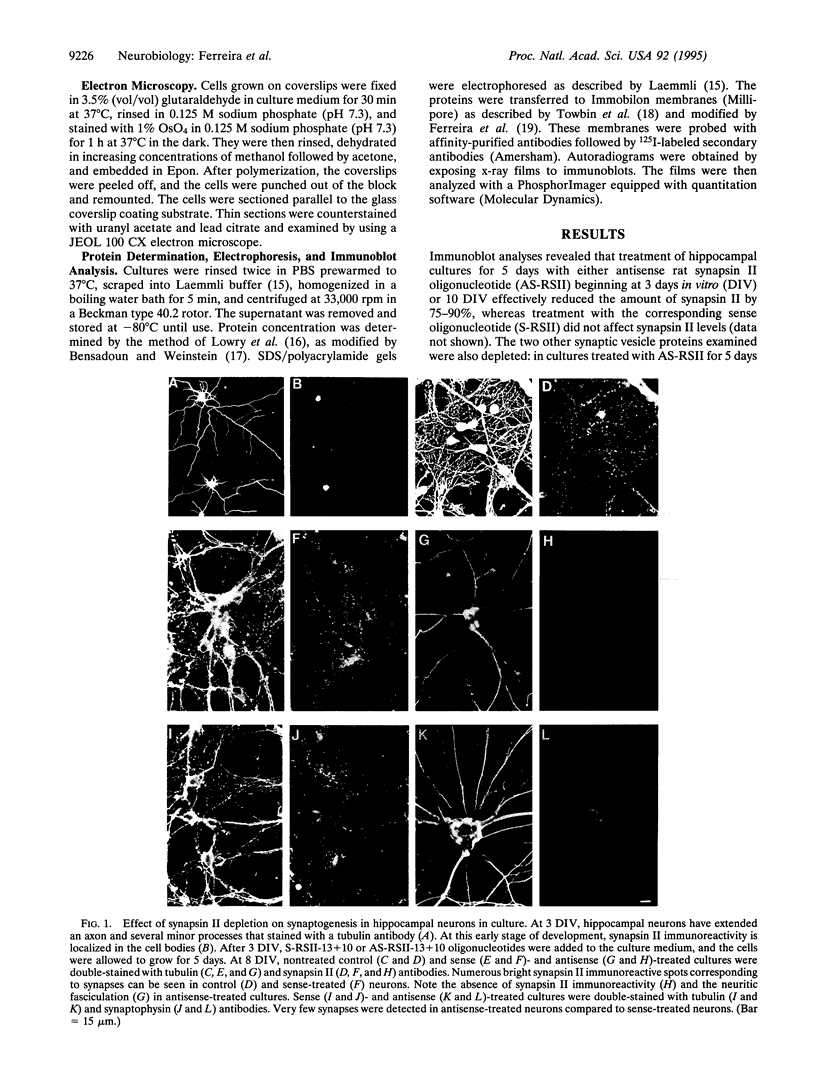
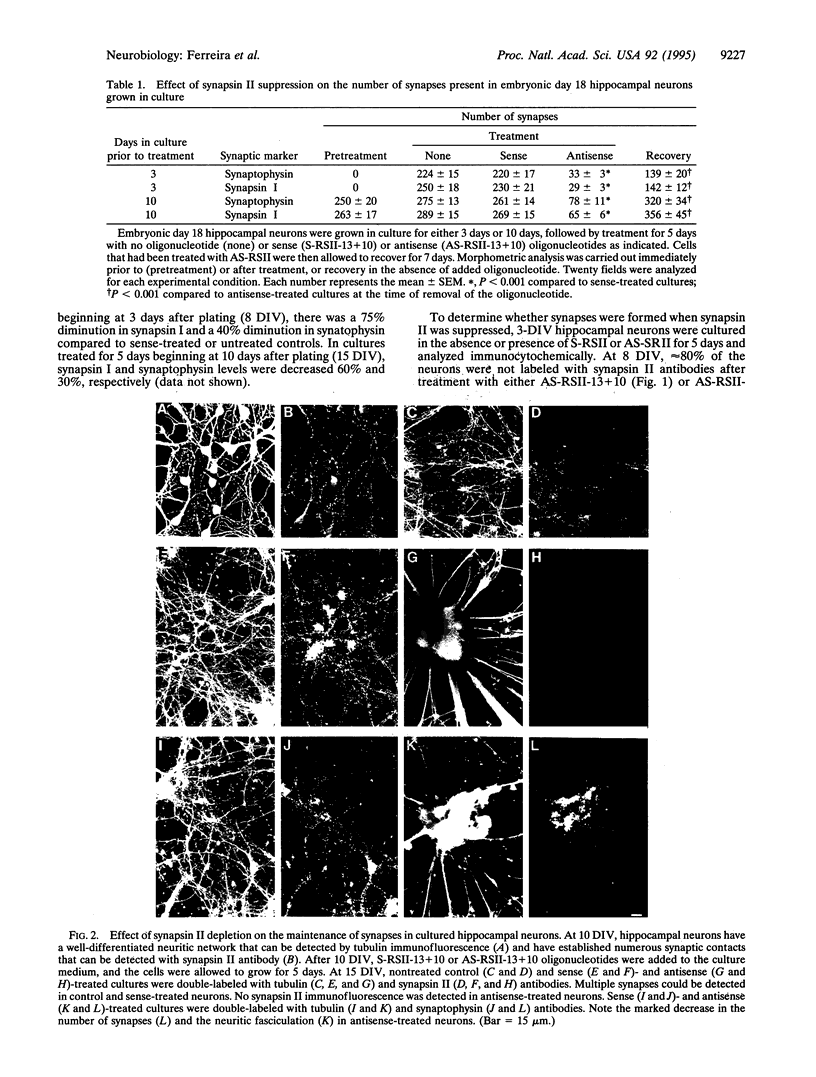
Abstract
Numerous synaptic proteins, including several integral membrane proteins, have been assigned roles in synaptic vesicle fusion with or retrieval from the presynaptic plasma membrane. In contrast, the synapsins, neuron-specific phosphoproteins associated with the cytoplasmic surface of synaptic vesicles, appear to play a much broader role, being involved in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and in the organization of the nerve terminal. Here we have administered antisense synapsin II oligonucleotides to dissociated hippocampal neurons, either before the onset of synaptogenesis or 1 week after the onset of synaptogenesis. In both cases, synapsin II was no longer detectable within 24-48 h of treatment. After 5 days of treatment, cultures were analyzed for the presence of synapses by synapsin I and synaptophysin antibody labeling and by electron microscopy. Cultures in which synapsin II was suppressed after axon elongation, but before synapse formation, did not develop synapses. Cultures in which synapsin II was suppressed after the development of synapses lost most of their synapses. Remarkably, with the removal of the antisense oligonucleotides, neurons and their synaptic connections recovered. These studies lead us to conclude that synapsin II is involved in the formation and maintenance of synapses in hippocampal neurons.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottenstein J. E., Sato G. H. Growth of a rat neuroblastoma cell line in serum-free supplemented medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):514–517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin L. S., Li L., Ferreira A., Kosik K. S., Greengard P. Impairment of axonal development and of synaptogenesis in hippocampal neurons of synapsin I-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9230–9234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotti C. G., Sullivan C. A., Banker G. A. The establishment of polarity by hippocampal neurons in culture. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1454–1468. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01454.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Busciglio J., Cáceres A. Microtubule formation and neurite growth in cerebellar macroneurons which develop in vitro: evidence for the involvement of the microtubule-associated proteins, MAP-1a, HMW-MAP2 and Tau. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1989 Oct 1;49(2):215–228. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(89)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Kosik K. S., Greengard P., Han H. Q. Aberrant neurites and synaptic vesicle protein deficiency in synapsin II-depleted neurons. Science. 1994 May 13;264(5161):977–979. doi: 10.1126/science.8178158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher T. L., Cameron P., De Camilli P., Banker G. The distribution of synapsin I and synaptophysin in hippocampal neurons developing in culture. J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;11(6):1617–1626. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-06-01617.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G., Han H. Q. Increase in synaptic vesicle proteins in synapsin-transfected NG108-15 cells: a subcellular fractionation study. Synapse. 1995 May;20(1):44–53. doi: 10.1002/syn.890200108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G., Han H. Q., Meister B., Hökfelt T., Greengard P. Laminin and neuropeptide Y are increased by synapsin transfection in cultured NG108-15 neuroblastoma/glioma hybrid cells. J Neurochem. 1995 Jun;64(6):2674–2680. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64062674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P., Valtorta F., Czernik A. J., Benfenati F. Synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins and regulation of synaptic function. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):780–785. doi: 10.1126/science.8430330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han H. Q., Nichols R. A., Rubin M. R., Bähler M., Greengard P. Induction of formation of presynaptic terminals in neuroblastoma cells by synapsin IIb. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):697–700. doi: 10.1038/349697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Chin L. S., Shupliakov O., Brodin L., Sihra T. S., Hvalby O., Jensen V., Zheng D., McNamara J. O., Greengard P. Impairment of synaptic vesicle clustering and of synaptic transmission, and increased seizure propensity, in synapsin I-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9235–9239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B., Greengard P., Poo M. M. Exogenous synapsin I promotes functional maturation of developing neuromuscular synapses. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90280-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieribone V. A., Shupliakov O., Brodin L., Hilfiker-Rothenfluh S., Czernik A. J., Greengard P. Distinct pools of synaptic vesicles in neurotransmitter release. Nature. 1995 Jun 8;375(6531):493–497. doi: 10.1038/375493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosahl T. W., Geppert M., Spillane D., Herz J., Hammer R. E., Malenka R. C., Südhof T. C. Short-term synaptic plasticity is altered in mice lacking synapsin I. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):661–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90487-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer E., Alder J., Greengard P., Poo M. M. Synapsin IIa accelerates functional development of neuromuscular synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3882–3886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Czernik A. J., Kao H. T., Takei K., Johnston P. A., Horiuchi A., Kanazir S. D., Wagner M. A., Perin M. S., De Camilli P. Synapsins: mosaics of shared and individual domains in a family of synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1474–1480. doi: 10.1126/science.2506642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtorta F., Iezzi N., Benfenati F., Lu B., Poo M. M., Greengard P. Accelerated structural maturation induced by synapsin I at developing neuromuscular synapses of Xenopus laevis. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 Feb 1;7(2):261–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb01062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. W. Gene inhibition using antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):333–335. doi: 10.1038/372333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]