Abstract
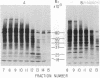
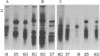
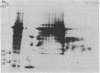
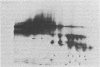
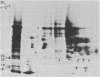
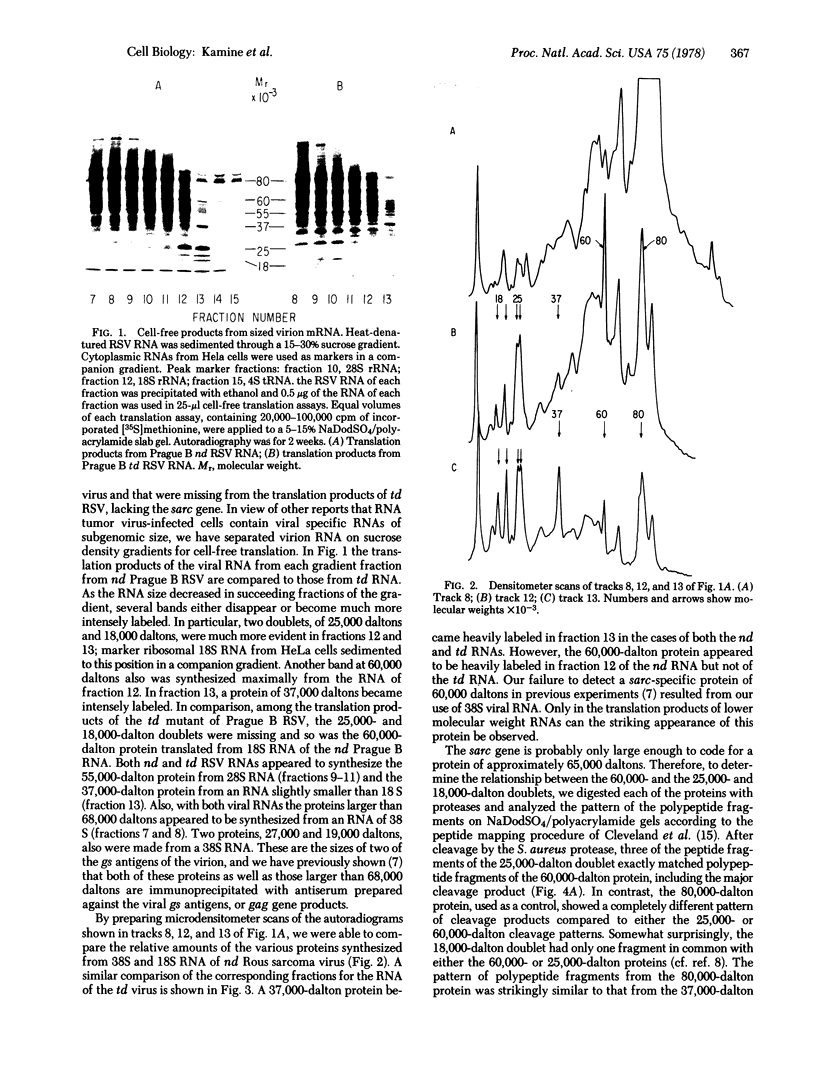
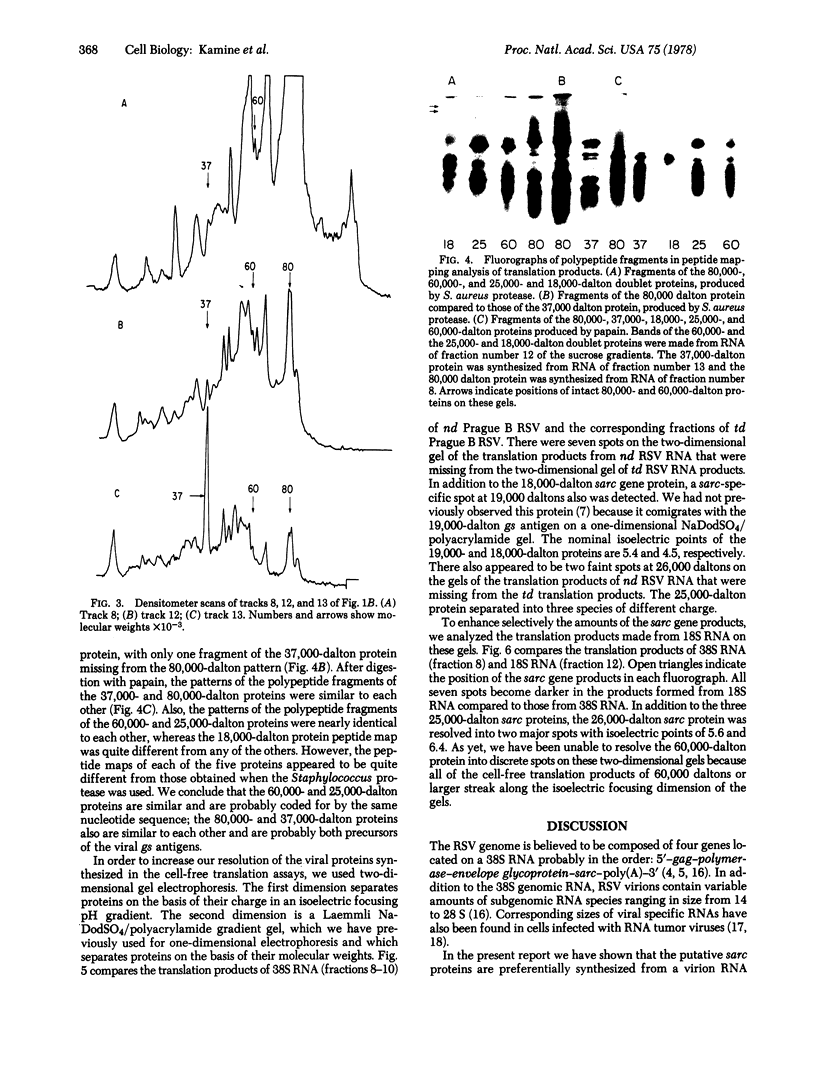
In a previous study we were able to identify two proteins of 25,000 and 18,000 daltons that were made from RNA of transforming virions of Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) and that were missing from the translation products of a transformation-defective deletion mutant of RSV. In the present study we have separated RSV virion RNA on sucrose gradients and have determined that the two putative sarc gene products are synthesized as doublets from an mRNA of approximately 18 S. There also appear to be several other sizes of virion mRNA that direct the synthesis of other viral proteins. These data are discussed in terms of the structure of the RSV genome. In addition to the 25,000- and 18,000-dalton doublets, there also is a 60,000-dalton protein whose synthesis is directed by 18S viral RNA from transforming virion of RSV. Peptide mapping has shown that the 60,000- and 25,000-dalton doublet are structurally related. In addition, the use of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis has allowed us to resolve both bands of the 25,000-dalton doublet into several differently charged species.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beemon K., Hunter T. In vitro translation yields a possible Rous sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3302–3306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein A., MacCormick R., Martin G. S. Transformation-defective mutants of avian sarcoma viruses: the genetic relationship between conditional and nonconditional mutants. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):206–209. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90254-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung K. S., Smith R. E., Stone M. P., Joklik W. K. Comparison of immature (rapid harvest) and mature Rous sarcoma virus particles. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):851–864. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90439-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M. Genes responsible for transformation by avian RNA tumor viruses. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4282–4288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Vogt P. K. RNA species obtained from clonal lines of avian sarcoma and from avian leukosis virus. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Baltimore D. RNA metabolism of murine leukemia virus: detection of virus-specific RNA sequences in infected and uninfected cells and identification of virus-specific messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 15;80(1):93–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gielkens A. L., Salden M. H., Bloemendal H. Virus-specific messenger RNA on free and membrane-bound polyribosomes from cells infected with Rauscher leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1093–1097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Polypeptide cleavages in the formation of poliovirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):77–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho R. H., Billeter M. A., Weissmann C. Mapping of biological functions on RNA of avian tumor viruses: location of regions required for transformation and determination of host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junghans R. P., Hu S., Knight C. A., Davidson N. Heteroduplex analysis of avian RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):477–481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamine J., Buchanan J. M. Cell-free synthesis of two proteins unique to RNA of transforming virions of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2011–2015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Harvey R., Smith A. E. The size of Rous sarcoma virus mRNAs active in cell-free translation. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):416–420. doi: 10.1038/268416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Allfrey V. G., Hanafusa H. Microinjection analysis of envelope-glycoprotein messenger activities of avian leukosis viral RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1614–1618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., McDowell M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Translation of reovirus mRNA, poliovirus RNA and bacteriophage Qbeta RNA in cell-free extracts of mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:709–723. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P., Beemon K., Vogt P. K. Mapping RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of avian tumor virus RNAs: sarcoma-specific oligonucleotides are near the poly(A) end and oligonucleotides common to sarcoma and transformation-defective viruses are at the poly(A) end. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):1051–1070. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.1051-1070.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke J. A. Temperature sensitive mutants of avian sarcoma viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 11;417(2):91–121. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(75)90001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaane D. V., Gielkens A. L., Hesselink W. G., Bloemers H. P. Identification of Rauscher murine leukemia virus-specific mRNAs for the synthesis of gag- and env-gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1855–1859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]