Abstract
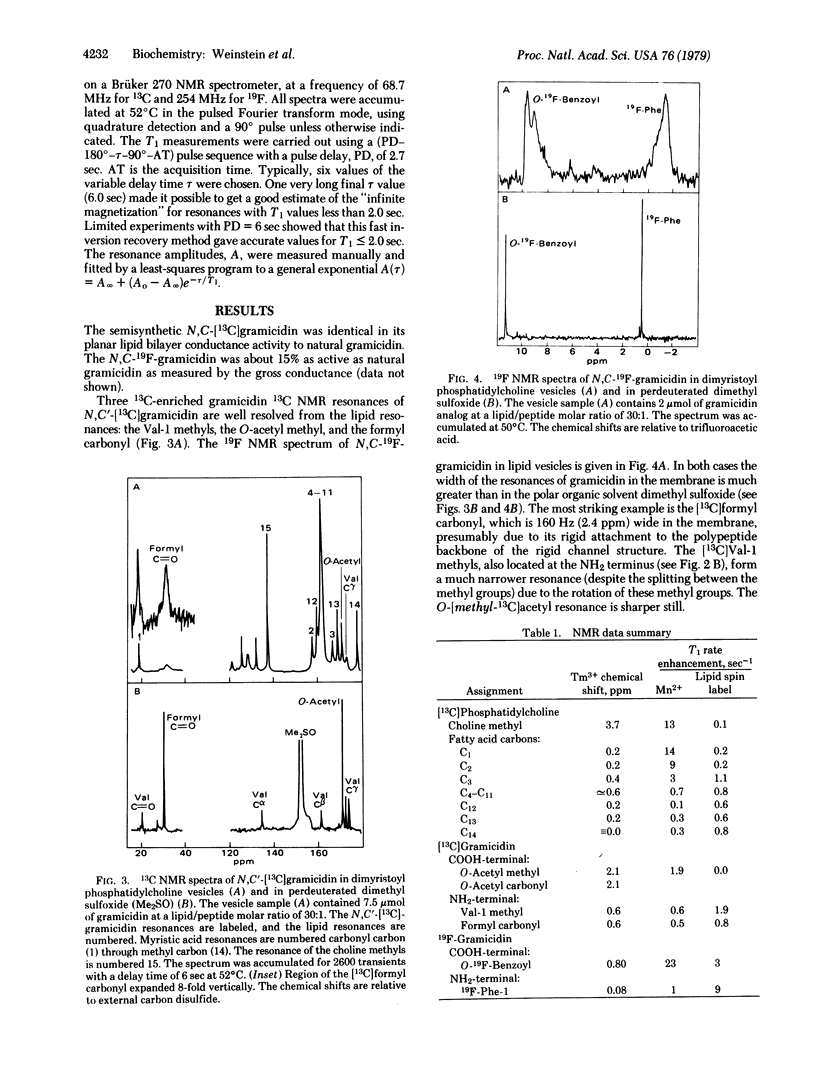
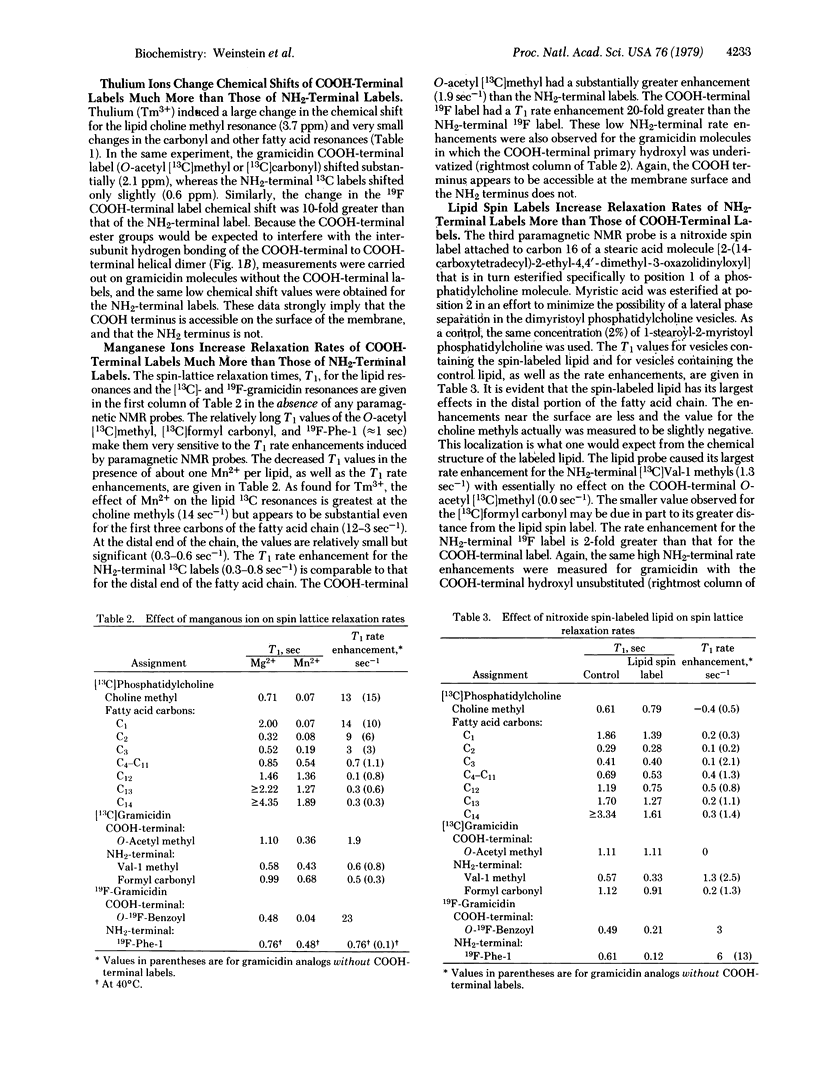
We have determined the conformation of the channel-forming polypeptide antibiotic gramicidin A in phosphatidylcholine vesicles by using 13C and 19F NMR spectroscopy. The models previously proposed for the conformation of the dimer channel differ in the surface localization of the NH2 and COOH termini. We have incorporated specific 13C and 19F nuclei at both the NH2, and COOH termini of gramicidin and have used 13C and 19F chemical shifts and spin lattice relaxation time measurements to determine the accessibility of these labels to three paramagnetic NMR probes--two in aqueous solution and one attached to the phosphatidylcholine fatty acid chain9 all of our results indicate that the COOH terminus of gramicidin in the channel is located near the surface of the membrane and the NH2 terminus is buried deep within the lipid bilayer. These findings strongly favor an NH2-terminal to NH2-terminal helical dimer as the major conformation for the gramicidin channel in phosphatidylcholine vesicles.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apell H. J., Bamberg E., Alpes H., Läuger P. Formation of ion channels by a negatively charged analog of gramicidin A. J Membr Biol. 1977 Feb 24;31(1-2):171–188. doi: 10.1007/BF01869403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Apell H. J., Alpes H. Structure of the gramicidin A channel: discrimination between the piL,D and the beta helix by electrical measurements with lipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2402–2406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Janko K. The action of a carbonsuboxide dimerized gramicidin A on lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 17;465(3):486–499. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley R. J., Urry D. W., Okamoto K., Rapaka R. Channel structures of gramicidin: characterization of succinyl derivatives. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):435–437. doi: 10.1126/science.77040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPPELL J. B., CROFTS A. R. GRAMICIDIN AND ION TRANSPORT IN ISOLATED LIVER MITOCHONDRIA. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:393–402. doi: 10.1042/bj0950393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigenson G. W., Meers P. R., Kingsley P. B. NMR observation of gramicidin A' in phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 15;471(3):487–491. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall M. C. Thickness dependence in the action of gramicidin A on lipid bilayers. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Nov;147(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. J., Pressman B. C. Obligate cation exchanges in red cells. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):918–920. doi: 10.1038/216918a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Discreteness of conductance change in bimolecular lipid membranes in the presence of certain antibiotics. Nature. 1970 Jan 31;225(5231):451–453. doi: 10.1038/225451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. I. Studies of the unit conductance channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):294–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P., Rudin D. O. Development of K+-Na+ discrimination in experimental bimolecular lipid membranes by macrocyclic antibiotics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Feb 21;26(4):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90559-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARGES R., WITKOP B. GRAMICIDIN A. V. THE STRUCTURE OF VALINE- AND ISOLEUCINE-GRAMICIDIN A. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 May 5;87:2011–2020. doi: 10.1021/ja01087a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson D. C., Andreoli T. E., Tieffenberg M., Cook P. The effects of macrocyclic compounds on cation transport in sheep red cells and thin and thick lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1968 May;51(5 Suppl):373S+–373S+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Goodall M. C., Glickson J. D., Mayers D. F. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: characteristics of head-to-head dimerized (L,D) helices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1907–1911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Blout E. R. The aggregation of gramicidin A in solution. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5257–5264. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Fossel E. T., Blout E. R. The conformation of gramicidin A. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5249–5256. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Mathies R., Eisenberg M., Stryer L. Simultaneous fluorescence and conductance studies of planar bilayer membranes containing a highly active and fluorescent analog of gramicidin A. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 25;99(1):75–92. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80160-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W., Stryer L. The dimeric nature of the gramicidin A transmembrane channel: conductance and fluorescence energy transfer studies of hybrid channels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A., Blout E. R. Conformation of an oligopeptide in phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1775–1779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


