Abstract
Cutaneous manifestations occur frequently in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and are pathognomonic in subacute-cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) and chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CCLE). Although B-cell depletion therapy (BCDT) has demonstrated efficacy in SLE with visceral involvement, its usefulness for patients with predominant skin manifestations has not been fully established. In this single-centre, retrospective study 14 consecutive SLE, one CCLE and two SCLE patients with recalcitrant skin involvement were treated with 2 × rituximab 1 g, and 1 × cyclophosphamide 750 mg.
Six months after BCDT, nine of 17 (53%) patients were in complete (CR) or partial remission (PR). Relapses occurred in 12 patients (71%) at a mean time of 10 ± 1.8 months after BCDT. A second cycle of BCDT achieved a more sustained remission in seven of nine patients (78%) lasting for a mean time of 18.4 ± 2.7 months. Minor adverse events were experienced by three patients. Mean follow-up was 30 months.
Our own results and the literature review demonstrate that BCDT based on rituximab is well tolerated and may be effective for cutaneous lesions of lupus erythematosus. Randomized controlled trials are necessary to further evaluate the value of BCDT for this group of patients.
Keywords: Cutaneous lupus, discoid lupus, subacute lupus erythematosus, systemic lupus erythematosus
Introduction
Cutaneous manifestations are present in about 80% of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients at some stage during the disease course, and may be clinically diverse.1 The wide range of mucocutaneous manifestations is reflected in the new SLICC (Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics) classification criteria for SLE,2 which include acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (ACLE), subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CCLE), oral ulcers and nonscarring alopecia.3 In the absence of lupus nephritis, the SLICC classification criteria suggest a diagnosis of SLE if ≥4 SLICC criteria (including at least one clinical and one immunological criterion) are present. Patients with cutaneous lesions who do not fulfil these criteria will rather be diagnosed as SCLE if psoriasiform or annular lesions in sun-exposed areas (frequently associated with anti-Ro/anti-La antibodies) are present, or as CCLE without SLE. Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) represents the most frequent clinical subtype of CCLE. Other clinical manifestations are lupus profundus/lupus panniculitis, lupus tumidus and chilblain lupus. Less than 10% of CCLE patients evolve into SLE during the disease course.4
First-line therapy for cutaneous lupus erythematosus consists of antimalarials, and oral or topical corticosteroids.4 In severe cases or patients with SLE additional immunosuppressive drugs (e.g. azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, or cyclophosphamide) are added. To date, there is no reliable evidence to confirm the optimal therapeutic regimen.5
Treatment-associated complications such as osteopaenia due to corticosteroids or infections are common, and in some patients cutaneous manifestations of lupus erythematosus prove to be extremely refractory to conventional therapy.6 Therefore, the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab (RTX) has been used as an off-label therapeutic option in patients with intolerance or resistance to standard therapy.
CD20-positive B-cells play an important role in the pathogenesis of SLE and probably SCLE:7 in addition to their role as antigen-presenting cells, B-cells produce pathogenic autoantibodies, secrete cytokines, and therefore enhance inflammation.8 We and others have reported that B-cell depletion therapy (BCDT) based on RTX is effective against SLE.9–11 Unfortunately, two recently completed randomized controlled clinical trials (EXPLORER, LUNAR) failed to confirm the positive effects of RTX, probably because of issues in the study design with regard to concomitant therapies.12,13 In case reports and observational studies, RTX was effective over all organ systems including the mucocutaneous system.9 However, the efficacy of this biologic with regard to different clinical manifestations of cutaneous involvement in lupus erythematosus has not yet been investigated in detail and there are very few data on long-term outcomes currently available.
Here, we report the long-term clinical efficacy and immunological follow-up of 17 consecutive lupus erythematosus patients with predominant and therapy-refractory skin involvement necessitating BCDT from 2007 to 2011 at University College London Hospital (UCLH). Furthermore, we reviewed all previously published case reports and three observational studies on the use of RTX-based BCDT for cutaneous manifestations of lupus erythematosus.
Patients and methods
Patients and healthy control subjects
Consecutive patients were retrospectively selected from our well-characterized lupus erythematosus patient cohort attending UCLH. Inclusion criteria were i) treatment with RTX-based BCDT between 2007 and 2011, and ii) active and severe cutaneous lesions before BCDT reflected by an A or B score for the mucocutaneous component of the British Isles Lupus Assessment (BILAG) score in all SLE patients.14 The BILAG score is an ordinal scale index that assesses all organ systems including the mucocutaneous system. Disease activity is categorized into five different levels from A (very active) to E (no current or previous activity in this organ system).
At least four of the SLICC classification criteria2 and of the revised American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria15 were fulfilled by 14 SLE patients included in this study. To identify the clinical subtype of cutaneous involvement and to assess the clinical efficacy of BCDT, all patients were examined by the same dermatologist before and after BCDT. Cutaneous manifestations of the SLE patients were classified as ACLE in three patients, SCLE in one, CCLE in seven (DLE in six and/or lupus profundus in two), and non-specific SLE-associated lesions (vasculitis or urticaria) in addition to oral ulcers in three patients. Furthermore, two SCLE patients and one patient with DLE and rheumatoid arthritis were assessed. All SLE patients had a positive antinuclear antibodies (ANA) titre (≥1:80 by immunofluorescence), and eight of 14 (57%) had anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (Shield Diagnostics, Dundee, UK; normal <50 IU/ml). Both SCLE patients and the DLE patient had positive ANA and anti-Ro antibodies, but not anti-dsDNA antibodies. Demographic and clinical data of the patients and previously failed treatments are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of the 17 patients with cutaneous manifestations of lupus erythematosus treated with B-cell depletion therapy at University College London Hospital
| Patient (no./sex/age, y./ethnicity)a | Type of cutaneous manifestationsb | Extra-cutaneous ACR criteria | Disease duration (years) | Previous therapyc | Date of BCDT | BILAG before, 6 mo. After BCDT | Relapse (months after last BCDT) | Follow-up (months) | Maintenance therapyc | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/M/43/W | SLE (ACLE: malar and disseminated rash) | Lymphopaenia, dsDNA | 10 | HCQ, Pred, Aza, MTX | 09/08; 01/09 | A → A A → C | 3 20 | 36 | HCQ, Pred 5 mg, topical steroids | Urticaria during second cycle of RTX |
| 2/F/50/W | SLE (CCLE: LP) | Pleurisy | 11 | HCQ, Pred, MMF | 08/08; 07/09; 04/11 | B → B B → C B → C | 6 9 11 | 36 | HCQ, Pred 7.5 mg | None |
| 3/F/47/W | SLE (ACLE: generalized rash) | Arthritis | 13 | HCQ, Pred, Aza, MMF, CPM | 04/09 | A → D | 18 | 30 | HCQ, Pred 5 mg | Urticaria and angioedema at second infusion |
| 4/F/57/W | SLE (urticarial vasculitis) | Arthritis | 13 | HCQ, Pred, Aza, MTX | 07/09; 06/11 | A → A A → A | n.a. n.a. | 28 | MMF, HCQ, Pred 5–30 mg | None |
| 5/F/40/AC | SLE (annular SCLE) | Epilepsy | 15 | HCQ, Pred, MTX, MMF | 01/07; 05/11 | A → B A → B | n.a. n.a. | 60 | HCQ, MMF, Pred 10 mg | None |
| 6/F/33/AC | SLE (CCLE: DLE) | Arthritis, Pleurisy,dsDNA | 2 | HCQ, Pred, Aza | 03/10 | A → C | 12 | 21 | HCQ, Aza | None |
| 7/F/46/AC | SLE (ACLE: malar and disseminated rash) | Arthritis, pleurisy, dsDNA | 23 | HCQ, Pred | 05/08; 09/09 | A → D A → D | 15 None | 46 | Pred 5 mg | None |
| 8/F/24/A | SLE (vasculitis) | Arthritis, dsDNA | 9 | HCQ, Pred | 04/08; 09/08 | B → C B → D | 6 None | 37 | HCQ, Pred 5 mg | None |
| 9/F/47/AC | SLE (CCLE: DLE) | Arthritis, pleurisy, epilepsy, dsDNA | 3 | HCQ, Pred, Aza | 12/08; 10/09 | B → B B → C | 4 24 | 25 | HCQ, Pred 10 | None |
| 10/F/48/AC | SLE (CCLE: DLE) | Nephritis, dsDNA | 1 | HCQ, Pred | 10/08 | B → D | None | 25 | HCQ | None |
| 11/F/25/A | SLE (vasculitis) | Arthritis, dsDNA | 16 | HCQ, Pred | 04/10 | B → D | 22 | 24 | HCQ, Pred 3 mg | None |
| 12/F/33/AC | SLE (CCLE: DLE and LP) | Arthritis | 4 | HCQ, Pred | 09/11 | B → B | 6 | 5 | None | None |
| 13/F/23/AC | SLE (CCLE: DLE) | Arthritis | 14 | HCQ, Pred, Aza | 01/10; 09/10 | B → B B → D | 5 16 | 26 | HCQ, Pred 5 mg | None |
| 14/F/23/AC | SLE (CCLE: DLE) | Arthritis, dsDNA | 13 | HCQ, Pred, MTX | 04/09 | A → D | None | 25 | HCQ, Pred 5 mg | None |
| 15/F/74/W | Annular SCLE | None | 3 | Pred, Aza, MTX | 07/06; 07/08 | n.a. | 23 24 | 47 | MTX, Pred 5 mg | None |
| 16/F/65/W | Annular SCLE | None | 7 | Pred, MMF | 03/10 | n.a. | 9 | 20 | Pred 7.5 mg | Recurrent infections |
| 17/F/54/W | DLE + RA | None | 30 | HCQ, Pred, MTX, thalidomide | 07/10 | n.a. | n.a. | 18 | HCQ, Pred 5 mg, MTX | None |
F: female; M: male; W: white, AC: Afro-Caribbean; A: Asian;
bSLE: systemic lupus erythematosus; ACLE: acute cutaneous lupus; CCLE: chronic cutaneous lupus; SCLE: subacute-cutaneous lupus; DLE: discoid lupus erythematosus; LP: lupus erythematosus profundus: RA: rheumatoid arthritis.
HCQ: hydroxychloroquine (administered for ≥6 months); Pred: oral prednisolone; Aza: azathioprine (≥1.5 mg/kg/d); MTX: methotrexate (≥15 mg/week), CPM: cyclophosphamide (750 mg intravenous (i.v.) pulses for ≥3 months): MMF: mycophenolate mofetil (≥2 g/d); n.a.: not applicable; (British Isles Lupus Assessment (BILAG) was used only for SLE patients; relapses were documented only if patient achieved remission after B-cell depletion therapy (BCDT)); dsDNA: double-stranded DNA.
All 17 patients received a combination of 1 g RTX and 100 mg methylprednisolone intravenously (i.v.) on two occasions two weeks apart, and 750 mg cyclophosphamide i.v. the day after the first RTX infusion. In the majority of patients (12/17) immunosuppressive drugs were withdrawn at the first cycle of BCDT to reduce the risk of infectious complications, and only hydroxychloroquine (at a stable dose) and prednisolone (in tapering doses) were continued. In patients no. 4, 5, 6, 15 and 17 BCDT was added to stable immunosuppressive therapy with azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil or methotrexate. Patients were followed up in the lupus clinic every one to three months, and at each visit the BILAG activity index and the level of anti-dsDNA antibodies and C3 (laser nephelometry, normal 0.9–1.9 mg/l) were used to help assess the disease activity of SLE patients. CD19 counts were monitored to assess depletion and the time to B-cell repopulation. Clinical and serological data were collected prospectively. The study was approved by the UCLH ethics committee.
Outcome measures
The response to BCDT was assessed at six months after the last RTX infusion. Complete remission (CR) was defined as absence of skin lesions (reflected by a mucocutaneous BILAG D for the group of SLE patients) for at least two months and treatment with ≤ 5 mg prednisolone ± hydroxychloroquine. Partial remission (PR) was defined as improvement of cutaneous manifestations (to BILAG C) of at least 50% or complete clearance of skin lesions (BILAG D) with continuation of immunosuppressants after BCDT. Stable disease (SD) was defined as no or only minor improvement of cutaneous lesions (mucocutaneous BILAG A or B). The effect of BCDT on organ systems other than the mucocutaneous system was not investigated in this study.
Statistical procedures
Descriptive statistics are reported as frequency or percentage for categorical variables and as mean ± SE for continuous variables. Statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism (Chicago, IL, USA), using the nonparametrical Mann-Whitney U test. P values of <0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
Results
Efficacy and safety of BCDT in our patients
In this study, one man and 16 women of different ethnicities (seven Whites, eight Afro-Caribbeans and two Asians) were included. The mean age was 43 ± 3.6 years, and the mean disease duration prior to BCDT was 11 ± 1.8 years. All patients were refractory to previous treatments including oral prednisolone and antimalarials, topical steroids and/or topical tacrolimus for at least six months with the exception of patient 16, who did not tolerate antimalarials. In addition, 12/17 patients (71%) had received classical immunosuppressive agents without improvement.
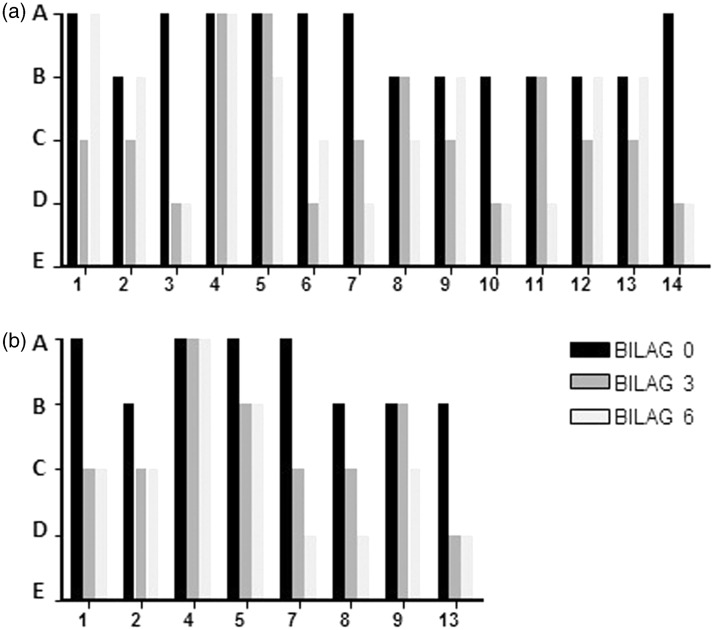
B-cell depletion defined as CD19 absolute numbers <0.005 × 109/l was achieved by all patients following BCDT. Mean time to B-cell repopulation was 7.7 ± 1.2 months (range three to 18 months). Although 12 patients (71%) demonstrated a fast improvement of at least 50% of their skin lesions within three months after the first BCDT treatment, it was, however, only of short duration in some patients. Two patients (no. 8 and 11) demonstrated a slower response, with CR or PR occurring four and five months after BCDT, respectively. Six months after the first BCDT, CR was observed in five of 17 patients (29.4%) and PR in four of 17 patients (23.5%). Eight patients had SD (47.1%). These results are shown as changes in the mucocutaneous BILAG score in Figure 1 (a) for the SLE patients. Of the three patients without SLE and therefore lacking BILAG assessment (patients no. 15–17), both patients with SCLE achieved PR while the patient with DLE and rheumatoid arthritis remained active (SD).
Figure 1.
Clinical response to BCDT treatment in lupus erythematosus patients with severe cutaneous manifestations treated at UCLH. (a) Bars represent the mucocutaneous BILAG score at zero, three and six months after BCDT in 14 SLE patients. Numbers on the x-axis refer to the patients as described in Table 1. BILAG A indicates a severe mucocutaneous involvement, BILAG B moderate, BILAG C mild and BILAG D inactive mucocutaneous disease. (b) BILAG scores of eight SLE patients who relapsed and received a second cycle of BCDT (mucocutaneous score at zero, three and six months after BCDT).
With regard to the subtype of cutaneous lesions, two of three ACLE patients (66.6%), two of three SCLE patients (66.6%) and two of three SLE patients with non-specific lesions (66.6%) were in CR or PR six months after the first cycle of BCDT, in contrast to only three of eight (37.5%) patients with CCLE lesions. We have not observed any transition from one type of cutaneous manifestation to another type following BCDT.
Eight of 17 (47%) patients had elevated dsDNA antibodies prior to BCDT (mean 476.9 ± 220.6 IU/ml). There was a trend to a reduction of dsDNA levels within six months to 242.8 IU/ml ± 138.9 which did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.38). CR or PR was obtained by six of eight (75%) patients with anti-dsDNA antibodies compared to five of nine (56%) of anti-dsDNA negative patients.
Low complement C3 was detectable in 10/17 (59%) patients (mean 0.71 g/l ± 0.05) before treatment, but improved significantly (mean 0.95 g/l ± 0.04) after six months (p = 0.001). Adverse events were experienced by two patients (urticaria post-infusion or recurrent chest infections after BCDT), but no serious complications occurred.
Although six patients (35%) maintained PR or CR for more than 12 months (patients no. 3 and 7 with ACLE, patient no. 15 with SCLE, patients no. 10 and 14 with DLE, and patient no. 11 with cutaneous vasculitis), relapses were frequent and occurred in 12 patients (71%) at a mean time of 10 ± 1.8 months after the first cycle of BCDT (range three to 23 months) (Table 1). The time interval between the first cycle of BCDT and occurrence of a relapse was not different between SLE patients with CCLE and those with other subtypes of cutaneous lupus erythematosus (ACLE, SCLE and non-specific lesions) (p = 0.8).
Of patients with a flare of their cutaneous lupus erythematosus or with SD after the first BCDT, eight SLE patients and one SCLE patient received a second course of BCDT resulting in CR in three of nine patients (33.3%), and in PR in four of nine patients (44.4%), while patients no. 4 and 5 again failed to respond (Figure 1(b)). Of the seven responding patients, five experienced another flare (71%) occurring at a mean time of 18.4 ± 2.7 months (range nine to 24) after the second cycle of BCDT. One patient (no. 1) experienced an allergic reaction during the RTX infusion at this time, while there were no side effects in the remaining patients. Mean time to B-cell repopulation after the second cycle of BCDT was 7.0 ± 1.3 months (range three to 13 months) and mean follow-up 29.9 ± 3.1 months (six to 60).
Discussion
Rituximab is an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody that is United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for treatment of B-cell lymphomas and rheumatoid arthritis. In dermatology, intravenous administration of RTX has been used off-label with promising results in several autoimmune disorders, e.g. pemphigus diseases, graft-versus-host disease and vasculitis.16,17
In the literature, seven cases of SLE patients with cutaneous manifestations (three ACLE, two SCLE, one CCLE and one patient with non-specific lesions) and three SCLE patients treated with RTX-based BCDT due to otherwise refractory cutaneous manifestations are published (Table 2). These reports suggested that BCDT may be beneficial for patients with severe cutaneous lesions of lupus erythematosus if first-line treatment was not sufficient or tolerated:18–24 of the 10 patients, eight (80%) achieved CR, two patients PR. Three patients (30%) experienced a relapse within one year, but their skin lesions were cleared by another cycle of BCDT. Serious side effects were not reported in any of these patients.
Table 2.
Overview of previously published cases and observational studies on lupus erythematosus with skin manifestations treated with rituximab-based BCDT
| Patient (sex/age, y.)a | Disease | Disease duration (y.) | Previous therapyb | BCDT regimen | Responsec | Relapse (mo. after BCDT) | Follow-up (mo.) | Maintenance therapy | Complications | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case reports | ||||||||||
| F/52 | SLE (vasculitis, urticaria) | 8 | HCQ, Pred, Aza, CPM, MTX, IVIG | 2 × 1 g RTX | CR | None | 4 | Pred < 15 mg | None | Risselada and Kallenberg18 |
| F/44 | SLE (ACLE) | 16 | HCQ, Pred, Aza, thalidomide | 2 × 1 g RTX | CR | None | 4 | Pred 12.5 mg | None | Risselada and Kallenberg18 |
| M/44 | SLE (SCLE) | 12 | HCQ, Pred, Aza, MMF | 2 × 1 g RTX | PR | None | 6 | None | None | Uthman et al.19 |
| F/22 | SLE (CCLE: LE profundus) | 0.5 | HCQ, Pred, CPM | 2 × 1 g RTX | CR | None | Not reported | HCQ, Pred | None | McArdle and Baker20 |
| F/48 | SCLE | 5 | HCQ, Pred, MTX, Aza, dapsone | 4 × 375 mg/m2 RTX | CR | 11f | 15 | HCQ | None | Kieu et al.21 |
| F/30 | SLE (ACLE) | 17 | HCQ, Pred, Aza | 2 × 1 g RTX | CR | 9f | 12 | Pred 7.5 mg | None | Kok et al.22 |
| F/61 | SLE (ACLE/ bullous SLE) | 8 | HCQ, Pred, MMF, Aza | 2 × 1 g RTX | CR | No | 6 | Pred 10 mg | None | Alsanafi et al.23 |
| F/54 | SCLE | Not specified | HCQ, Pred, MMF, thalidomide, IVIG, etanercept | 4 × 375 mg/m2 RTX | CR | <12f, yearly BCDT | 48 | Pred 5–10 mg | None | Cieza-Díaz et al.24 |
| F/37 | SCLE | 3 | HCQ, Pred, Aza | 4 × 375 mg/m2 RTX | CR | Yearly BCDT | 20 | HCQ | None | Cieza-Díaz et al.24 |
| F/28 | SLE (SCLE) | 0.5 | HCQ, Pred | 4 × 375 mg/m2 RTX | PR | Yearly BCDT | un known | Pred 10–20 mg, HCQ | None | Cieza-Díaz et al.24 |
| Observational retrospective studies | ||||||||||
| Six children | SLE with cutaneous lesions | Mean 3.9 | i.v.-MP, CPM, MMF or Aza | 2 × 750 mg/m2 RTX | 3/6 (50.0%) CRd 2/6 (33.3%) PR 1/6 (16.6%) SD | Not specified | 12 (mean) | Pred ± MMF or Aza | None | Marks et al.25 |
| 16 Adult patients | SLE with cutaneous lesions | Mean 8.9 | HCQ, Pred, various immunosuppressants | 2 × 1 g RTX + CPM 750 mg | 9/16 (56.3%) CR4 5/16 (31.3%) PR 2/16 (12.5%) SD | Not specified | 6 (mean) | Not specified | One patient died of adult respiratory distress syndrome | Lu et al.9 |
| 61 Adult patients | SLE with cutaneous lesions | Mean 10.4 | HCQ, Pred, various immunosuppressants | 2 × 1 g RTX or 4 × 375 mg/m2 | 29/61 (47.5%) CRe 14/61 (23.0%) PR 18/61 (29.5%) SD | Not specified | 6 ± 3 months (mean) | Not specified | Not specified | Terrier et al.11 |
F: female; M: male;
HCQ: hydroxychloroquine; Pred: oral prednisolone; Aza: azathioprine; MTX: methotrexate; CPM: cyclophosphamide, MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; IVIG: intravenous immunoglobulins; MP: methylprednisolone; cCR: complete remission; PR: partial remission, SD, stable disease;
CR of cutaneous lesions: British Isles Lupus Assessment (BILAG) A or B → BILAG D after rituximab (RTX); PR of cutaneous lesions: BILAG A or B → BILAG C;
CR of cutaneous lesions: disappearance of baseline manifestations; PR ≥ 50% improvement; fCR achieved after retreatment with another cycle of B-cell depletion therapy (BCDT).
Although these reports are encouraging, the rather short mean follow-up of these patients (14.3 ± 5.2 months) and the fact that usually only successfully treated cases are published, prompted us to investigate retrospectively the long-term outcome of consecutive patients treated with BCDT at UCLH for severe cutaneous manifestations of lupus erythematosus between 2007 and 2011. Our results indicate that BCDT based on 2 × 1 g RTX and a single dose of 750 mg cyclophosphamide led to a significant clinical improvement in 53% of SLE patients who were previously refractory to immunosuppressive treatment including antimalarials, high-dose oral corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs (Table 1).
A good clinical response to BCDT was previously reported in three open-label studies (Table 2): in childhood-onset SLE with skin lesions, CR was achieved by three of six (50%) children after one cycle of BCDT.25 Two retrospective studies reported CR in nine of 16 (56%) and 29/61 (48%) of adult SLE patients with mucocutaneous lesions after a first cycle of BCDT, respectively.9,11
Although we used a slightly more aggressive regimen including 100 mg methylprednisolone twice and a single administration of 750 mg cyclophosphamide to achieve maximal B-cell depletion, our remission rate (CR in 29% of patients after one cycle of BCDT) is lower than reported in the open-label study of SLE patients from the French AutoImmunity and Rituximab Registry11 and in our own retrospective study9 including some SLE patients with cutaneous lesions. The higher response rates in these studies may be explained by a shorter follow-up (six months ± 3 months in the study by Terrier et al.11) and/or differences in the subtype of cutaneous manifestations of the included patients. While the clinical subtypes of the mucocutaneous lesions were not specified in these previously published studies, we here demonstrate that BCDT was beneficial in particular in patients with ACLE, SCLE or non-specific cutaneous lesions. In contrast, less than a third of CCLE patients, whether or not in the context of SLE, achieved complete remission after BCDT. These differences in response rates to BCDT depending on the type of cutaneous manifestations are potentially reflected in the fact that only one of the reviewed case reports20 demonstrated remission in a patient with CCLE (lupus erythematosus profundus) in the context of SLE while the remaining cases featured patients with ACLE, SCLE or non-specific skin lesions. It is conceivable that different mechanisms play a role in the pathogenesis of CCLE compared to ACLE, SCLE or non-specific cutaneous lesions in SLE. CCLE patients without SLE present with ANA in only 10%–30% of cases3 compared to > 80% in SCLE and SLE, which suggests that B-cells are not playing an essential role in the development of DLE lesions. In contrast, skin homing of CCR4 expressing CD8+ cytotoxic T cells has been implicated to be of major importance in the pathogenesis, particularly of the disseminated and scarring type of DLE.26 Furthermore, ACLE and non-specific cutaneous lesions are manifestations that usually reflect acuteness of SLE. Most immunosuppressive treatments used for cutaneous lupus erythematosus are more efficient in treating acute disease than long-standing CCLE lesions,4 and this observation seems to hold true also for BCDT. In contrast, immunomodulatory therapies such as thalidomide were shown to achieve higher rates of remission in DLE compared to ACLE.27
Despite the fact that antibody-producing plasma cells are CD20 negative, the clinical response to BCDT treatment commonly parallels a reduction – though often not a normalization – of anti-dsDNA autoantibody levels presumably by preventing formation of new plasma cells.9 In this study, only 47% of patients initially demonstrated elevated anti-dsDNA antibodies, which improved after BCDT in all patients. Similarly, 59% of patients had low C3 levels prior to BCDT and C3 levels normalized in all but one patient after BCDT, in line with previous studies.28
In our patients, B-cell repopulation occurred at a mean of 7.7 and 7.0 months after the first and second cycle of BCDT, respectively, indicating that regeneration of the peripheral B cell population is not impaired by repeated treatments. Furthermore, the tolerability profile of RTX did not change after a second cycle of RTX, a finding that has also been observed in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.29 Noteworthy, despite B-cell repopulation at approximately seven months, patients who achieved remission after BCDT usually remained disease free for 10 months after the first cycle of BCDT, and for even 18 months after repeated BCDT. Nearly all of these patients received maintenance treatment with only antimalarials and low-dose prednisolone.
This single-centre study evaluated only a small number of patients, and a quantitative scoring system for severity of skin lesions such as the Revised Cutaneous Lupus Activity and Severity Index (RCLASI)30 was not used because it is too detailed to be applied retrospectively. Despite these limitations, our analysis demonstrates that some lupus erythematosus patients with active mucocutaneous lesions, in particular those with ACLE, SCLE or vasculitis, achieve a long-lasting clinical remission and benefit from BCDT, even if they were previously resistant to conventional therapy. Moreover, BCDT was well tolerated both at short and long term. Randomized controlled trials should be conducted to further evaluate the value of BCDT for the treatment of cutaneous manifestations of lupus erythematosus.
Funding
This work was supported by a postdoctoral research fellowship (LPDS 2009-34) from the German Academy of Sciences Leopoldina to SCH.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- 1. Rothfield N, Sontheimer RD, Bernstein M. Lupus erythematosus: Systemic and cutaneous manifestations. Clin Dermatol 2006; 24: 348–362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Petri M, Orbai AM, Alarcón GS, et al. Derivation and validation of Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2012; 64: 2677–2686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Werth VP. Cutaneous lupus: Insights into pathogenesis and disease classification. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 2007; 65: 200–204 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Kuhn A, Ruland V, Bonsmann G. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: Update of therapeutic options part I. J Am Acad Dermatol 2011; 65: e179–e193 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Jessop S, Whitelaw DA, Delamere FM. Drugs for discoid lupus erythematosus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009, pp. CD002954–CD002954 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Borchers AT, Keen CL, Shoenfeld Y, Gershwin ME. Surviving the butterfly and the wolf: Mortality trends in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 2004; 3: 423–453 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Kind P, Lipsky PE, Sontheimer RD. Circulating T- and B-cell abnormalities in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol 1986; 86: 235–239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Batista FD, Harwood NE. The who, how and where of antigen presentation to B cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 15–27 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Lu TY, Ng KP, Cambridge G, et al. A retrospective seven-year analysis of the use of B cell depletion therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus at University College London Hospital: The first fifty patients. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 61: 482–487 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Ramos-Casals M, Soto MJ, Cuadrado MJ, Khamashta MA. Rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review of off-label use in 188 cases. Lupus 2009; 18: 767–776 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Terrier B, Amoura Z, Ravaud P, et al. Safety and efficacy of rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus: Results from 136 patients from the French AutoImmunity and Rituximab registry. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62: 2458–2466 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Looney RJ. B cell-targeted therapies for systemic lupus erythematosus: An update on clinical trial data. Drugs 2010; 70: 529–540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Merrill J, Buyon J, Furie R, et al. Assessment of flares in lupus patients enrolled in a phase II/III study of rituximab (EXPLORER). Lupus 2011; 20: 709–716 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Isenberg DA, Allen E, Farewell V, et al. An assessment of disease flare in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A comparison of BILAG 2004 and the flare version of SELENA. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70: 54–59 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1982; 25: 1271–1277 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Hertl M, Zillikens D, Borradori L, et al. Recommendations for the use of rituximab (anti-CD20 antibody) in the treatment of autoimmune bullous skin diseases [in English and German]. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2008; 6: 366–373 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Emer JJ, Claire W. Rituximab: A review of dermatological applications. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 2009; 2: 29–37 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Risselada AP, Kallenberg CG. Therapy-resistent lupus skin disease successfully treated with rituximab. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006; 45: 915–916 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Uthman I, Taher A, Abbas O, Menassa J, Ghosn S. Successful treatment of refractory skin manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus with rituximab: Report of a case. Dermatology 2008; 216: 257–259 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. McArdle A, Baker JF. A case of “refractory” lupus erythematosus profundus responsive to rituximab [case report]. Clin Rheumatol 2009; 28: 745–746 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Kieu V, O’Brien T, Yap LM, et al. Refractory subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus successfully treated with rituximab. Australas J Dermatol 2009; 50: 202–206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Kok MR, Vos K, Bos JD, Tak PP. Remission of incapacitating acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus by B cell–depletive therapy. J Clin Rheumatol 2010; 16: 345–345 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Alsanafi S, Kovarik C, Mermelstein AL, Werth VP. Rituximab in the treatment of bullous systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Rheumatol 2011; 17: 142–144 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Cieza-Díaz DE, Avilés-Izquierdo JA, Ceballos-Rodríguez C, Suárez-Fernández R. Refractory subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus treated with rituximab [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr 2012; 103: 555–557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Marks SD, Patey S, Brogan PA, et al. B lymphocyte depletion therapy in children with refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: 3168–3174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Wenzel J, Zahn S, Tuting T. Pathogenesis of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: Common and different features in distinct subsets. Lupus 2010; 19: 1020–1028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Cortés-Hernández J, Torres-Salido M, Castro-Marrero J, Vilardell-Tarres M, Ordi-Ros J. Thalidomide in the treatment of refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus: Prognostic factors of clinical outcome. Br J Dermatol 2012; 166: 616–623 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Merrill JT, Neuwelt CM, Wallace DJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in moderately-to-severely active systemic lupus erythematosus: The randomized, double-blind, phase II/III systemic lupus erythematosus evaluation of rituximab trial. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62: 222–233 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Popa C, Leandro MJ, Cambridge G, Edwards JC. Repeated B lymphocyte depletion with rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis over 7 yrs. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2007; 46: 626–630 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Kuhn A, Meuth AM, Bein D, et al. Revised Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index (RCLASI): A modified outcome instrument for cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol 2010; 163: 83–92 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]