Abstract
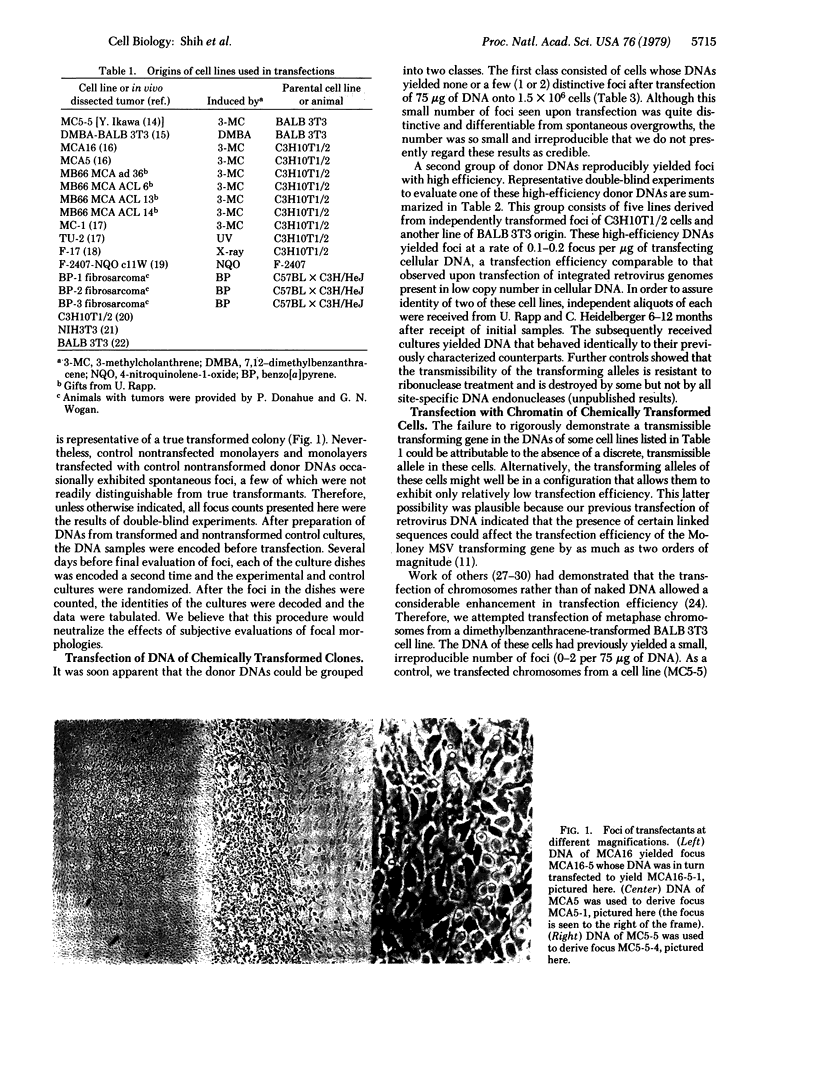
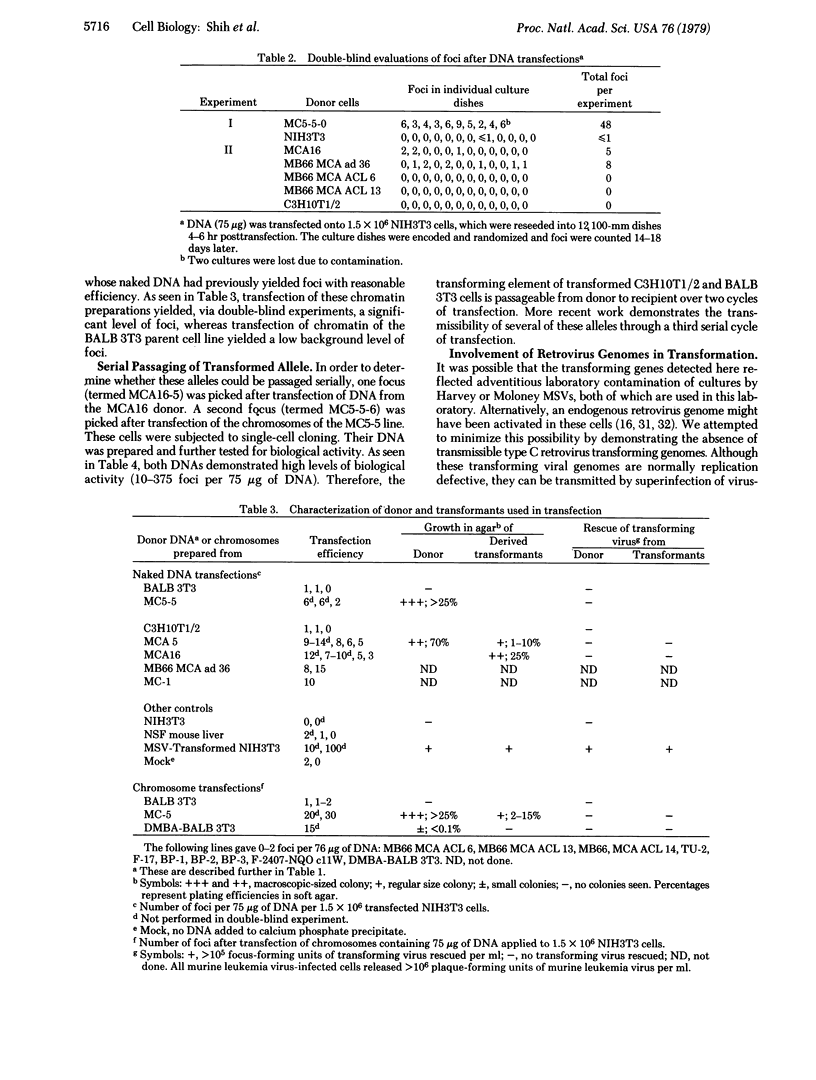
DNA was prepared from 15 different mouse and rat cell lines transformed by chemical carcinogens in vitro and in vivo. These DNAs were applied to NIH3T3 mouse fibroblast cultures by using the calcium phosphate transfection technique. DNAs of five donor lines were able to induce foci on the recipient monolayers. Ten other donor DNAs yielded few or no foci. DNAs from control, nontransformed parental cell lines induced few or no foci. Chromosomes were transfected from one donor whose naked DNA was unable to induce foci, and morphologic transformation of recipients was observed. These experiments prove that in five of these cell lines the chemically induced phenotype is encoded in DNA, and the sequences specifying the transformed phenotype behave as a dominant allele in the NIH3T3 recipient cells. The sequences encoding the transformation are likely found on a single fragment of DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Basis for the acquisition of malignant potential by mouse cells cultivated in vitro. Science. 1968 Nov 29;162(3857):1024–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3857.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson P., Goldfarb M. P., Weinberg R. A. A defined subgenomic fragment of in vitro synthesized Moloney sarcoma virus DNA can induce cell transformation upon transfection. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. C., Tsutsui T., Ts'o P. O. Neoplastic transformation induced by a direct perturbation of DNA. Nature. 1978 Jul 20;274(5668):229–232. doi: 10.1038/274229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J., Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P. Partial transcription of murine type C viral genomes in BALB c cell lines. J Virol. 1973 Oct;12(4):711–720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.4.711-720.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouck N., di Mayorca G. Somatic mutation as the basis for malignant transformation of BHK cells by chemical carcinogens. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):722–727. doi: 10.1038/264722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges B. A. Short term screening tests for carcinogens. Nature. 1976 May 20;261(5557):195–200. doi: 10.1038/261195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan G. L., Little J. B. Induction of oncogenic transformation in vitro by ultraviolet light. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):442–444. doi: 10.1038/264442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPaolo J. A., Casto B. C. In vitro carcinogenesis with cells in early passage. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1978 May;(48):245–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getz M. J., Elder P. K., Moses H. L. Equivalent expression of endogenous murine leukemia virus-related genes in C3H/10T1/2 cells and chemically transformed derivative cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):566–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Graessmann M., Mueller C. Regulatory mechanism of simian virus 40 gene expression in permissive and in nonpermissive cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):854–858. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.854-858.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger C. Chemical carcinogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:79–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Mager R., Sachs L. Mutagenesis and transformation of normal cells by chemical carcinogens. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):360–361. doi: 10.1038/264360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolph J. R., Heidelberger C. Chemical carcinogens produce mutations to ouabain resistance in transformable C3H/10T1/2 Cl 8 mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):930–934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., MONTAGNIER L. AGAR SUSPENSION CULTURE FOR THE SELECTIVE ASSAY OF CELLS TRANSFORMED BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Jun;23:291–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Ozer H. L. Transfer of genetic information by purified metaphase chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1258–1262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J., Ames B. N. Detection of carcinogens as mutagens in the Salmonella/microsome test: assay of 300 chemicals: discussion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):950–954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J., Choi E., Yamasaki E., Ames B. N. Detection of carcinogens as mutagens in the Salmonella/microsome test: assay of 300 chemicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5135–5139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. L., Ruddle F. H. Co-transfer of human X-linked markers into murine somatic cells via isolated metaphase chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3346–3350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshiro Y., DiPaolo J. A. Loss of density-dependent regulation of multiplication of BALB-3T3 cells chemically transformed in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Feb;81(1):133–138. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040810116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Nowinski R. C., Reznikoff C. A., Heidelberger C. Endogenous oncornaviruses in chemically induced transformation. I. Transformation independent of virus production. Virology. 1975 Jun;65(2):392–409. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff C. A., Brankow D. W., Heidelberger C. Establishment and characterization of a cloned line of C3H mouse embryo cells sensitive to postconfluence inhibition of division. Cancer Res. 1973 Dec;33(12):3231–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Berg P. Does simian virus 40 DNA integrate into cellular DNA during productive infection? J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):475–489. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.475-489.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg E., Smotkin D., Baltimore D., Weinberg R. A. In vitro synthesis of infectious DNA of murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):122–126. doi: 10.1038/269122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin S. I., Freedman V. H., Risser R., Pollack R. Tumorigenicity of virus-transformed cells in nude mice is correlated specifically with anchorage independent growth in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4435–4439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Gianni A. M., Rozenblatt S., Weinberg R. A. Infectious viral DNA of murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4910–4913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Siminovitch L. Transfer of anchorage independence by isolated metaphase chromosomes in hamster cells. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90267-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D., Weinberg R. A. The integrated genome of murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tereba A. Chemical activation and regulation of a C-type virus from ring-necked pheasant cells. Virology. 1979 Mar;93(2):340–347. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi M., Little J. B. X-radiation-induced transformation in a C3H mouse embryo-derived cell line. Cancer Res. 1976 Apr;36(4):1367–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters R., Mishra N., Bouck N., DiMayorca G., Regan J. D. Partial inhibition of postreplication repair and enhanced frequency of chemical transformation in rat cells infected with leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):238–242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willecke K., Ruddle F. H. Transfer of the human gene for hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase via isolated human metaphase chromosomes into mouse L-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1792–1796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]