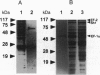
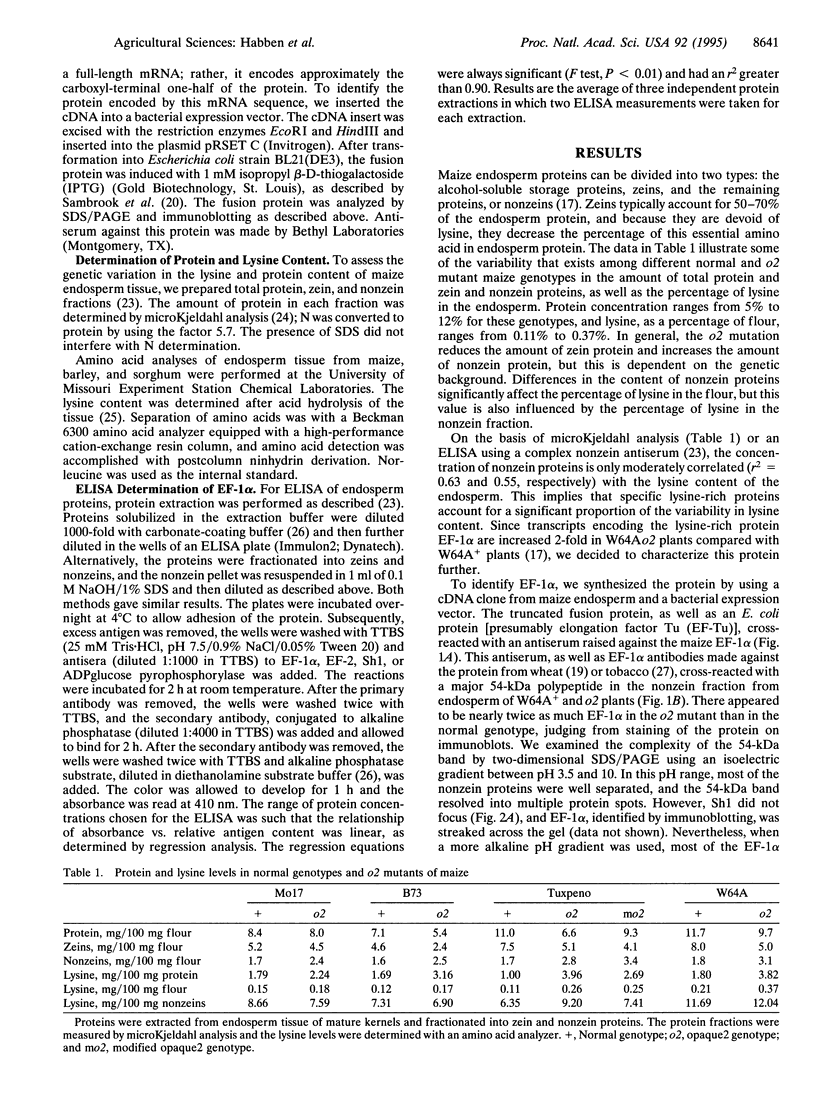
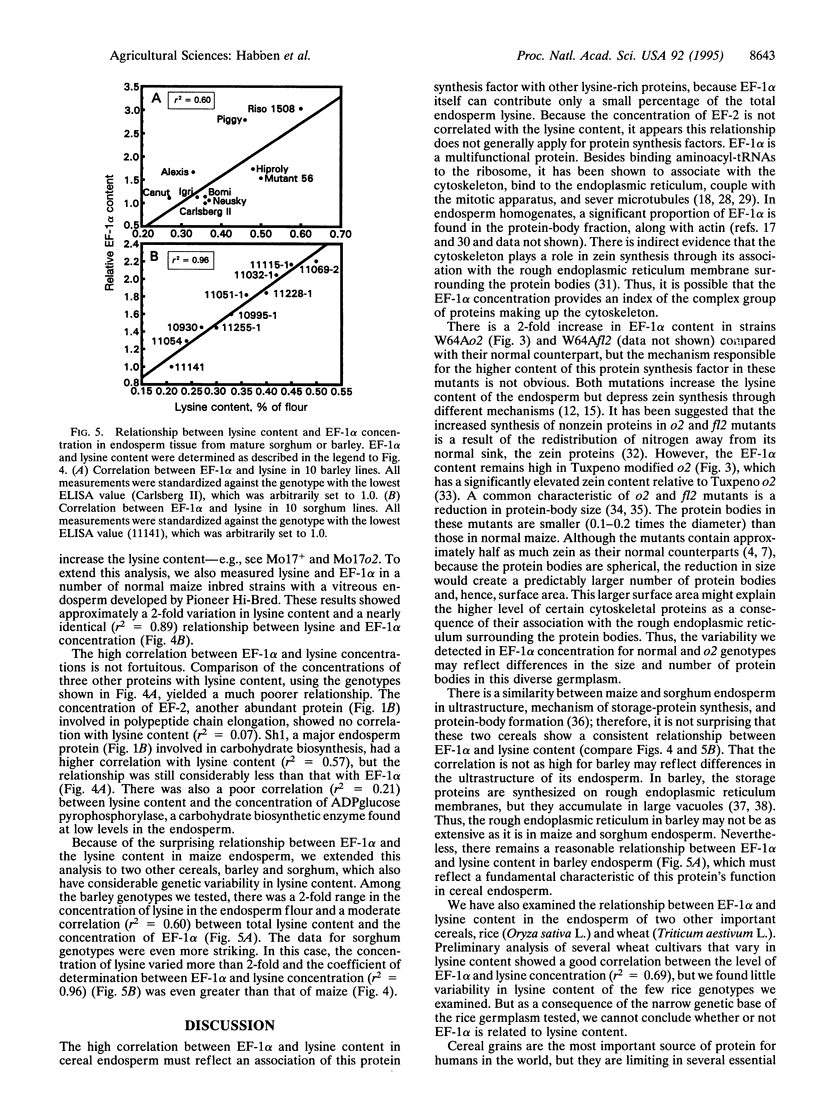
Abstract
Lysine is the most limiting essential amino acid in cereals, and for many years plant breeders have attempted to increase its concentration to improve the nutritional quality of these grains. The opaque2 mutation in maize doubles the lysine content in the endosperm, but the mechanism by which this occurs is unknown. We show that elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) is overexpressed in opaque2 endosperm compared with its normal counterpart and that there is a highly significant correlation between EF-1 alpha concentration and the total lysine content of the endosperm. This relationship is also true for two other cereals, sorghum and barley. It appears that genetic selection for genotypes with a high concentration of EF-1 alpha can significantly improve the nutritional quality of maize and other cereals.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bostwick D. E., Dannenhoffer J. M., Skaggs M. I., Lister R. M., Larkins B. A., Thompson G. A. Pumpkin phloem lectin genes are specifically expressed in companion cells. Plant Cell. 1992 Dec;4(12):1539–1548. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.12.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning K. S., Humphreys J., Hobbs W., Smith G. B., Ravel J. M. Determination of the amounts of the protein synthesis initiation and elongation factors in wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17967–17973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman C. E., Lopes M. A., Gillikin J. W., Boston R. S., Larkins B. A. A defective signal peptide in the maize high-lysine mutant floury 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6828–6831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durso N. A., Cyr R. J. A calmodulin-sensitive interaction between microtubules and a higher plant homolog of elongation factor-1 alpha. Plant Cell. 1994 Jun;6(6):893–905. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.6.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geetha K. B., Lending C. R., Lopes M. A., Wallace J. C., Larkins B. A. opaque-2 modifiers increase gamma-zein synthesis and alter its spatial distribution in maize endosperm. Plant Cell. 1991 Nov;3(11):1207–1219. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.11.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habben J. E., Kirleis A. W., Larkins B. A. The origin of lysine-containing proteins in opaque-2 maize endosperm. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Nov;23(4):825–838. doi: 10.1007/BF00021537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes M. A., Coleman C. E., Kodrzycki R., Lending C. R., Larkins B. A. Synthesis of an unusual alpha-zein protein is correlated with the phenotypic effects of the floury2 mutation in maize. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Dec 1;245(5):537–547. doi: 10.1007/BF00282216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTZ E. T., BATES L. S., NELSON O. E. MUTANT GENE THAT CHANGES PROTEIN COMPOSITION AND INCREASES LYSINE CONTENT OF MAIZE ENDOSPERM. Science. 1964 Jul 17;145(3629):279–280. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3629.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C. Mechanism and regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jun;56(2):291–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.2.291-315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck L., Karlsson K. E., Hagberg A., Eggum B. O. Gene for improved nutritional value in barley seed protein. Science. 1970 May 22;168(3934):985–987. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3934.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson O. E., Mertz E. T., Bates L. S. Second Mutant Gene Affecting the Amino Acid Pattern of Maize Endosperm Proteins. Science. 1965 Dec 10;150(3702):1469–1470. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3702.1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Or E., Boyer S. K., Larkins B. A. opaque2 modifiers act post-transcriptionally and in a polar manner on gamma-zein gene expression in maize endosperm. Plant Cell. 1993 Nov;5(11):1599–1609. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.11.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechinger K. B., Simpson D. J., Svendsen I., Cameron-Mills V. A role for gamma 3 hordein in the transport and targeting of prolamin polypeptides to the vacuole of developing barley endosperm. Plant J. 1993 Nov;4(5):841–853. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.04050841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. J., Burr F. A., Aukerman M. J., Burr B. Maize regulatory gene opaque-2 encodes a protein with a "leucine-zipper" motif that binds to zein DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B., Carneiro N., Torres-Jerez I., Stevenson B., McCreery T., Helentjaris T., Baysdorfer C., Almira E., Ferl R. J., Habben J. E. Partial sequencing and mapping of clones from two maize cDNA libraries. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Nov;26(4):1085–1101. doi: 10.1007/BF00040691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiina N., Gotoh Y., Kubomura N., Iwamatsu A., Nishida E. Microtubule severing by elongation factor 1 alpha. Science. 1994 Oct 14;266(5183):282–285. doi: 10.1126/science.7939665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. J., Khoo U., Seckinger H. L. Subcellular structure of endosperm protein in high-lysine and normal corn. Science. 1967 Aug 4;157(3788):556–557. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3788.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. K., Damsz B., Kononowicz A. K., Bressan R. A., Hasegawa P. M. A higher plant extracellular vitronectin-like adhesion protein is related to the translational elongation factor-1 alpha. Plant Cell. 1994 Mar;6(3):393–404. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]