Abstract
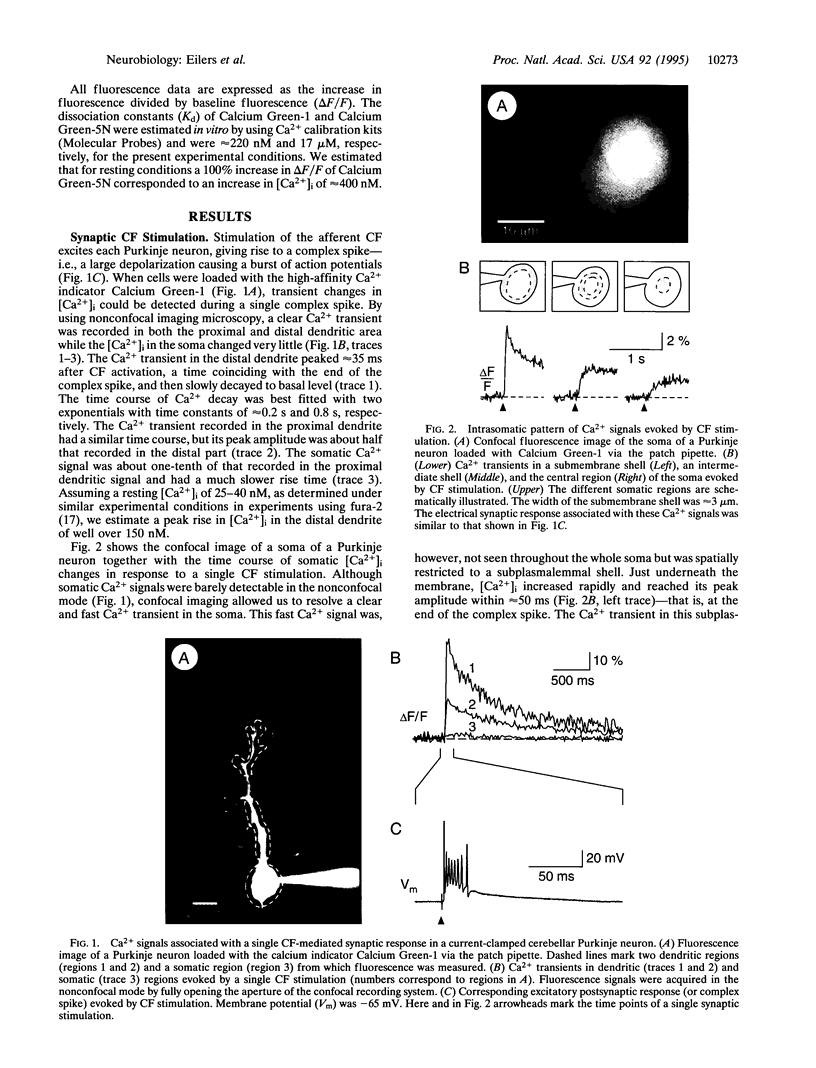
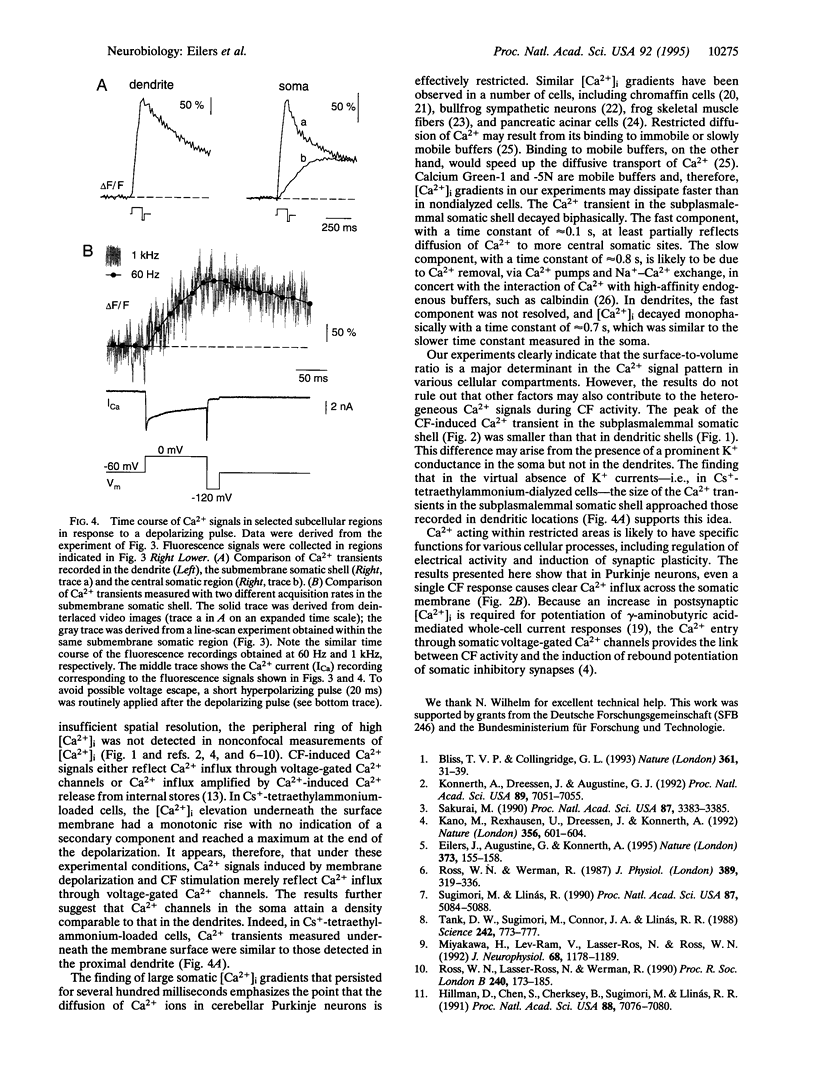
Temporal and spatial changes in the intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) were examined in dendrites and somata of rat cerebellar Purkinje neurons by combining whole-cell patch-clamp recording and fast confocal laser-scanning microscopy. In cells loaded via the patch pipette with the high-affinity Ca2+ indicator Calcium Green-1 (Kd approximately 220 nM), a single synaptic climbing fiber response, a so-called complex spike, resulted in a transient elevation of [Ca2+]i that showed distinct differences among various subcellular compartments. With conventional imaging, the Ca2+ signals were prominent in the dendrites and almost absent in the soma. Confocal recordings from the somatic region, however, revealed steep transient increases in [Ca2+]i that were confined to a submembrane shell of 2- to 3-microns thickness. In the central parts of the soma [Ca2+]i increases were much slower and had smaller amplitudes. The kinetics and amplitudes of the changes in [Ca2+]i were analyzed in more detail by using the fast, low-affinity Ca2+ indicator Calcium Green-5N (Kd approximately 17 microM). We found that brief depolarizing pulses produced [Ca2+]i increases in a narrow somatic submembrane shell that resembled those seen in the dendrites. These results provide direct experimental evidence that the surface-to-volume ratio is a critical determinant of the spatiotemporal pattern of Ca2+ signals evoked by synaptic activity in neurons.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bliss T. V., Collingridge G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):31–39. doi: 10.1038/361031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chard P. S., Bleakman D., Christakos S., Fullmer C. S., Miller R. J. Calcium buffering properties of calbindin D28k and parvalbumin in rat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:341–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers J., Augustine G. J., Konnerth A. Subthreshold synaptic Ca2+ signalling in fine dendrites and spines of cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):155–158. doi: 10.1038/373155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Cruz A., Sala F., Adams P. R. Subcellular calcium transients visualized by confocal microscopy in a voltage-clamped vertebrate neuron. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):858–862. doi: 10.1126/science.2154851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman D., Chen S., Aung T. T., Cherksey B., Sugimori M., Llinás R. R. Localization of P-type calcium channels in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7076–7080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano M., Garaschuk O., Verkhratsky A., Konnerth A. Ryanodine receptor-mediated intracellular calcium release in rat cerebellar Purkinje neurones. J Physiol. 1995 Aug 15;487(1):1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano M., Rexhausen U., Dreessen J., Konnerth A. Synaptic excitation produces a long-lasting rebound potentiation of inhibitory synaptic signals in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):601–604. doi: 10.1038/356601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Li Y. X., Miyashita Y. Subcellular distribution of Ca2+ release channels underlying Ca2+ waves and oscillations in exocrine pancreas. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):669–677. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90514-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konnerth A., Dreessen J., Augustine G. J. Brief dendritic calcium signals initiate long-lasting synaptic depression in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7051–7055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konnerth A., Llano I., Armstrong C. M. Synaptic currents in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2662–2665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., DiPolo R., Marty A. Calcium-induced calcium release in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1994 Mar;12(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., Leresche N., Marty A. Calcium entry increases the sensitivity of cerebellar Purkinje cells to applied GABA and decreases inhibitory synaptic currents. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., Marty A., Armstrong C. M., Konnerth A. Synaptic- and agonist-induced excitatory currents of Purkinje cells in rat cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1991 Mar;434:183–213. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa H., Lev-Ram V., Lasser-Ross N., Ross W. N. Calcium transients evoked by climbing fiber and parallel fiber synaptic inputs in guinea pig cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Oct;68(4):1178–1189. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.4.1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monck J. R., Robinson I. M., Escobar A. L., Vergara J. L., Fernandez J. M. Pulsed laser imaging of rapid Ca2+ gradients in excitable cells. Biophys J. 1994 Aug;67(2):505–514. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80554-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Augustine G. J. Calcium gradients and buffers in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A. J., Cheek T. R., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Burgoyne R. D. Localization and heterogeneity of agonist-induced changes in cytosolic calcium concentration in single bovine adrenal chromaffin cells from video imaging of fura-2. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):401–411. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03391.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. N., Lasser-Ross N., Werman R. Spatial and temporal analysis of calcium-dependent electrical activity in guinea pig Purkinje cell dendrites. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 May 22;240(1297):173–185. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. N., Werman R. Mapping calcium transients in the dendrites of Purkinje cells from the guinea-pig cerebellum in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:319–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai M. Calcium is an intracellular mediator of the climbing fiber in induction of cerebellar long-term depression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3383–3385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimori M., Llinás R. R. Real-time imaging of calcium influx in mammalian cerebellar Purkinje cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5084–5088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tank D. W., Sugimori M., Connor J. A., Llinás R. R. Spatially resolved calcium dynamics of mammalian Purkinje cells in cerebellar slice. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):773–777. doi: 10.1126/science.2847315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usowicz M. M., Sugimori M., Cherksey B., Llinás R. P-type calcium channels in the somata and dendrites of adult cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1185–1199. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90076-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent P., Armstrong C. M., Marty A. Inhibitory synaptic currents in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells: modulation by postsynaptic depolarization. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:453–471. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Neher E. Mobile and immobile calcium buffers in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1993 Sep;469:245–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]