Abstract
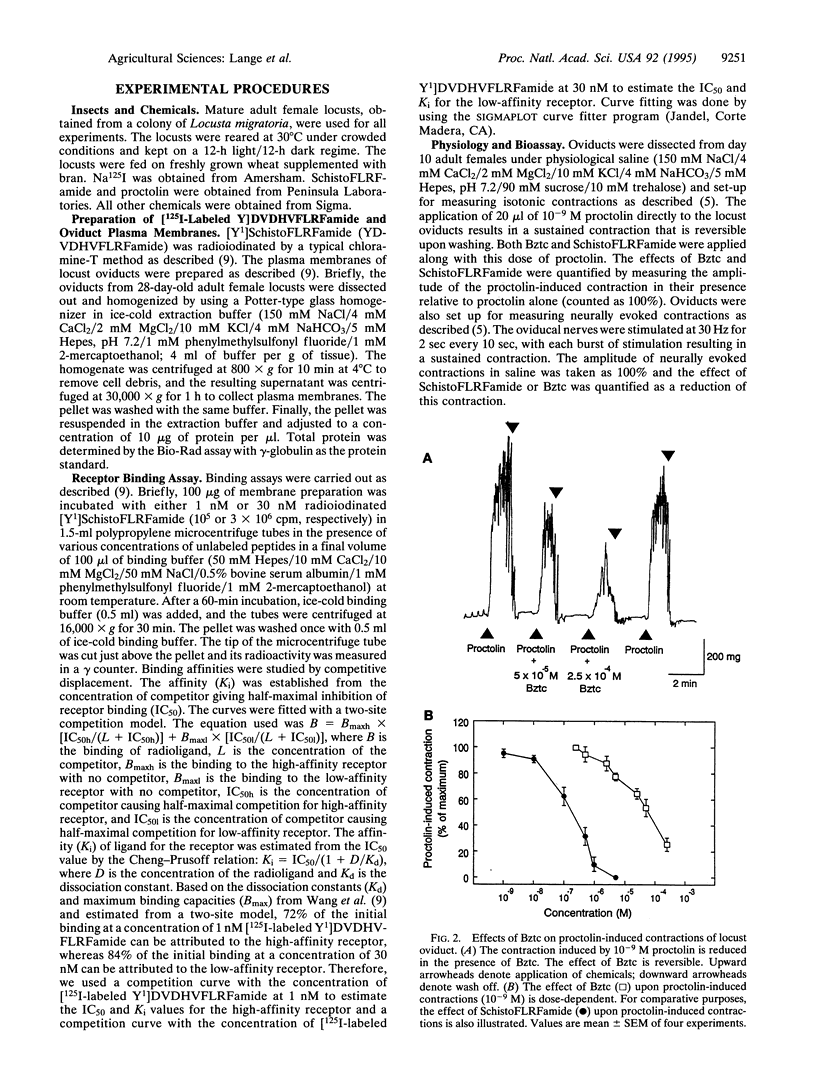
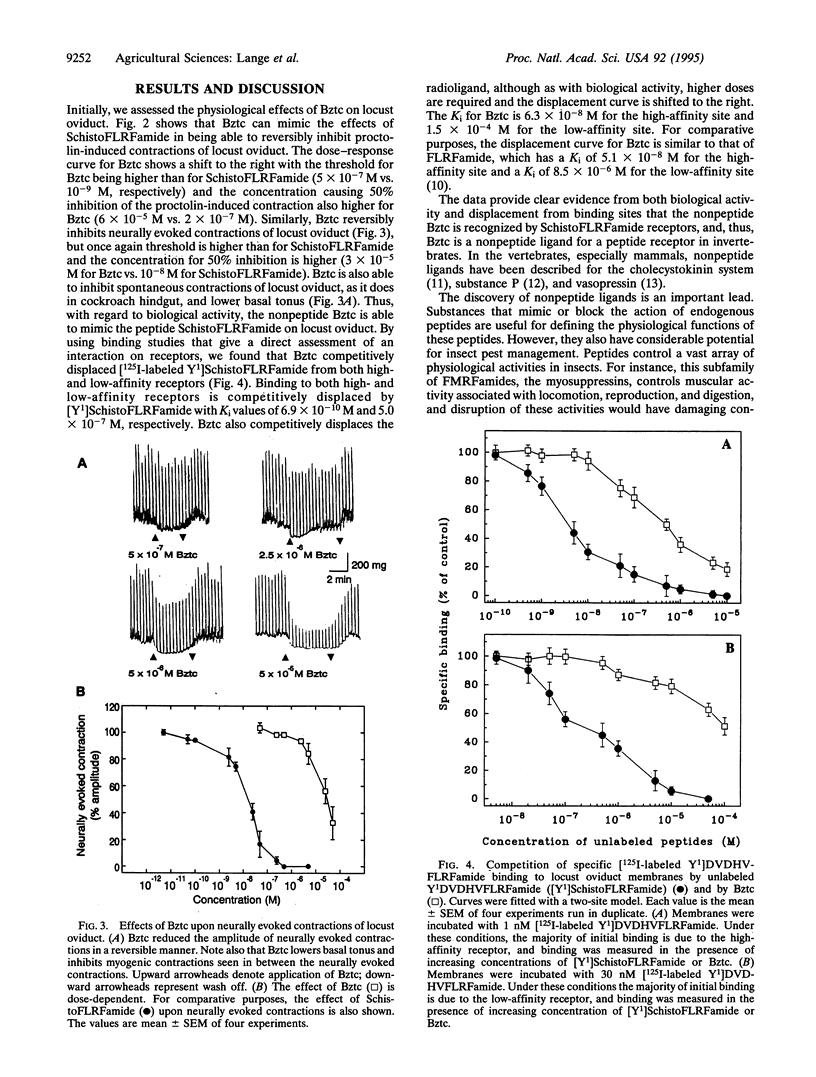
We describe a nonpeptide mimetic analog of an invertebrate peptide receptor. Benzethonium chloride (Bztc) is an agonist of the SchistoFLRFamide (PDVDHVFLRFamide) receptors found on locust oviducts. Bztc competitively displaces [125I-labeled Y1]SchistoFLRFamide binding to both high- and low-affinity receptors of membrane preparations. Bztc mimics the physiological effects of SchistoFLRFamide on locust oviduct, by inhibiting myogenic and induced contractions in a dose-dependent manner. Bztc is therefore recognized by the binding and activation regions of the SchistoFLRFamide receptors. This discovery provides a unique opportunity within insects to finally target a peptide receptor for the development of future pest management strategies.
Full text
PDF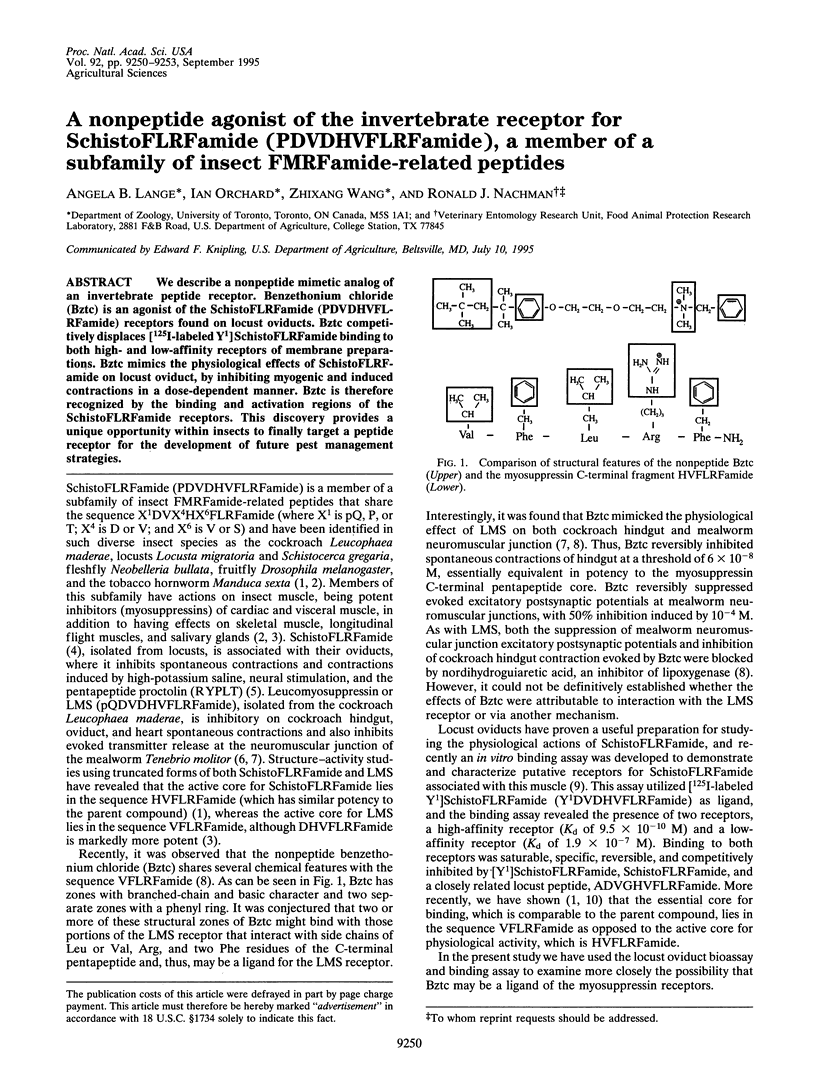

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Evans B. E., Bock M. G., Rittle K. E., DiPardo R. M., Whitter W. L., Veber D. F., Anderson P. S., Freidinger R. M. Design of potent, orally effective, nonpeptidal antagonists of the peptide hormone cholecystokinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4918–4922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masler E. P., Kelly T. J., Menn J. J. Insect neuropeptides: discovery and application in insect management. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1993;22(1-2):87–111. doi: 10.1002/arch.940220109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. J., Holman G. M., Haddon W. F. Leads for insect neuropeptide mimetic development. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1993;22(1-2):181–197. doi: 10.1002/arch.940220115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. J., Holman G. M., Hayes T. K., Beier R. C. Structure-activity relationships for inhibitory insect myosuppressins: contrast with the stimulatory sulfakinins. Peptides. 1993 Jul-Aug;14(4):665–670. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(93)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeff N. M., Orchard I., Lange A. B. Isolation, sequence, and bioactivity of PDVDHVFLRFamide and ADVGHVFLRFamide peptides from the locust central nervous system. Peptides. 1994;15(3):387–392. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(94)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb S., Packman L. C., Evans P. D. Isolation, primary structure and bioactivity of schistoflrf-amide, a FMRF-amide-like neuropeptide from the locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 28;160(2):850–856. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92512-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider R. M., Constantine J. W., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Longo K. P., Lebel W. S., Woody H. A., Drozda S. E., Desai M. C., Vinick F. J., Spencer R. W. A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):435–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1703323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Orchard I., Lange A. B. Identification and characterization of two receptors for SchistoFLRFamide on locust oviduct. Peptides. 1994;15(5):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(94)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto D., Ishikawa S., Holman G. M., Nachman R. J. Leucomyosuppressin, a novel insect neuropeptide, inhibits evoked transmitter release at the mealworm neuromuscular junction. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Dec 19;95(1-3):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura Y., Ogawa H., Chihara T., Kondo K., Onogawa T., Nakamura S., Mori T., Tominaga M., Yabuuchi Y. OPC-21268, an orally effective, nonpeptide vasopressin V1 receptor antagonist. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):572–574. doi: 10.1126/science.1850553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


