Abstract
A number of infants with an autosomal recessive form of combined immunodeficiency disease also lack adenosine deaminase (adenosine aminohydrolase; EC 3.5.4.4) activity in their erythrocytes. Other tissues from these infants contain only a few percent of the adenosine-deaminating activity present in corresponding normal tissue. The residual adenosine-deaminating activity in extracts from the spleen of a combined immunodeficient, adenosine deaminase-deficient patient was compared with adenosine deaminase from normal spleen. Affinity and immunoadsorbant column chromatography revealed distinct differences between the adenosine-deaminating activity in the patient's spleen and adenosine deaminase from normal spleen. The point of maximum activity and general configuration of the pH optimum curves were also different. erythro-9-(2-Hydroxyl-3-nonyl)adenine, a potent inhibitor of adenosine deaminase from normal spleen, had relatively little effect on the activity from the patient's spleen. In contrast, adenine was a better inhibitor of the activity in the patient's spleen than it was of the enzyme from normal tissue. An adenosine-deaminating activity with the same characteristics and specific activity as that in the patient's spleen was also isolated from normal spleen. These results suggest that the adenosine-deaminating activity in the spleen of this patient is not due to a mutant form of adenosine deaminase.
Keywords: enzyme deficiency
Full text
PDF
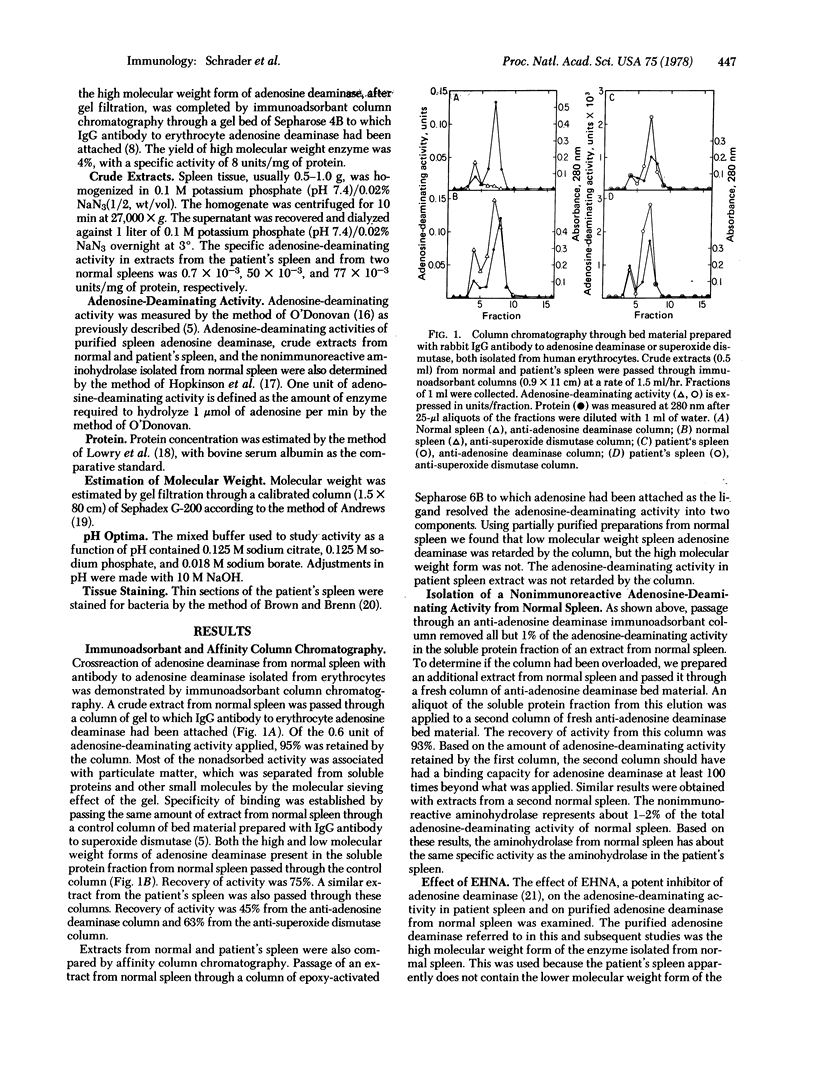
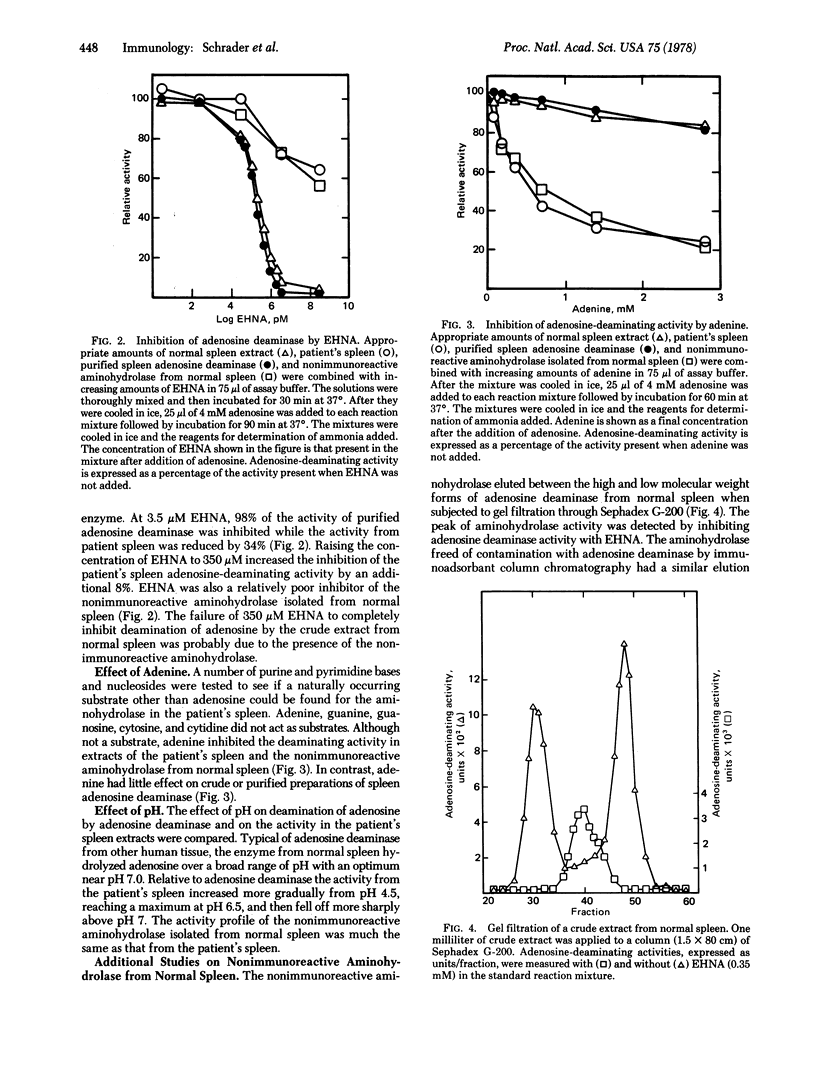
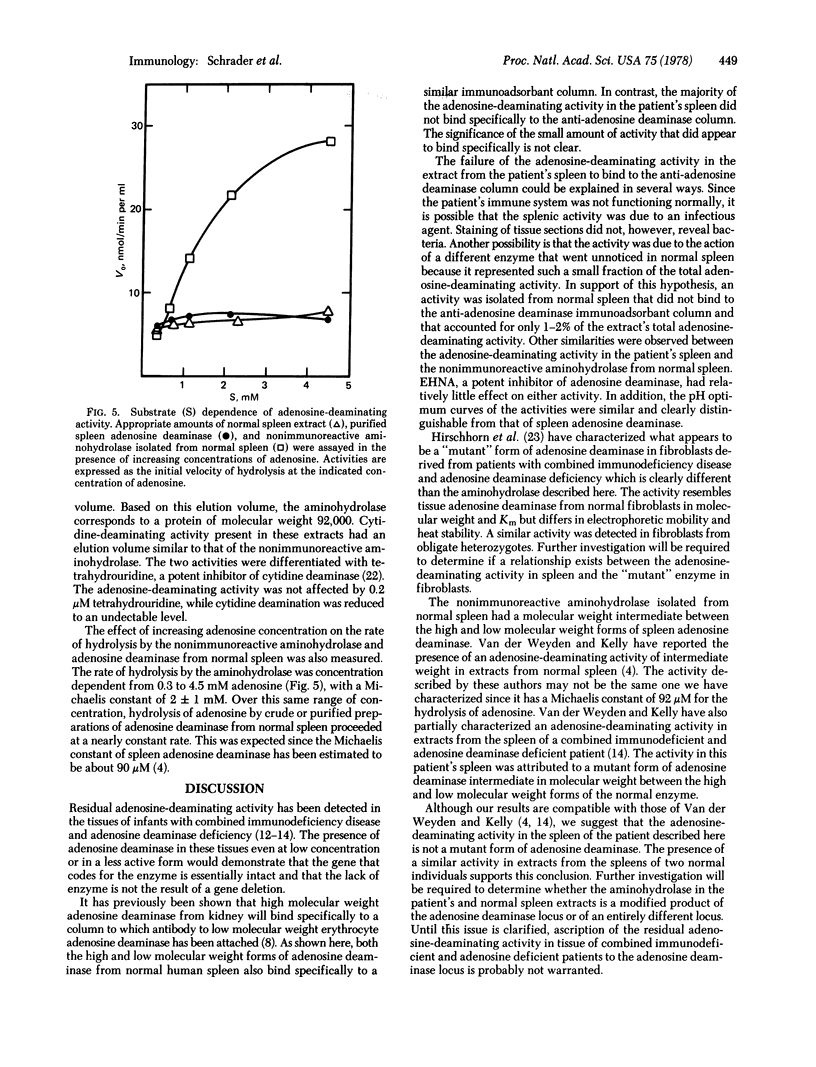

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akedo H., Nishihara H., Shinkai K., Komatsu K., Ishikawa S. Multiple forms of human adenosine deaminase. I. Purification and characterization of two molecular species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 13;276(1):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabner B. A., Johns D. G., Coleman C. N., Drake J. C., Evans W. H. Purification and properties of cytidine deaminase from normal and leukemic granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):922–931. doi: 10.1172/JCI107633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Scott C. R., Swedberg D. R. Heterogeneity for adenosine deaminase deficiency: Expression of the enzyme in cultured skin fibroblasts and amniotic fluid cells. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Jan;27(1):46–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daddona P. E., Kelley W. N. Human adenosine deaminase. Purification and subunit structure. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):110–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards Y. H., Hopkinson D. A., Harris H. Adenosine deaminase isozymes in human tissues. Ann Hum Genet. 1971 Oct;35(2):207–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1956.tb01393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Anderson J. E., Cohen F., Pollara B., Meuwissen H. J. Adenosine-deaminase deficiency in two patients with severely impaired cellular immunity. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1067–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R., Beratis N., Rosen F. S. Characterization of residual enzyme activity in fibroblasts from patients with adenosine deaminase deficiency and combined immunodeficiency: evidence for a mutant enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):213–217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R. Conversion of human erythrocyte-adenosine deaminase activity to different tissue-specific isozymes. Evidence for a common catalytic unit. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):661–667. doi: 10.1172/JCI107974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkinson D. A., Cook P. J., Harris H. Further data on the adenosine deaminase (ADA) polymprphism and a report of a new phenotype. Ann Hum Genet. 1969 May;32(4):361–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1969.tb00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen H. J., Pollara B., Pickering R. J. Combined immunodeficiency disease associated with adenosine deaminase deficiency. Report on a workshop held in Albany, New York, October 1, 1973. J Pediatr. 1975 Feb;86(2):169–181. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80463-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan D. J. Inhibition of the indophenol reaction in the spectrophotometric determination of ammonia. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Mar;32(1):59–61. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90463-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne W. R., Spencer N. Partial purification and properties of the common inherited forms of adenosine deaminase from human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1973 May;133(1):117–123. doi: 10.1042/bj1330117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkman R., Gelfand E. W., Rosen F. S., Sanderson A., Hirschhorn R. Severe combined immunodeficiency and adenosine deaminase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1975 Apr 3;292(14):714–719. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197504032921402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer H. J., Schwender C. F. Enzyme inhibitors. 26. Bridging hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions on adenosine deaminase with some 9-(2-hydroxy-3-alkyl)adenines. J Med Chem. 1974 Jan;17(1):6–8. doi: 10.1021/jm00247a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader W. P., Stacy A. R., Pollara B. Purification of human erythrocyte adenosine deaminase by affinity column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):4026–4032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader W. P., Stacy A. R. Purification and subunit structure of adenosine deaminase from human kidney. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6409–6415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Weyden M. B., Buckley R. H., Kelley W. N. Molecular form of adenosine deaminase in severe combined immunodeficiency. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 8;57(3):590–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90587-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Weyden M. B., Kelley W. N. Human adenosine deaminase. Distribution and properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5448–5456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


