Abstract
In the title compound, C20H22N2O2, the piperidine ring adopts a chair conformation. The phenyl rings are inclined to one another by 80.1 (1)° and make dihedral angles of 46.1 (1) and 40.2 (1)° with the mean plane of the piperidine ring. In the crystal, pairs of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into inversion dimers. C—H⋯O interactions further link the molecules, forming a three-dimensional supramolecular network.
Related literature
For the synthesis of the title compound, see: Prathebha et al. (2013 ▶); Venkatraj et al. (2008 ▶). For the biological activity of piperdine derivatives, see: Ramalingan et al. (2004 ▶); Sergeant & May (1970 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For related structures, see: Al-abbasi et al. (2010 ▶); Ávila et al. (2010 ▶). For puckering parameters, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶).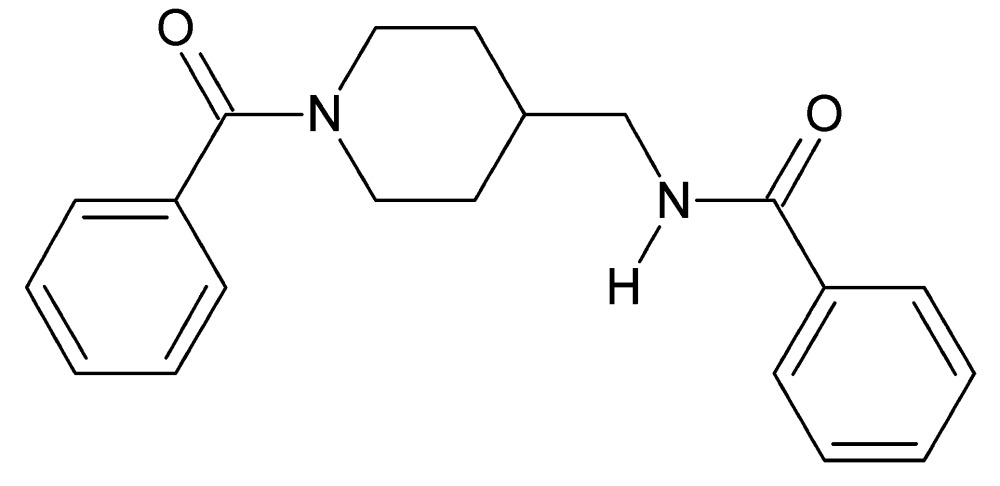
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H22N2O2
M r = 322.40
Triclinic,

a = 9.8039 (2) Å
b = 10.4453 (2) Å
c = 10.6765 (2) Å
α = 62.208 (1)°
β = 66.009 (1)°
γ = 68.150 (1)°
V = 860.80 (3) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.22 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.982, T max = 0.984
12912 measured reflections
3562 independent reflections
2929 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.028
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.043
wR(F 2) = 0.125
S = 1.04
3531 reflections
217 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.56 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2 and SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT and XPREP (Bruker, 2004 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR92 (Altomare et al., 1993 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012793/bt6968sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012793/bt6968Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012793/bt6968Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 987515
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C13—H13A⋯O1i | 0.97 | 2.60 | 3.5548 (18) | 169 |
| C3—H3⋯O2ii | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.3803 (17) | 167 |
| N2—H2A⋯O2ii | 0.86 | 2.11 | 2.9401 (15) | 162 |
| C8—H8⋯O1iii | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.4506 (19) | 176 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Professor Velmurugan, Centre for Advanced Study in Crystallography and Biophysics, University of Madras, for providing data-collection and computer facilities.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
Biologically active alkaloids of substituted piperidines have been targeted for their total or partial synthesis (Ramalingan et al., 2004). Piperidines are known to have CNS depressant action at low dosage levels and stimulant activity with increased doses. In addition, the nucleus also possesses analgesic, anglionic blocking and anesthetic properties as well (Sergeant & May, 1970). We report in this communication, the synthesis and crystal structure of a new piperidine derivative.
The phenyl rings form dihedral angles of 46.1 (1)° and 40.2 (1)°, respectively, with the best plane through the piperidine ring atoms. The C—N distances [1.337 (2)- 1.468 (2) Å] are in the normal range and are in good agreement with values of a similar reported structure (Ávila et al., 2010). The piperdine ring adopts a chair conformation with puckering parameters (Cremer & Pople, 1975) of q2 = 0.0351 (1) Å, phi2 = -50.61 (3)° q3 = 0.5633 (1) Å, QT = 0.5644 (2) Å and θ2 = 3.67 (2)°.
The crystal packing shows N-H···O hydrogen bonds linking the molecules to centrosymmetric dimers (Fig. 2).
S2. Experimental
The procedure (Prathebha et al., 2013, Venkatraj et al., 2008) adopted in the synthesis of the typical diamide is as follows: In a 250 mL round-bottomed flask 4-methyl piperidine (0.01 mol) was taken in, to which 100 mL of ethyl methyl ketone was added and stirred at room temperature. After 5 minutes, triethylamine (0.02 mol) was added and the mixture was stirred for 15 minutes. Then, benzoyl chloride (0.02 mol) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for about 2 h. A white precipitate of triethyl ammonium chloride was formed. It was filtered and the filterate was evaporated to get the crude product. The crude product was recrystallized twice from ethyl methyl ketone. Melting Point: 127 °C, yield: 85%.
S3. Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and treated as riding on their parent atoms with C—H = 0.93 - 0.97 Å and N—H. 87 with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq (C-methyl) and = 1.2U eq(N,C) for other H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.

The molecular structure of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The packing of the molecules in the crystal structure. The dashed lines indicate the hydrogen bonds.
Fig. 3.

Experimental procedure
Crystal data
| C20H22N2O2 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 322.40 | F(000) = 344 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.244 Mg m−3Dm = 1.188 Mg m−3Dm measured by not measured |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.8039 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 3562 reflections |
| b = 10.4453 (2) Å | θ = 2.3–26.5° |
| c = 10.6765 (2) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| α = 62.208 (1)° | T = 293 K |
| β = 66.009 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| γ = 68.150 (1)° | 0.22 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| V = 860.80 (3) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3562 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2929 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.028 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 26.5°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.982, Tmax = 0.984 | k = −13→13 |
| 12912 measured reflections | l = −13→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.125 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0625P)2 + 0.1352P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3531 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 217 parameters | Δρmax = 0.56 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.8259 (2) | 0.13083 (19) | −0.42562 (19) | 0.0716 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.8464 | 0.0451 | −0.4428 | 0.086* | |
| C2 | 0.9233 (2) | 0.14731 (18) | −0.37349 (19) | 0.0687 (4) | |
| H2 | 1.0097 | 0.0725 | −0.3554 | 0.082* | |
| C3 | 0.89322 (16) | 0.27493 (16) | −0.34793 (16) | 0.0557 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.9605 | 0.2865 | −0.3147 | 0.067* | |
| C4 | 0.76373 (14) | 0.38484 (14) | −0.37167 (13) | 0.0462 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.6671 (2) | 0.3663 (2) | −0.4234 (2) | 0.0706 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.5791 | 0.4396 | −0.4391 | 0.085* | |
| C6 | 0.6987 (2) | 0.2410 (2) | −0.4522 (2) | 0.0805 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.6338 | 0.2313 | −0.4895 | 0.097* | |
| C7 | 0.75109 (14) | 0.87255 (14) | 0.19275 (14) | 0.0459 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.68184 (17) | 0.89913 (16) | 0.32258 (16) | 0.0555 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.6521 | 0.8227 | 0.4115 | 0.067* | |
| C9 | 0.65695 (19) | 1.03945 (18) | 0.32005 (18) | 0.0655 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.6091 | 1.0571 | 0.4075 | 0.079* | |
| C10 | 0.7016 (2) | 1.15236 (17) | 0.1911 (2) | 0.0705 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.6842 | 1.2465 | 0.1904 | 0.085* | |
| C11 | 0.7722 (2) | 1.12603 (19) | 0.0627 (2) | 0.0797 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.8044 | 1.2023 | −0.0254 | 0.096* | |
| C12 | 0.7961 (2) | 0.98681 (18) | 0.06295 (17) | 0.0687 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.8428 | 0.9704 | −0.0251 | 0.082* | |
| C13 | 0.74162 (16) | 0.54026 (13) | 0.13846 (15) | 0.0491 (3) | |
| H13A | 0.6493 | 0.5026 | 0.1824 | 0.059* | |
| H13B | 0.8142 | 0.4717 | 0.1942 | 0.059* | |
| C14 | 0.80986 (15) | 0.55186 (13) | −0.02091 (15) | 0.0489 (3) | |
| H14A | 0.8293 | 0.4553 | −0.0244 | 0.059* | |
| H14B | 0.9072 | 0.5801 | −0.0608 | 0.059* | |
| C15 | 0.70474 (15) | 0.66528 (13) | −0.11683 (15) | 0.0485 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.6124 | 0.6289 | −0.0839 | 0.058* | |
| C16 | 0.65720 (17) | 0.81395 (14) | −0.09792 (16) | 0.0545 (3) | |
| H16A | 0.7453 | 0.8581 | −0.1435 | 0.065* | |
| H16B | 0.5798 | 0.8810 | −0.1483 | 0.065* | |
| C17 | 0.59429 (16) | 0.79586 (15) | 0.06342 (16) | 0.0535 (3) | |
| H17A | 0.5726 | 0.8908 | 0.0712 | 0.064* | |
| H17B | 0.4992 | 0.7629 | 0.1067 | 0.064* | |
| C18 | 0.78445 (14) | 0.71670 (14) | 0.20002 (14) | 0.0455 (3) | |
| C19 | 0.78213 (19) | 0.68686 (15) | −0.27908 (16) | 0.0573 (3) | |
| H19A | 0.7154 | 0.7658 | −0.3369 | 0.069* | |
| H19B | 0.8762 | 0.7184 | −0.3109 | 0.069* | |
| C20 | 0.71745 (15) | 0.52476 (14) | −0.34233 (14) | 0.0483 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.70509 (12) | 0.68746 (11) | 0.14379 (12) | 0.0470 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.81811 (14) | 0.55385 (12) | −0.30954 (13) | 0.0534 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.9056 | 0.4929 | −0.3064 | 0.064* | |
| O1 | 0.59104 (12) | 0.60806 (12) | −0.34789 (13) | 0.0697 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.88170 (13) | 0.62016 (11) | 0.25938 (13) | 0.0689 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0865 (11) | 0.0708 (10) | 0.0764 (10) | −0.0293 (9) | −0.0096 (9) | −0.0448 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0719 (10) | 0.0632 (9) | 0.0812 (11) | −0.0047 (7) | −0.0229 (8) | −0.0417 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0563 (8) | 0.0607 (8) | 0.0644 (8) | −0.0080 (6) | −0.0217 (6) | −0.0346 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0523 (7) | 0.0514 (7) | 0.0393 (6) | −0.0144 (5) | −0.0127 (5) | −0.0186 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0704 (10) | 0.0781 (11) | 0.0874 (11) | −0.0067 (8) | −0.0393 (9) | −0.0430 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0848 (12) | 0.0992 (13) | 0.0971 (13) | −0.0290 (10) | −0.0304 (10) | −0.0573 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0473 (7) | 0.0477 (7) | 0.0529 (7) | −0.0087 (5) | −0.0160 (5) | −0.0267 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0653 (8) | 0.0561 (8) | 0.0526 (7) | −0.0163 (6) | −0.0129 (6) | −0.0274 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0734 (10) | 0.0675 (9) | 0.0698 (9) | −0.0176 (7) | −0.0082 (8) | −0.0455 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0833 (11) | 0.0542 (8) | 0.0871 (11) | −0.0199 (8) | −0.0168 (9) | −0.0393 (8) |
| C11 | 0.1130 (14) | 0.0594 (9) | 0.0692 (10) | −0.0401 (9) | −0.0106 (10) | −0.0232 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0919 (11) | 0.0662 (9) | 0.0542 (8) | −0.0308 (8) | −0.0042 (8) | −0.0314 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0590 (7) | 0.0381 (6) | 0.0579 (8) | −0.0068 (5) | −0.0231 (6) | −0.0217 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0568 (7) | 0.0382 (6) | 0.0582 (8) | −0.0033 (5) | −0.0214 (6) | −0.0244 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0561 (7) | 0.0432 (7) | 0.0580 (8) | −0.0076 (5) | −0.0229 (6) | −0.0251 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0682 (8) | 0.0403 (7) | 0.0666 (8) | 0.0011 (6) | −0.0362 (7) | −0.0249 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0558 (7) | 0.0474 (7) | 0.0720 (9) | 0.0045 (6) | −0.0318 (7) | −0.0344 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0471 (6) | 0.0467 (7) | 0.0497 (7) | −0.0062 (5) | −0.0158 (5) | −0.0249 (5) |
| C19 | 0.0773 (9) | 0.0465 (7) | 0.0576 (8) | −0.0108 (6) | −0.0268 (7) | −0.0228 (6) |
| C20 | 0.0530 (7) | 0.0493 (7) | 0.0442 (6) | −0.0080 (6) | −0.0163 (5) | −0.0190 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0534 (6) | 0.0408 (5) | 0.0580 (6) | −0.0019 (4) | −0.0242 (5) | −0.0265 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0609 (7) | 0.0520 (6) | 0.0609 (7) | −0.0032 (5) | −0.0262 (5) | −0.0314 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0602 (6) | 0.0635 (6) | 0.0921 (8) | 0.0024 (5) | −0.0320 (6) | −0.0379 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0756 (7) | 0.0571 (6) | 0.0973 (8) | 0.0054 (5) | −0.0534 (6) | −0.0382 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C6 | 1.369 (3) | C13—N1 | 1.4665 (14) |
| C1—C2 | 1.377 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.5166 (18) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C13—H13A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3854 (19) | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C14—C15 | 1.5272 (18) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3782 (19) | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3788 (19) | C15—C19 | 1.5236 (19) |
| C4—C20 | 1.5026 (17) | C15—C16 | 1.5319 (16) |
| C5—C6 | 1.378 (2) | C15—H15 | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C16—C17 | 1.517 (2) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C16—H16A | 0.9700 |
| C7—C12 | 1.376 (2) | C16—H16B | 0.9700 |
| C7—C8 | 1.3830 (18) | C17—N1 | 1.4610 (16) |
| C7—C18 | 1.5065 (16) | C17—H17A | 0.9700 |
| C8—C9 | 1.3823 (19) | C17—H17B | 0.9700 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C18—O2 | 1.2277 (15) |
| C9—C10 | 1.363 (2) | C18—N1 | 1.3367 (16) |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C19—N2 | 1.4573 (16) |
| C10—C11 | 1.369 (2) | C19—H19A | 0.9700 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9300 | C19—H19B | 0.9700 |
| C11—C12 | 1.383 (2) | C20—O1 | 1.2270 (16) |
| C11—H11 | 0.9300 | C20—N2 | 1.3387 (17) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9300 | N2—H2A | 0.8600 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 119.84 (14) | C13—C14—C15 | 112.38 (10) |
| C6—C1—H1 | 120.1 | C13—C14—H14A | 109.1 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 120.1 | C15—C14—H14A | 109.1 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.26 (15) | C13—C14—H14B | 109.1 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.9 | C15—C14—H14B | 109.1 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.9 | H14A—C14—H14B | 107.9 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.12 (13) | C19—C15—C14 | 111.50 (11) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C19—C15—C16 | 109.95 (11) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C14—C15—C16 | 109.78 (10) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.85 (13) | C19—C15—H15 | 108.5 |
| C3—C4—C20 | 124.40 (11) | C14—C15—H15 | 108.5 |
| C5—C4—C20 | 116.74 (12) | C16—C15—H15 | 108.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.14 (15) | C17—C16—C15 | 111.99 (11) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.4 | C17—C16—H16A | 109.2 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.4 | C15—C16—H16A | 109.2 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.76 (14) | C17—C16—H16B | 109.2 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.1 | C15—C16—H16B | 109.2 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 | H16A—C16—H16B | 107.9 |
| C12—C7—C8 | 118.99 (12) | N1—C17—C16 | 110.21 (10) |
| C12—C7—C18 | 122.18 (12) | N1—C17—H17A | 109.6 |
| C8—C7—C18 | 118.70 (12) | C16—C17—H17A | 109.6 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 119.91 (13) | N1—C17—H17B | 109.6 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.0 | C16—C17—H17B | 109.6 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.0 | H17A—C17—H17B | 108.1 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.86 (14) | O2—C18—N1 | 122.09 (11) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.6 | O2—C18—C7 | 119.08 (11) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.6 | N1—C18—C7 | 118.82 (11) |
| C9—C10—C11 | 119.43 (14) | N2—C19—C15 | 113.75 (11) |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120.3 | N2—C19—H19A | 108.8 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.3 | C15—C19—H19A | 108.8 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 120.43 (15) | N2—C19—H19B | 108.8 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 119.8 | C15—C19—H19B | 108.8 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.8 | H19A—C19—H19B | 107.7 |
| C7—C12—C11 | 120.36 (14) | O1—C20—N2 | 121.84 (12) |
| C7—C12—H12 | 119.8 | O1—C20—C4 | 120.44 (12) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.8 | N2—C20—C4 | 117.72 (11) |
| N1—C13—C14 | 109.34 (10) | C18—N1—C17 | 126.14 (10) |
| N1—C13—H13A | 109.8 | C18—N1—C13 | 120.63 (10) |
| C14—C13—H13A | 109.8 | C17—N1—C13 | 112.60 (9) |
| N1—C13—H13B | 109.8 | C20—N2—C19 | 121.23 (11) |
| C14—C13—H13B | 109.8 | C20—N2—H2A | 119.4 |
| H13A—C13—H13B | 108.3 | C19—N2—H2A | 119.4 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.1 (3) | C12—C7—C18—O2 | 107.97 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.3 (2) | C8—C7—C18—O2 | −67.72 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.1 (2) | C12—C7—C18—N1 | −73.19 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4—C20 | 177.72 (13) | C8—C7—C18—N1 | 111.12 (14) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.4 (2) | C14—C15—C19—N2 | 63.59 (15) |
| C20—C4—C5—C6 | −179.32 (15) | C16—C15—C19—N2 | −174.42 (11) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.4 (3) | C3—C4—C20—O1 | −170.49 (13) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.7 (3) | C5—C4—C20—O1 | 8.4 (2) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | 0.9 (2) | C3—C4—C20—N2 | 9.15 (19) |
| C18—C7—C8—C9 | 176.74 (12) | C5—C4—C20—N2 | −172.00 (13) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.8 (2) | O2—C18—N1—C17 | −176.01 (13) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.1 (3) | C7—C18—N1—C17 | 5.18 (19) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.0 (3) | O2—C18—N1—C13 | −5.8 (2) |
| C8—C7—C12—C11 | 0.0 (2) | C7—C18—N1—C13 | 175.39 (11) |
| C18—C7—C12—C11 | −175.70 (15) | C16—C17—N1—C18 | 110.77 (14) |
| C10—C11—C12—C7 | −1.0 (3) | C16—C17—N1—C13 | −60.11 (14) |
| N1—C13—C14—C15 | −56.11 (14) | C14—C13—N1—C18 | −111.16 (13) |
| C13—C14—C15—C19 | 174.11 (10) | C14—C13—N1—C17 | 60.29 (14) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | 52.02 (15) | O1—C20—N2—C19 | −0.2 (2) |
| C19—C15—C16—C17 | −174.15 (11) | C4—C20—N2—C19 | −179.78 (11) |
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | −51.14 (15) | C15—C19—N2—C20 | 89.66 (15) |
| C15—C16—C17—N1 | 55.05 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C13—H13A···O1i | 0.97 | 2.60 | 3.5548 (18) | 169 |
| C3—H3···O2ii | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.3803 (17) | 167 |
| N2—H2A···O2ii | 0.86 | 2.11 | 2.9401 (15) | 162 |
| C8—H8···O1iii | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.4506 (19) | 176 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (ii) −x+2, −y+1, −z; (iii) x, y, z+1.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT6968).
References
- Al-abbasi, A. A., Yarmo, M. A. & Kassim, M. B. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Ávila, R. M. D., Landre, I. M. R., Souza, T. E., Veloso, M. P. & Doriguetto, A. C. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT, XPREP and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Prathebha, K., Revathi, B. K., Usha, G., Ponnuswamy, S. & Abdul Basheer, S. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ramalingan, C., Balasubramanian, S., Kabilan, S. & Vasudevan, M. (2004). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 39, 527–533. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sergeant, L. J. & May, E. L. (1970). J. Med. Chem. 13, 1061–1063.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Venkatraj, M., Ponnuswamy, S. & Jeyaraman, R. (2008). Indian J. Chem. Sect. B, 47, 411–426.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012793/bt6968sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012793/bt6968Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012793/bt6968Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 987515
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



