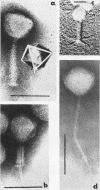
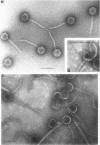
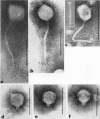
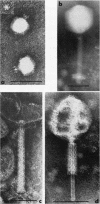
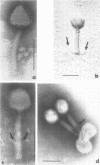
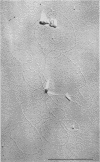
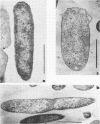
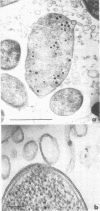
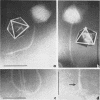
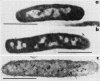
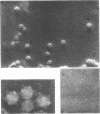
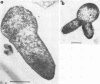
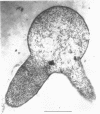
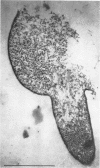
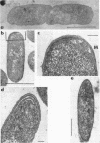
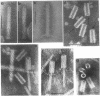
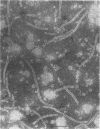
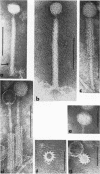
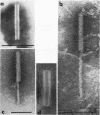
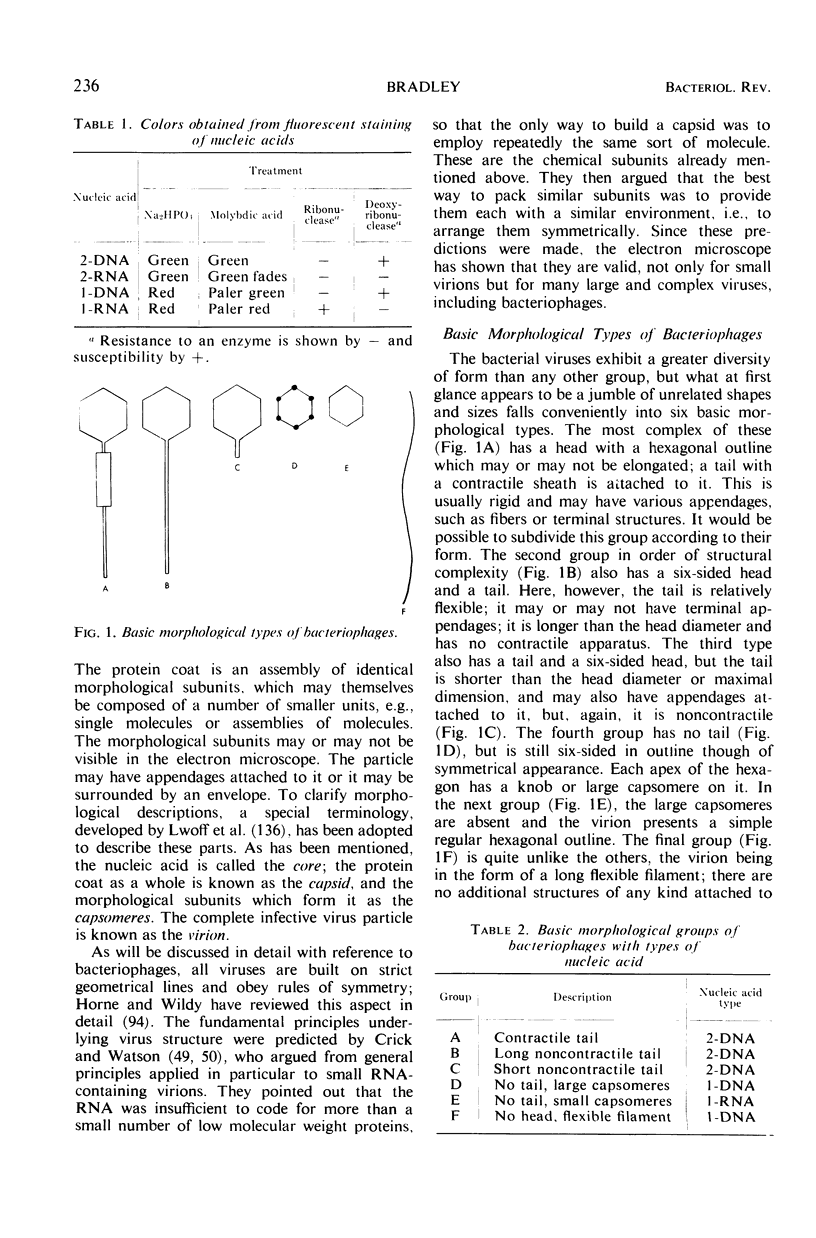
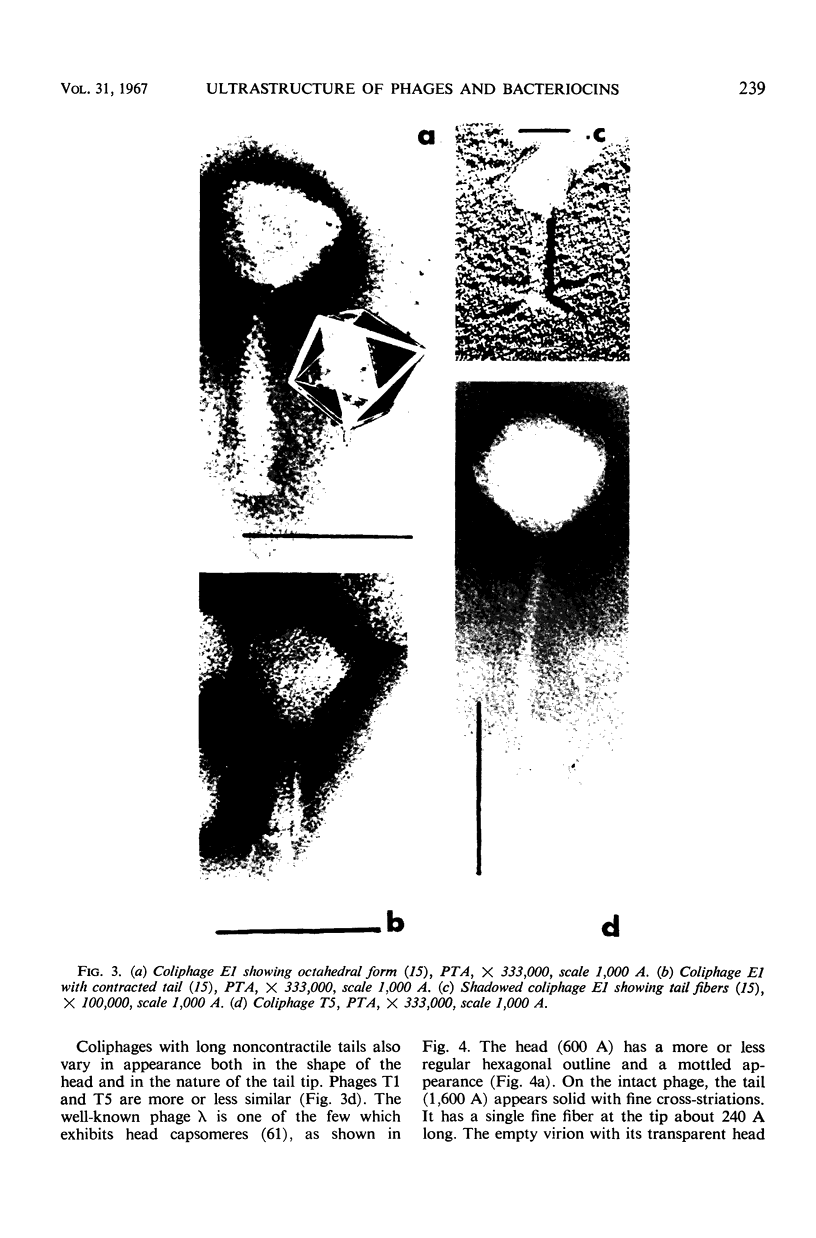
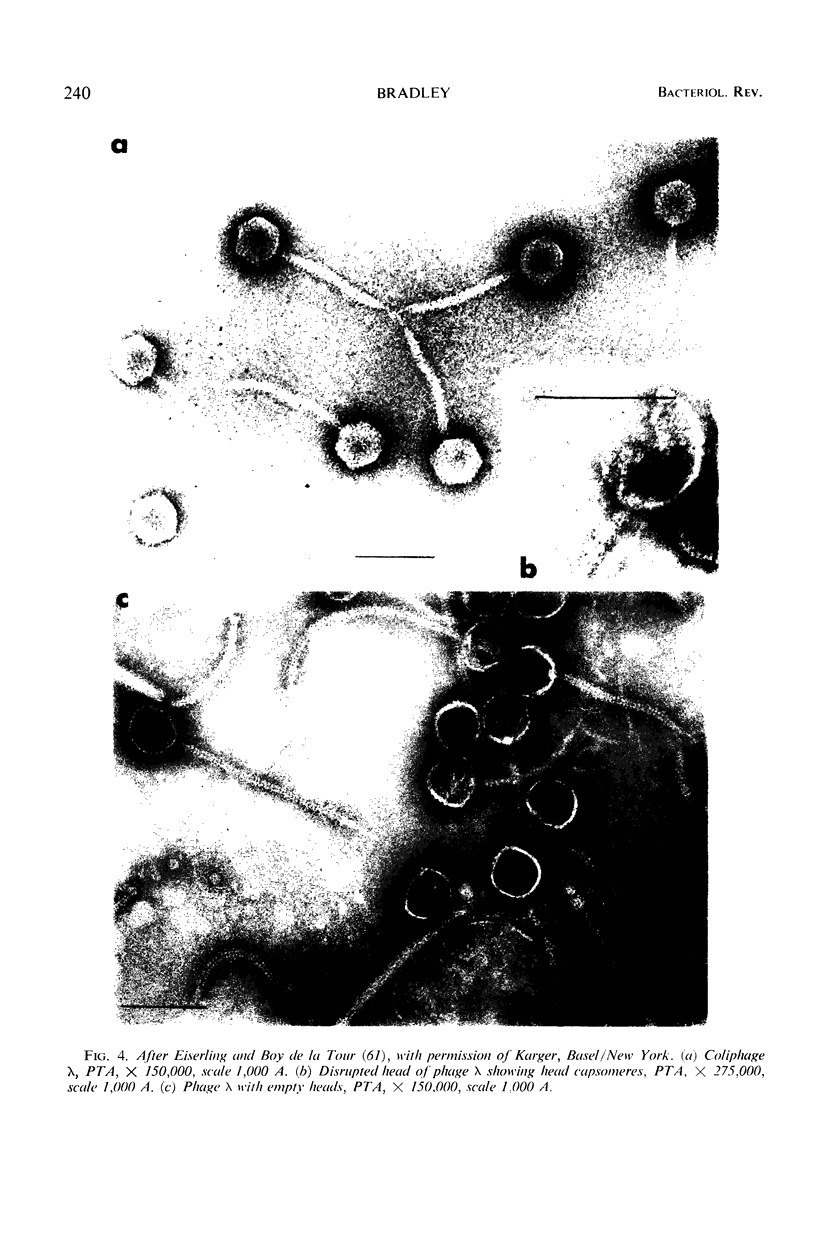
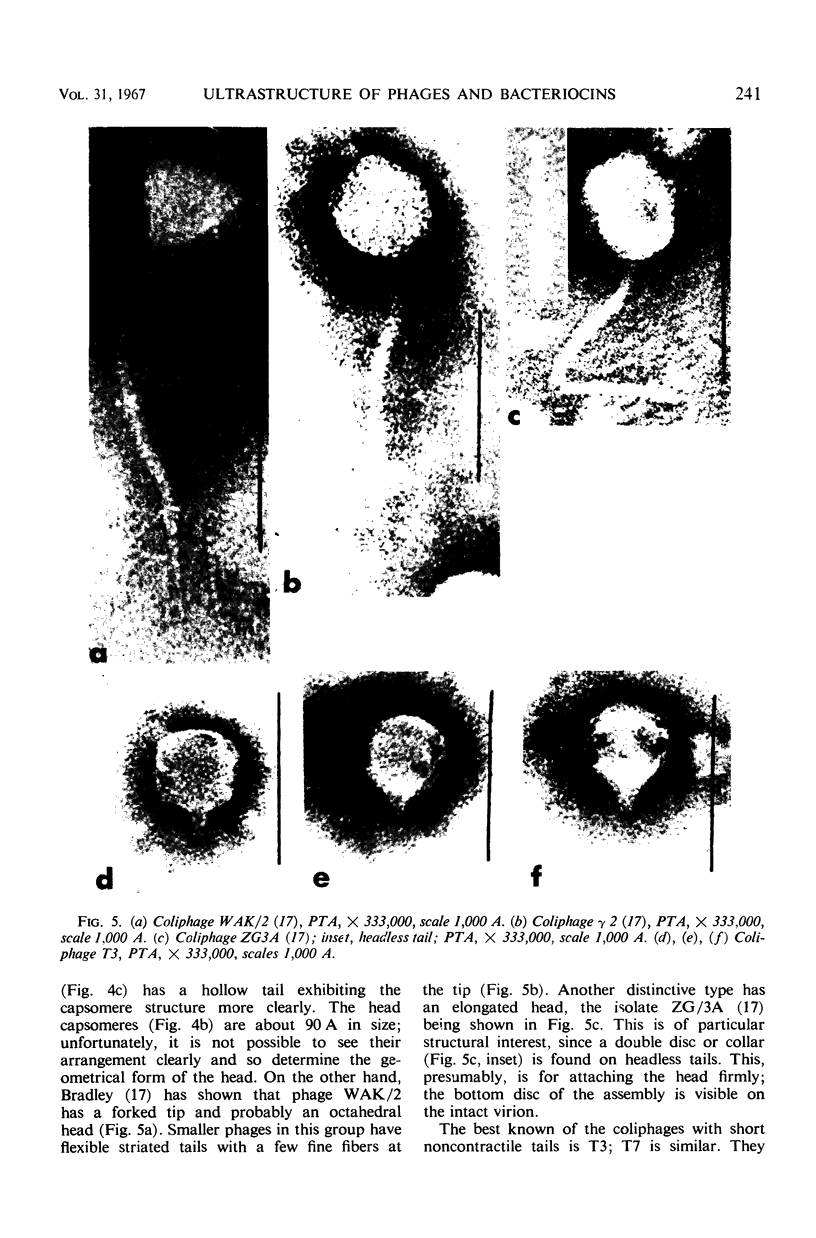
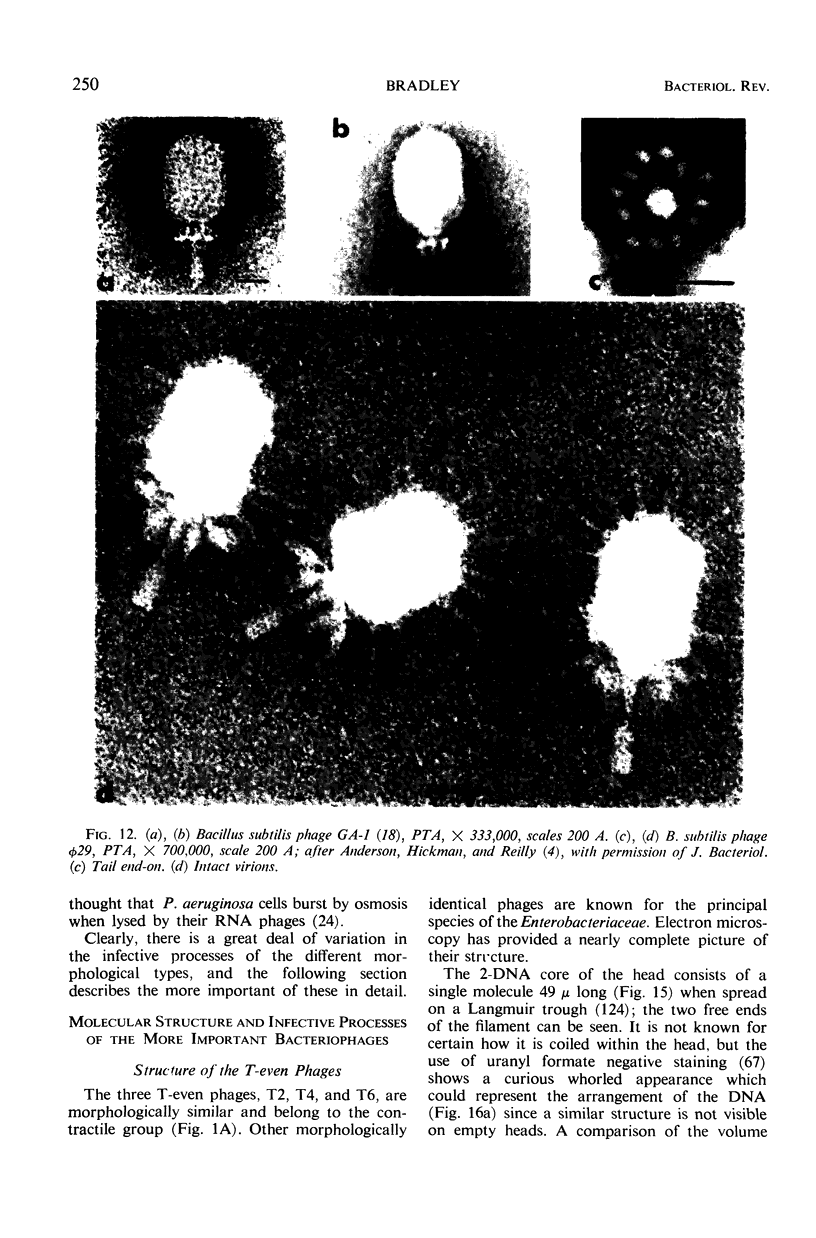
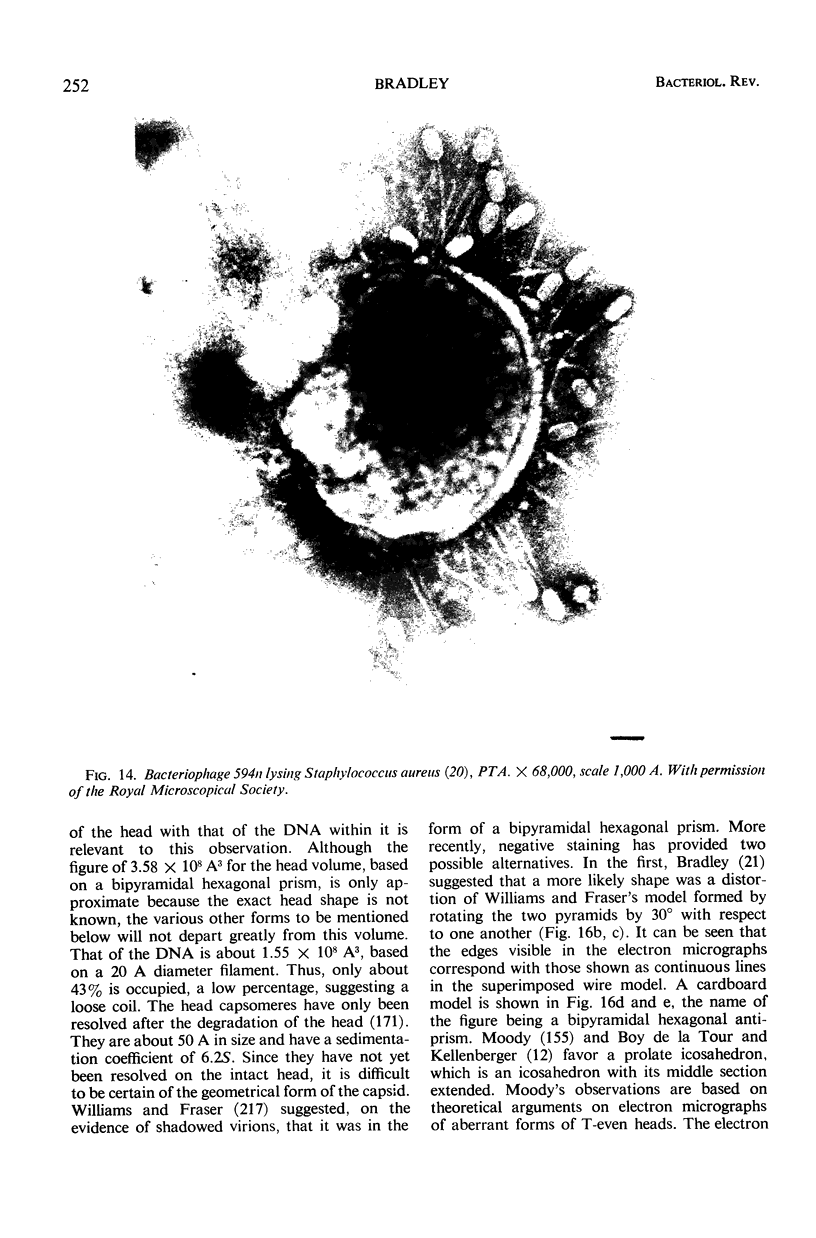
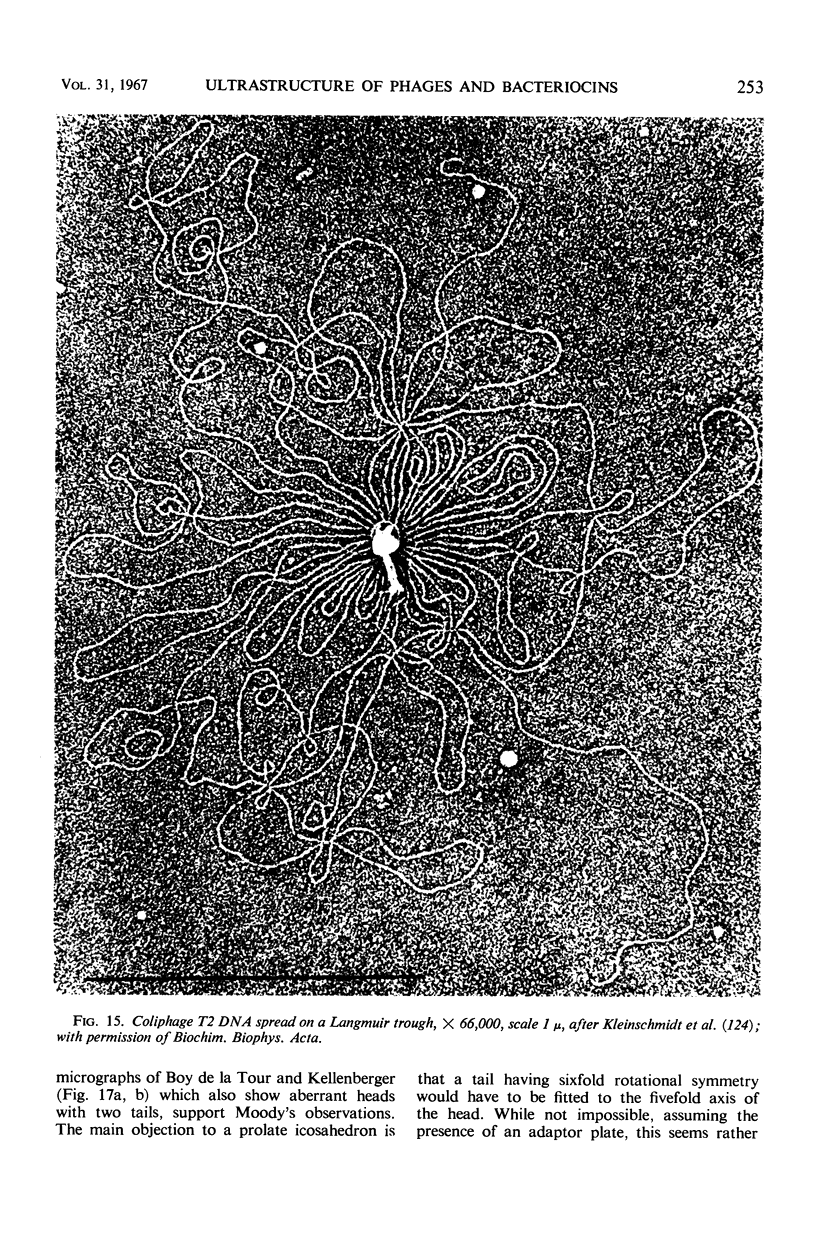
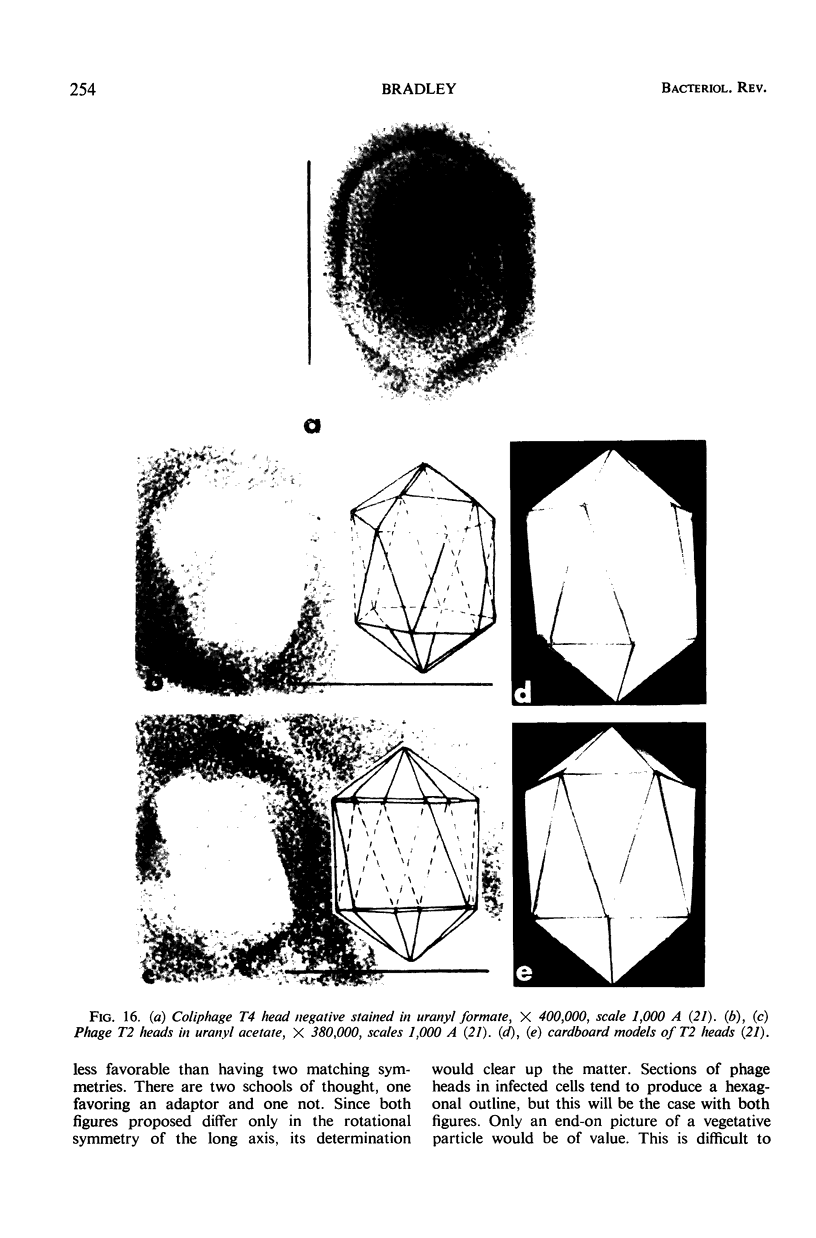
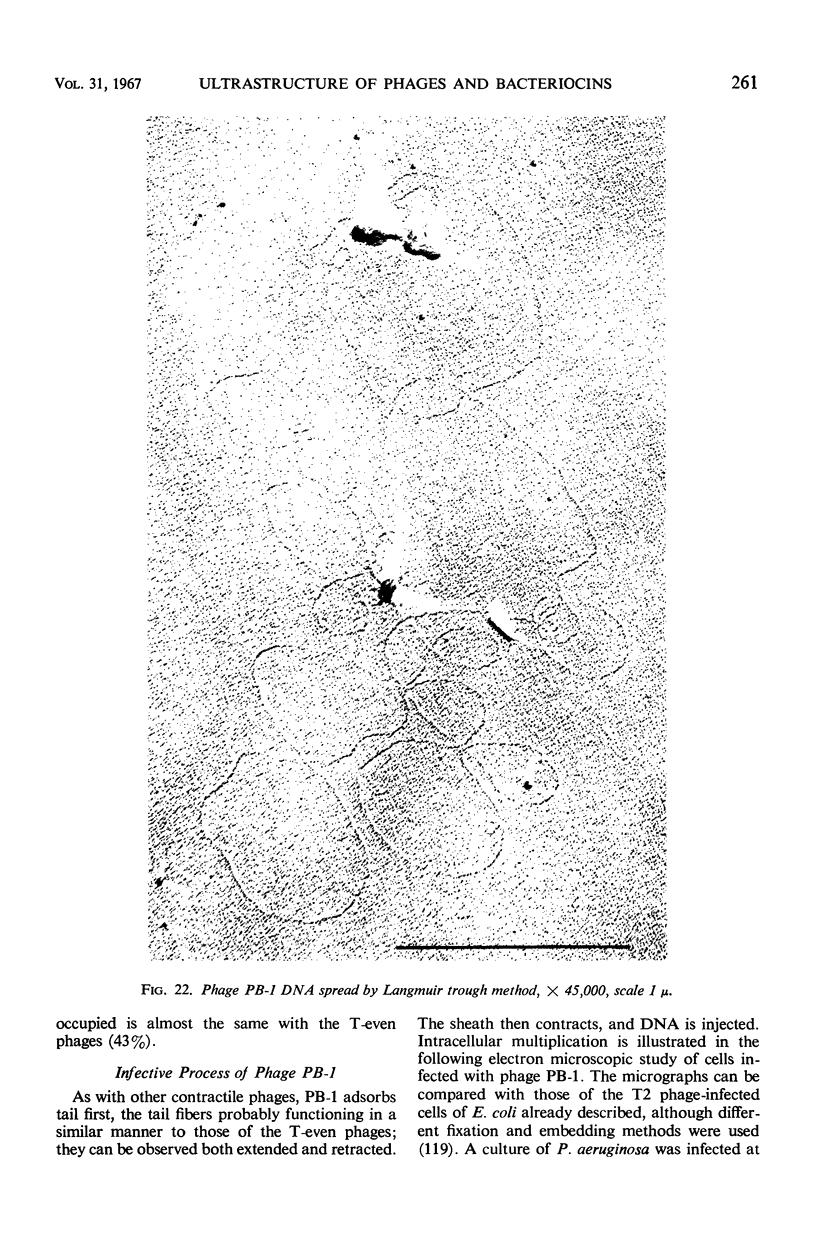
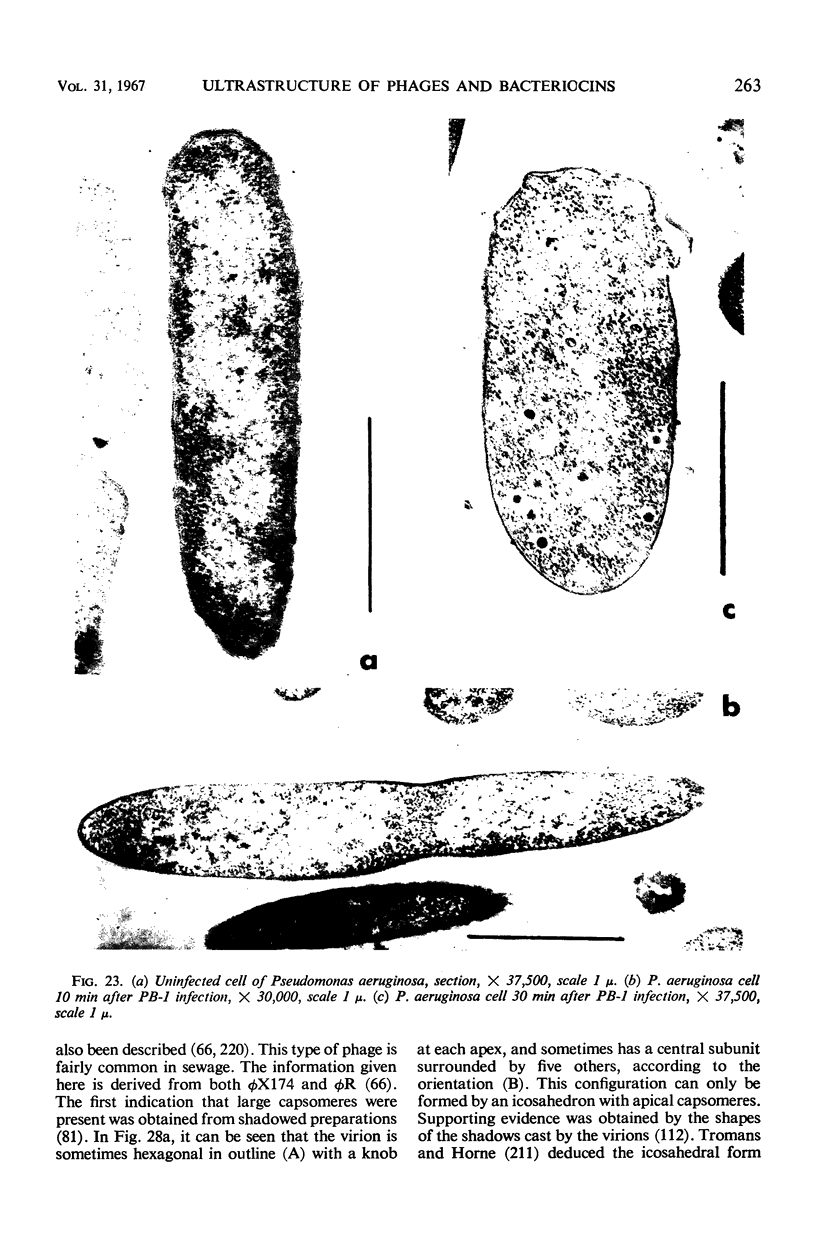
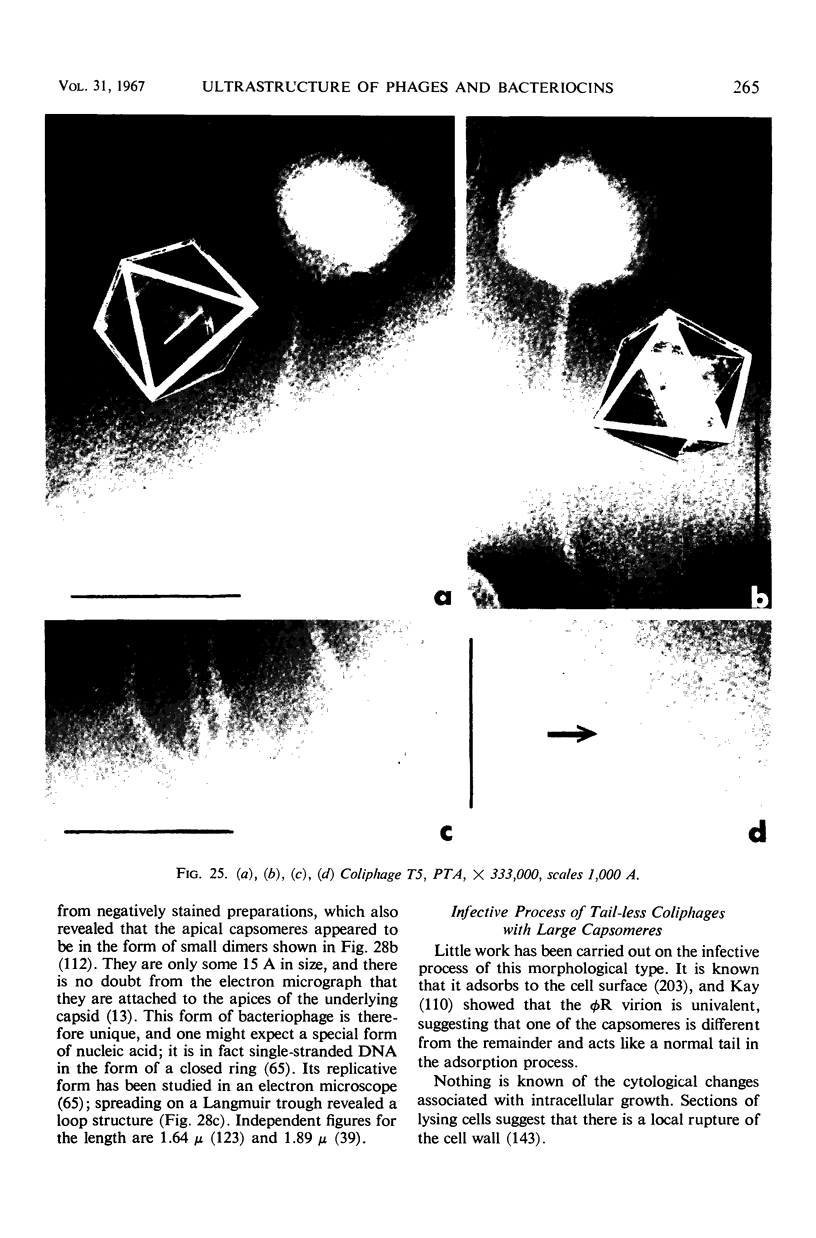
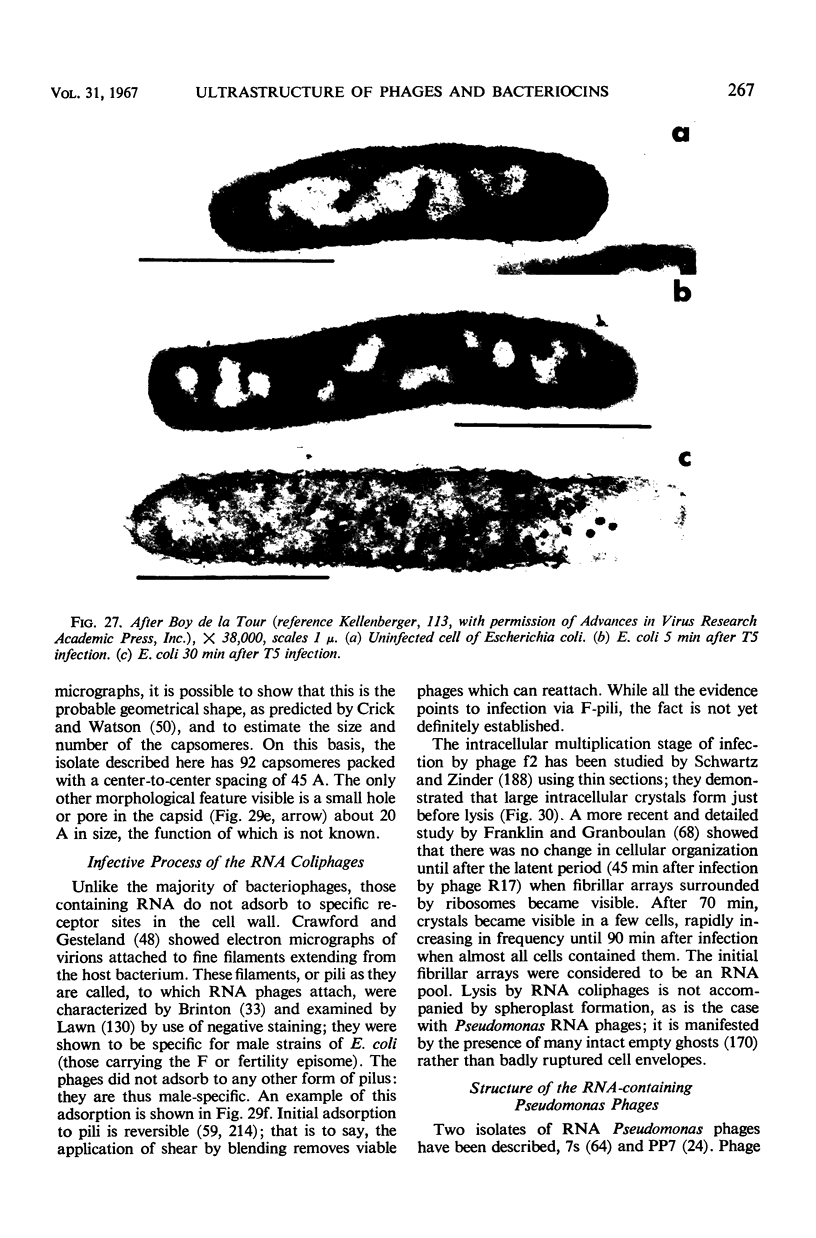
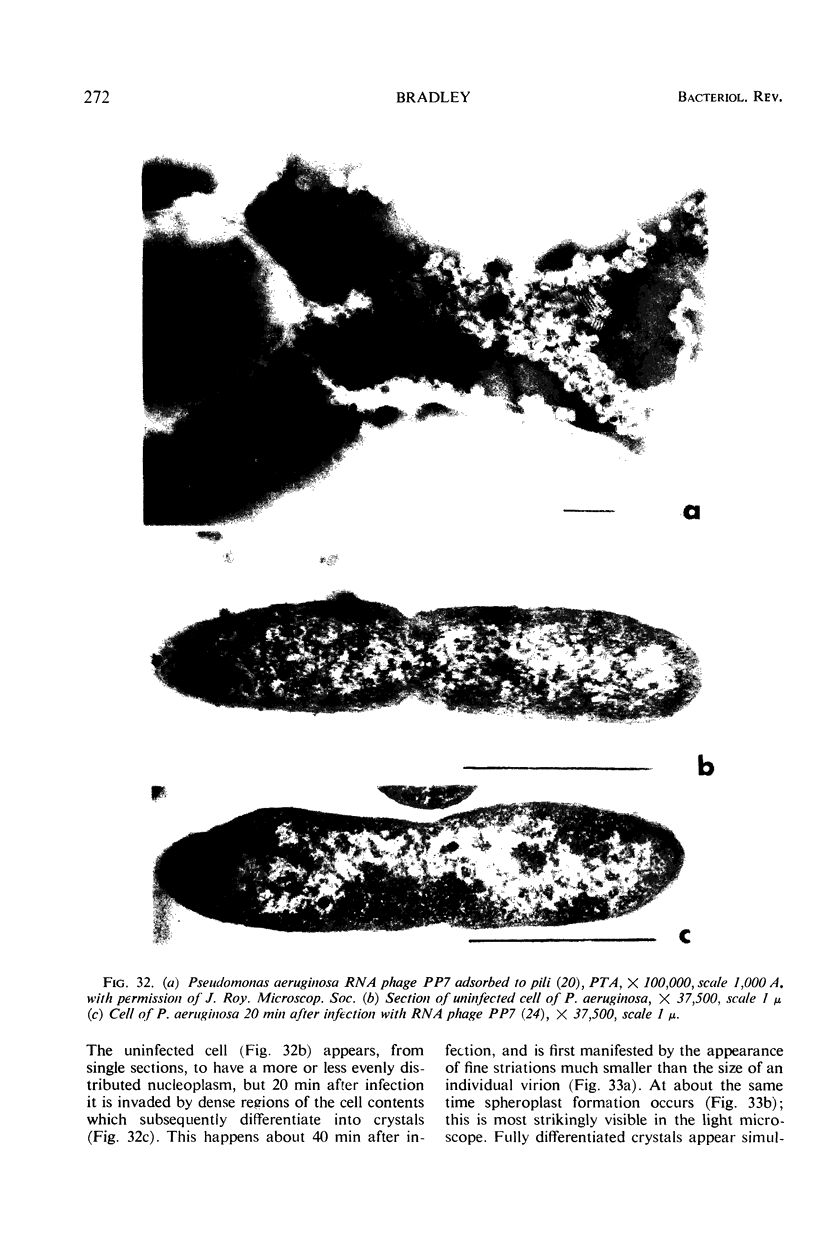
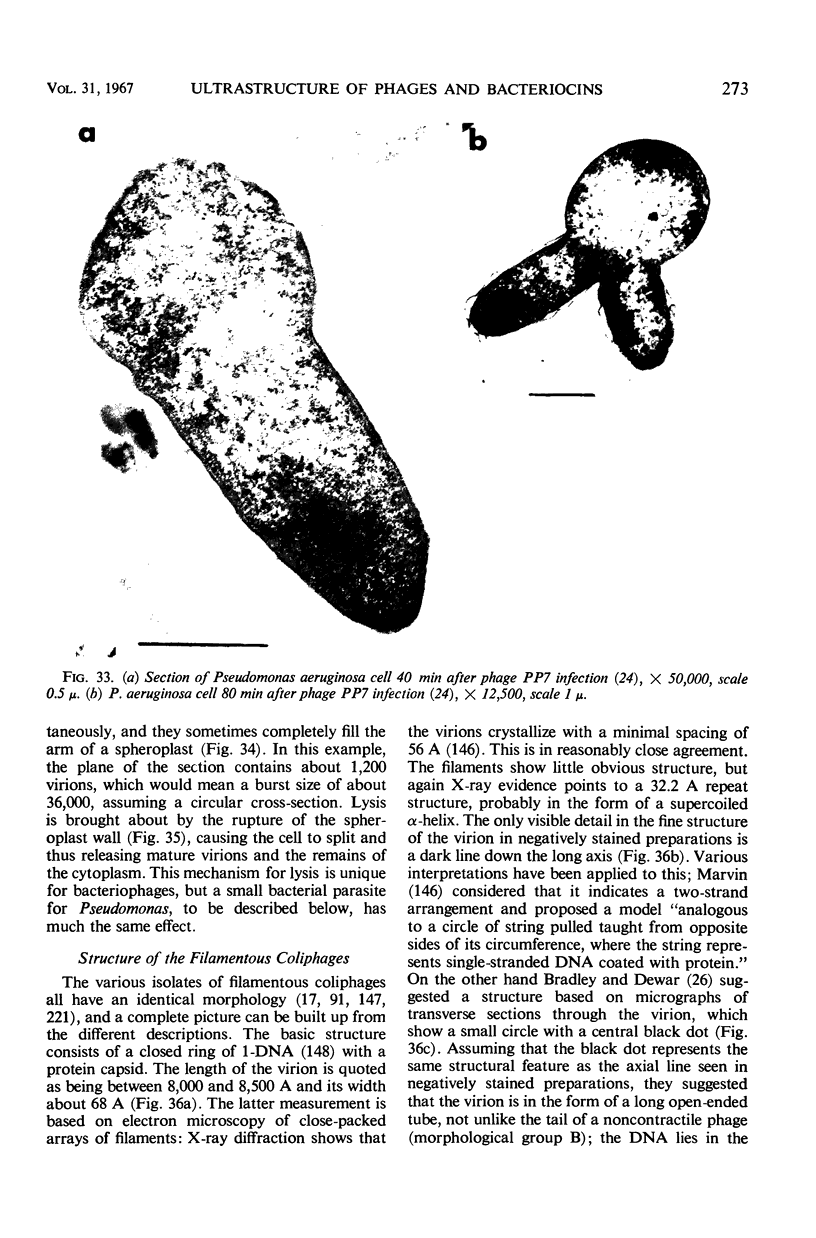
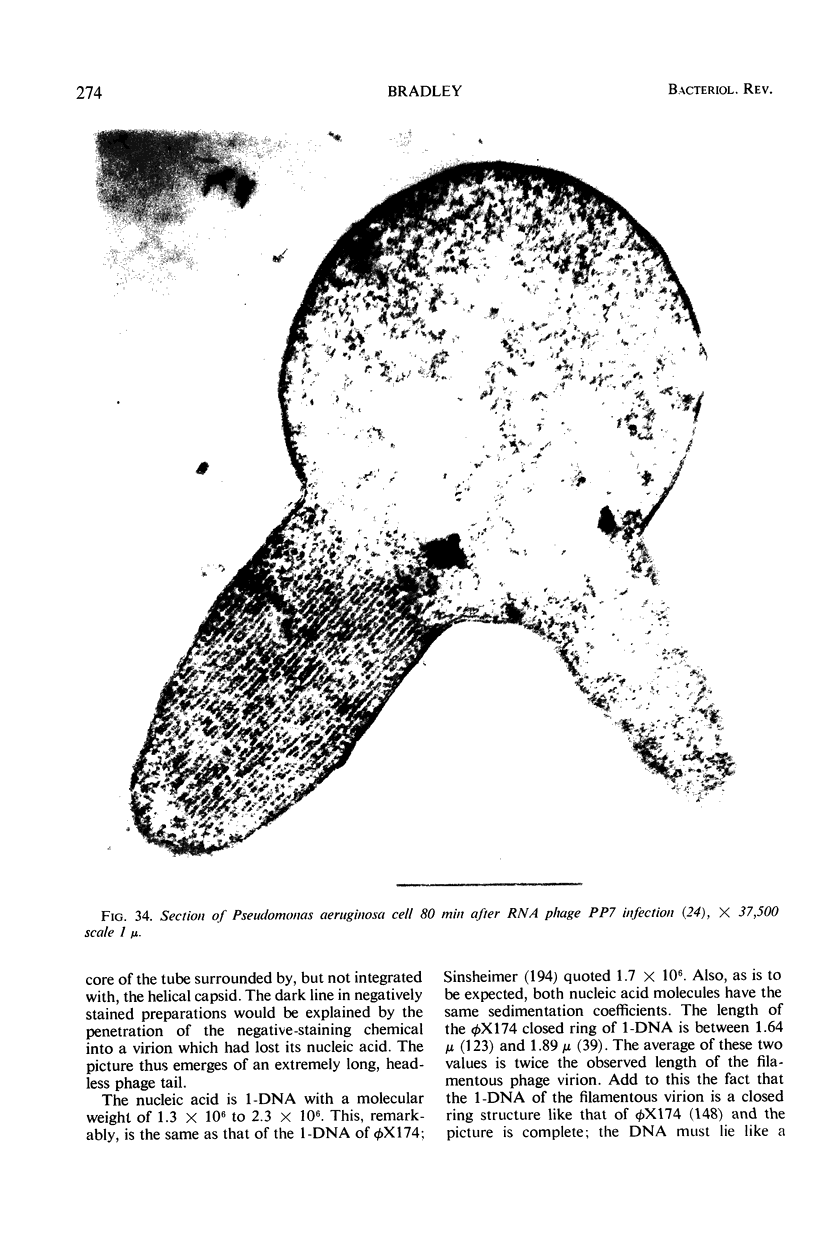
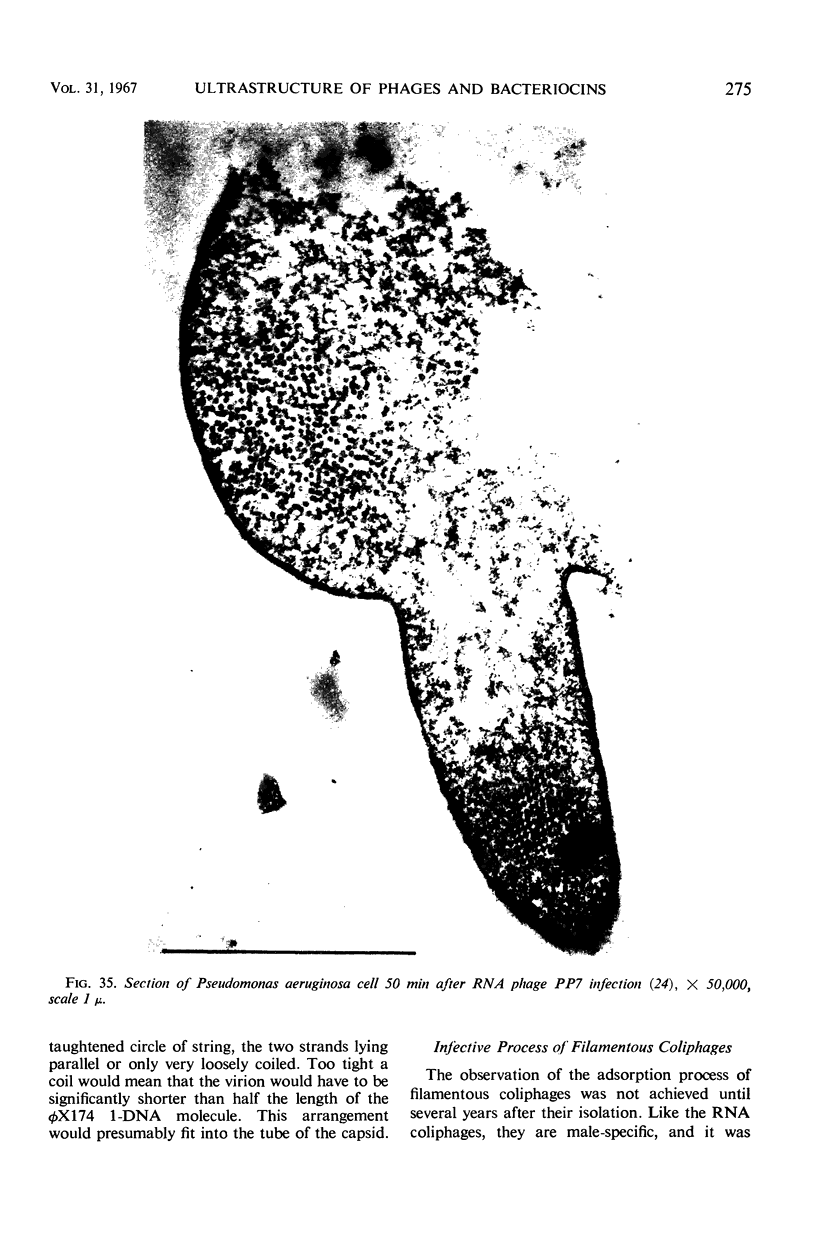
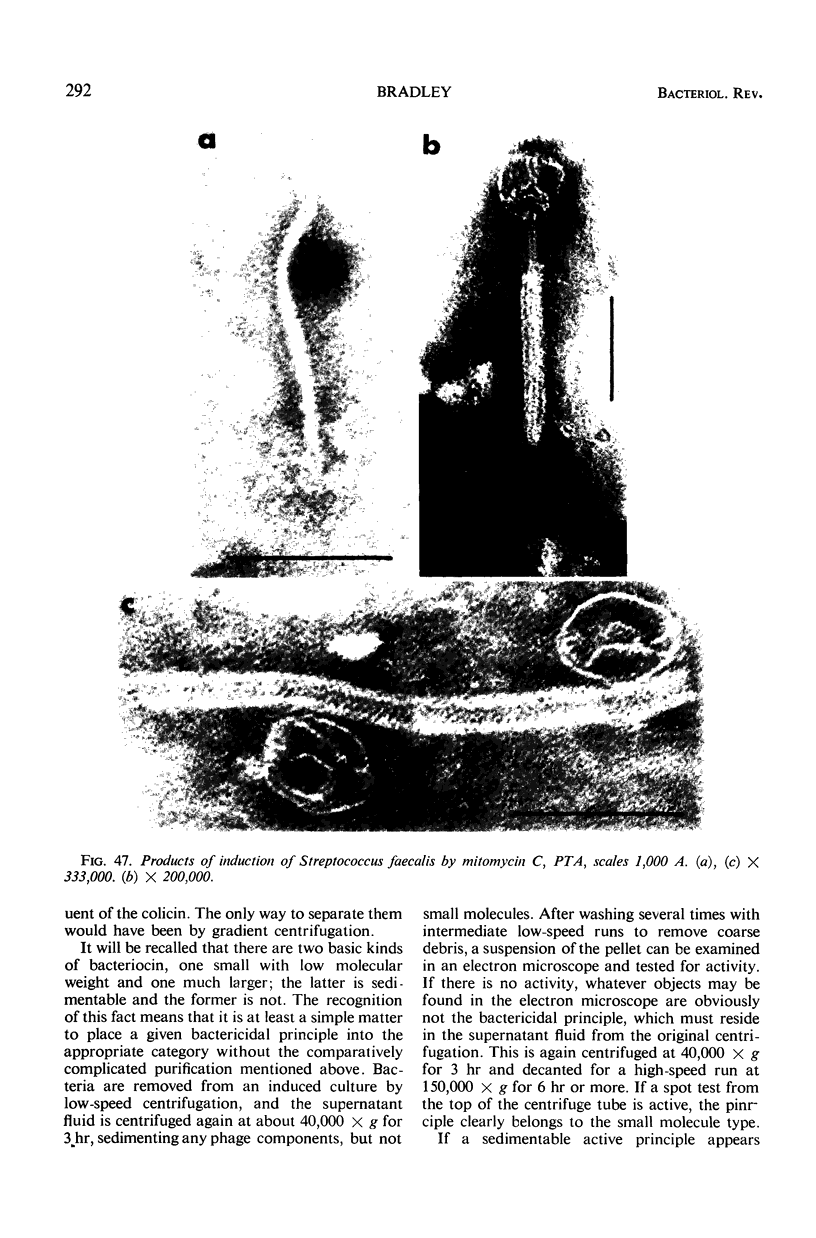
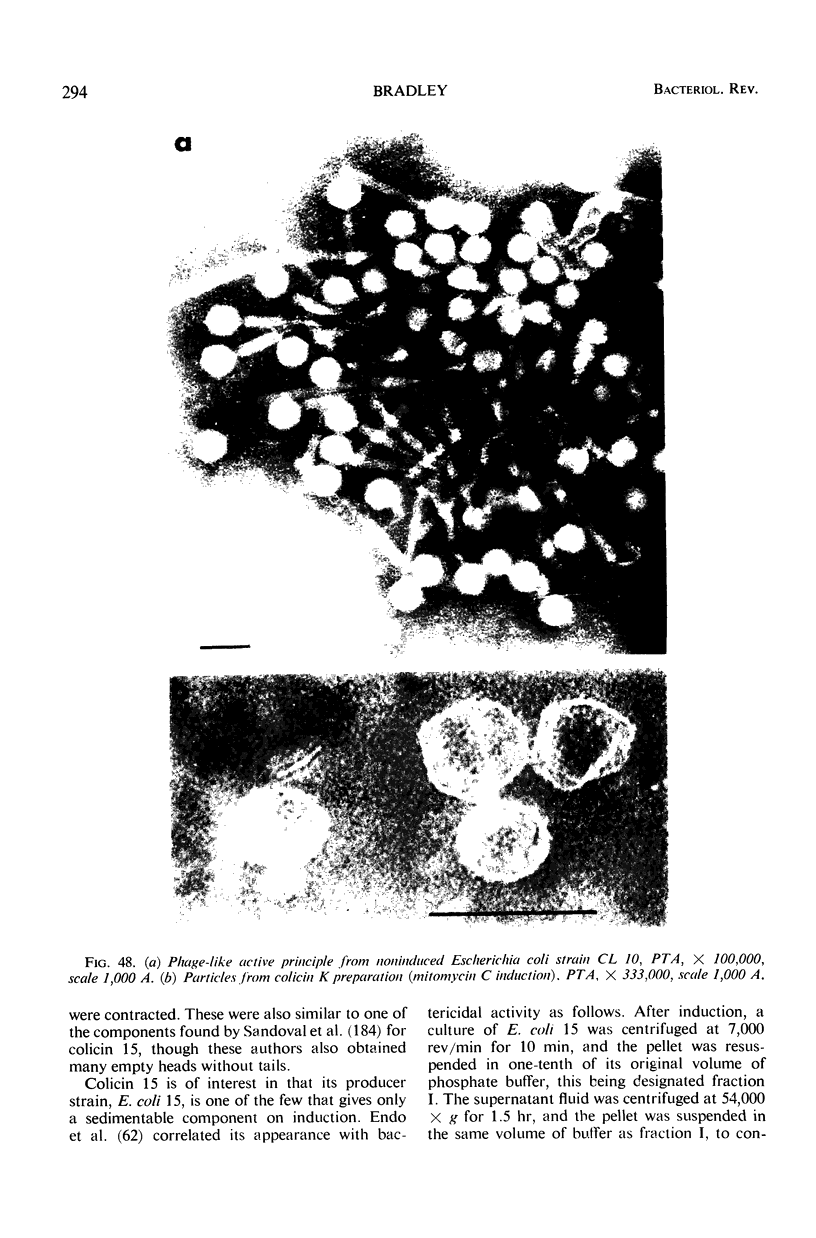
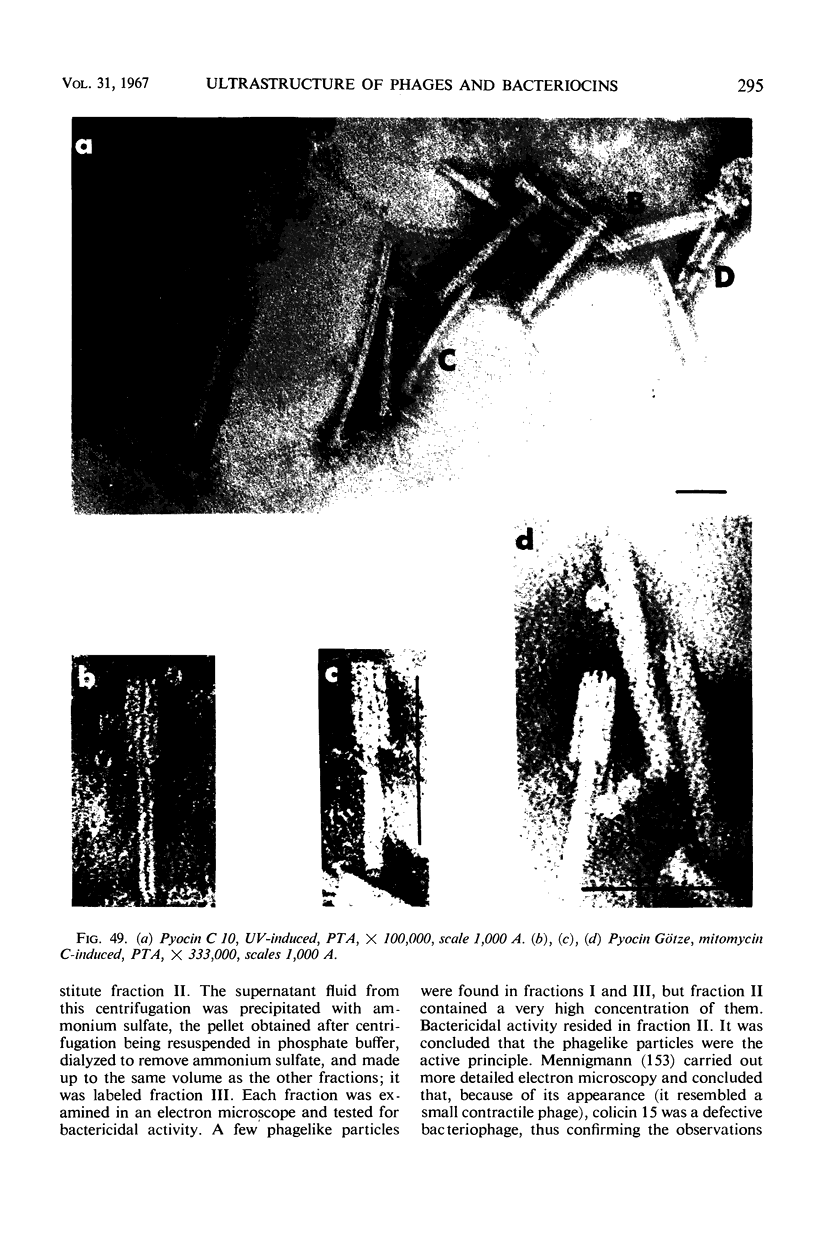
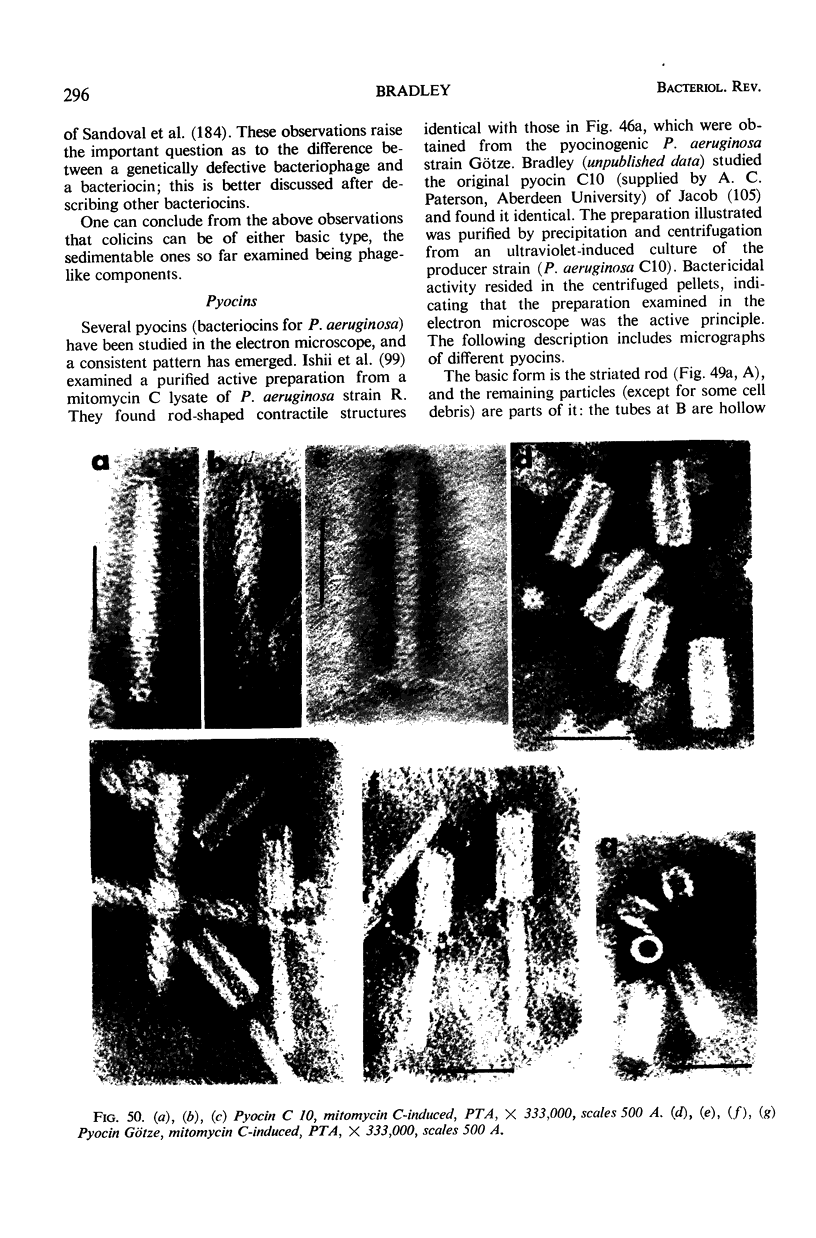
Full text
PDF
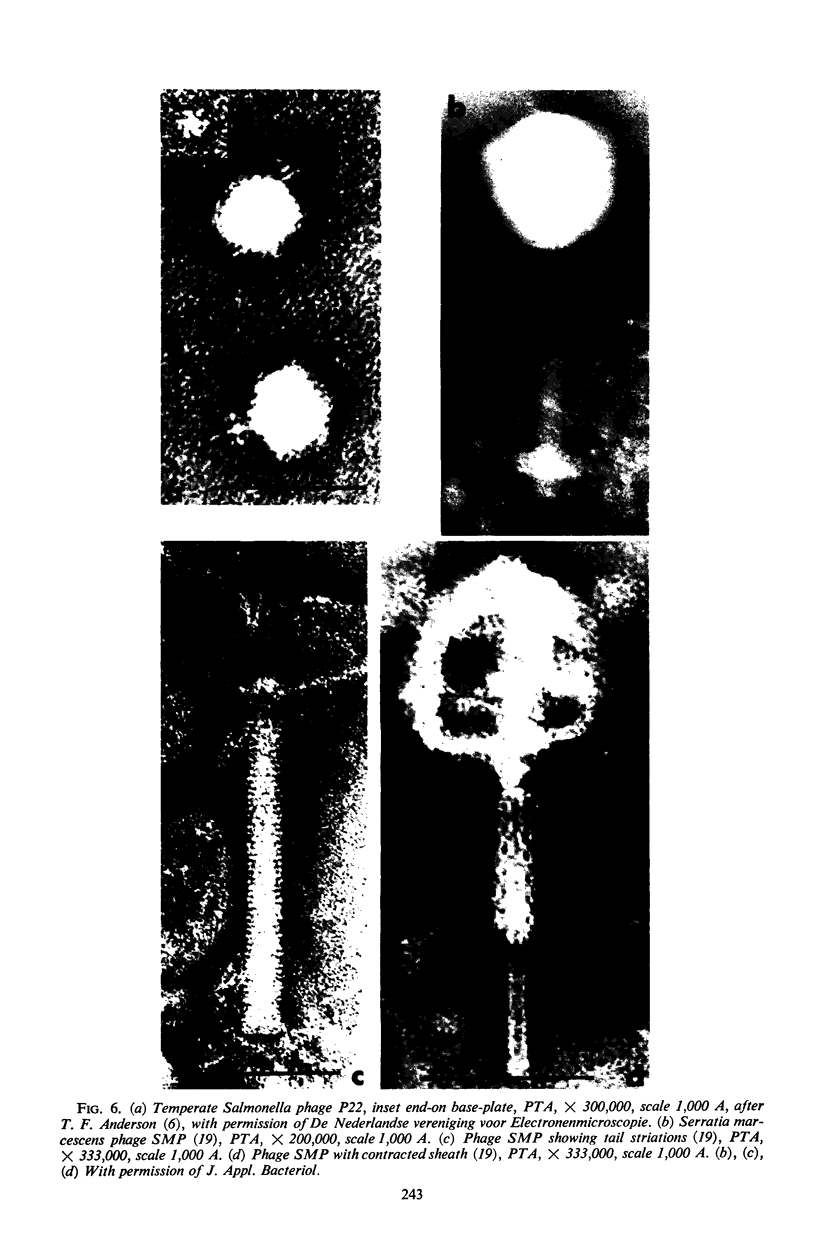
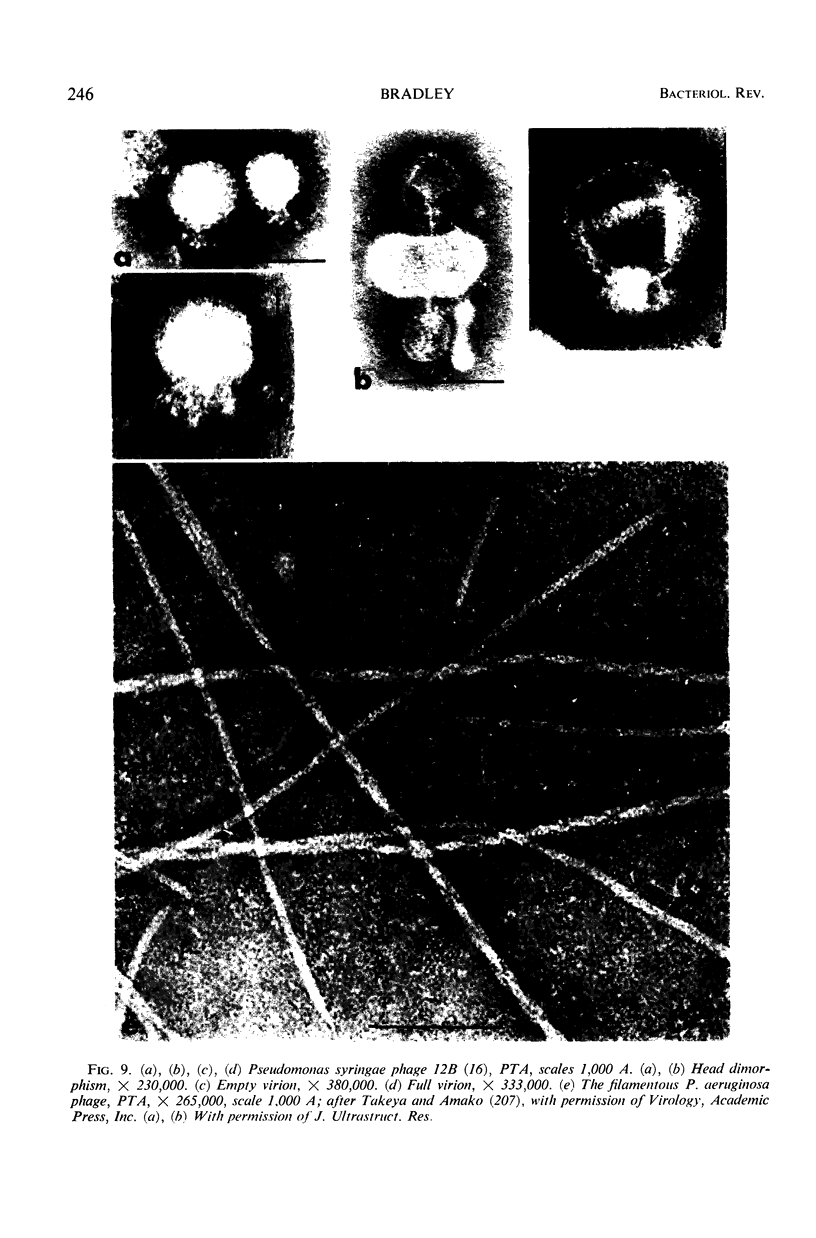



























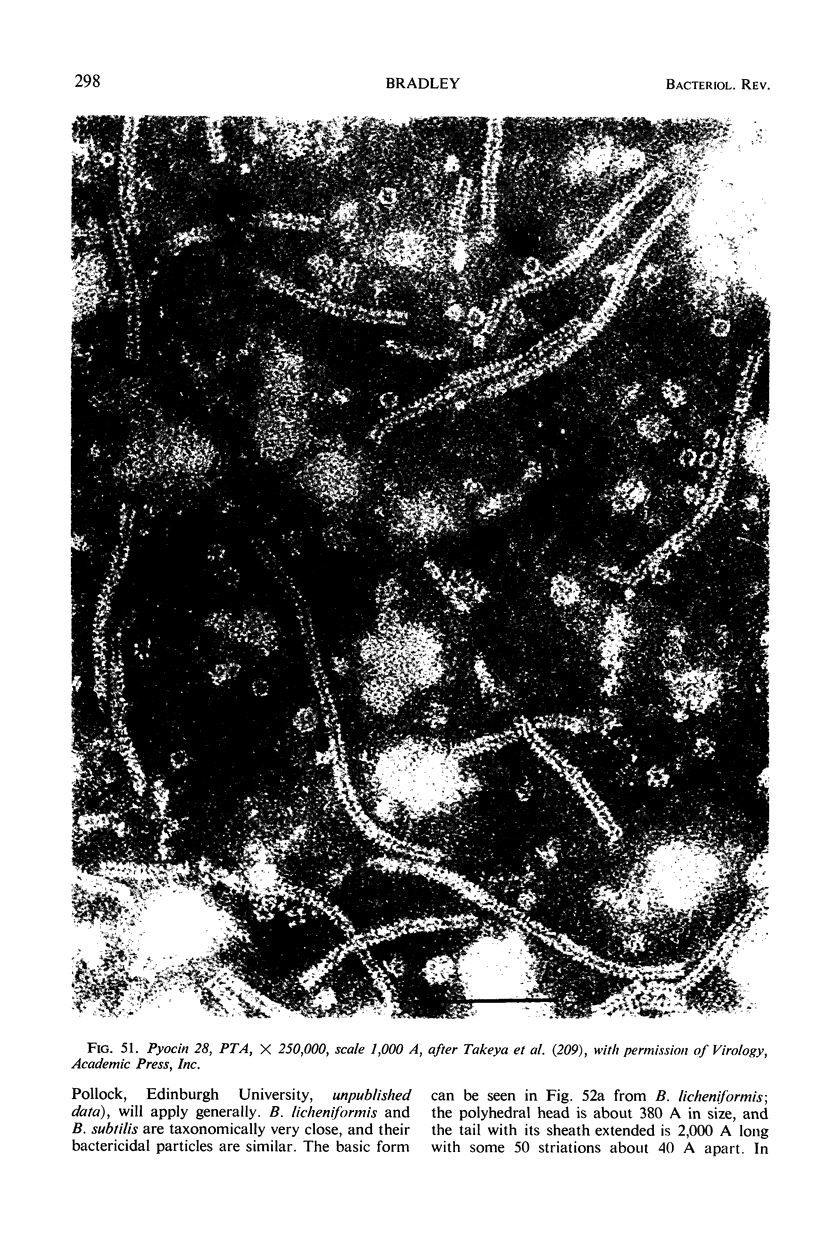
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS M. H. Criteria for a biological classification of bacterial viruses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1953 Mar 31;56(3):442–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1953.tb30236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALTENBERN R. A., STULL H. B. INDUCIBLE LYTIC SYSTEMS IN THE GENUS BACILLUS. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Apr;39:53–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON T. F., RAPPAPORT C., MUSCATINE N. A. On the structure and osmotic properties of phage particles. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Jan;84(1):5–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. L., Hickman D. D., Reilly B. E. Structure of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29 and the length of phi 29 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2081–2089. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2081-2089.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson T. F., Stephens R. Decomposition of T6 bacteriophage in alkaline solutions. Virology. 1964 May;23(1):113–117. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(64)80017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEN-GURION R., HERTMAN I. Bacteriocin-like material produced by Pasteurella pestis. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Oct;19(2):289–297. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLLE A., KELLENBERGER E. Etude de l'action du laurylsulfate de sodium sur E. coli. Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol. 1958;21(3):714–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
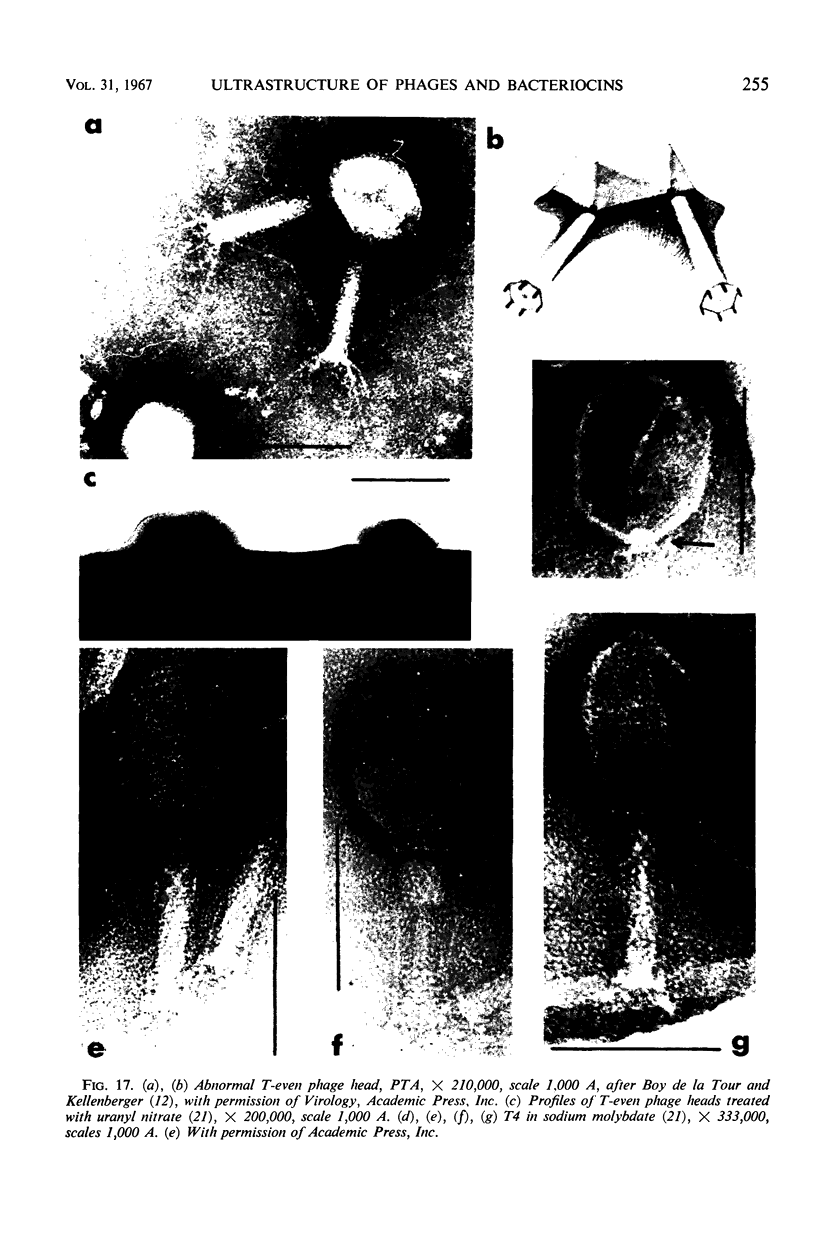
- BOYD J. S. K. Development of bacteriophage in Escherichia coli B. Nature. 1949 Nov 19;164(4177):874–874. doi: 10.1038/164874a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY D. E. Negative staining of bacteriophage phi-R at various pH values. Virology. 1961 Oct;15:203–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY D. E. THE STRUCTURE OF SOME BACTERIOPHAGES ASSOCIATED WITH MALE STRAINS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Jun;35:471–482. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-3-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
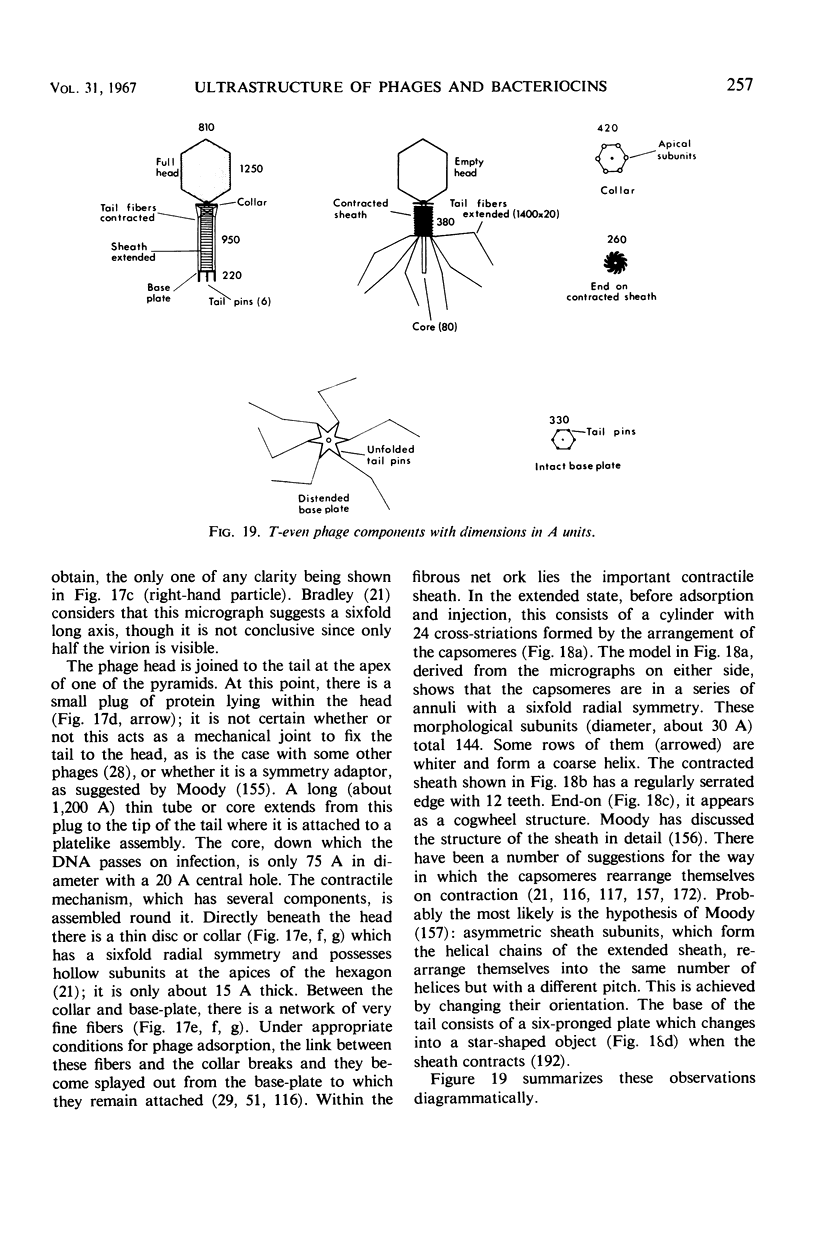
- BRADLEY D. E. THE STRUCTURE OF THE HEAD, COLLAR AND BASE-PLATE OF 'T-EVEN' TYPE BACTERIOPHAGES. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Mar;38:395–408. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY D. E. The structure of coliphages. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jun;31:435–445. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-3-435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY D. E. The structure of some Staphylococcus and Pseudomonas phages. J Ultrastruct Res. 1963 Jun;8:552–565. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(63)80055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRENNER S., CHAMPE S. P., STREISINGER G., BARNETT L. On the interaction of adsorption cofactors with bacteriophages T2 and T4. Virology. 1962 May;17:30–39. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRENNER S., HORNE R. W. A negative staining method for high resolution electron microscopy of viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:103–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D., PEACHER B., PIERSON D. SURVEY OF THE BACTERIOCINES OF ENTEROCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:702–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.702-707.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boy de la Tour E., Kellenberger E. Aberrant forms of the T-even phage head. Virology. 1965 Oct;27(2):222–225. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
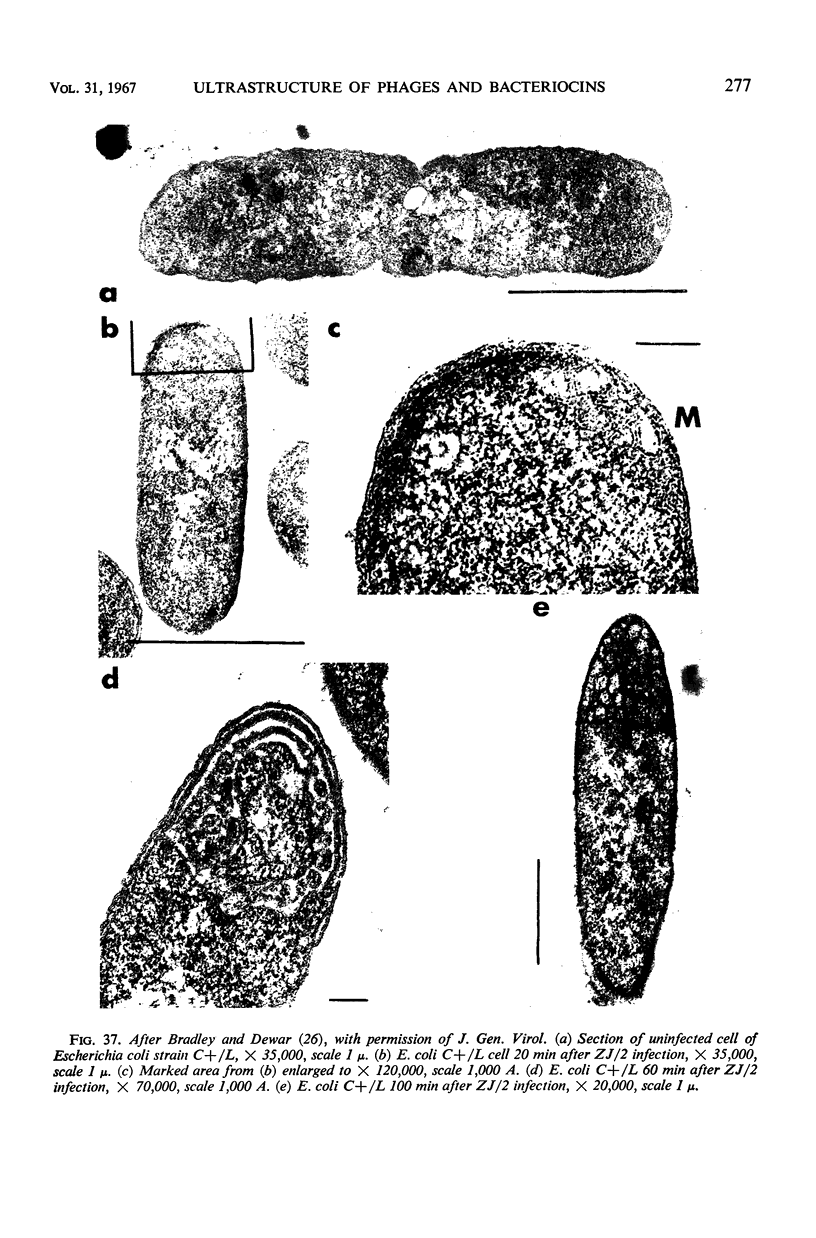
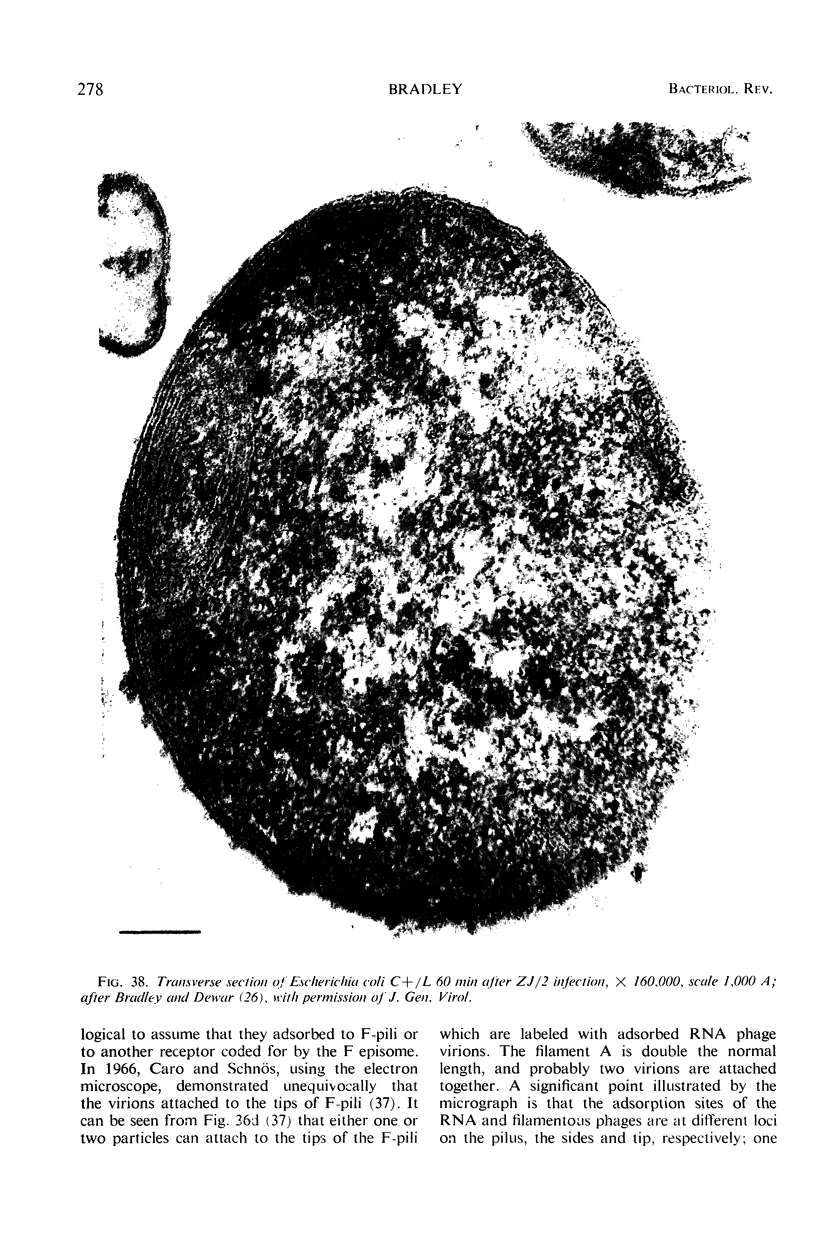
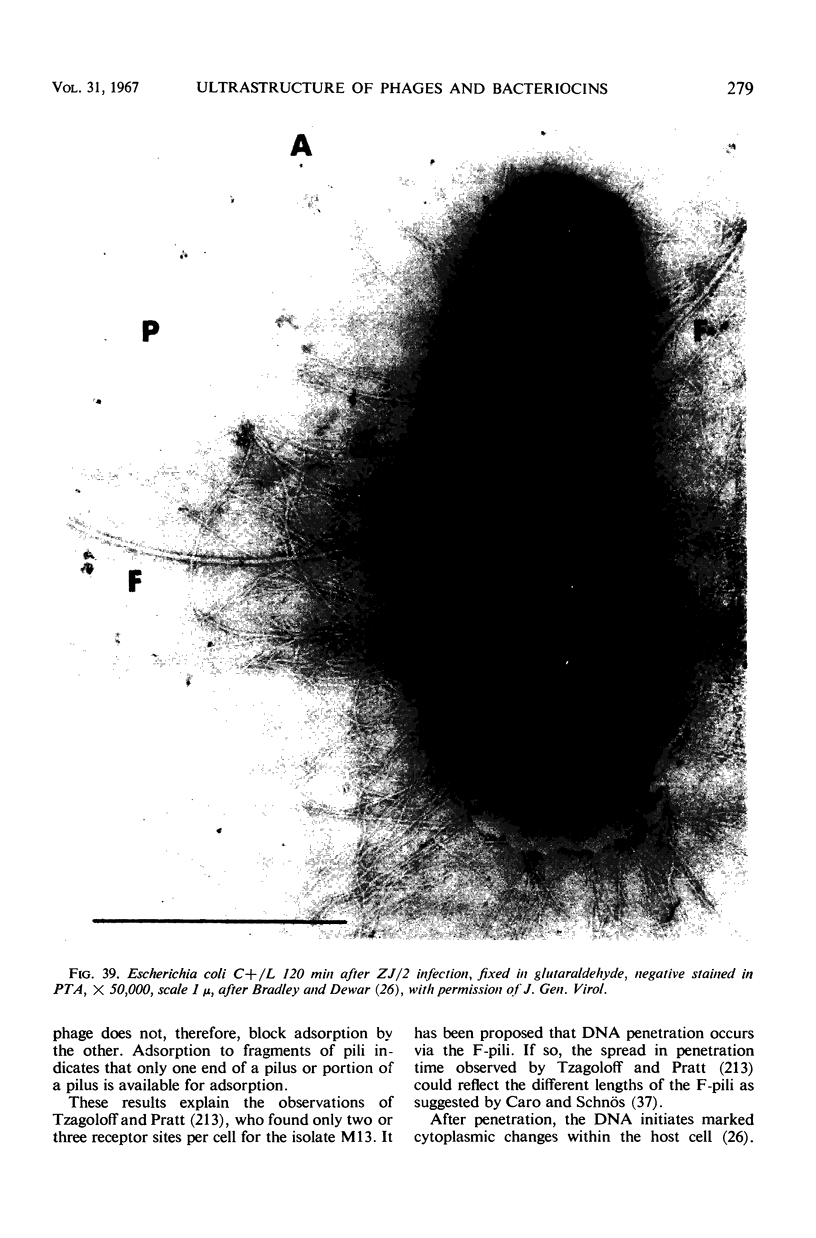
- Bradley D. E., Dewar C. A. Intracellular changes in cells of Escherichia coli infected with a filamentous bacteriophage. J Gen Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):179–188. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. The fluorescent staining of bacteriophage nucleic acids. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Sep;44(3):383–391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. The isolation and morphology of some new bacteriophages specific for Bacillus and Acetobacter species. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):233–241. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. The morphology and physiology of bacteriophages as revealed by the electron microscope. J R Microsc Soc. 1965 Sep;84(3):257–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. The morphology of some bacteriophages specific to Serratia marcescens. J Appl Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;28(2):271–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1965.tb02152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard R. P., Dworkin M. A bacteriophage for Myxococcus xanthus: isolation, characterization and relation of infectivity to host morphogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1305–1313. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1305-1313.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASPAR D. L., KLUG A. Physical principles in the construction of regular viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:1–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANDLER B., HAYASHI M., HAYASHI M. N., SPIEGELMAN S. CIRCULARITY OF THE REPLICATING FORM OF A SINGLE-STRANDED DNA VIRUS. Science. 1964 Jan 3;143(3601):47–49. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3601.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORRELL D. L., LEWIN R. A. ROD-SHAPED RIBONUCLEOPROTEIN PARTICLES FROM SAPROSPIRA. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Feb;10:63–74. doi: 10.1139/m64-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
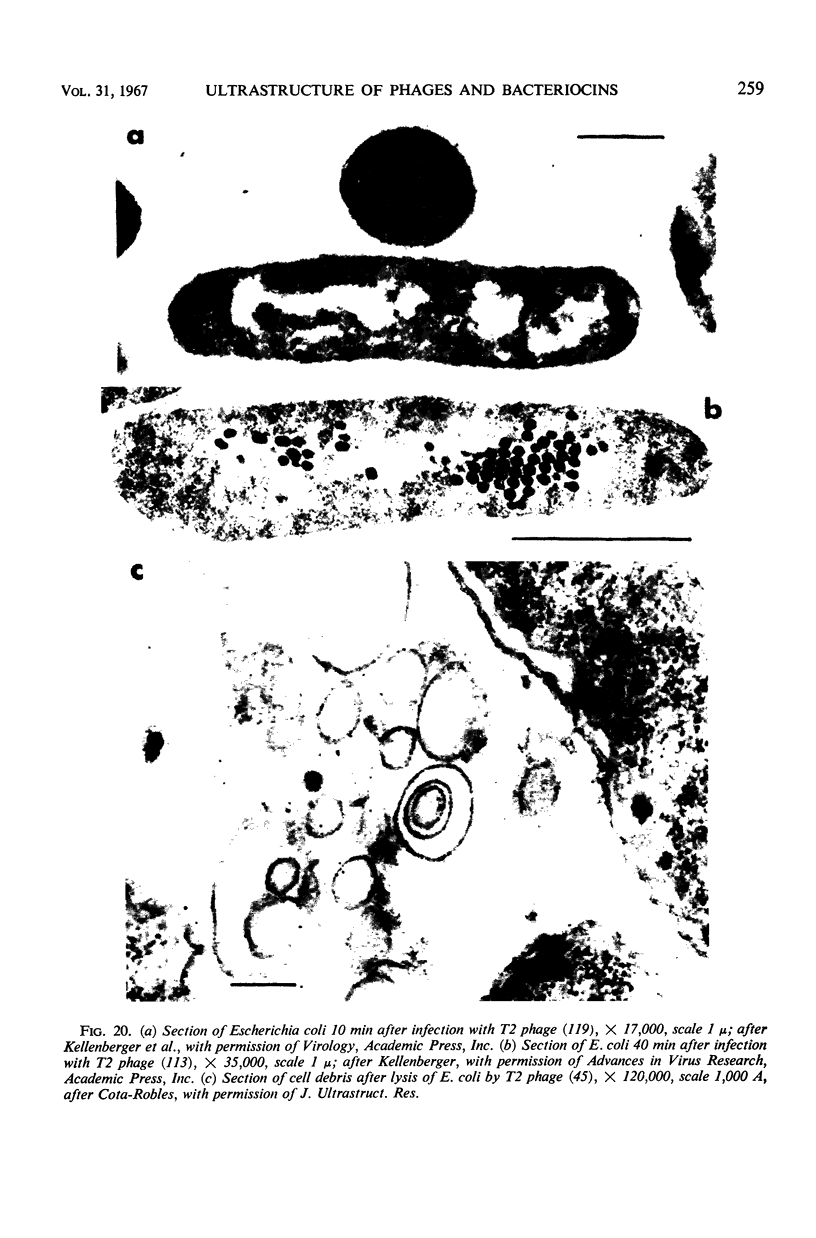
- COTA-ROBLES E. H., COFFMAN M. D. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF LYSIS FROM WITHOUT OF ESCHERICHIA COLI B BY COLIPHAGE T2. J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Apr;10:305–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTA-ROBLES E. H. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF "LYSIS FROM WITHIN" OF ESCHERICHIA COLI BY COLIPHAGE T2. J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Aug;11:112–122. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)80096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRICK F. H., WATSON J. D. Structure of small viruses. Nature. 1956 Mar 10;177(4506):473–475. doi: 10.1038/177473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINGS D. J. SEDIMENTATION AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF T-PHAGES OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Virology. 1964 Jul;23:408–418. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90264-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro L. G., Schnös M. The attachment of the male-specific bacteriophage F1 to sensitive strains of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):126–132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee J. N., Smit J. A., Prozesky O. W. Properties of Providence and Proteus morganii transducing phages. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Aug;44(2):167–176. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colvill A. J., Van Bruggen E. F., Fernández-Morán H. Physical properties of a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):302–304. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyette J., Calberg-Bacq C. M. Morphological characteristics of three new actinophages. J Gen Virol. 1967 Jan;1(1):13–18. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON P. F. THE STRUCTURE OF BACTERIOPHAGE SP8. Virology. 1963 Oct;21:146–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE MARS R. I. The production of phage-related materials when bacteriophage development in interrupted by proflavine. Virology. 1955 May;1(1):83–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ZWAIG R. N., ANTON D. N., PUIG J. The genetic control of colicinogenic factors E2, I and V. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Nov;29:473–484. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-3-473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEKLERK H. C., COETZEE J. N., FOURIE J. T. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF LACTOBACILLUS BACTERIOPHAGES. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jan;38:35–38. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUFF J. T., WYSS O. Isolation and classification of a new series of Azotobacter bacteriophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Feb;24:273–289. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demerec M, Fano U. Bacteriophage-Resistant Mutants in Escherichia Coli. Genetics. 1945 Mar;30(2):119–136. doi: 10.1093/genetics/30.2.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISERLING F. A., BOYDELATOUR E. CAPSOMERES AND OTHER STRUCTURES OBSERVED ON SOME BACTERIOPHAGES. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1965;28:175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENDO H., AYABE K., AMAKO K., TAKEYA K. INDUCIBLE PHAGE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI 15. Virology. 1965 Mar;25:469–471. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiserling F. A. The structure of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage PBS 1. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Feb;17(3):342–347. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
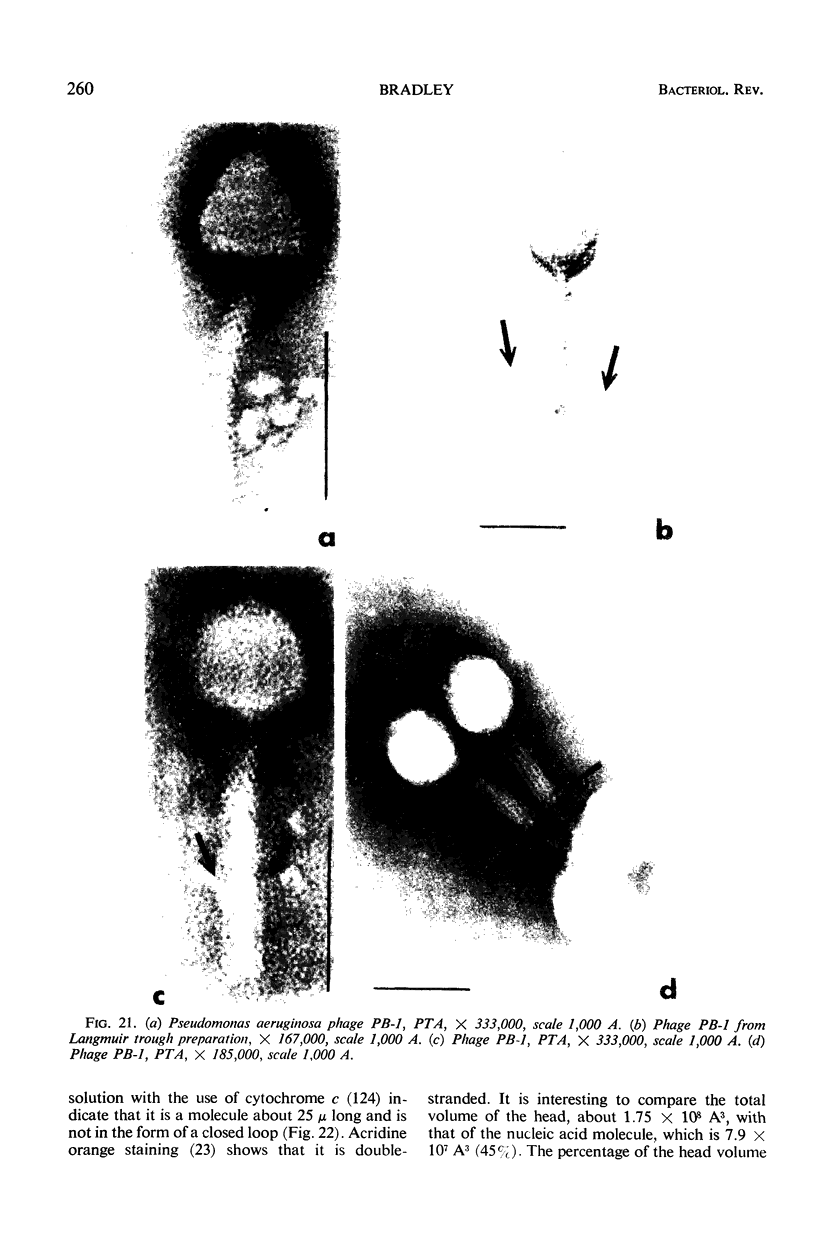
- FEARY T. W., FISHER E., Jr, FISHER T. N. ISOLATION AND PRELIMINARY CHARACTERISTICS OF THREE BACTERIOPHAGES ASSOCIATED WITH A LYSOGENIC STRAIN OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:196–208. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.196-208.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIERS W., SINSHEIMER R. L. The structure of the DNA of bacteriophage phi-X174. III. Ultracentrifugal evidence for a ring structure. J Mol Biol. 1962 Oct;5:424–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FILDES P. The relation of divalent metals to lysis of typhoid bacilli by bacteriophages. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Apr;35(2):122–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINCH J. T. RESOLUTION OF THE SUBSTRUCTURE OF TOBACCO MOSAIC VIRUS IN THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jun;8:872–874. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P., BETZ-BAREAU M. Transfert génétique de la propriété colinogène en rapport avec la polarité F des parents. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1953 Dec;147(23-24):2043–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. COLICINES ET AUTRES BACTERIOCINES. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1963;37:114–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Colicins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1957;11:7–22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.11.100157.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUCHS E., ZILLIG W., HOFSCHNEIDER P. H., PREUSS A. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF RNA-POLYMERASE PARTICLES. J Mol Biol. 1964 Dec;10:546–550. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M., Granboulan N. Ultrastructure of Escherichia coli cells infected with bacteriophage R17. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):834–848. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.834-848.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredericq P. On the nature of colicinogenic factors: a review. J Theor Biol. 1963 Mar;4(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(63)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOEBEL W. F., BARRY G. T., JESAITIS M. A., MILLER E. M. Colicine K. Nature. 1955 Oct 8;176(4484):700–701. doi: 10.1038/176700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs A. J., Harrison B. D., Watson D. H., Wildy P. What's in a virus name? Nature. 1966 Jan 29;209(5022):450–454. doi: 10.1038/209450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL C. E. Electron densitometry of stained virus particles. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Jan;1(1):1–12. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMON Y., PERON Y. QUELQUES REMARQUES SUR LES BACT'ERIOCINES PRODUITES PAR LES MICROBES GRAM-POSITIFS. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Jul 29;257:1191–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMON Y., PERON Y. [Individualization of some new families of enterobacteriocins]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Jul 1;257:309–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMON Y., PERON Y. [Study of the bacteriocinogenic potency in the genus Listeria. II. Individuality and classification of the bacteriocins in question]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 Jan;104:55–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMON Y., PERON Y. [Study of the bacteriocinogenic property in the genus Serratia]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1961 Jun;100:818–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRIOTT R. M., BARLOW J. L. The protein coats or ghosts of coliphage T2. I. Preparation, assay, and some chemical properties. J Gen Physiol. 1957 May 20;40(5):809–825. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.5.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFSCHNEIDER P. H., PREUSS A. M 13 BACTERIOPHAGE LIBERATION FROM INTACT BACTERIA AS REVEALED BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Mol Biol. 1963 Oct;7:450–451. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORNE R. W., WILDY P. Symmetry in virus architecture. Virology. 1961 Nov;15:348–373. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTON J. J., GOEBEL W. F. The isolation of colicine V and a study of its immunological properties. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Mar;45(4):125–141. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.4.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamon Y., Péron Y. Sur la nature des bactériocines produites par Listeria monocytogenes. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1966 Jul 11;263(2):198–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IONESCO H., RYTER A., SCHAEFFER P. SUR UN BACT'ERIOPHAGE H'EBERG'E PAR LA SOUCHE MARBURG DE BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Dec;107:764–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVANOVICS G., ALFOLDI L., NAGY E. Mode of action of megacin. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:51–60. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVANOVICS G., ALFOLDI L. Observations on lysogenesis in B. megaterium and on megacine, the antibacterial principle of this bacillus species. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):275–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S. I., Nishi Y., Egami F. The fine structure of a pyocin. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):428–431. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel J. V., Anderson T. F., Levine M. in vitro MORPHOGENESIS OF PHAGE P22 FROM HEADS AND BASE-PLATE PARTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):284–291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanovics G. BACTERIOCINS AND BACTERIOCIN-LIKE SUBSTANCES. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Jun;26(2 Pt 1):108–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F. Biosynthèse induite et mode d'action d'une pyocine, antibiotique de Pseudomonas pyocyanea. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1954 Feb;86(2):149–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., SIMINOVITCH L., WOLLMAN E. Sur la biosynthèse d'une colicine et sur son mode d'action. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1952 Sep;83(3):295–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., WOLLMAN E. L. Les épisomes, éléments génétiques ajoutés. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1958 Jul 7;247(1):154–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. Correlation between susceptibility to bacteriophage PBS1 and motility in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1575–1577. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1575-1577.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAY D., BRADLEY D. E. The structure of bacteriophage phi R. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Feb;27:195–200. doi: 10.1099/00221287-27-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAY D. The nucleic acid composition of bacteriophage phi R. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Feb;27:201–207. doi: 10.1099/00221287-27-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., BOLLE A., BOYDELATOUR E., EPSTEIN R. H., FRANKLIN N. C., JERNE N. K., REALE SCAFATI A., SECHAUD J. FUNCTIONS AND PROPERTIES RELATED TO THE TAIL FIBERS OF BACTERIOPHAGE T4. Virology. 1965 Jul;26:419–440. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., KELLENBERGER G. Etude de souches colicinogènes au microscope électronique. Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol. 1956;19(5):582–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SCHWAB W. L'utilisation d'un copolymère du groupe des polyesters comme matériel d'inclusion en ultramicrotomie. Experientia. 1956 Nov 15;12(11):421–422. doi: 10.1007/BF02157363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., SECHAUD J., RYTER A. Electron microscopical studies of phage multiplication. IV. The establishment of the DNA pool of vegetative phage and the maturation of phage particles. Virology. 1959 Aug;8:478–498. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E. Vegetative bacteriophage and the maturation of the virus particles. Adv Virus Res. 1961;8:1–61. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER G., KELLENBERGER E. La lysogénie d'une souche bacillus cereus. Mise en évidence par le microscope électronique. Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol. 1952;15(2):224–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINSCHMIDT A. K., BURTON A., SINSHEIMER R. L. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF THE REPLICATIVE FORM OF THE DNA OF THE BACTERIOPHAGE PHI-X174. Science. 1963 Nov 15;142(3594):961–961. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3594.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINSCHMIDT A. K., LANG D., JACHERTS D., ZAHN R. K. [Preparation and length measurements of the total desoxyribonucleic acid content of T2 bacteriophages]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 31;61:857–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLUG A., BERGER J. E. AN OPTICAL METHOD FOR THE ANALYSIS OF PERIODICITIES IN ELECTRON MICROGRAPHS, AND SOME OBSERVATIONS ON THE MECHANISM OF NEGATIVE STAINING. J Mol Biol. 1964 Dec;10:565–569. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Ordal E. J. Bacteriophage infecting the myxobacterium Chondrococcus columnaris. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1327–1332. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1327-1332.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANNI Y. T. Invasion by bacteriophage T5. II. Dissociation of calcium-independent and calcium-dependent processes. Virology. 1960 Apr;10:514–529. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANNI Y. T., MCCORQUODALE D. J., WILSON C. M. MOLECULAR ASPECTS OF DNA TRANSFER FROM PHAGE T5 TO HOST CELLS. II. ORIGIN OF FIRST-STEP-TRANSFER DNA FRAGMENTS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:19–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE M. Mutations in the temperate phage P22 and lysogeny in Salmonella. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):22–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIN R. A., CROTHERS D. M., CORRELL D. L., REIMANN B. E. A PHAGE INFECTING SAPROSPIRA GRANDIS. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Feb;10:75–85. doi: 10.1139/m64-011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEB T., ZINDER N. D. A bacteriophage containing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Mar 15;47:282–289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.3.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LWOFF A., HORNE R., TOURNIER P. A system of viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:51–55. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LWOFF A. Lysogeny. Bacteriol Rev. 1953 Dec;17(4):269–337. doi: 10.1128/br.17.4.269-337.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanni Y. T. DNA transfer from phage T5 to host cells: dependence on intercurrent protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):969–973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn A. M. Morphological features of the pili associated with Escherichia coli K 12 carrying R factors or the F factor. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Nov;45(2):377–383. doi: 10.1099/00221287-45-2-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAALØE O., BIRCH-ANDERSEN A., SJOSTRAND F. S. Electron micrographs of sections of E. coli cells infected with the bacteriophage T4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Sep;15(1):12–19. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKERT A., ZILLIG W. STUDIES ON THE LYSIS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI C BY BACTERIOPHAGE PHI-X174. Virology. 1965 Jan;25:88–97. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKHAM R., HITCHBORN J. H., HILLS G. J., FREY S. THE ANATOMY OF THE TOBACCO MOSAIC VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Mar;22:342–359. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYOR H. D., HILL N. O. Acridine orange staining of a single-stranded DNA bacteriophage. Virology. 1961 Jun;14:264–266. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCORQUODALE D. J., LANNI Y. T. MOLECULAR ASPECTS OF DNA TRANSFER FROM PHAGE T5 TO HOST CELLS. I. CHARACTERIZATION OF FIRST-STEP-TRANSFER MATERIAL. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:10–18. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL E. W. A bacteriophage for motile bacteria. Nature. 1961 May 6;190:564–564. doi: 10.1038/190564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUKAI F. H. Interrelationship between colicin sensitivity and phage resistance. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:539–551. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margaretten W., Morgan C., Rosenkranz H. S., Rose H. M. Effect of hydroxyurea on virus development. I. Electron microscopic study of the effect on the development of bacteriophage T4. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):823–833. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.823-833.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvin D. A., Schaller H. The topology of DNA from the small filamentous bacteriophage fd. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvin D. A. X-ray diffraction and electron microscope studies on the structure of the small filamentous bacteriophage fd. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):8–17. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maré I. J., de Klerk H. C., Prozesky O. W. The morphology of Alcaligenes faecalis bacteriophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jul;44(1):23–26. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. M., Miller P. A., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Morphological observations on some diphtherial phages. Virology. 1966 Jul;29(3):402–409. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennigmann H. D. Electron microscopy of the anti-bacterial agent produced by Escherichia coli 15. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):151–154. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. F. Structure of the sheath of bacteriophage T4. I. Structure of the contracted sheath and polysheath. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):167–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. F. Structure of the sheath of bacteriophage T4. II. Rearrangement of the sheath subunits during contraction. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. F. The shape of the T-even bacteriophage head. Virology. 1965 Aug;26(4):567–576. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON N., BEVIS R. E. Purification of animal viruses with Zn(OH)2. Virology. 1959 Jul;8(3):344–351. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel De Zwaig R. Association between colicinogenic and fertility factors. Genetics. 1966 Aug;54(2):381–390. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARNAS J., BRADLEY D. E., BURDZY K. WEITERE CHARAKTERISTIK DER BRUCELLAPHAGEN: MORPHOLOGIE. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1963;191:459–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POGLAZOV B. F., TIKHONENKO A. S. IZUCHENIE SVOISTV SOKRATITEL'NOGO BELKA FAGA T2) (RUS) Biokhimiia. 1963 Sep-Oct;28:888–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POINDEXTER J. S. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE CAULOBACTER GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:231–295. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.231-295.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Shilo M., Kislev N. Isolation of "cyanophages" from freshwater ponds and their interaction with Plectonema boryanum. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):234–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poglazov B. F., Mesyanzhinov V. V. Crystallization of the protein of the head of bacteriophage T2 in vitro. Virology. 1967 Mar;31(3):449–452. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90225-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prozesky O. W., De Klerk H. C., Coetzee J. N. The morphology of Proteus bacteriophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Oct;41(1):29–36. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVES P. THE BACTERIOCINS. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:24–45. doi: 10.1128/br.29.1.24-45.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS B. L., REEVES P. R. Some observations on the mode of action of colicin F. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Apr 23;11:140–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAFFERMAN R. S., MORRIS M. E. Algal virus: isolation. Science. 1963 May 10;140(3567):679–680. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3567.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAFFERMAN R. S., MORRIS M. E. GROWTH CHARACTERISTICS OF THE BLUE-GREEN ALGAL VIRUS LPP-1. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:771–775. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.771-775.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALIVAR W. O., TZAGOLOFF H., PRATT D. SOME PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF THE ROD-SHAPED COLIPHAGE M13. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:359–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDOVAL H. K., REILLY H. C., TANDLER B. COLICIN 15: POSSIBLY A DEFECTIVE BACTERIOPHAGE. Nature. 1965 Jan 30;205:522–523. doi: 10.1038/205522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT J. M., STANIER R. Y. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BACTERIOPHAGES ACTIVE AGAINST STALKED BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Apr;39:95–107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER I. R., DIENER T. O., SAFFERMAN R. S. BLUE-GREEN ALGAL VIRUS LPP-1: PURIFICATION AND PARTIAL CHARACTERIZATION. Science. 1964 May 29;144(3622):1127–1130. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3622.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ F. M., ZINDER N. D. CRYSTALLINE AGGREGATES IN BACTERIAL CELLS INFECTED WITH THE RNA BACTERIOPHAGE F2. Virology. 1963 Oct;21:276–278. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEAMAN E., TARMY E., MARMUR J. INDUCIBLE PHAGES OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:607–613. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLAYTER H. S., HOLLOWAY B. W., HALL C. E. THE STRUCTURE OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA PHAGES B3, E79, AND F116. J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Oct;11:274–281. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STICKLER D. J., TUCKER R. G., KAY D. BACTERIOPHAGE-LIKE PARTICLES RELEASED FROM BACILLUS SUBTILIS AFTER INDUCTION WITH HYDROGEN PEROXIDE. Virology. 1965 May;26:142–145. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLP H., STARR M. P. BDELLOVIBRIO BACTERIOVORUS GEN. ET SP. N., A PREDATORY, ECTOPARASITIC, AND BACTERIOLYTIC MICROORGANISM. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1963;29:217–248. doi: 10.1007/BF02046064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOUTHAMER A. H., DAEMS W. T., EIGNER J. Electron microscope studies of bacteriophage adsorption with negative and positive staining. Virology. 1963 Jun;20:246–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWORD C. P., PICKETT M. J. The isolation and characterization of bacteriophages from Listeria monocytogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:241–248. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. M. Observations on the adsorption of Caulobacter bacteriophages containing ribonucleic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Nov;45(2):347–353. doi: 10.1099/00221287-45-2-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafia F., Thompson T. L. Isolation and preliminary characterization of bacteriophage phi-mu-4. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):999–1002. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.999-1002.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. D., Anderson T. F. The infection of Escherichia coli by T2 and T4 bacteriophages as seen in the electron microscope. I. Attachment and penetration. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):279–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. D., Anderson T. F. The infection of Escherichia coli by T2 and T4 bacteriophages as seen in the electron microscope. II. Structure and function of the baseplate. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):298–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90278-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. M., Brown R. M., Jr, Goldstein D. A., Walne P. L. Culture methods for the blue-green alga Plectonema boryanum and its virus, with an electron microscope study of virus-infected cells. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):580–591. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. M., Brown R. M., Jr, Walne P. L. Ultrastructural and time-lapse studies on the replication cycle of the blue-green algal virus LPP-1. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
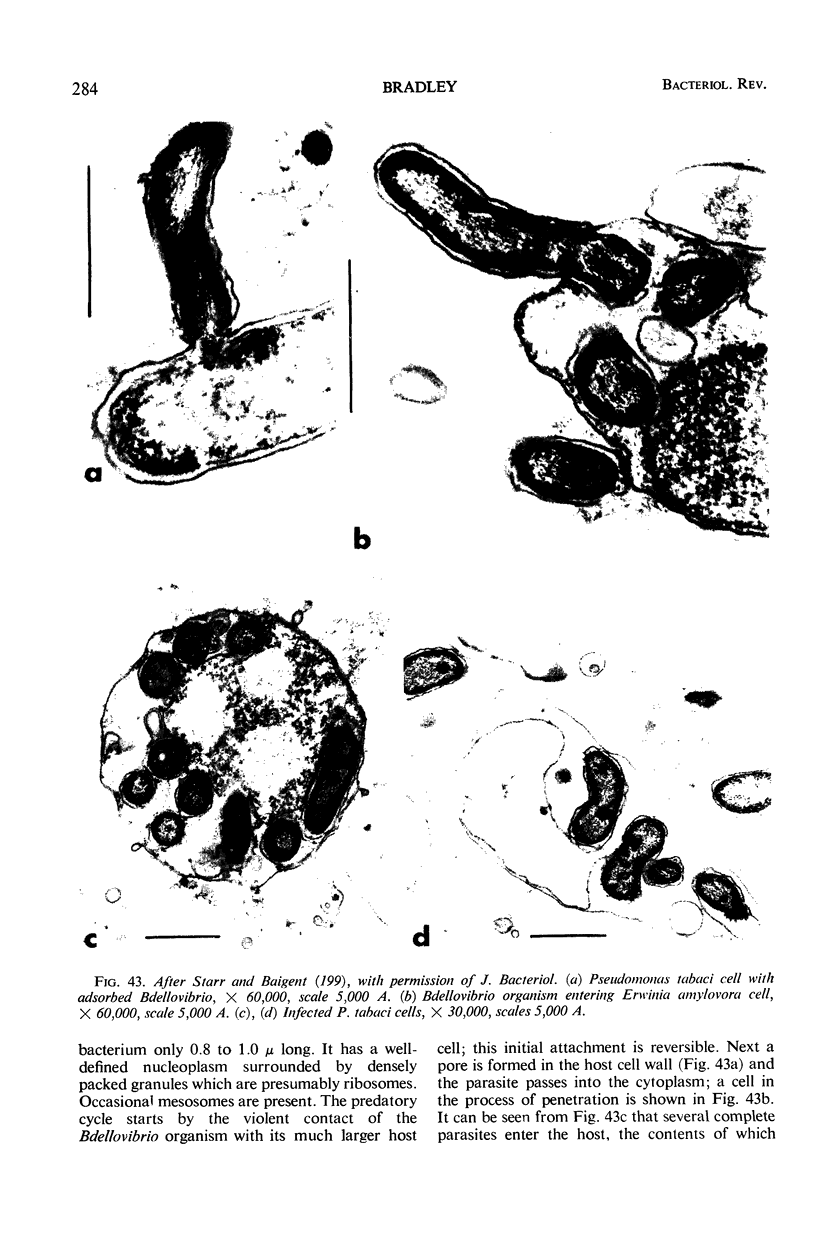
- Starr M. P., Baigent N. L. Parasitic interaction of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus with other bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2006–2017. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2006-2017.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEYA K., AMAKO K. THE STRUCTURE OF MYCOBACTERIOPHAGES. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:461–466. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEYA K., KOIKE M., MORI R., TODA T. Light and electron microscope studies of mycobacterium--mycobacteriophage interactions. III. Further studies on the ultrathin sections. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Nov;11:441–447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROMANS W. J., HORNE R. W. The structure of bacteriophage phi-X174. Virology. 1961 Sep;15:1–7. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TZAGOLOFF H., PRATT D. THE INITIAL STEPS IN INFECTION WITH COLIPHAGE M13. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:372–380. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya K., Amako K. A rod-shaped Pseudomonas phage. Virology. 1966 Jan;28(1):163–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90317-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya K., Minamishima Y., Amako K., Ohnishi Y. A small rod-shaped pyocin. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):166–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Wedel H., Ippen K. A. F-pili requirement for RNA bacteriophage adsorption. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90189-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieu J. F., Guélin A., Dauguet C. Morphologie du bactériophage 80 de Welchia perfringens. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Jul;109(1):157–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., KELLENBERGER E. The E. coli B-receptor for the phage T5. II. Electron microscopic studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 May;17(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., FRASER D. Morphology of the seven T-bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(4):458–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.4.458-464.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., FRASER D. Structural and functional differentiation in T2 bacteriophage. Virology. 1956 Jun;2(3):289–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(56)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. E., RIPPON J. E., DOWSETT L. M. Bacteriophage typing of strains of Staphylococcus aureus from various sources. Lancet. 1953 Mar 14;1(6759):510–514. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)92357-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAHLER S. A. Some biological properties of bacteriophages S13 and theta X-174. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):310–315. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.310-315.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINDER N. D., VALENTINE R. C., ROGER M., STOECKENIUS W. F1, A ROD-SHAPED MALE-SPECIFIC BACTERIOPHAGE THAT CONTAINS DNA. Virology. 1963 Aug;20:638–640. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90290-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Iterson W., Hoeniger J. F., Nijman van Zanten E. A "microtubule" in a bacterium. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jan;32(1):1–10. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]