Abstract
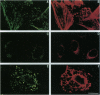
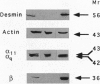
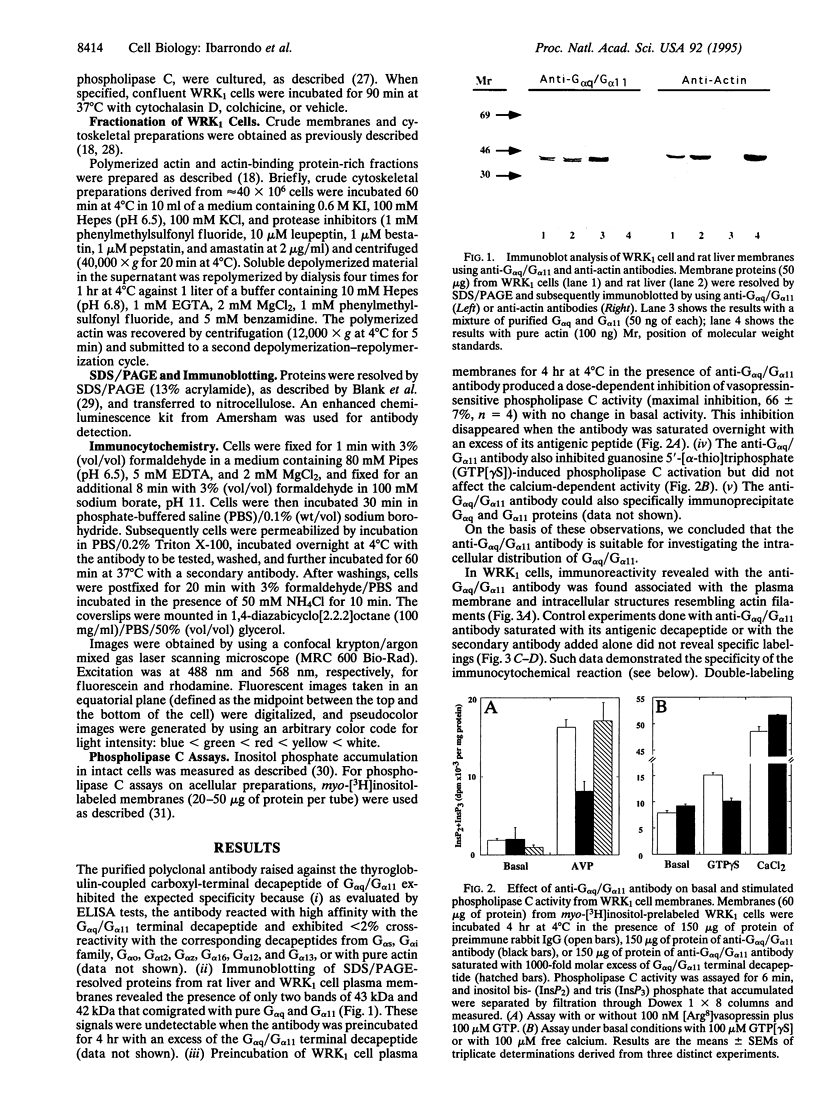
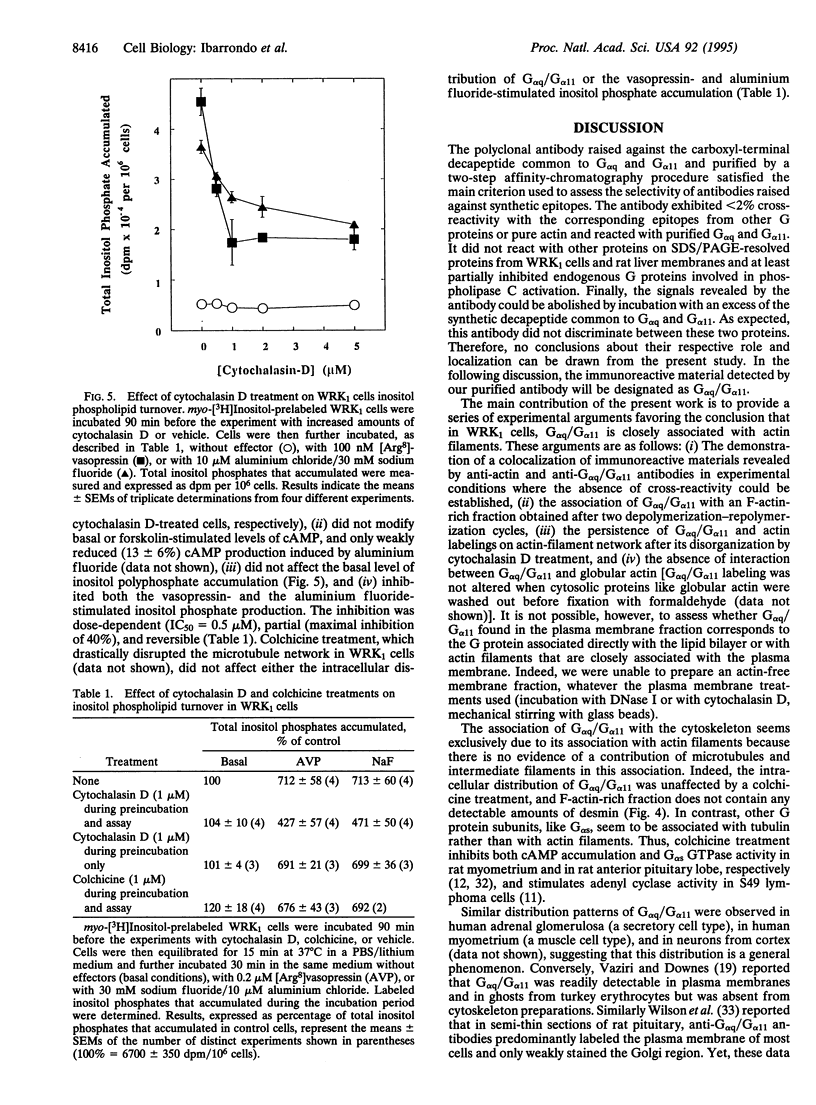
A selective polyclonal antibody directed toward the C-terminal decapeptide common to the alpha subunits of Gq and G11 G proteins (G alpha q/G alpha 11) was prepared and used to investigate the subcellular distribution fo these proteins in WRK1 cells, a rat mammary tumor cell line. In immunoblots, the antibody recognized purified G alpha q and G alpha 11 proteins and labeled only two bands corresponding to these alpha subunits. Functional studies indicated that this antibody inhibited vasopressin- and guanosine 5'-[alpha-thio]triphosphate-sensitive phospholipase C activities. Immunofluorescence experiments done with this antibody revealed a filamentous labeling corresponding to intracytoplasmic and perimembranous actin-like filament structures. Colocalization of G alpha q/G alpha 11 and F-actin filaments (F-actin) was demonstrated by double-labeling experiments with anti-G alpha q/G alpha 11 and anti-actin antibodies. Immunoblot analysis of membrane, cytoskeletal, and F-actin-rich fractions confirmed the close association of G alpha q/G alpha 11 with actin. Large amounts of G alpha q/G alpha 11 were recovered in the desmin- and tubulin-free F-actin-rich fraction obtained by a double depolymerization-repolymerization cycle. Disorganization of F-actin filaments with cytochalasin D preserved G alpha q/G alpha 11 and F-actin colocalization but partially inhibited vasopressin- and fluoroaluminate-sensitive phospholipase C activity, suggesting that actin-associated G alpha q/G alpha 11 proteins play a role in signal transduction.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L. Receptor-to-effector signaling through G proteins: roles for beta gamma dimers as well as alpha subunits. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank J. L., Ross A. H., Exton J. H. Purification and characterization of two G-proteins that activate the beta 1 isozyme of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Identification as members of the Gq class. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18206–18216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Walker G., Huang H. S. Interactions between a lymphoma membrane-associated guanosine 5'-triphosphate-binding protein and the cytoskeleton during receptor patching and capping. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2242–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Carozzi A., Schnabel P., Scheer A., Parker P. J., Gierschik P. Isozyme-selective stimulation of phospholipase C-beta 2 by G protein beta gamma-subunits. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):684–686. doi: 10.1038/360684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson K. E., Woolkalis M. J., Newhouse M. G., Manning D. R. Fractionation of the beta subunit common to guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins with the cytoskeleton. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;30(5):463–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colson P., Ibarondo J., Devilliers G., Balestre M. N., Duvoid A., Guillon G. Upregulation of V1a vasopressin receptors by glucocorticoids. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 1):E1054–E1062. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.2006.263.6.E1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin B. R., Bourne H. R. Structural elements of G alpha subunits that interact with G beta gamma, receptors, and effectors. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90245-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter S., Rodbell M. Heterotrimeric G proteins in synaptoneurosome membranes are crosslinked by p-phenylenedimaleimide, yielding structures comparable in size to crosslinked tubulin and F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBell K. E., Conti A., Alava M. A., Hoffman T., Bonvini E. Microfilament assembly modulates phospholipase C-mediated signal transduction by the TCR/CD3 in murine T helper lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2271–2280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DoKhac L., Tanfin Z., Harbon S. Differential role of microtubules in the control of prostaglandin E2 and beta-adrenergic stimulation of cyclic AMP accumulation in the rat myometrium. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Sep 1;32(17):2535–2541. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuilloley M., Desrues L., Vaudry H. Effect of cytochalasin-B on the metabolism of polyphosphoinositides in andrenocortical cells. Endocrinology. 1993 Nov;133(5):2319–2326. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.5.8404684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeser D., Neubig R. R. Compartmentation of receptors and guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in NG108-15 cells: lack of cross-talk in agonist binding among the alpha 2-adrenergic, muscarinic, and opiate receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;43(3):434–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon G., Kirk C. J., Balestre M. N. Characterization of specific V1a vasopressin-binding sites on a rat mammary-tumour-cell line. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):189–196. doi: 10.1042/bj2400189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homburger V., Brabet P., Audigier Y., Pantaloni C., Bockaert J., Rouot B. Immunological localization of the GTP-binding protein Go in different tissues of vertebrates and invertebrates. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;31(4):313–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibarrondo J., Marino A., Guillon G., Trueba M., Macarulla J. M. Dual effects of ATP on phosphatidylinositol breakdown in rat hepatocyte membranes. Cell Signal. 1991;3(6):577–585. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(91)90034-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahangeer S., Rodbell M. The disaggregation theory of signal transduction revisited: further evidence that G proteins are multimeric and disaggregate to monomers when activated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8782–8786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiber D., Jasper J. R., Alousi A. A., Martin J., Bernstein D., Insel P. A. Alteration in Gs-mediated signal transduction in S49 lymphoma cells treated with inhibitors of microtubules. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3833–3837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao L., Jaken S. Effect of alpha-protein kinase C neutralizing antibodies and the pseudosubstrate peptide on phosphorylation, migration, and growth of REF52 cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Apr;4(4):309–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna E. J., Hitt A. L. Cytoskeleton--plasma membrane interactions. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):955–964. doi: 10.1126/science.1439807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molski T. F., Sha'afi R. I. Intracellular acidification, guanine-nucleotide binding proteins, and cytoskeletal actin. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;8(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/cm.970080102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouillac B., Balestre M. N., Guillon G. Positive feedback regulation of phospholipase C by vasopressin-induced calcium mobilization in WRK1 cells. Cell Signal. 1990;2(5):497–507. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90046-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Kleuss C., Gilman A. G. Receptor regulation of G-protein palmitoylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Hanasaki K., Arita H. Possible involvement of cytoskeleton in collagen-stimulated activation of phospholipases in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5400–5406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman J. C., Price L. S., Ridley A. J., Hall A., Koffer A. Actin filament organization in activated mast cells is regulated by heterotrimeric and small GTP-binding proteins. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(4):1005–1015. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omann G. M., Harter J. M., Hassan N., Mansfield P. J., Suchard S. J., Neubig R. R. A threshold level of coupled G-proteins is required to transduce neutrophil responses. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):2172–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Zahler-Bentz K., Dukes R. E. Regulation of the affinity state of the N-formylated peptide receptor of neutrophils: role of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins and the cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):2959–2971. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payrastre B., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Breton M., den Hartigh J. C., Plantavid M., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. Phosphoinositide kinase, diacylglycerol kinase, and phospholipase C activities associated to the cytoskeleton: effect of epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):121–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravindra R., Aronstam R. S. Effect of colchicine and taxol on stimulation of G protein GTPase activity in anterior pituitary lobe of rats by gonadotrophin- and thyrotrophin-releasing hormones. J Reprod Fertil. 1993 Jan;97(1):27–33. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0970027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefcyk J., Yassin R., Volpi M., Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Munoz J. J., Becker E. L., Feinstein M. B., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis but not cholera toxin inhibits the stimulated increase in actin association with the cytoskeleton in rabbit neutrophils: role of the "G proteins" in stimulus-response coupling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 15;126(3):1174–1181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90309-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Cytochalasins inhibit arachidonic acid metabolism in thrombin-stimulated platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7709–7713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Särndahl E., Bokoch G. M., Stendahl O., Andersson T. Stimulus-induced dissociation of alpha subunits of heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins from the cytoskeleton of human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6552–6556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Chae H. Z., Rhee S. G., Exton J. H. Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):516–518. doi: 10.1038/350516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifaró J. M., Vitale M. L., Rodríguez Del Castillo A. Cytoskeleton and molecular mechanisms in neurotransmitter release by neurosecretory cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 13;225(2):83–104. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaziri C., Downes C. P. Association of a receptor and G-protein-regulated phospholipase C with the cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22973–22981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedegaertner P. B., Wilson P. T., Bourne H. R. Lipid modifications of trimeric G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):503–506. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Komuro M., Farquhar M. G. Cellular variations in heterotrimeric G protein localization and expression in rat pituitary. Endocrinology. 1994 Jan;134(1):233–244. doi: 10.1210/endo.134.1.8275939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haelst C., Rothstein T. L. Cytochalasin stimulates phosphoinositide metabolism in murine B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1256–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]