Abstract
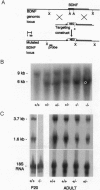
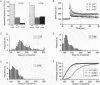
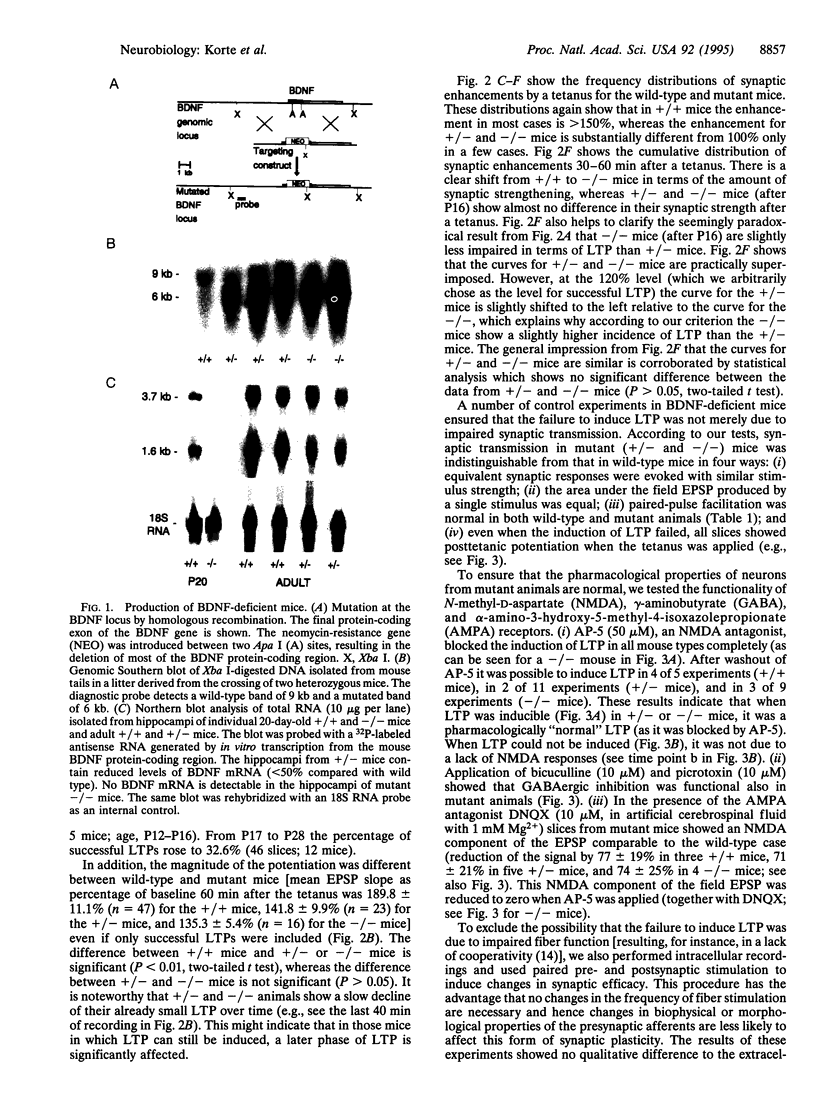
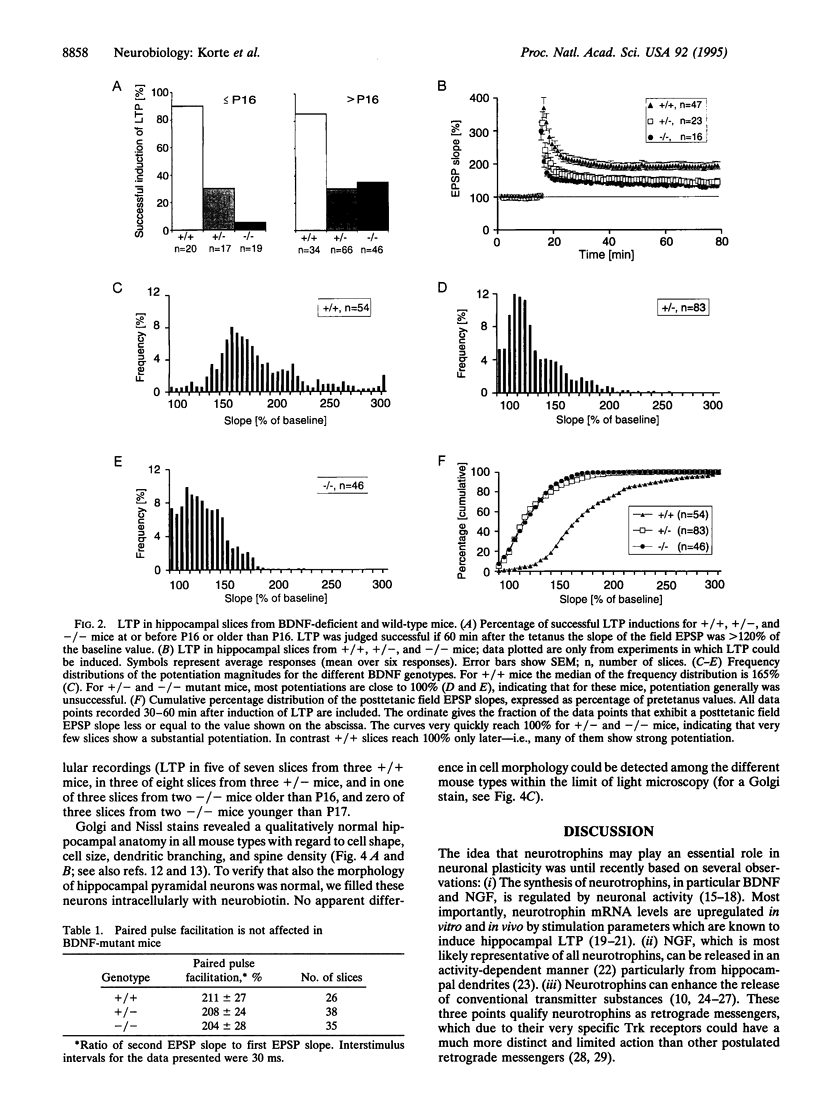
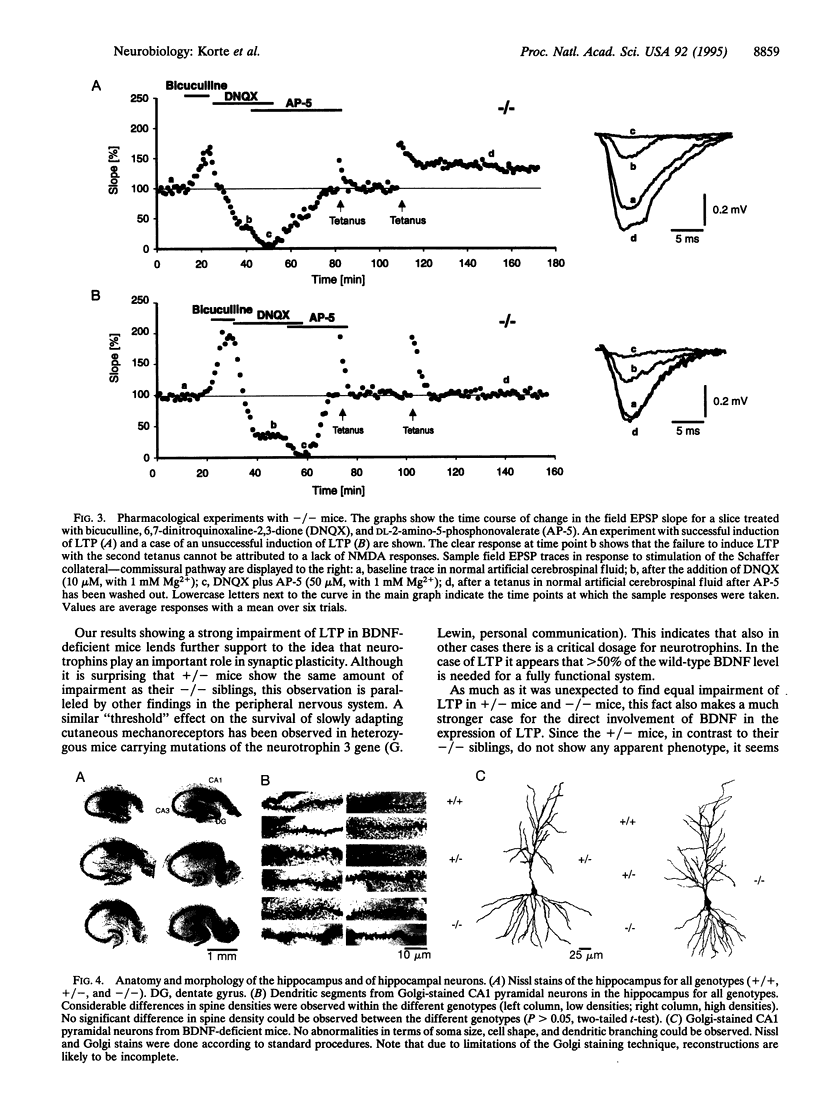
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a member of the nerve growth factor (NGF) gene family, has been shown to influence the survival and differentiation of specific classes of neurons in vitro and in vivo. The possibility that neurotrophins are also involved in processes of neuronal plasticity has only recently begun to receive attention. To determine whether BDNF has a function in processes such as long-term potentiation (LTP), we produced a strain of mice with a deletion in the coding sequence of the BDNF gene. We then used hippocampal slices from these mice to investigate whether LTP was affected by this mutation. Homo- and heterozygous mutant mice showed significantly reduced LTP in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. The magnitude of the potentiation, as well as the percentage of cases in which LTP could be induced successfully, was clearly affected. According to the criteria tested, important pharmacological, anatomical, and morphological parameters in the hippocampus of these animals appear to be normal. These results suggest that BDNF might have a functional role in the expression of LTP in the hippocampus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barde Y. A. The nerve growth factor family. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1990;2(4):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(90)90021-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Collingridge G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):31–39. doi: 10.1038/361031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blöchl A., Thoenen H. Characterization of nerve growth factor (NGF) release from hippocampal neurons: evidence for a constitutive and an unconventional sodium-dependent regulated pathway. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 Jun 1;7(6):1220–1228. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb01112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabelli R. J., Hohn A., Shatz C. J. Inhibition of ocular dominance column formation by infusion of NT-4/5 or BDNF. Science. 1995 Mar 17;267(5204):1662–1666. doi: 10.1126/science.7886458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castren E., Thoenen H., Lindholm D. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger RNA is expressed in the septum, hypothalamus and in adrenergic brain stem nuclei of adult rat brain and is increased by osmotic stimulation in the paraventricular nucleus. Neuroscience. 1995 Jan;64(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)00386-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrén E., Pitkänen M., Sirviö J., Parsadanian A., Lindholm D., Thoenen H., Riekkinen P. J. The induction of LTP increases BDNF and NGF mRNA but decreases NT-3 mRNA in the dentate gyrus. Neuroreport. 1993 Jul;4(7):895–898. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199307000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrén E., Zafra F., Thoenen H., Lindholm D. Light regulates expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in rat visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9444–9448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. M. The role of neurotrophins in the developing nervous system. J Neurobiol. 1994 Nov;25(11):1334–1348. doi: 10.1002/neu.480251103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenici L., Berardi N., Carmignoto G., Vantini G., Maffei L. Nerve growth factor prevents the amblyopic effects of monocular deprivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8811–8815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragunow M., Beilharz E., Mason B., Lawlor P., Abraham W., Gluckman P. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression after long-term potentiation. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Oct 1;160(2):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90420-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernfors P., Bengzon J., Kokaia Z., Persson H., Lindvall O. Increased levels of messenger RNAs for neurotrophic factors in the brain during kindling epileptogenesis. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90084-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernfors P., Lee K. F., Jaenisch R. Mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor develop with sensory deficits. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):147–150. doi: 10.1038/368147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K., Zahs K. Critical period control in sensory cortex. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994 Feb;4(1):112–119. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(94)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall C. M., Isackson P. J. Limbic seizures increase neuronal production of messenger RNA for nerve growth factor. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):758–761. doi: 10.1126/science.2549634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isackson P. J., Huntsman M. M., Murray K. D., Gall C. M. BDNF mRNA expression is increased in adult rat forebrain after limbic seizures: temporal patterns of induction distinct from NGF. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):937–948. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90234-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. R., Fariñas I., Backus C., Reichardt L. F. Targeted disruption of the BDNF gene perturbs brain and sensory neuron development but not motor neuron development. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):989–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90377-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang H., Schuman E. M. Long-lasting neurotrophin-induced enhancement of synaptic transmission in the adult hippocampus. Science. 1995 Mar 17;267(5204):1658–1662. doi: 10.1126/science.7886457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipper M., Leung L. S., Zhao D., Rylett R. J. Short-term modulation of glutamatergic synapses in adult rat hippocampus by NGF. Neuroreport. 1994 Dec 20;5(18):2433–2436. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199412000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipper M., da Penha Berzaghi M., Blöchl A., Breer H., Thoenen H., Lindholm D. Positive feedback between acetylcholine and the neurotrophins nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1994 Apr 1;6(4):668–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1994.tb00312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkman A., Hannay T., Stratford K., Jack J. Presynaptic release probability influences the locus of long-term potentiation. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):70–73. doi: 10.1038/360070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessmann V., Gottmann K., Heumann R. BDNF and NT-4/5 enhance glutamatergic synaptic transmission in cultured hippocampal neurones. Neuroreport. 1994 Dec 30;6(1):21–25. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199412300-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1154–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3306916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm D., Castrén E., Berzaghi M., Blöchl A., Thoenen H. Activity-dependent and hormonal regulation of neurotrophin mRNA levels in the brain--implications for neuronal plasticity. J Neurobiol. 1994 Nov;25(11):1362–1372. doi: 10.1002/neu.480251105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohof A. M., Ip N. Y., Poo M. M. Potentiation of developing neuromuscular synapses by the neurotrophins NT-3 and BDNF. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):350–353. doi: 10.1038/363350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton B. L., Douglas R. M., Goddard G. V. Synaptic enhancement in fascia dentata: cooperativity among coactive afferents. Brain Res. 1978 Nov 24;157(2):277–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S. L., Grover L. M., Schwartzkroin P. A., Bothwell M. Neurotrophin expression in rat hippocampal slices: a stimulus paradigm inducing LTP in CA1 evokes increases in BDNF and NT-3 mRNAs. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1081–1088. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90067-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H. The changing scene of neurotrophic factors. Trends Neurosci. 1991 May;14(5):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90097-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. H., Errington M. L., Lynch M. A., Bliss T. V. Arachidonic acid induces a long-term activity-dependent enhancement of synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Nature. 1989 Oct 26;341(6244):739–742. doi: 10.1038/341739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo M., Small S. A., Kandel E. R., Hawkins R. D. Nitric oxide and carbon monoxide produce activity-dependent long-term synaptic enhancement in hippocampus. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1946–1950. doi: 10.1126/science.8100368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]