Abstract
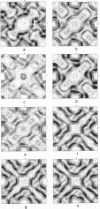
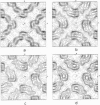
The crystal structure of halorhodopsin was determined in (centrosymmetric) projection to 6-A resolution by direct methods that use only the amplitudes of the electron diffraction pattern. A multisolution technique was used to generate initial 15-A-resolution basis sets, and after selection of the best phase set (by the closest match of magnitude of Eobs and magnitude of Ecalc), annealing of individual reflections was used to improve its accuracy. The Sayre equation was then used to expand the phase terms to 10 A, followed again by phase annealing. A final expansion with the Sayre equation enlarged this corrected phase set to 6 A. When the condition of density flatness was used to locate the best phase solution after each extension, a final structure could be observed that was quite similar to the one found earlier by analysis of electron micrographs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos L. A., Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional structure determination by electron microscopy of two-dimensional crystals. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;39(3):183–231. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(83)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Pitts J. E., Tickle I. J., Wood S. P., Wu C. W. X-ray analysis (1. 4-A resolution) of avian pancreatic polypeptide: Small globular protein hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4175–4179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan S. W., Schirmer T., Rummel G., Steiert M., Ghosh R., Pauptit R. A., Jansonius J. N., Rosenbusch J. P. Crystal structures explain functional properties of two E. coli porins. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):727–733. doi: 10.1038/358727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorset D. L. Direct determination of crystallographic phases for diffraction data from lipid bilayers. II. Refinement of phospholipid structures. Biophys J. 1991 Dec;60(6):1366–1373. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82174-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorset D. L., Kopp S., Fryer J. R., Tivol W. F. The Sayre equation in electron crystallography. Ultramicroscopy. 1995 Jan;57(1):59–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(94)00161-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacovazzo C., Siliqi D., Spagna R. The ab initio crystal structure solution of proteins by direct methods. II. The procedure and its first applications. Acta Crystallogr A. 1994 Sep 1;50(Pt 5):609–621. doi: 10.1107/s0108767394002369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havelka W. A., Henderson R., Heymann J. A., Oesterhelt D. Projection structure of halorhodopsin from Halobacterium halobium at 6 A resolution obtained by electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 5;234(3):837–846. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jap B. K., Walian P. J., Gehring K. Structural architecture of an outer membrane channel as determined by electron crystallography. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):167–170. doi: 10.1038/350167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jap B. K., Zulauf M., Scheybani T., Hefti A., Baumeister W., Aebi U., Engel A. 2D crystallization: from art to science. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Oct;46(1-4):45–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühlbrandt W., Wang D. N., Fujiyoshi Y. Atomic model of plant light-harvesting complex by electron crystallography. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):614–621. doi: 10.1038/367614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzati V., Tardieu A., Taupin D. A pattern-recognition approach to the phase problem: application to the X-ray diffraction study of biological membranes and model systems. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):269–286. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick G. M., Dauter Z., Wilson K. S., Hope H., Sieker L. C. The application of direct methods and Patterson interpretation to high-resolution native protein data. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1993 Jan 1;49(Pt 1):18–23. doi: 10.1107/S0907444992007364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Klug A. Electron microscopy of the stacked disk aggregate of tobacco mosaic virus protein. I. Three-dimensional image reconstruction. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 25;87(4):641–656. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks C. M., Hauptman H. A., Smith G. D., Blessing R. H., Teeter M. M., Miller R Crambin: a direct solution for a 400-atom structure. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1995 Jan 1;51(Pt 1):33–38. doi: 10.1107/S090744499400925X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]