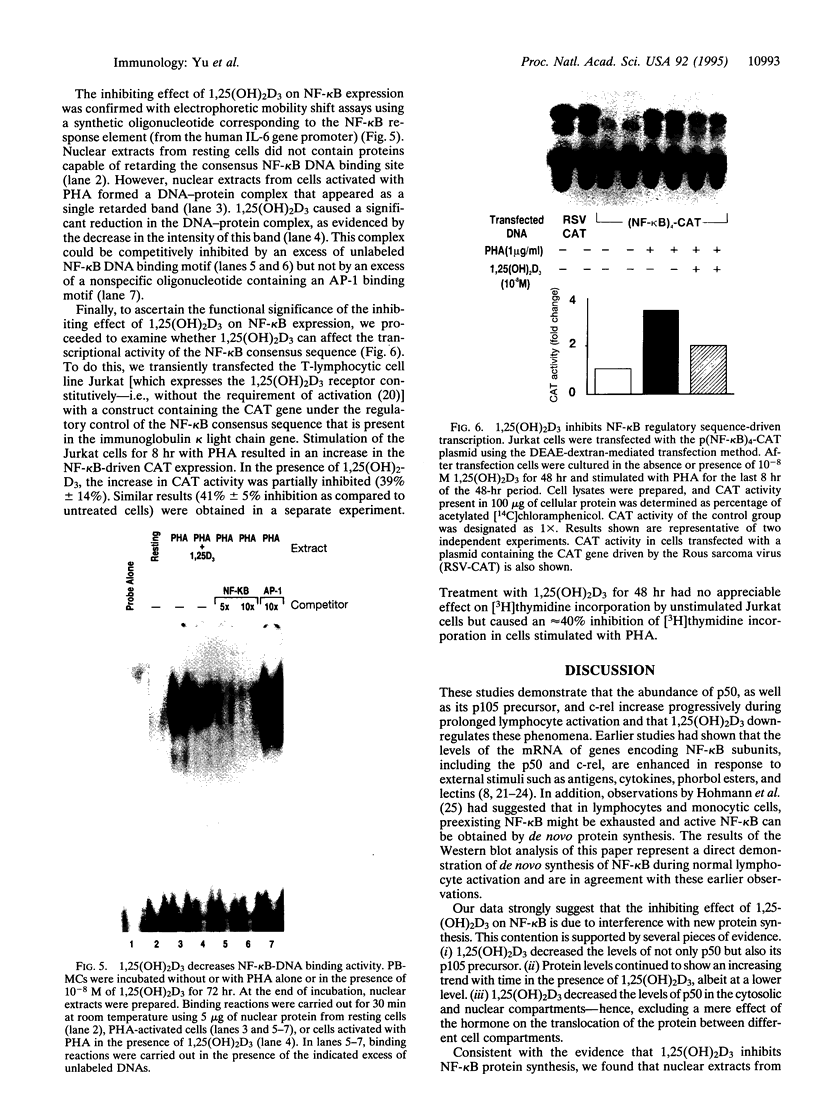
The effect of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25(OH)2)D3], a steroid hormone with immunomodulating properties, on nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) proteins was examined in in vitro activated normal human lymphocytes by Western blot analysis. Over a 72-hr period of activation, the expression of the 50-kDa NF-kappa B, p50, and its precursor, p105, was increased progressively. When cells were activated in the presence of 1,25(OH)2D3, the levels of the mature protein as well as its precursor were decreased. The effect of the hormone on the levels of p50 was demonstrable in the cytosolic and nuclear compartments; it required between 4 and 8 hr and was specific, as 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 were ineffective. Besides p50, 1,25(OH)2D3 decreased the levels of another NF-kappa B protein, namely c-rel. In addition, 1,25(OH)2D3 decreased the abundance of a specific DNA-protein complex formed upon incubation of nuclear extracts from activated lymphocytes with a labeled NF-kappa B DNA binding motif. Further, 1,25(OH)2D3 inhibited the transcriptional activity of NF-kappa B in Jurkat cells transiently transfected with a construct containing four tandem repeats of the NF-kappa B binding sequence of the immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene linked to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene. These observations demonstrate directly that there is de novo synthesis of NF-kappa B during human lymphocyte activation and suggest that this process is hormonally regulated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Villalobos J., Burd P. R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. Cloning of a mitogen-inducible gene encoding a kappa B DNA-binding protein with homology to the rel oncogene and to cell-cycle motifs. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):76–80. doi: 10.1038/348076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Transcriptional induction of the murine c-rel gene with serum and phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate in fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5239–5243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm S., Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription factor NF-kappa B: structure-function relationship of its protein subunits. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 1;290(Pt 2):297–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2900297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass R., Brach M., Gunji H., Kharbanda S., Kufe D. Inhibition of EGR-1 and NF-kappa B gene expression by dexamethasone during phorbol ester-induced human monocytic differentiation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Oct 20;44(8):1569–1576. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90474-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann H. P., Remy R., Scheidereit C., van Loon A. P. Maintenance of NF-kappa B activity is dependent on protein synthesis and the continuous presence of external stimuli. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):259–266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A., Gibbons R., Perkins S., Gazit D. Age-related bone loss. A hypothesis and initial assessment in mice. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995 Apr;(313):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochel T., Mushinski J. F., Rice N. R. The v-rel and c-rel proteins exist in high molecular weight complexes in avian and murine cells. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):615–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolagas S. C., Provvedini D. M., Tsoukas C. D. Interactions of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and the immune system. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Dec;43(2-3):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolagas S. C., Yu X. P., Girasole G., Bellido T. Vitamin D and the hematolymphopoietic tissue: a 1994 update. Semin Nephrol. 1994 Mar;14(2):129–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio F., Didonato J., Rosette C., Karin M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel Rel/NF-kappa B family member displaying structural and functional homology to NF-kappa B p50/p105. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;11(7):523–537. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R., Hatada E. N., Hohmann H. P., Haiker M., Bartsch C., Röthlisberger U., Lahm H. W., Schlaeger E. J., van Loon A. P., Scheidereit C. Cloning of the DNA-binding subunit of human nuclear factor kappa B: the level of its mRNA is strongly regulated by phorbol ester or tumor necrosis factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):966–970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. The inhibitory ankyrin and activator Rel proteins. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pottratz S. T., Bellido T., Mocharla H., Crabb D., Manolagas S. C. 17 beta-Estradiol inhibits expression of human interleukin-6 promoter-reporter constructs by a receptor-dependent mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1994 Mar;93(3):944–950. doi: 10.1172/JCI117100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., MacKichan M. L., Israël A. The precursor of NF-kappa B p50 has I kappa B-like functions. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90353-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Evans R. M. Functional antagonism between oncoprotein c-Jun and steroid hormone receptors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:119–127. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Franzoso G., Brown K. Structure, regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994;10:405–455. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.10.110194.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stylianou E., O'Neill L. A., Rawlinson L., Edbrooke M. R., Woo P., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 induces NF-kappa B through its type I but not its type II receptor in lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15836–15841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su M. S., Semerjian A. Activation of transcription factor NF kappa B in Jurkat cells is inhibited selectively by FK 506 in a signal-dependent manner. Transplant Proc. 1991 Dec;23(6):2912–2915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten R. M., Paya C. V., Israël N., Le Bail O., Mattei M. G., Virelizier J. L., Kourilsky P., Israël A. The characterization of the promoter of the gene encoding the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B indicates that it participates in its own regulation. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):195–203. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X. P., Mocharla H., Hustmyer F. G., Manolagas S. C. Vitamin D receptor expression in human lymphocytes. Signal requirements and characterization by western blots and DNA sequencing. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7588–7595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]