Abstract
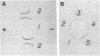
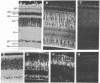
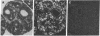
The cellular localization of glutamine synthetase [GSase; L-glutamate:ammonia ligase(ADP)-forming), EC 6.3.1.2] induced by cortisol in the neural retina of chicken embryos was investigated by immunostaining with GSase-specific antiserum and indirect immunofluorescence. In organ cultures of retina tissue, and in the retina in vivo, hormone-induced GSase was found to be confined only to the Müller fibers (retinoglia). Also, in mature chicken retina, which contains a very high level of GSase, the enzyme was detected solely in Müller fibers. In short-term monolayer cultures of dispersed embryonic retina cells, there was no GSase induction and no immunodetectable increase in enzyme level. However, when the dispersed cells were reaggregated and they restituted retinotypic cell associations, GSase could be induced and it was localized in Müller fibers. The results suggest that, in addition to the hormonal stimulus, contact-dependent interactions between Müller glia cells and retina neurons are involved in the mechanism of GSase induction in the retina.
Full text
PDF

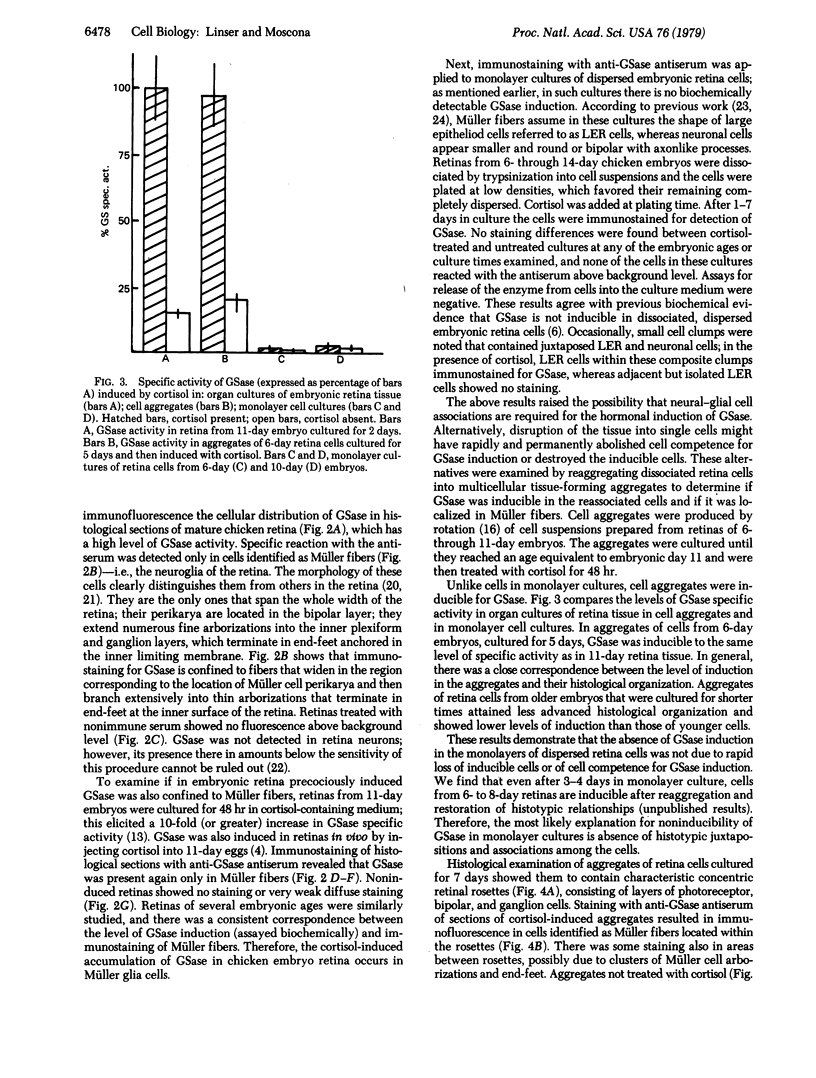


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Combes P. C., Privat A., Pessac B., Calothy G. Differentiation of chick embryo neuroretina cells in monolayer cultures. An ultrastructural study. I. Seven-day retina. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Dec 13;185(2):159–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00220661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E., Sellinger O. Z., Rodríguez de Lores, Alberici M., Zieher L. M. Nerve endings in methionine sulphoximine convulsant rats, a neurochemical and ultrastructural study. J Neurochem. 1967 Jan;14(1):81–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfield S., Moscona A. A. Glutamine synthetase in the embryonic chick neural retina: the effects of cycloheximide on the conservation of labile templates for enzyme synthesis. Mech Ageing Dev. 1974 Nov-Dec;3(5-6):253–269. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(74)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. E., Moscona A. A. Effects of cytosine arabinoside on differential gene expression in embryonic neural retina. II. Immunochemical studies on the accumulation of glutamine synthetase. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):30–42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz P. B., Moscona A. A. Stimulation of DNA synthesis by ouabain and concanavalin A in cultures of embryonic neural retina cells. Cell Differ. 1976 Jul;5(2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(76)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy A. J., Voaden M. J., Marshall J. Glutamate metabolism in the frog retina. Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):50–52. doi: 10.1038/252050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labourdette G., Mahony J. B., Brown I. R., Marks A. Regulation of synthesis of a brain-specific protein in monolayer cultures of clonal rat glial cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec;81(3):591–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELLER K., GLEES P. THE DIFFERENTIATION OF NEUROGLIA-MUELLER-CELLS IN THE RETINA OF CHICK. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1965 May 6;66(3):321–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00334715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSCONA A. Rotation-mediated histogenetic aggregation of dissociated cells. A quantifiable approach to cell interactions in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Jan;22:455–475. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Hernandez A., Bell K. P., Norenberg M. D. Glutamine synthetase: glial localization in brain. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1356–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.14400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. E., Moscona A. A. The induction of glutamine synthetase in cell aggregates of embryonic neural retina: correlations with differentation and multicellular organization. Dev Biol. 1971 Jul;25(3):420–444. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Moscona M. H. Aggregation of embryonic cells in a serum-free medium and its inhibition at suboptimal temperatures. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Mar;41(3):697–702. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(66)80126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Moscona M. H., Saenz N. Enzyme induction in embryonic retina: the role of transcription and translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Piddington R. Stimulation by hydrocortisone of premature changes in the developmental pattern of glutamine synthetase in embryonic retina. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 29;121(2):409–411. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Wiens A. W. Proflavine as a differential probe of gene expression: inhibition of glutamine synthetase induction in embryonic retina. Dev Biol. 1975 May;44(1):33–45. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90374-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona M., Frenkel N., Moscona A. A. Regulatory mechanisms in the induction of glutamine synthetase in the embryonic retina: immunochemical studies. Dev Biol. 1972 May;28(1):229–241. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norenberg M. D. Distribution of glutamine synthetase in the rat central nervous system. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Mar;27(3):756–762. doi: 10.1177/27.3.39099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piddington R., Moscona A. A. Precocious induction of retinal glutamine synthetase by hydrocortisone in the embryo and in culture. Age-dependent differences in tissue response. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 25;141(2):429–432. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piddington R. Steroid control of the normal development of glutamine synthetase in the embryonic chick retina. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1970 Jun;23(3):729–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Mirsky R., Fields K. L., Lisak R. P., Dorfman S. H., Silberberg D. H., Gregson N. A., Leibowitz S., Kennedy M. C. Galactocerebroside is a specific cell-surface antigenic marker for oligodendrocytes in culture. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepe R. E., Norenberg M. D. Glutamine synthetase in the developing rat retina: an immunohistochemical study. Exp Eye Res. 1978 Oct;27(4):435–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(78)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepe R. E., Norenburg M. D. Müller cell localisation of glutamine synthetase in rat retina. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):654–655. doi: 10.1038/268654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar P. K., Fischman D. A., Goldwasser E., Moscona A. A. Isolation and characterization of glutamine synthetase from chicken neural retina. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7743–7749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar P. K., Moscona A. A. Glutamine synthetase induction in embryonic neural retina: immunochemical identification of polysomes involved in enzyme synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1667–1671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soh B. M., Sarkar P. K. Control of glutamine synthetase messenger RNA by hydrocortisone in the embryonic chick retina. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):316–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. S. Evidence for the compartmentation of glutamate metabolism in isolated rat retina. J Neurochem. 1974 Aug;23(2):337–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]