Abstract
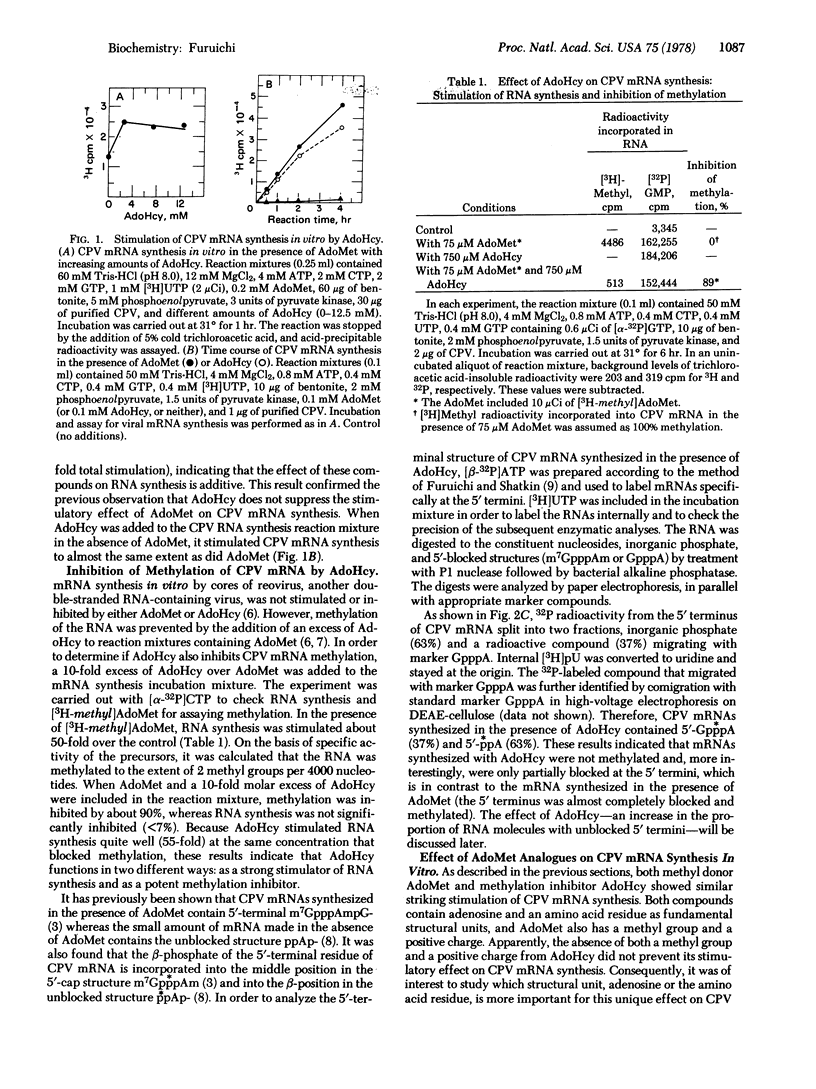
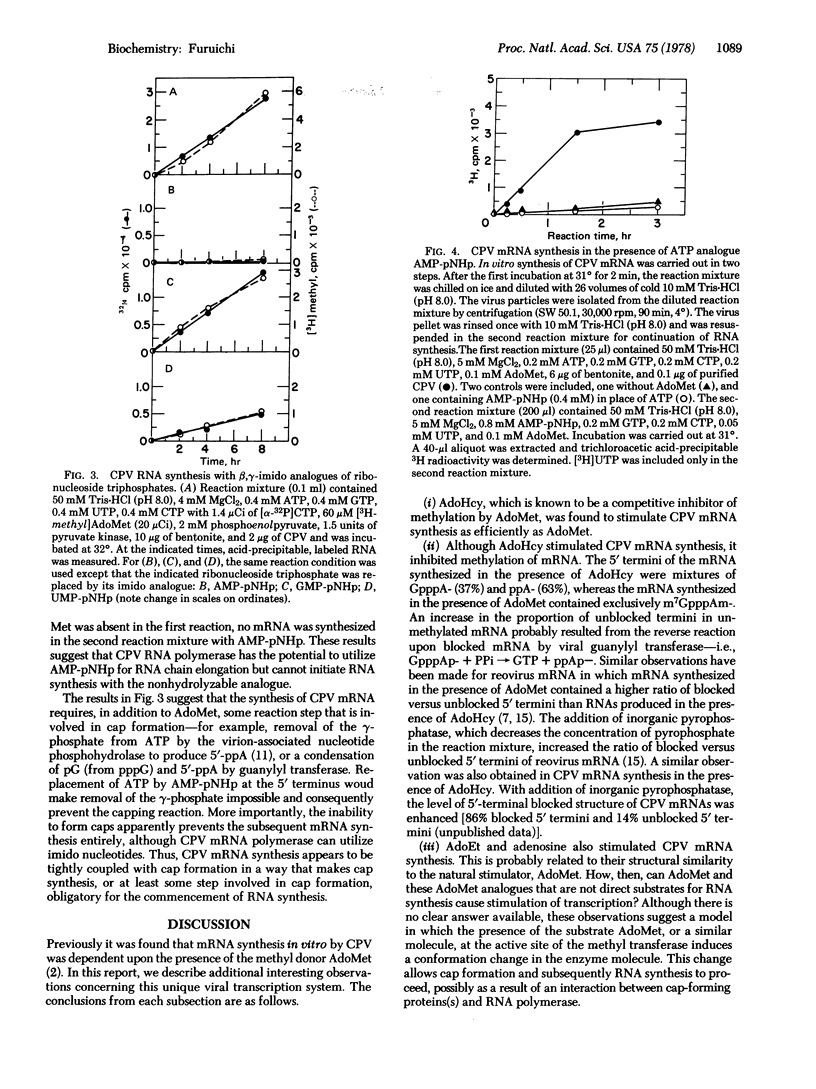
The in vitro synthesis of cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus (CPV) mRNA was previously shown to be dependent upon the presence of the methyl donor S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet). We now find that the competitive inhibitor of methylation, S-adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy), also stimulates CPV mRNA synthesis efficiently, resulting in the synthesis of viral mRNAs containing 5′-terminal GpppA and ppA, rather than m7GpppAm as observed with Adomet. In addition to AdoHcy, other AdoMet analogues, including S-adenosylethionine and adenosine, also stimulate CPV mRNA synthesis but to a smaller extent than does AdoHcy or AdoMet. In order to study the relationship between cap formation and mRNA synthesis, nucleoside triphosphates were replaced in the RNA-synthesizing reaction mixture (containing AdoMet) by the corresponding β,γ-imido analogues, which are resistant to nucleotide phosphohydrolase, an enzyme involved in cap formation. Although mRNA synthesis occurred in the presence of UMP-pNHp or GMP-pNHp, none was observed when AMP-pNHp was substituted for ATP. Because the ATP molecule that becomes the 5′-terminal nucleotide of CPV mRNA must be cleaved at the β-γ position during cap formation, the results suggest that, in this viral transcription system, cap formation is prerequisite to mRNA synthesis—i.e., a “pretranscriptional” event.
Keywords: S-adenosylmethionine, mRNA methylation, initiation of transcription, virus gene expression
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Rhodes D. P., Banerjee A. K. Novel initiation of RNA synthesis in vitro by vesicular stomatitis virus. Nature. 1975 May 1;255(5503):37–40. doi: 10.1038/255037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Furuichi Y., Muthukrishnan S., Shatkin A. J. Ribosome binding to reovirus mRNA in protein synthesis requires 5' terminal 7-methylguanosine. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y. "Methylation-coupled" transcription by virus-associated transcriptase of cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus containing double-stranded RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Jun;1(6):809–822. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.6.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., LaFiandra A., Shatkin A. J. 5'-Terminal structure and mRNA stability. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):235–239. doi: 10.1038/266235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Miura K. I. Identity of the 3'-terminal sequences in ten genome segments of silkworm cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):418–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Miura K. A blocked structure at the 5' terminus of mRNA from cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus. Nature. 1975 Jan 31;253(5490):374–375. doi: 10.1038/253374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Morgan M., Muthukrishnan S., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus messenger RNA contains a methylated, blocked 5'-terminal structure: m-7G(5')ppp(5')G-MpCp-. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):362–366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Muthukrishnan S., Tomasz J., Shatkin A. J. Mechanism of formation of reovirus mRNA 5'-terminal blocked and methylated sequence, m7GpppGmpC. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):5043–5053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Shatkin A. J. 5'-termini of reovirus mRNA: ability of viral cores to form caps post-transcriptionally. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):566–578. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Shatkin A. J. A simple method for the preparation of [beta-32P]purine nucleoside triphosphase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Oct;4(10):3341–3355. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.10.3341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Shatkin A. J. Differential synthesis of blocked and unblocked 5'-termini in reovirus mRNA: effect of pyrophosphate and pyrophosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3448–3452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Characterization of ribosome-protected fragments from reovirus messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4259–4266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D., Kitron N. Influenza virion RNA-dependent RNA polymerase: stimulation by guanosine and related compounds. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):686–695. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.686-695.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Gershowitz A., Wei C. M., Boone R. Formation of the guanylylated and methylated 5'-terminus of vaccinia virus mRNA. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):341–351. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E. Kinetics of formation of 5' terminal caps in mRNA. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):433–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER M. F., O'BRIEN B. M. Polynucleotide phosphorylase of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. II. Further purification of the enzyme and the arsenolysis of polyribonucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:328–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Methylated messenger RNA synthesis in vitro by purified reovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3204–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Miura K. i. The process of formation of the 5' -terminal modified structure in messenger RNA of cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus. FEBS Lett. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):204–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80284-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotono K., Miura K. 5'-Terminal structure of messenger RNA transcribed by RNA polymerase of silkworm cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus containing double-stranded RNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 15;86(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(74)80004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Sakuma S., Tanaka S. A possible biological function of the protein kinase associated with vaccinia and vesicular stomatitis virions. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 1;41(2):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


