Abstract
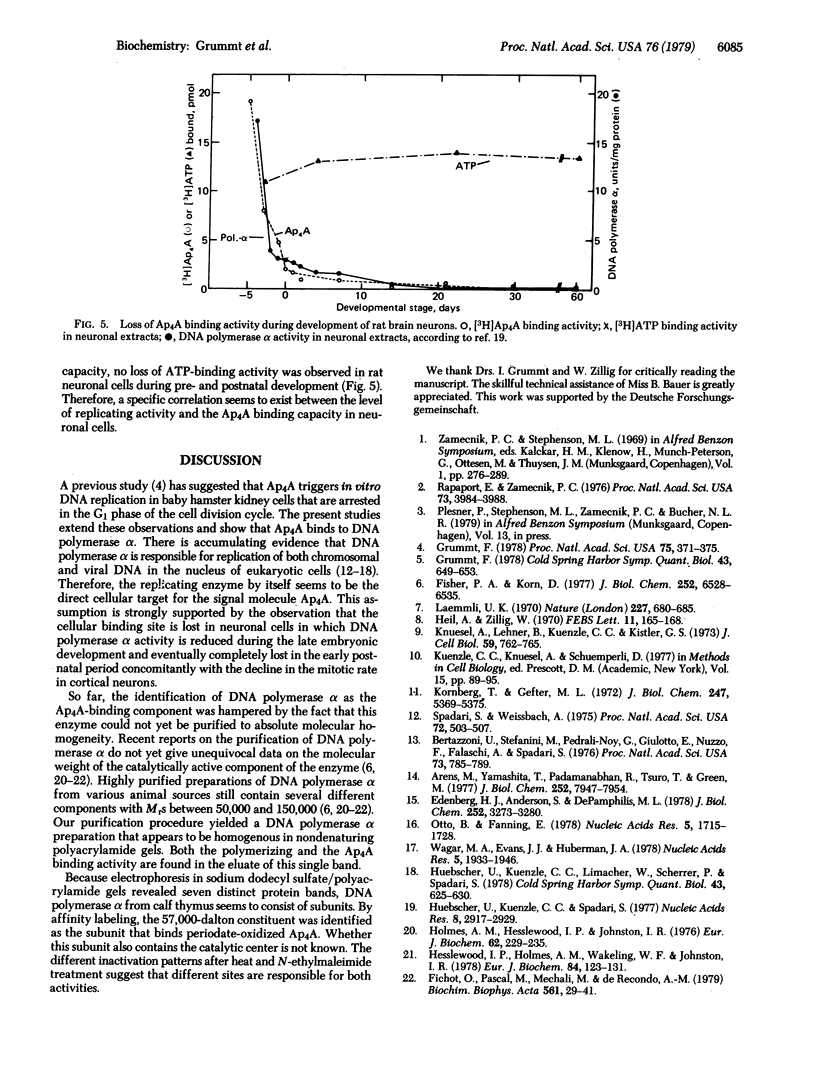
By equilibrium dialysis a disadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P2-tetraphosphate (Ap4A) binding activity is shown to be present in mammalian cells. The Ap4A binding activity copurifies with DNA polymerase alpha during the isolation procedure, which includes chromatography on phospho-, DEAE-, and DNA-cellulose; gel filtration; sucrose gradient centrifugation; and electrophoresis in nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels. After these purification steps, DNA polymerase alpha appears to be homogeneous in nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels. Sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of such a purified DNA polymerase alpha preparation reveals seven distinct protein bands with apparent Mrs of 64,000, 63,000, 62,000, 60,000, 57,000, 55,000, and 52,000. By affinity labeling, the protein with Mr 57,000 has been shown to be the Ap4A-binding constituent of DNA polymerase alpha. The binding activity of DNA polymerase alpha for Ap4A is highly specific because neither structural analogs nor several other adenine nucleotides compete effectively with Ap4A for its binding site. The Ap4A binding site is lost in neuronal cells during maturation of rat brains concomitantly with the loss of DNA polymerase alpha and mitotic activity in those cells. From these results, DNA polymerase seems to be the intracellular target of Ap4A. This is discussed in respect to the recently reported of Ap4A to trigger DNA replication in quiescent mammalian cells [Grummt, F. (1978) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 371-375].
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arens M., Yamashita T., Padmanabhan R., Tsuruo T., Green M. Adenovirus deoxyribonucleic acid replication. Characterization of the enzyme activities of a soluble replication system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):7947–7954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertazzoni U., Stefanini M., Noy G. P., Giulotto E., Nuzzo F., Falaschi A., Spadari S. Variations of DNA polymerase-alpha and -beta during prolonged stimulation of human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):785–789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenberg H. J., Anderson S., DePamphilis M. L. Involvement of DNA polymerase alpha in simian virus 40 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3273–3280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichot O., Pascal M., Mechali M., de Recondo A. M. DNA polymerase-alpha from regenerating rat liver. Catalytic properties of the highly purified enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 26;561(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90487-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Korn D. DNA polymerase-alpha. Purification and structural characterization of the near homogeneous enzyme from human KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6528–6535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt F. Diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P4-tetraphosphate triggers initiation of in vitro DNA replication in baby hamster kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):371–375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt F. Diadenosine tetraphosphate triggers in vitro DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):649–653. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heil A., Zillig W. Reconstitution of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase from isolated subunits as a tool for the elucidation of the role of the subunits in transcription. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec;11(3):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80519-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesslewood I. P., Holmes A. M., Wakeling W. F., Johnston I. R. Studies on the purification and properties of a 6.8-S DNA polymerase activity found in calf-thymus DNA polymerase-alpha fraction. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):123–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes A. M., Hesslewood I. P., Johnston I. R. Evidence that DNA polymerase-alpha of calf thymus contains a subunit of molecular weight 155000. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 16;62(2):229–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Kuenzle C. C., Limacher W., Scherrer P., Spadari S. Functions of DNA polymerases alpha, beta, and gamma in neurons during development. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):625–629. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Kuenzle C. C., Spadari S. Variation of DNA polymerases-alpha, -beta. and -gamma during perinatal tissue growth and differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2917–2929. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knüsel A., Lehner B., Kuenzle C. C., Kistler G. S. Isolation of neuronal nuclei from rat brain cortex. J Cell Biol. 1973 Dec;59(3):762–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.3.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto B., Fanning E. DNA polymerase alpha is associated with replicating SV40 nucleoprotein complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1715–1728. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport E., Zamecnik P. C. Presence of diadenosine 5',5''' -P1, P4-tetraphosphate (Ap4A) in mamalian cells in levels varying widely with proliferative activity of the tissue: a possible positive "pleiotypic activator". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3984–3988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadari S., Weissbach A. RNA-primed DNA synthesis: specific catalysis by HeLa cell DNA polymerase alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):503–507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waqar M. A., Evans M. J., Huberman J. A. Effect of 2',3'-dideoxythymidine-5'-triphosphate on HeLa cell in vitro DNA synthesis: evidence that DNA polymerase alpha is the only polymerase required for cellular DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):1933–1946. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]