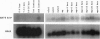Abstract
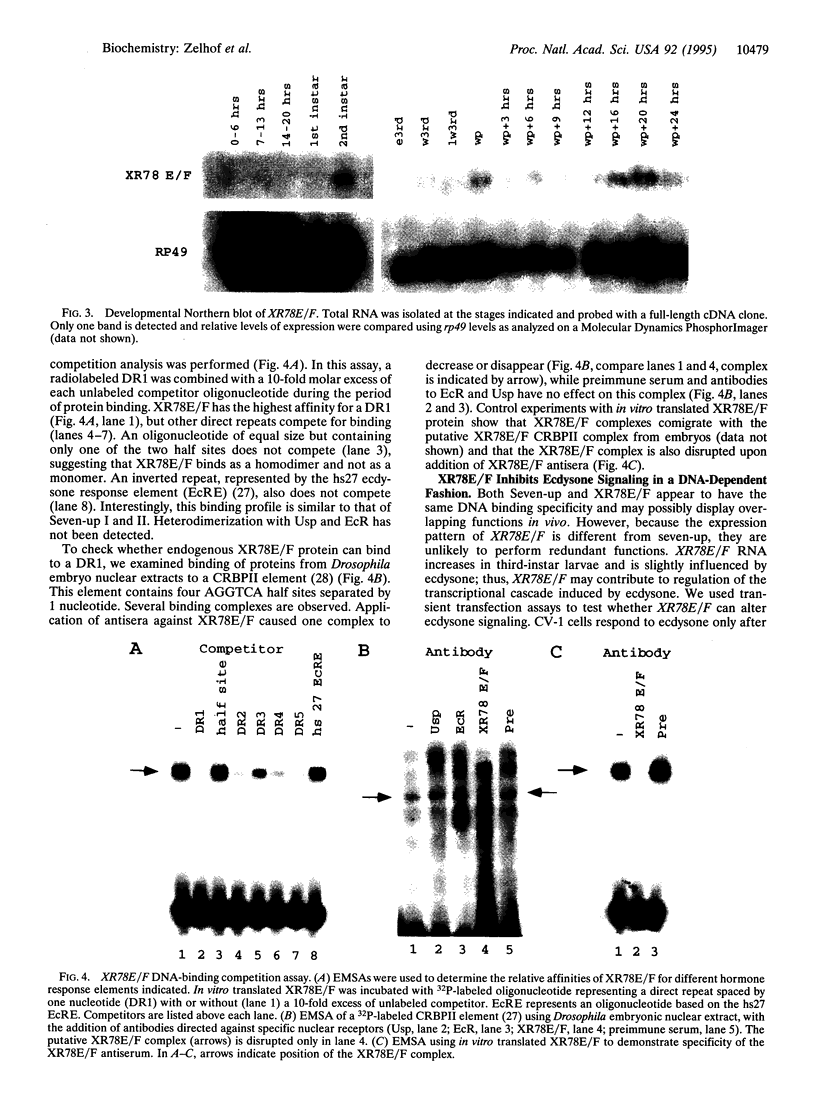
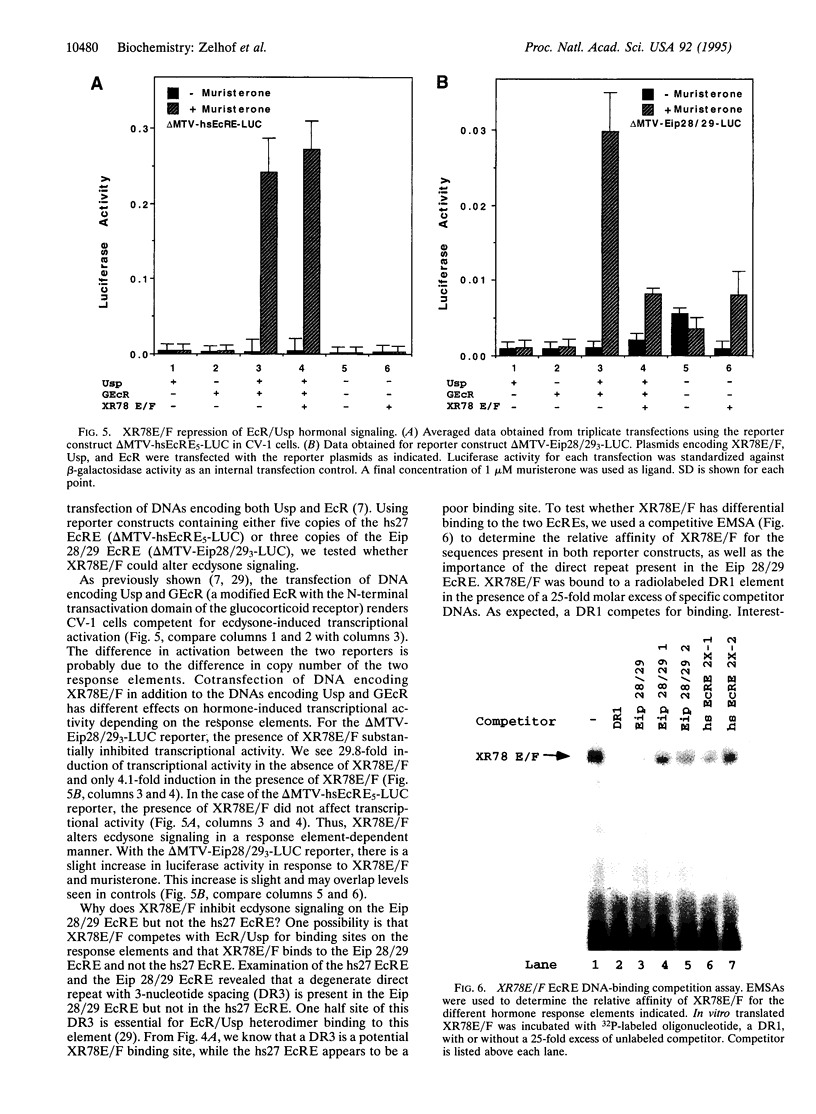
In a search for retinoid X receptor-like molecules in Drosophila, we have identified an additional member of the nuclear receptor superfamily, XR78E/F. In the DNA-binding domain, XR78E/F is closely related to the mammalian receptor TR2, as well as to the nuclear receptors Coup-TF and Seven-up. We demonstrate that XR78E/F binds as a homodimer to direct repeats of the sequence AGGTCA. In transient transfection assays, XR78E/F represses ecdysone signaling in a DNA-binding-dependent fashion. XR78E/F has its highest expression in third-instar larvae and prepupae. These experiments suggest that XR78E/F may play a regulatory role in the transcriptional cascade triggered by the hormone ecdysone in Drosophila.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arriza J. L., Weinberger C., Cerelli G., Glaser T. M., Handelin B. L., Housman D. E., Evans R. M. Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3037703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Da Silva S. L., Ideta R., Lee Y., Yeh S., Burbach J. P. Human and rat TR4 orphan receptors specify a subclass of the steroid receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6040–6044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Kokontis J., Acakpo-Satchivi L., Liao S., Takeda H., Chang Y. Molecular cloning of new human TR2 receptors: a class of steroid receptor with multiple ligand-binding domains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 15;165(2):735–741. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Kokontis J. Identification of a new member of the steroid receptor super-family by cloning and sequence analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):971–977. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherbas L., Lee K., Cherbas P. Identification of ecdysone response elements by analysis of the Drosophila Eip28/29 gene. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):120–131. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney A. J., Leng X., Tsai S. Y., O'Malley B. W., Tsai M. J. Multiple mechanisms of chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor-dependent repression of transactivation by the vitamin D, thyroid hormone, and retinoic acid receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4152–4160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney A. J., Tsai S. Y., O'Malley B. W., Tsai M. J. Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor (COUP-TF) dimers bind to different GGTCA response elements, allowing COUP-TF to repress hormonal induction of the vitamin D3, thyroid hormone, and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4153–4163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose T., Fujimoto W., Tamaai T., Kim K. H., Matsuura H., Jetten A. M. TAK1: molecular cloning and characterization of a new member of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Dec;8(12):1667–1680. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.12.7708055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor-COUP-TF interactions modulate retinoic acid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1448–1452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Noonan D. J., Heyman R. A., Evans R. M. Convergence of 9-cis retinoic acid and peroxisome proliferator signalling pathways through heterodimer formation of their receptors. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):771–774. doi: 10.1038/358771a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Umesono K., Kliewer S. A., Borgmeyer U., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. A direct repeat in the cellular retinol-binding protein type II gene confers differential regulation by RXR and RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown M., Belote J. M., Baker B. S. A molecular analysis of transformer, a gene in Drosophila melanogaster that controls female sexual differentiation. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90199-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Relationship between the product of the Drosophila ultraspiracle locus and the vertebrate retinoid X receptor. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):298–301. doi: 10.1038/347298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A., Hogness D. S. The E75 ecdysone-inducible gene responsible for the 75B early puff in Drosophila encodes two new members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):204–219. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., De Camilli P., Niemann H., Jahn R. Membrane fusion machinery: insights from synaptic proteins. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. E., Stunnenberg H. G., Stewart A. F. Heterodimerization of the Drosophila ecdysone receptor with retinoid X receptor and ultraspiracle. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):471–475. doi: 10.1038/362471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodard C. T., Baehrecke E. H., Thummel C. S. A molecular mechanism for the stage specificity of the Drosophila prepupal genetic response to ecdysone. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):607–615. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao T. P., Forman B. M., Jiang Z., Cherbas L., Chen J. D., McKeown M., Cherbas P., Evans R. M. Functional ecdysone receptor is the product of EcR and Ultraspiracle genes. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):476–479. doi: 10.1038/366476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao T. P., Segraves W. A., Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Drosophila ultraspiracle modulates ecdysone receptor function via heterodimer formation. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90266-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]