Abstract
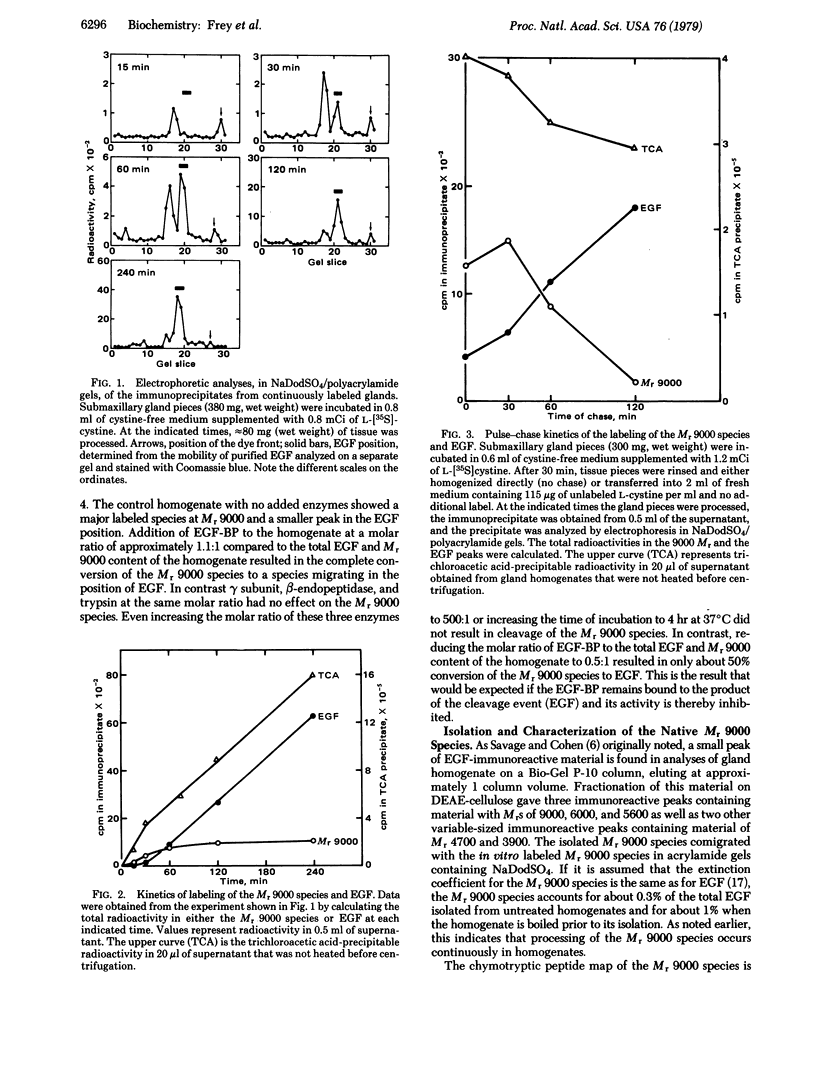
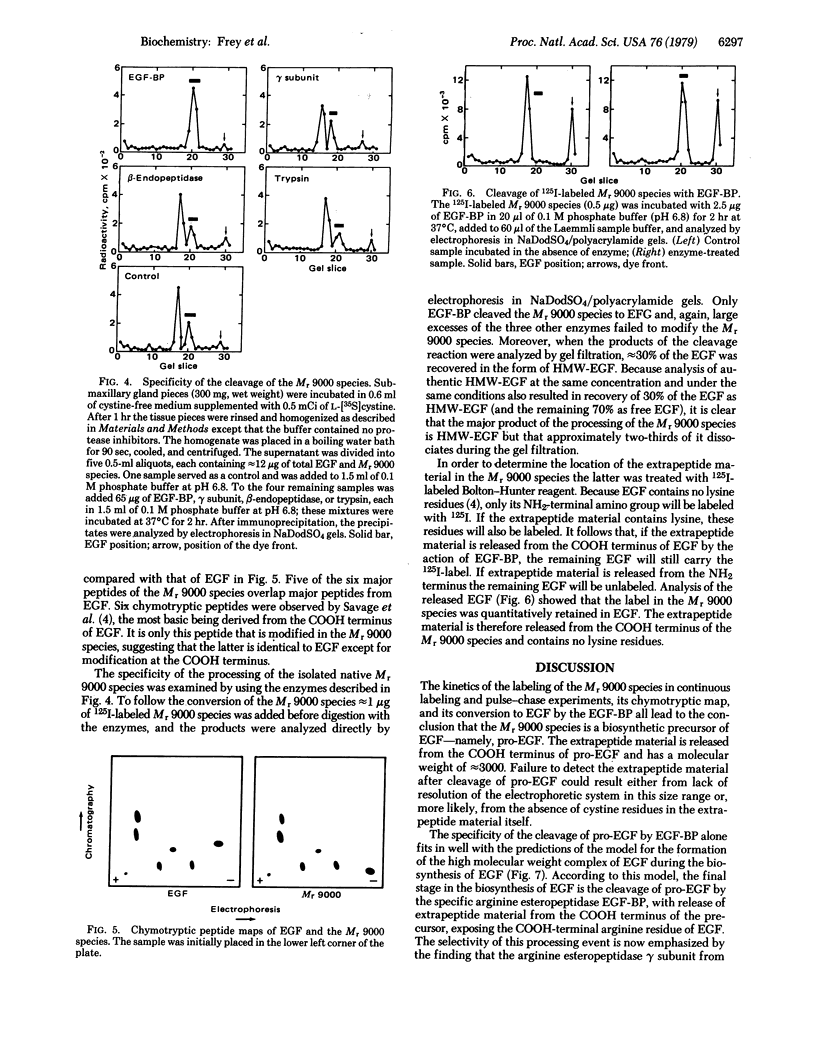
The biosynthesis of epidermal growth factor (EGF) was studied in mouse submaxillary glands incubated with L-[35S]cystine. EGF and EGF-like proteins were isolated from the gland homogenates by immunoprecipitation with anti-EGF antiserum. The major species appearing after short labeling periods is significantly larger (Mr, 9000) than EGF. The label in the Mr 9000 species plateaus after 1 hr whereas tha in EGF continuously increases. When glands are chased with unlabeled L-cystine after a brief period of labeling, the Mr 9000 peak decreases and a corresponding amount of label appears in EGF. The Mr 9000 species was isolated from boiled homogenates in which it accounts for approximately 1% of the total EGF content. It contains five of the six chymotryptic peptides of EGF and a sixth peptide which is a modified form of the COOH-terminal chymotryptic peptide of EGF. Of the arginyl esteropeptidases, gamma subunit of 7S nerve growth factor, beta-endopeptidase, trypsin, and EGF-binding protein, only the latter converts the isolated Mr 9000 species to EGF. The extrapeptide material released in the conversion comes from the COOH terminus of the Mr 9000 species. These results suggest that the Mr 9000 species is a biosynthetic precursor of EGF and that the EGF-binding protein is the specific intracellular cleaving enzyme that converts the precursor to EGF. In the process, the stable high molecular weight complex of EGF is formed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger E. A., Shooter E. M. Biosynthesis of beta nerve growth factor in mouse submaxillary glands. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):804–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Shooter E. M. Evidence for pro-beta-nerve growth factor, a biosynthetic precursor to beta-nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3647–3651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byyny R. L., Orth D. N., Cohen S. Radioimmunoassay of epidermal growth factor. Endocrinology. 1972 May;90(5):1261–1266. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-5-1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1555–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K., Tregear G. W. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay in antibody-coated tubes. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1570–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Keim P., Steiner D. F. Cell-free synthesis of rat preproinsulins: characterization and partial amino acid sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1964–1968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. T., Barker W. C., Dayhoff M. O. Epidermal growth factor: internal duplication and probable relationship to pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 8;60(3):1020–1028. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90415-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii D. N., Shooter E. M. Regulation of nerve growth factor synthesis in mouse submaxillary glands by testosterone. J Neurochem. 1975 Dec;25(6):843–851. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb04416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Habener J. F., Ernst M. D., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A. Pre-proparathyroid hormone: analysis of radioactive tryptic peptides and amino acid sequence. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 13;15(1):15–19. doi: 10.1021/bi00646a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R., Devillers-Thiery A., Blobel G. Nascent prehormones are intermediates in the biosynthesis of authentic bovine pituitary growth hormone and prolactin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2432–2436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Inagami T., Cohen S. The primary structure of epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7612–7621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Server A. C., Shooter E. M. Comparison of the arginine esteropeptidases associated with the nerve and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 10;251(1):165–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Server A. C., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:339–409. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Server A. C., Sutter A., Shooter E. M. Modification of the epidermal growth factor affecting the stability of its high molecular weight complex. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1188–1196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. P., Varon S., Shooter E. M. Multiple forms of the nerve growth factor protein and its subunits. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3259–3268. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Cohen S., Mitchell W. M. Epidermal growth factor: high and low molecular weight forms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):164–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Mitchell W. M., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Physical and chemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5928–5934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. H., Shooter E. M. Structural modification of the NH2 terminus of nerve growth factor. Purification and characterization of beta-nerve growth factor endopeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6002–6009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


