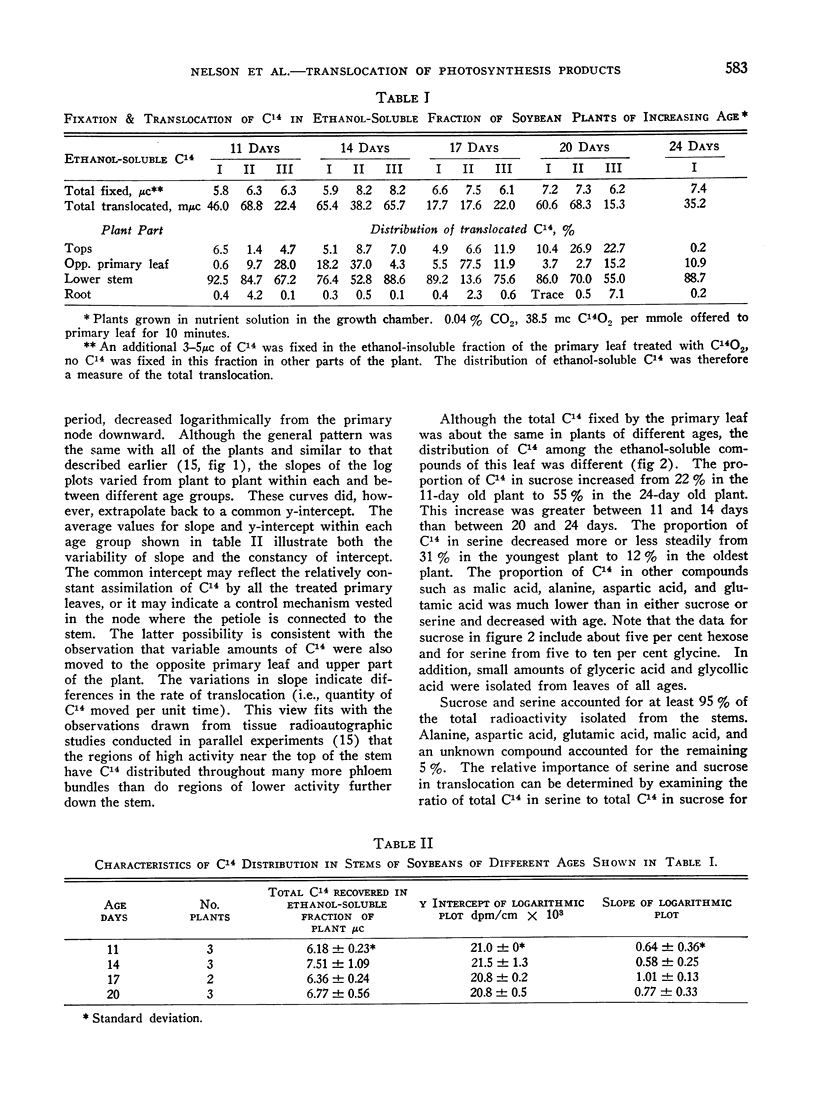
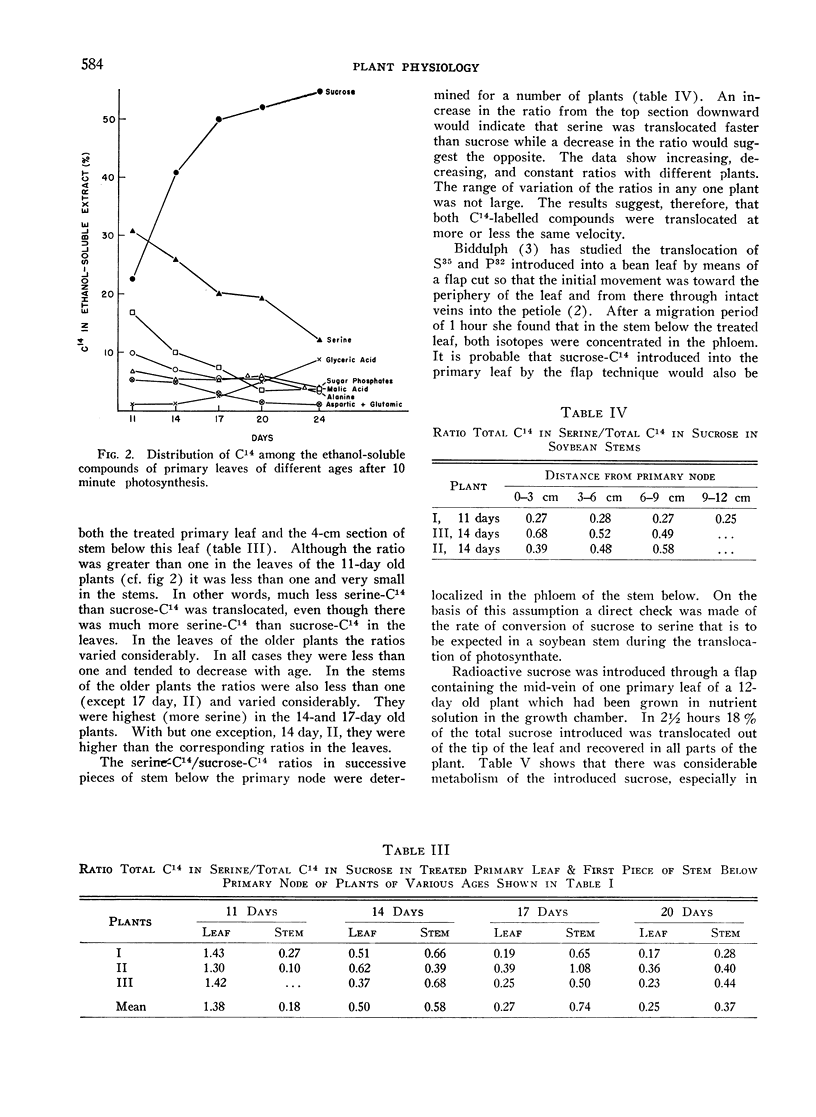
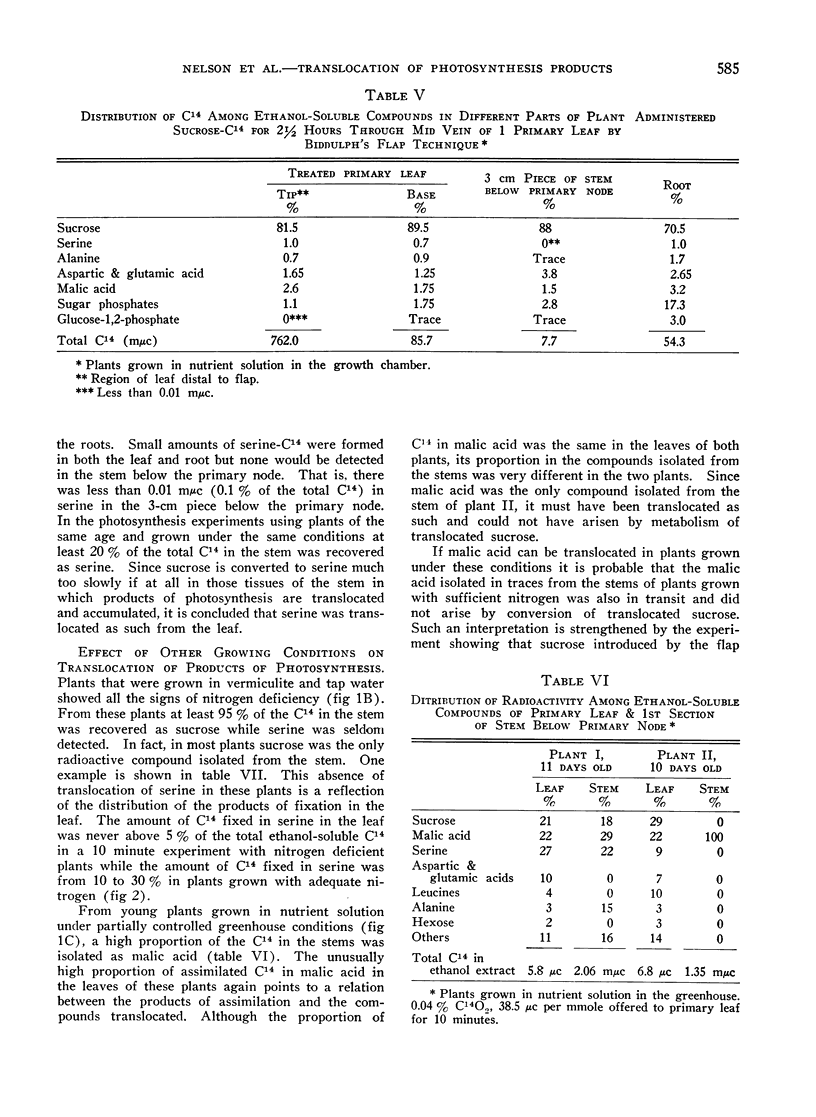
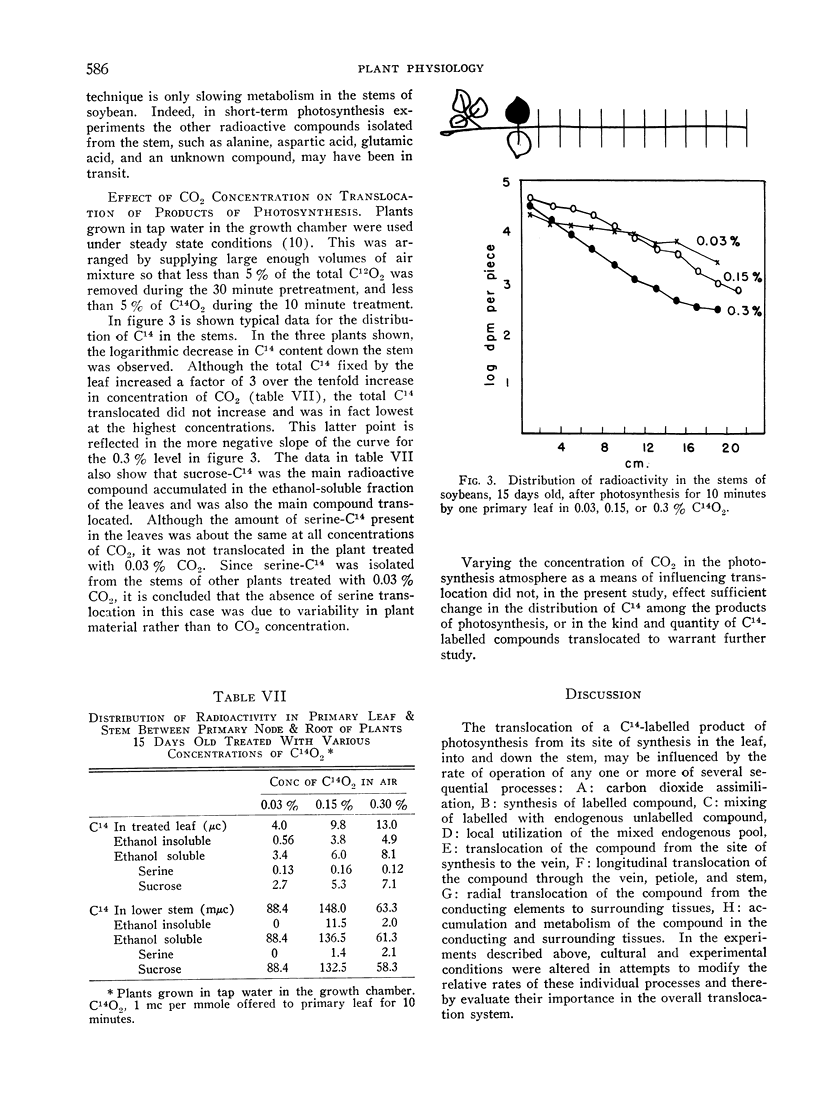
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURMA D. P., MORTIMER D. C. The fate of assimilated C14O2 in the sugar beet leaf studies by displacement with C12O2. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1957 Oct;35(10):835–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON C. D., MORTIMER D. C. The preparation of sucrose-C14 with high specific activity and high tracer yield using detached sugar best leaves. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Feb;37(2):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON C. D., PERKINS H. J., GORHAM P. R. Note on a rapid translocation of photosynthetically assimilated C14 out of the primary leaf of the young soybean plant. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1958 Dec;36(12):1277–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOWERS G. H., MORTIMER D. C. The role of keto acids in photosynthetic carbon dioxide assimilation. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1956 May;34(3):511–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERNON L. P., ARONOFF S. Metabolism of soybean leaves. IV. Translocation from soybean leaves. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Apr;36(2):383–398. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90424-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann M. H. Translocation of Organic Substances in Trees. II. On the Translocation Mechanism in the Phloem of White Ash (Fraxinus Americana L.). Plant Physiol. 1957 Sep;32(5):399–404. doi: 10.1104/pp.32.5.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



