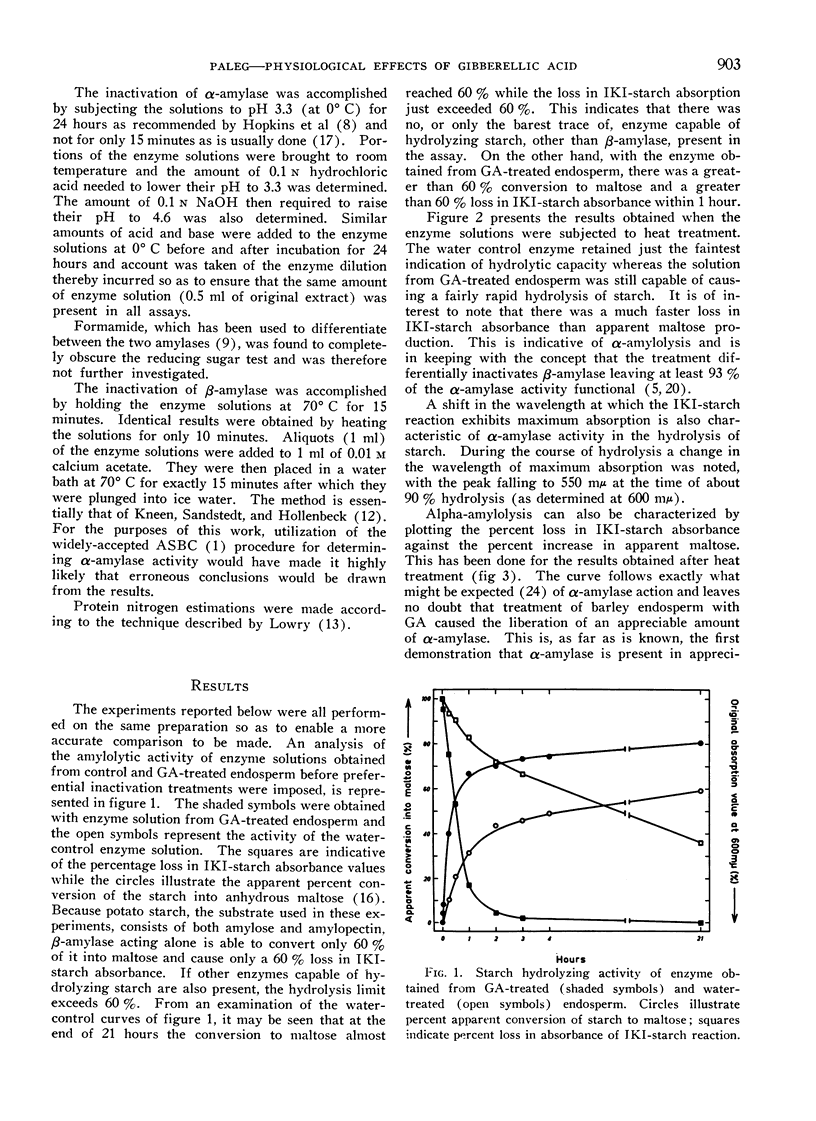
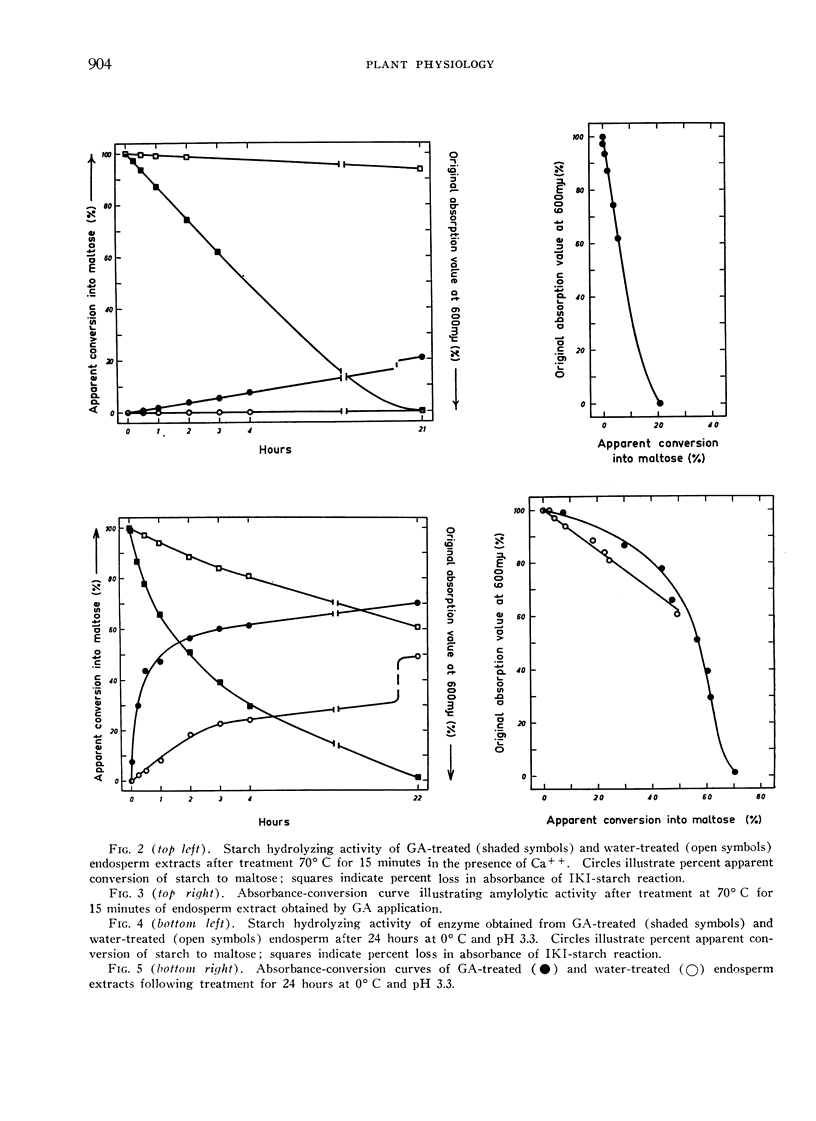
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRIAN P. W. Role of gibberellin-like hormones in regulation of plant growth & flowering. Nature. 1958 Apr 19;181(4616):1122–1123. doi: 10.1038/1811122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. H., Murray R. H., Lockwood A. R. The beta-amylase of barley. Biochem J. 1946;40(4):507–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACWILLIAM I. C., HARRIS G. The separation of limit dextrinase from R-enzyme and aspects of the activities of the separated enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Oct;84:442–454. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90606-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paleg L. G. Physiological Effects of Gibberellic Acid: I. On Carbohydrate Metabolism and Amylase Activity of Barley Endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1960 May;35(3):293–299. doi: 10.1104/pp.35.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preece I. A., Shadaksharaswamy M. Reducing-group production from starch by the action of alpha- and beta-amylases of barley malt. Activity of alpha- and beta-amylases. Biochem J. 1949;44(3):270–274. doi: 10.1042/bj0440270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


