Abstract
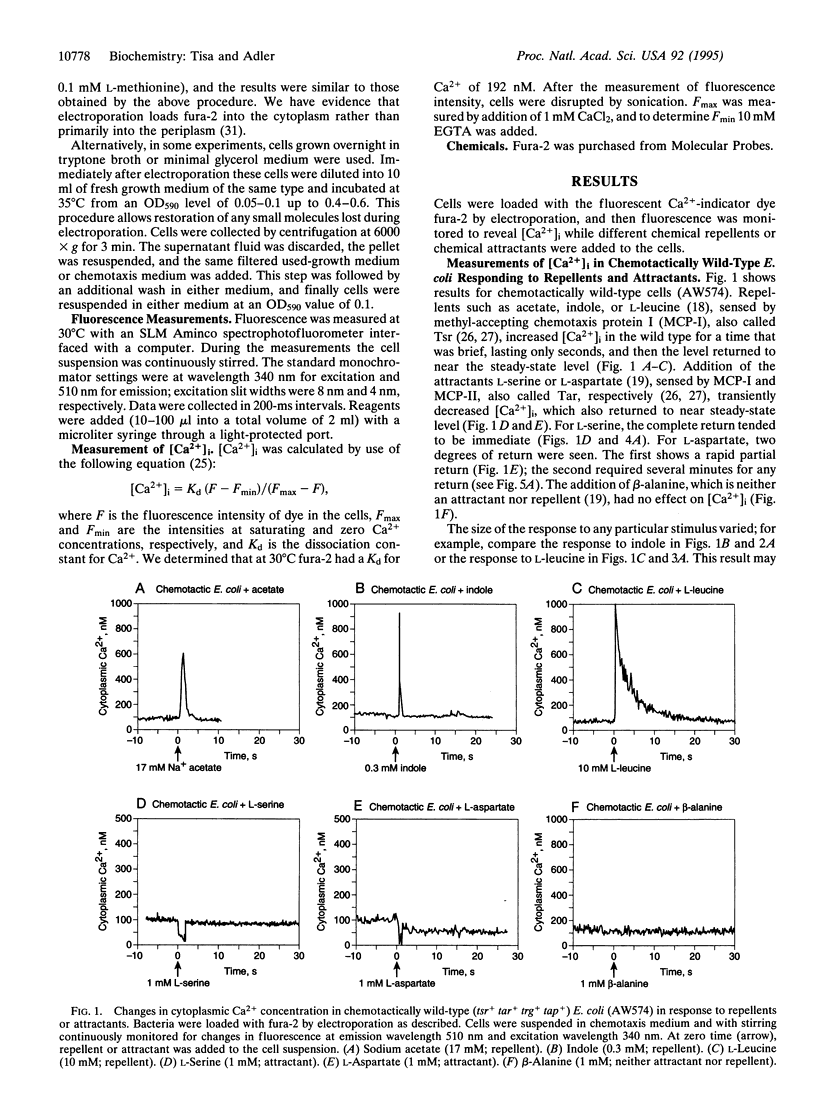
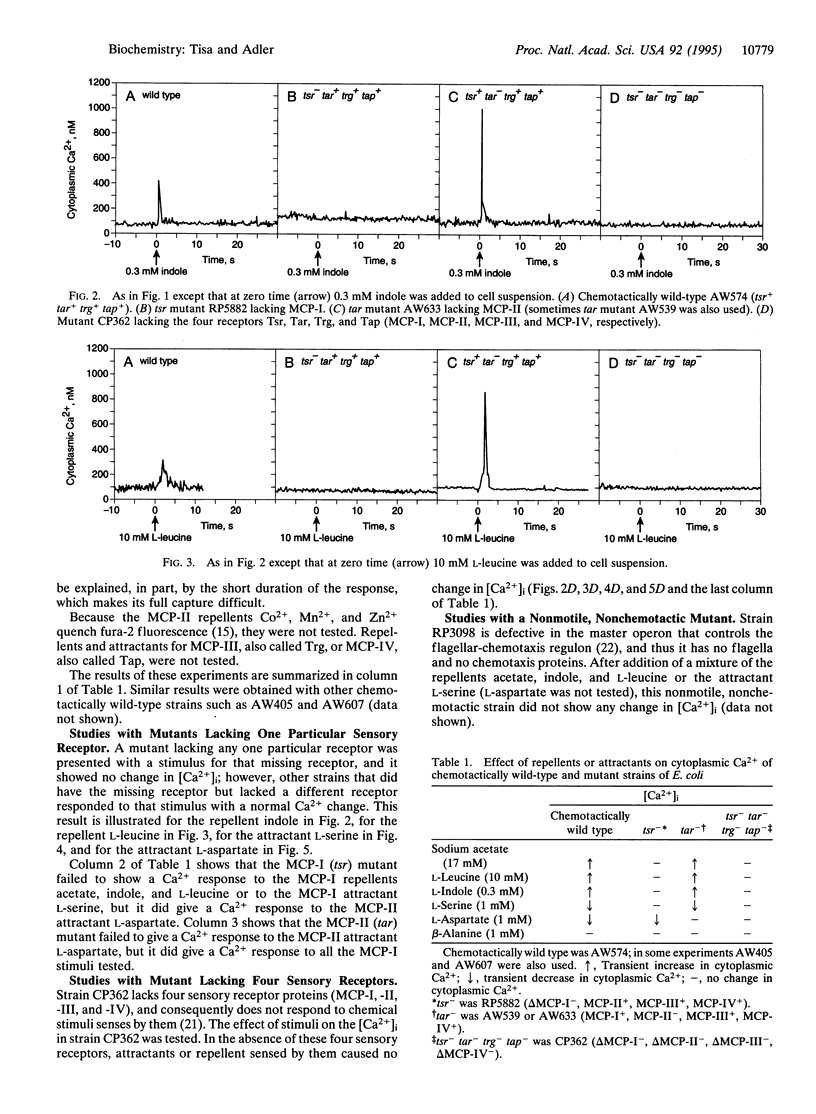
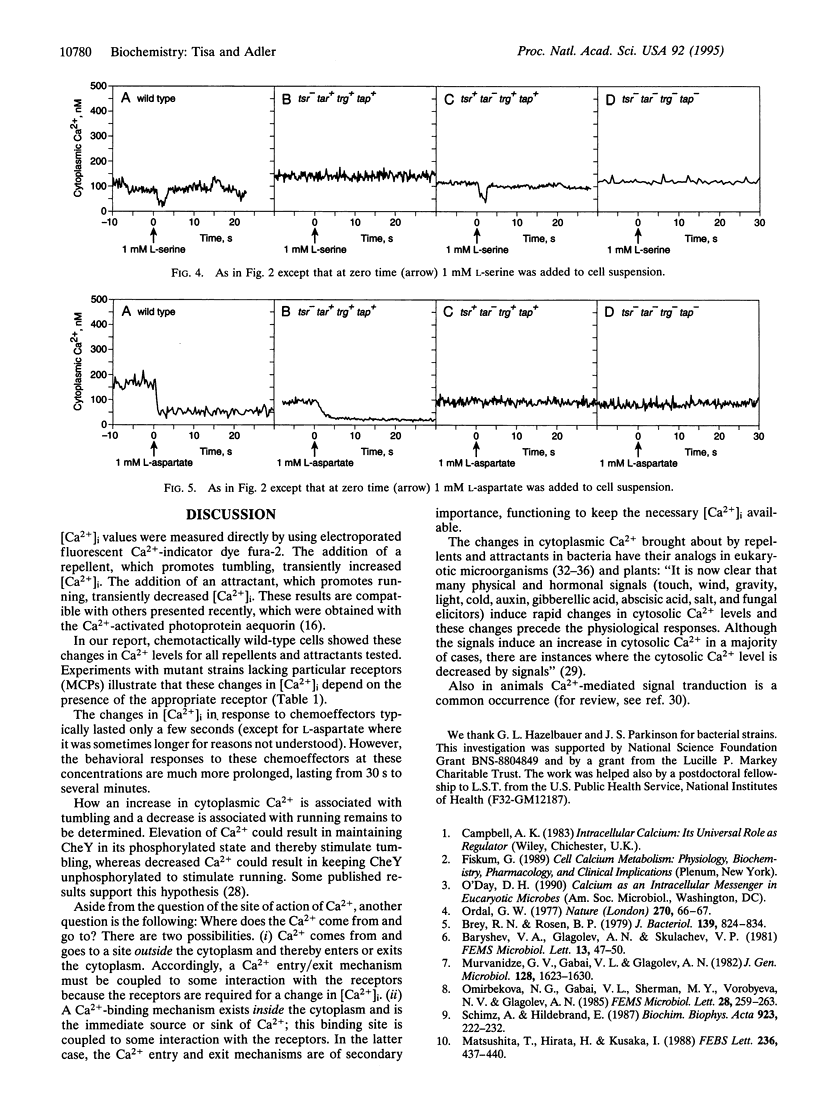
Cytoplasmic free-Ca2+ levels in Escherichia coli were measured by use of the fluorescent Ca(2+)-indicator dye fura-2. Chemotactically wild-type E. coli regulated cytoplasmic free Ca2+ at approximately 100 nM when no stimuli were encountered, but changes in bacterial behavior correlated with changes in cytoplasmic free-Ca2+ concentration. For chemotactically wild-type E. coli, addition of a repellent resulted in cells tumbling and a transient increase in cytoplasmic free-Ca2+ levels. Conversely, addition of an attractant to wild-type cells caused running and produced a transient decrease in cytoplasmic free-Ca2+ levels. Studies with mutant strains showed that the chemoreceptors were required for the observed changes in cytoplasmic free-Ca2+ levels in response to chemical stimuli.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J., Dahl M. M. Nonchemotactic mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):390–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.390-398.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P. Properties of Escherichia coli mutants altered in calcium/proton antiport activity. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):824–834. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.824-834.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangola P., Rosen B. P. Maintenance of intracellular calcium in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12570–12574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häder D. P. Photosensory behavior in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):1–21. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.1-21.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T., Komeda Y., Kutsukake K., Macnab R. M., Matsumura P., Parkinson J. S., Simon M. I., Yamaguchi S. New unified nomenclature for the flagellar genes of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):533–535. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.533-535.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukat G. S., Stock A. M., Stock J. B. Divalent metal ion binding to the CheY protein and its significance to phosphotransfer in bacterial chemotaxis. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5436–5442. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita T., Hirata H., Kusaka I. Calcium channel blockers inhibit bacterial chemotaxis. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):437–440. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesibov R., Adler J. Chemotaxis toward amino acids in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):315–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.315-326.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne J. L., Devreotes P. N. The surface cyclic AMP receptors, cAR1, cAR2, and cAR3, promote Ca2+ influx in Dictyostelium discoideum by a G alpha 2-independent mechanism. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Mar;4(3):283–292. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordal G. W. Calcium ion regulates chemotactic behaviour in bacteria. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):66–67. doi: 10.1038/270066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C., Hazelbauer G. L. Mutations specifically affecting ligand interaction of the Trg chemosensory transducer. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):101–109. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.101-109.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Houts S. E. Isolation and behavior of Escherichia coli deletion mutants lacking chemotaxis functions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poovaiah B. W., Reddy A. S. Calcium and signal transduction in plants. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1993;12(3):185–211. doi: 10.1080/07352689309701901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reader R. W., Tso W. W., Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Pleiotropic aspartate taxis and serine taxis mutants of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Apr;111(2):363–374. doi: 10.1099/00221287-111-2-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saran S., Nakao H., Tasaka M., Iida H., Tsuji F. I., Nanjundiah V., Takeuchi I. Intracellular free calcium level and its response to cAMP stimulation in developing Dictyostelium cells transformed with jellyfish apoaequorin cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 3;337(1):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80626-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli: methylation of che gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: two complementary pathways of information processing that involve methylated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm S. Ca2+ channels and signalling in cilia and flagella. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;4(9):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisa L. S., Adler J. Calcium ions are involved in Escherichia coli chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11804–11808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisa L. S., Olivera B. M., Adler J. Inhibition of Escherichia coli chemotaxis by omega-conotoxin, a calcium ion channel blocker. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(5):1235–1238. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.5.1235-1238.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins N. J., Knight M. R., Trewavas A. J., Campbell A. K. Free calcium transients in chemotactic and non-chemotactic strains of Escherichia coli determined by using recombinant aequorin. Biochem J. 1995 Mar 15;306(Pt 3):865–869. doi: 10.1042/bj3060865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B. Chlamydomonas phototaxis. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;3(11):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90091-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womack B. J., Gilmore D. F., White D. Calcium requirement for gliding motility in myxobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6093–6096. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6093-6096.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


