Abstract
Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae (A. A. Hildebrand) is a fungal stem and root rot-causing pathogen of soybeans. Glycoproteins secreted into the medium of the aseptically cultured fungus have been partially purified by (NH4)2SO4 precipitation and by column chromatography on norleucine-substituted Sepharose 4B and on DEAE-cellulose. Glycoprotein preparations from P. megasperma var. sojae races 1, 2, and 3 have been tested on four cultivars of soybeans. The partially purified glycoproteins from incompatible races of the pathogen (races that cannot successfully infect the plant), but not those from compatible races (races that can kill the plant), protect soybean seedlings from attack by compatible races. The seedlings are protected by introducing the glycoproteins into hypocotyl wounds of seedlings either 90 min prior to or at the time of inoculation of the wounds with mycelia of one of the pathogens. The glycoprotein preparations are poor nonspecific elicitors of phytoalexin accumulation; the glycoproteins have less than 1.0% of the elicitor activity of the glucans present in the mycelial walls of the pathogen.
Keywords: host—pathogen interactions, specificity factors, extracellular glycoproteins, disease resistance, gene-for-gene relationship
Full text
PDF

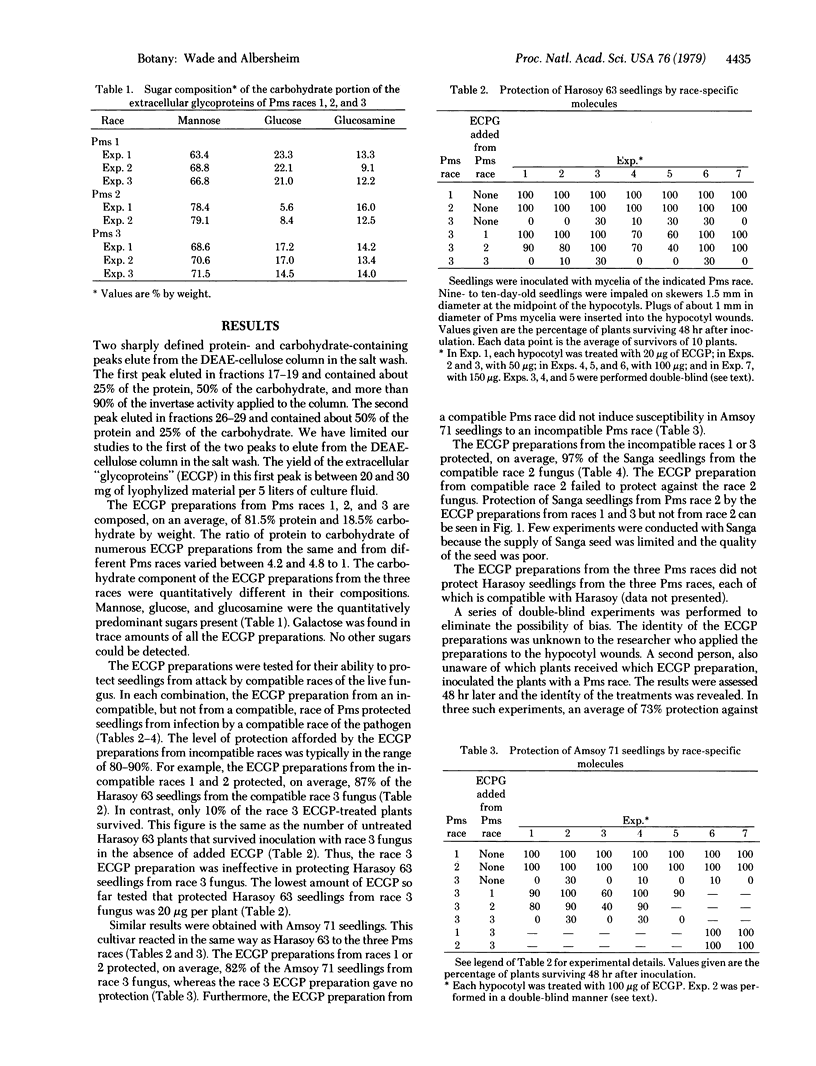
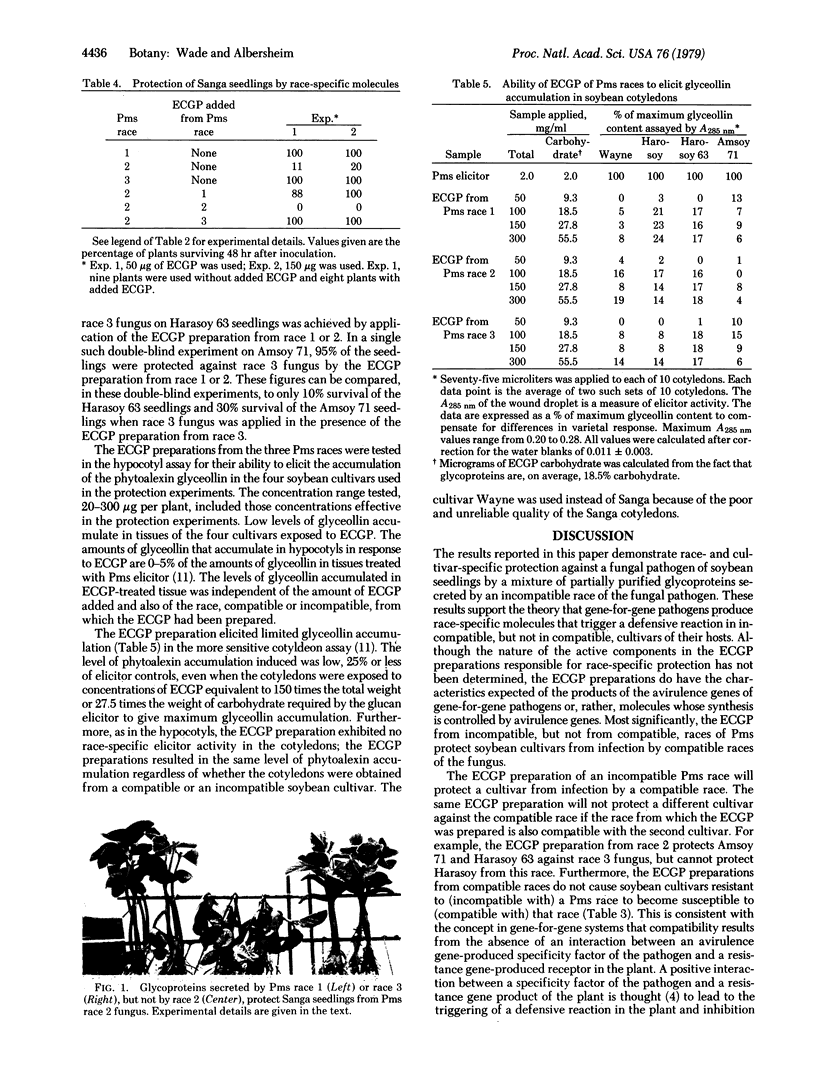

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayers A. R., Ebel J., Finelli F., Berger N., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: IX. Quantitative Assays of Elicitor Activity and Characterization of the Elicitor Present in the Extracellular Medium of Cultures of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):751–759. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Ebel J., Valent B., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: X. Fractionation and Biological Activity of an Elicitor Isolated from the Mycelial Walls of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):760–765. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Valent B., Ebel J., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: XI. Composition and Structure of Wall-released Elicitor Fractions. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):766–774. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou C. E., Raschke W. C. Polymorphism of the somatic antigen of yeast. Science. 1974 Apr 12;184(4133):127–134. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4133.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou C. E. Some aspects of the structure, immunochemistry, and genetic control of yeast mannans. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;40(0):239–270. doi: 10.1002/9780470122853.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey H., Rimerman R. A., Hatfield G. W. Specific ion mediated chromatography of glycoproteins and neutral polysaccharides on substituted agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 Apr;64(2):380–388. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90446-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Wade M., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: XV. Fungal Glucans Which Elicit Phytoalexin Accumulation in Soybean Also Elicit the Accumulation of Phytoalexins in Other Plants. Plant Physiol. 1978 Dec;62(6):918–921. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. M., Albersheim P. A gas chromatographic method for the determination of aldose and uronic Acid constituents of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jun;49(6):926–936. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.6.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. L., Ballou C. E. Immunochemical characterization of the mannan component of the external invertase (beta-fructofuranosidase) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):355–361. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: XIII. Extracellular Invertases Secreted by Three Races of a Plant Pathogen Are Glycoproteins Which Possess Different Carbohydrate Structures. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jun;59(6):1104–1110. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]