Abstract
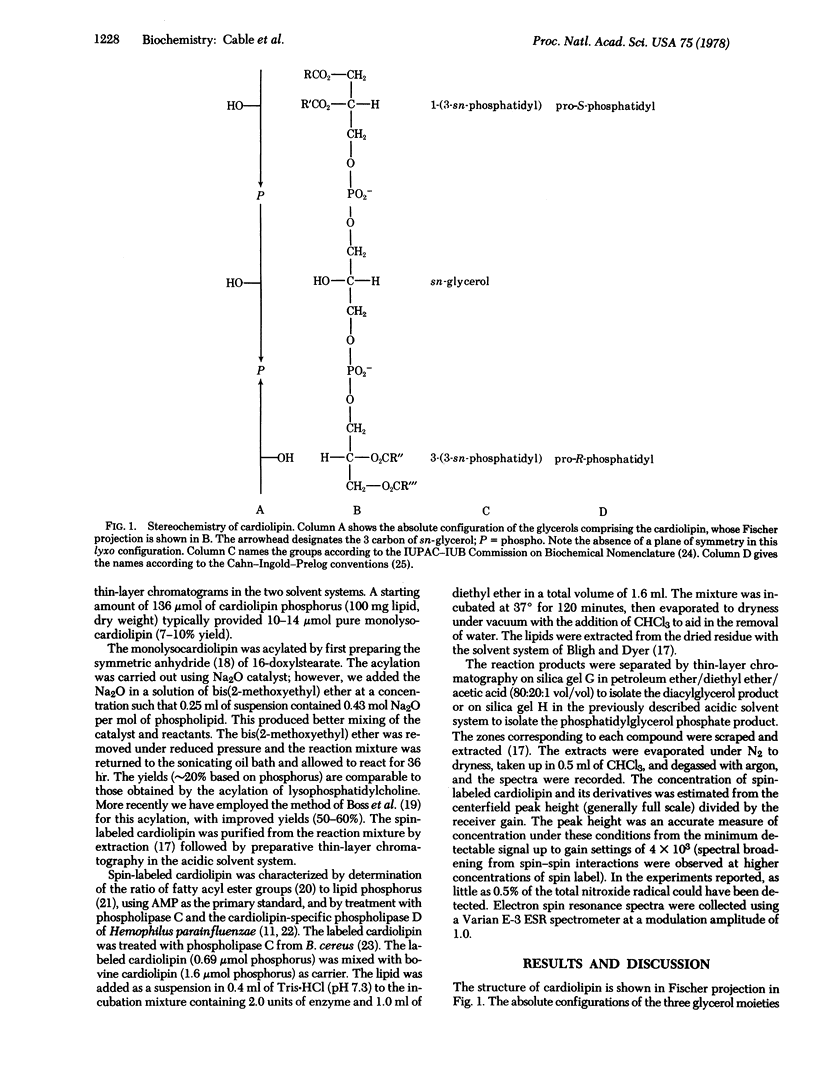
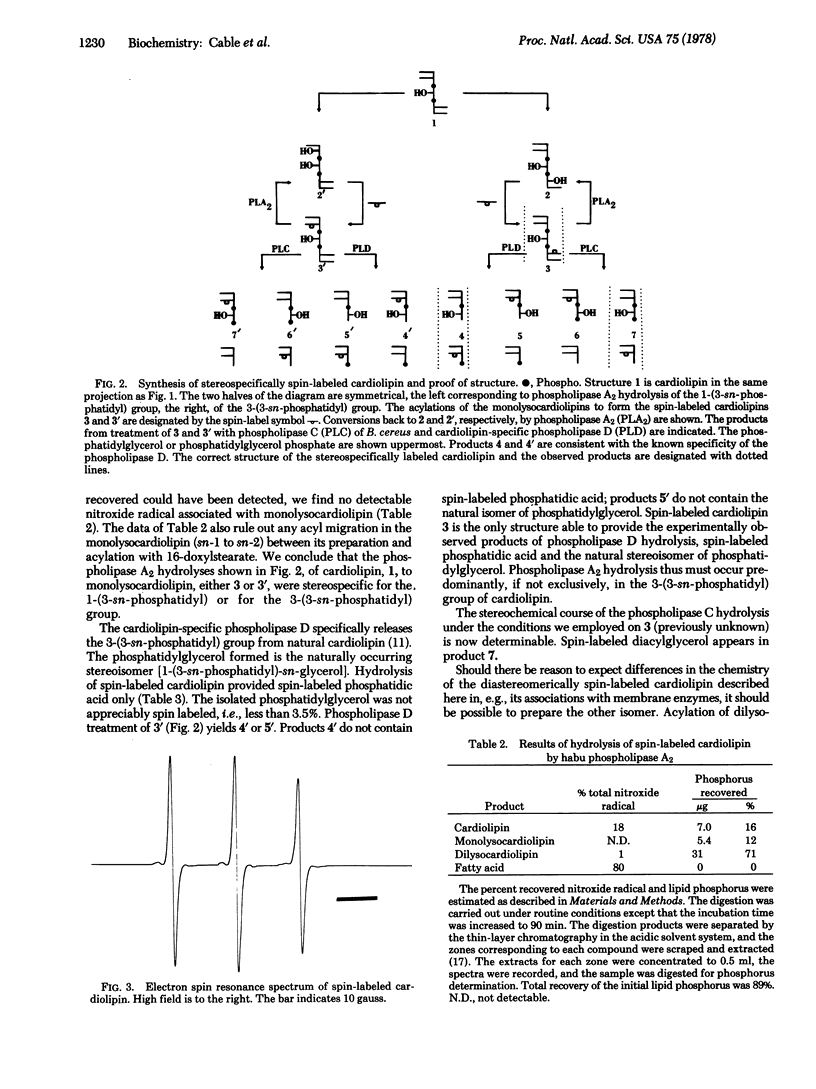
The spin-labeled cardiolipin 1-(3-sn-phosphatidyl)-3-[1-acyl-2-(16-doxylstearoyl)glycero(3)phosphol]-sn-glycerol has been prepared. The stereoselective synthesis makes use of the monolysocardiolipin 1-(3-sn-phosphatidyl)-3-[1-acyl-2-lyso-sn-glycero(3)phospho]-sn-glycerol, available from the stereospecific hydrolysis of cardiolipin by phospholipase A2 (phosphatide 2-acylhydrolase, EC 3.1.1.4) of Trimeresurus flavoviridis. The results of treatment of the spin-labeled cardiolipin with the cardiolipin-specific phospholipase D (phosphatidylcholine phosphatidohydrolase, EC 3.1.4.4) (Hemophilus parainfluenzae) of known specificity and with phospholipase C (phosphatidylcholine cholinephosphohydrolase, EC 3.1.4.3) of Bacillus cereus are consistent with the assigned structure. The spin-labeled cardiolipin is further characterized and the unique features of this diastereomer are discussed in the context of the unusual stereochemistry of the natural phospholipid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrachan L. The bond hydrolyzed by cardiolipin-specific phospholipase D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;296(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awasthi Y. C., Chuang T. F., Keenan T. W., Crane F. L. Tightly bound cardiolipin in cytochrome oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 12;226(1):42–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUBLITZ C., KENNEDY E. P. A note of the asymmetrical metabolism of glycerol. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):963–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss W. F., Kelley C. J., Landsberger F. R. A novel synthesis of spin label derivatives of phosphatidylcholine. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):289–292. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVERKATE F., VAN DEENENL THE STEREOCHEMICAL CONFIGURATION OF PHOSPHATIDYL GLYCEROL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 24;84:106–108. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson T. O., Glonek T., Myers T. C. Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):623–628. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P. C., Griffith O. H., Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. Evidence for boundary lipid in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):480–484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P. C., Nadakavukaren K. K., Griffith O. H. Phosphatidylcholine exchange between the boundary lipid and bilayer domains in cytochrome oxidase containing membranes. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3110–3114. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECOCQ J., BALLOU C. E. ON THE STRUCTURE OF CARDIOLIPIN. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:976–980. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry R. R., Tinsley I. J. A simple, sensitive method for lipid phosphorus. Lipids. 1974 Jul;9(7):491–492. doi: 10.1007/BF02534277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles D. S., Landsberger F. R. Sendai virus-induced hemolysis: reduction in heterogeneity of erythrocyte lipid bilayer fluidity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1918–1922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARINETTI G. V., ERBLAND J., KOCHEN J., STOTZ E. The phosphatide composition of a purified cytochrome oxidase preparation. J Biol Chem. 1958 Sep;233(3):740–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARINETTI G. V., ERBLAND J., STOTZ E. Phosphatides of pig heart cell fractions. J Biol Chem. 1958 Sep;233(3):562–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKUYAMA H., NOJIMA S. STUDIES ON HYDROLYSIS OF CARDIOLIPIN BY SNAKE VENOM PHOSPHOLIPASE A. J Biochem. 1965 Apr;57:529–538. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., White D. C. Cardiolipin-specific phospholipase D activity in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):111–115. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.111-115.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell G. L., Jacobus J. The nonequivalence of the phosphorus atoms in cardiolipin. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4024–4026. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Lapidot Y. Synthesis of fatty acid anhydrides by reaction with dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jan;7(1):174–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuhne-Sekalec L., Stanacev N. Z. Selective enzymatic radioactive and spin labelling of phospholipids in biological membranes: application to study of temperature-induced changes of microsomal phosphatidylinositols and mitochondrial polyglycerophosphatides. Can J Biochem. 1977 Feb;55(2):186–204. doi: 10.1139/o77-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haas G. H., Bonsen P. P., van Deenen L. L. Studies on cardiolipin. 3. Structural identity of ox-heart cardiolipin and synthetic diphosphatidyl glycerol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 1;116(1):114–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


