Abstract
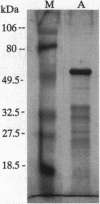
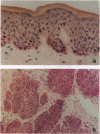
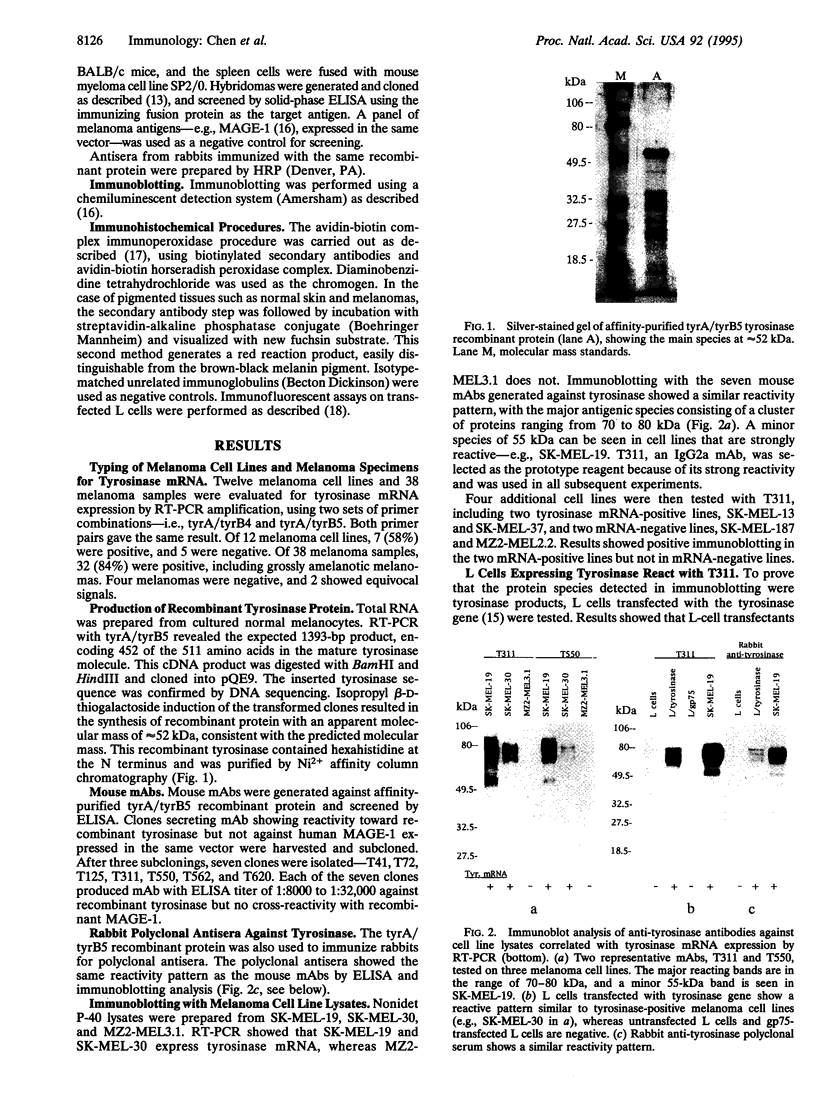
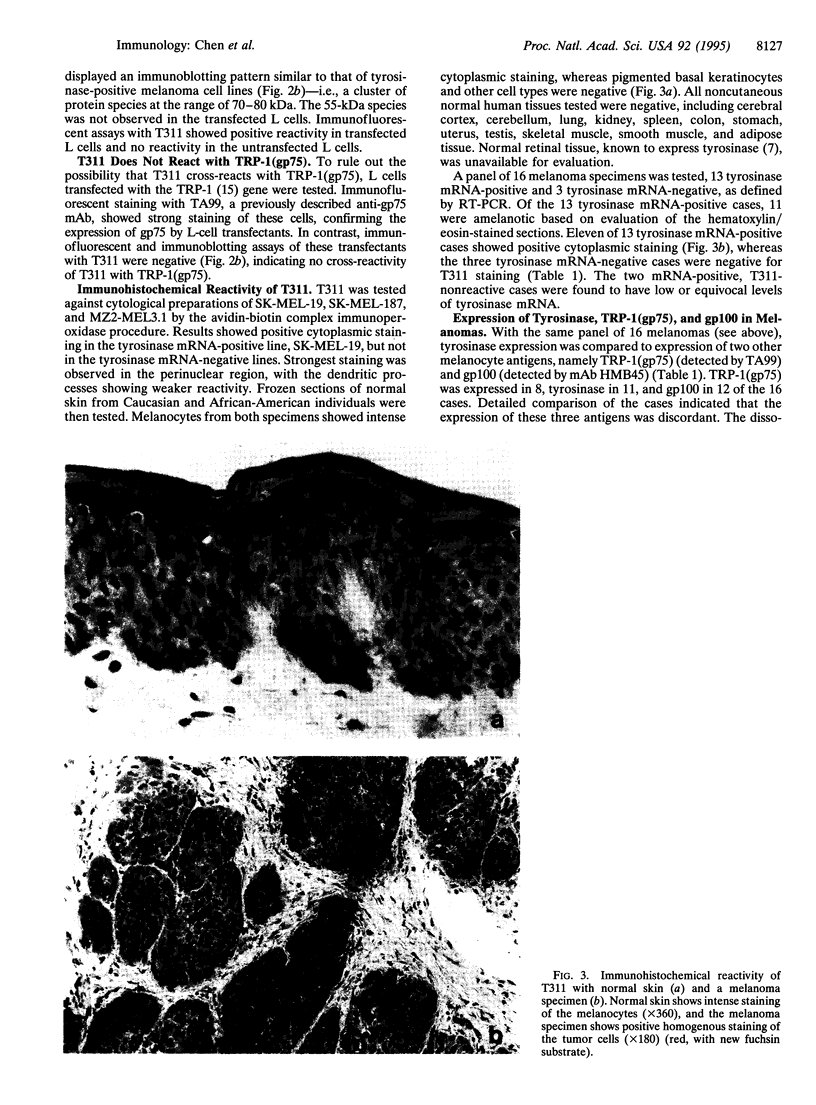
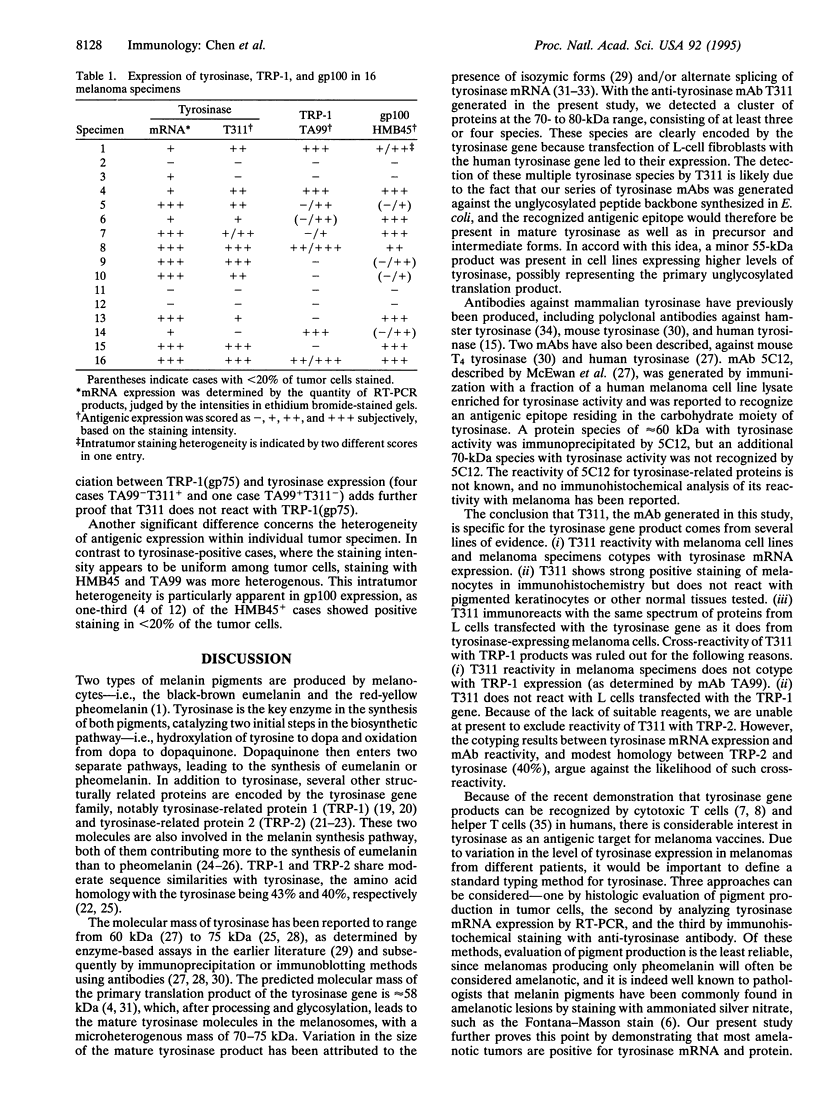
Tyrosinase (EC 1.14.18.1), the key enzyme in melanin synthesis, has been shown to be one of the targets for cytotoxic T-cell recognition in melanoma patients. To develop serological reagents useful for immunophenotyping melanoma for tyrosinase, human tyrosinase cDNA was expressed in an Escherichia coli expression vector. The purified recombinant tyrosinase was used to generate mouse monoclonal and rabbit polyclonal antibodies. The prototype monoclonal antibody, T311, recognized a cluster of protein moieties ranging from 70 to 80 kDa in tyrosinase mRNA-positive melanoma cell lines and melanoma specimens as well as in L cells transfected with tyrosinase cDNA. Untransfected L cells and L cells transfected with tyrosinase-related protein 1, TRP-1(gp75), were nonreactive. Immunohistochemical analysis of melanomas with T311 showed tyrosinase in melanotic and amelanotic variants, and tyrosinase expression correlated with the presence of tyrosinase mRNA. Melanocytes in skin stained with T311, whereas other normal tissues tested were negative. The expression pattern of three melanosome-associated proteins--tyrosinase, TRP-1(gp75), and gp100--in melanoma was also compared. Tyrosinase and gp100 are expressed in a higher percentage of melanomas than TRP-1(gp75), and the expression of these three antigens was discordant. Tyrosinase expression within individual tumor specimen is usually homogenous, distinctly different from the commonly observed heterogeneous pattern of gp100 expression.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Malek Z., Swope V., Collins C., Boissy R., Zhao H., Nordlund J. Contribution of melanogenic proteins to the heterogeneous pigmentation of human melanocytes. J Cell Sci. 1993 Dec;106(Pt 4):1323–1331. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.4.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard B., Del Marmol V., Jackson I. J., Cherif D., Dubertret L. Molecular characterization of a human tyrosinase-related-protein-2 cDNA. Patterns of expression in melanocytic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jan 15;219(1-2):127–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19922.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard B., Vijayasaradhi S., Houghton A. N. Production and characterization of antibodies against human tyrosinase. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Mar;102(3):291–295. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12371784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boël P., Wildmann C., Sensi M. L., Brasseur R., Renauld J. C., Coulie P., Boon T., van der Bruggen P. BAGE: a new gene encoding an antigen recognized on human melanomas by cytolytic T lymphocytes. Immunity. 1995 Feb;2(2):167–175. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(95)80053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brichard V., Van Pel A., Wölfel T., Wölfel C., De Plaen E., Lethé B., Coulie P., Boon T. The tyrosinase gene codes for an antigen recognized by autologous cytolytic T lymphocytes on HLA-A2 melanomas. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):489–495. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey T. E., Lloyd K. O., Takahashi T., Travassos L. R., Old L. J. AU cell-surface antigen of human malignant melanoma: solubilization and partial characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2898–2902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. T., Stockert E., Chen Y., Garin-Chesa P., Rettig W. J., van der Bruggen P., Boon T., Old L. J. Identification of the MAGE-1 gene product by monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1004–1008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen T., Muller R. M., Tomita Y., Shibahara S. Nucleotide sequence of the cDNA encoding human tyrosinase-related protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2807–2808. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulie P. G., Brichard V., Van Pel A., Wölfel T., Schneider J., Traversari C., Mattei S., De Plaen E., Lurquin C., Szikora J. P. A new gene coding for a differentiation antigen recognized by autologous cytolytic T lymphocytes on HLA-A2 melanomas. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):35–42. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dippold W. G., Lloyd K. O., Li L. T., Ikeda H., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cell surface antigens of human malignant melanoma: definition of six antigenic systems with mouse monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6114–6118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garin-Chesa P., Fellinger E. J., Huvos A. G., Beresford H. R., Melamed M. R., Triche T. J., Rettig W. J. Immunohistochemical analysis of neural cell adhesion molecules. Differential expression in small round cell tumors of childhood and adolescence. Am J Pathol. 1991 Aug;139(2):275–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaugler B., Van den Eynde B., van der Bruggen P., Romero P., Gaforio J. J., De Plaen E., Lethé B., Brasseur F., Boon T. Human gene MAGE-3 codes for an antigen recognized on a melanoma by autologous cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):921–930. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Vogel A. M., Hoak D., Gough F., McNutt M. A. Monoclonal antibodies specific for melanocytic tumors distinguish subpopulations of melanocytes. Am J Pathol. 1986 May;123(2):195–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaban R., Pomerantz S. H., Marshall S., Lambert D. T., Lerner A. B. Regulation of tyrosinase in human melanocytes grown in culture. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):480–488. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Ekel T. M., Montague P. M. Mammalian tyrosinase: isozymic forms of the enzyme. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90141-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez M., Tsukamoto K., Hearing V. J. Tyrosinases from two different loci are expressed by normal and by transformed melanocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1147–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami Y., Eliyahu S., Delgado C. H., Robbins P. F., Rivoltini L., Topalian S. L., Miki T., Rosenberg S. A. Cloning of the gene coding for a shared human melanoma antigen recognized by autologous T cells infiltrating into tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3515–3519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami Y., Eliyahu S., Delgado C. H., Robbins P. F., Sakaguchi K., Appella E., Yannelli J. R., Adema G. J., Miki T., Rosenberg S. A. Identification of a human melanoma antigen recognized by tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes associated with in vivo tumor rejection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6458–6462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Haq A. K., Pomerantz S. H., Halaban R. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone for human tyrosinase that maps at the mouse c-albino locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7473–7477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S. Pigmentation genes: the tyrosinase gene family and the pmel 17 gene family. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Feb;100(2 Suppl):134S–140S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12465022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattes M. J., Thomson T. M., Old L. J., Lloyd K. O. A pigmentation-associated, differentiation antigen of human melanoma defined by a precipitating antibody in human serum. Int J Cancer. 1983 Dec 15;32(6):717–721. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwan M., Parsons P. G., Moss D. J. Monoclonal antibody against human tyrosinase and reactive with melanotic and amelanotic melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Apr;90(4):515–519. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12461022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlow S. J., Boissy R. E., Moran D. J., Pifko-Hirst S. Subcellular distribution of tyrosinase and tyrosinase-related protein-1: implications for melanosomal biogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Jan;100(1):55–64. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12354138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponnazhagan S., Hou L., Kwon B. S. Structural organization of the human tyrosinase gene and sequence analysis and characterization of its promoter region. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 May;102(5):744–748. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12376924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter S., Mintz B. Multiple alternatively spliced transcripts of the mouse tyrosinase-encoding gene. Gene. 1991 Jan 15;97(2):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90063-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig W. J., Chesa P. G., Beresford H. R., Feickert H. J., Jennings M. T., Cohen J., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Differential expression of cell surface antigens and glial fibrillary acidic protein in human astrocytoma subsets. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6406–6412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. F., el-Gamil M., Kawakami Y., Stevens E., Yannelli J. R., Rosenberg S. A. Recognition of tyrosinase by tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from a patient responding to immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 15;54(12):3124–3126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert S., Müller G., Kwon B., Schütz G. Multiple transcripts of the mouse tyrosinase gene are generated by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2715–2722. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz-Thater E., Juretic A., Dellabona P., Lüscher U., Siegrist W., Harder F., Heberer M., Zuber M., Spagnoli G. C. MAGE-1 gene product is a cytoplasmic protein. Int J Cancer. 1994 Nov 1;59(3):435–439. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910590324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibahara S., Tomita Y., Tagami H., Müller R. M., Cohen T. Molecular basis for the heterogeneity of human tyrosinase. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1988 Dec;156(4):403–414. doi: 10.1620/tjem.156.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda A., Tomita Y., Matsunaga J., Tagami H., Shibahara S. Molecular basis of tyrosinase-negative oculocutaneous albinism. A single base mutation in the tyrosinase gene causing arginine to glutamine substitution at position 59. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17792–17797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita Y., Montague P. M., Hearing V. J. Anti-T4-tyrosinase monoclonal antibodies--specific markers for pigmented melanocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Nov;85(5):426–430. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita Y. The molecular genetics of albinism and piebaldism. Arch Dermatol. 1994 Mar;130(3):355–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topalian S. L., Rivoltini L., Mancini M., Markus N. R., Robbins P. F., Kawakami Y., Rosenberg S. A. Human CD4+ T cells specifically recognize a shared melanoma-associated antigen encoded by the tyrosinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9461–9465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto K., Jackson I. J., Urabe K., Montague P. M., Hearing V. J. A second tyrosinase-related protein, TRP-2, is a melanogenic enzyme termed DOPAchrome tautomerase. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):519–526. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05082.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Eynde B., Hainaut P., Hérin M., Knuth A., Lemoine C., Weynants P., van der Bruggen P., Fauchet R., Boon T. Presence on a human melanoma of multiple antigens recognized by autologous CTL. Int J Cancer. 1989 Oct 15;44(4):634–640. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayasaradhi S., Bouchard B., Houghton A. N. The melanoma antigen gp75 is the human homologue of the mouse b (brown) locus gene product. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1375–1380. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. F., Robbins P. F., Kawakami Y., Kang X. Q., Rosenberg S. A. Identification of a gene encoding a melanoma tumor antigen recognized by HLA-A31-restricted tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1995 Feb 1;181(2):799–804. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.2.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wölfel T., Van Pel A., Brichard V., Schneider J., Seliger B., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Boon T. Two tyrosinase nonapeptides recognized on HLA-A2 melanomas by autologous cytolytic T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Mar;24(3):759–764. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama K., Suzuki H., Yasumoto K., Tomita Y., Shibahara S. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of a cDNA coding for human DOPAchrome tautomerase/tyrosinase-related protein-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Apr 6;1217(3):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Marmol V., Ito S., Jackson I., Vachtenheim J., Berr P., Ghanem G., Morandini R., Wakamatsu K., Huez G. TRP-1 expression correlates with eumelanogenesis in human pigment cells in culture. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 2;327(3):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81010-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bruggen P., Traversari C., Chomez P., Lurquin C., De Plaen E., Van den Eynde B., Knuth A., Boon T. A gene encoding an antigen recognized by cytolytic T lymphocytes on a human melanoma. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1643–1647. doi: 10.1126/science.1840703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]