Abstract
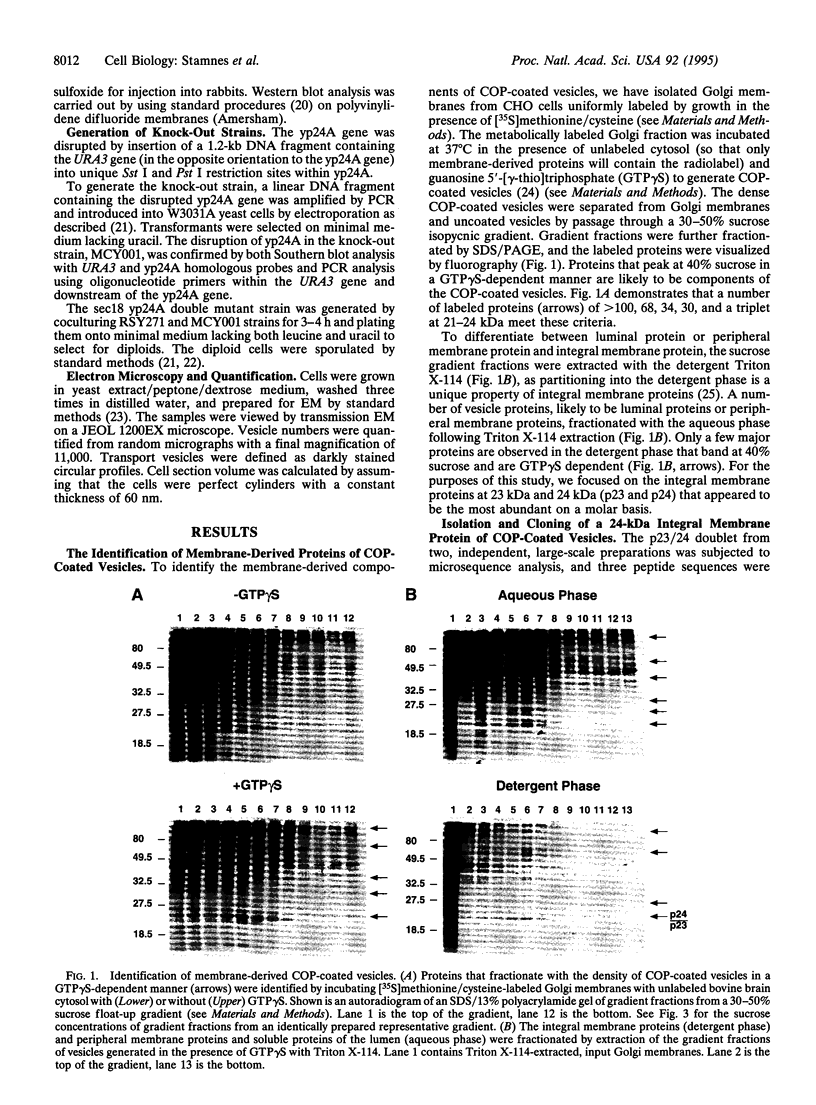
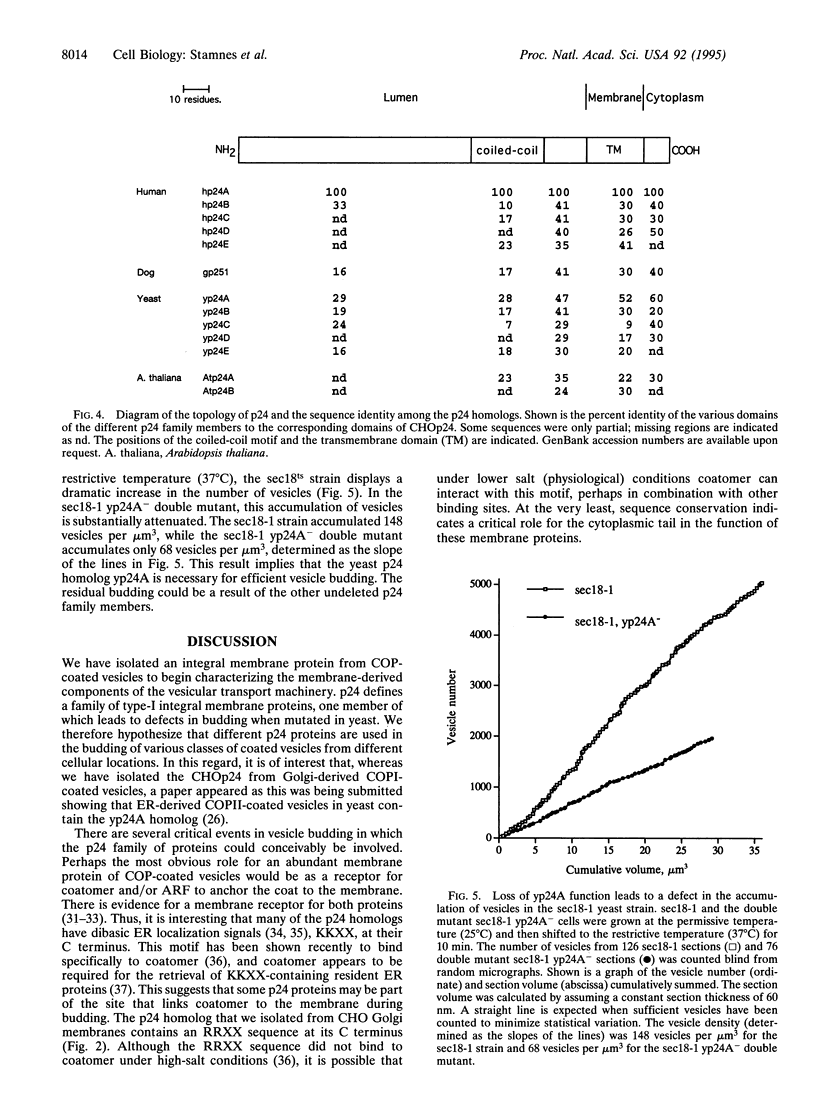
We have isolated a major integral membrane protein from Golgi-derived coatomer-coated vesicles. This 24-kDa protein, p24, defines a family of integral membrane proteins with homologs present in yeast and humans. In addition to sequence similarity, all p24 family members contain a motif with the characteristic heptad repeats found in coiled coils. When the yeast p24 isoform, yp24A, is knocked out in a strain defective for vesicle fusion, a dramatic reduction in the accumulation of transport vesicles is observed. Together, these results indicate a role for this protein family in the budding of coatamer-coated and other species of coated vesicles.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Dunphy W. G., Braell W. A., Rothman J. E. Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of the Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlowe C., Orci L., Yeung T., Hosobuchi M., Hamamoto S., Salama N., Rexach M. F., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Schekman R. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):895–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullough P. A., Hughson F. M., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion. Nature. 1994 Sep 1;371(6492):37–43. doi: 10.1038/371037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosson P., Letourneur F. Coatomer interaction with di-lysine endoplasmic reticulum retention motifs. Science. 1994 Mar 18;263(5153):1629–1631. doi: 10.1126/science.8128252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Cassel D., Kahn R. A., Klausner R. D. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding protein, is required for binding of the coatomer protein beta-COP to Golgi membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Finazzi D., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A inhibits Golgi membrane-catalysed exchange of guanine nucleotide onto ARF protein. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):350–352. doi: 10.1038/360350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio R. J., Jackson-Machelski E., Heuckeroth R. O., Olins P. O., Devine C. S., Yonemoto W., Slice L. W., Taylor S. S., Gordon J. I. Protein N-myristoylation in Escherichia coli: reconstitution of a eukaryotic protein modification in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elicone C., Lui M., Geromanos S., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P. Microbore reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic purification of peptides for combined chemical sequencing-laser-desorption mass spectrometric analysis. J Chromatogr A. 1994 Jul 29;676(1):121–137. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(94)00089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms J. B., Palmer D. J., Rothman J. E. Two distinct populations of ARF bound to Golgi membranes. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(4):751–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.4.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. R., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. Identification of a consensus motif for retention of transmembrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3153–3162. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Schekman R. Distinct sets of SEC genes govern transport vesicle formation and fusion early in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):723–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90483-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Gaynor E. C., Hennecke S., Démollière C., Duden R., Emr S. D., Riezman H., Cosson P. Coatomer is essential for retrieval of dilysine-tagged proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1199–1207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra V., Serafini T., Orci L., Shepherd J. C., Rothman J. E. Purification of a novel class of coated vesicles mediating biosynthetic protein transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90847-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Jackson M., Peterson P. A. Short cytoplasmic sequences serve as retention signals for transmembrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):707–718. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Palmer D. J., Ravazzola M., Perrelet A., Amherdt M., Rothman J. E. Budding from Golgi membranes requires the coatomer complex of non-clathrin coat proteins. Nature. 1993 Apr 15;362(6421):648–652. doi: 10.1038/362648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann J., Orci L., Tani K., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Elazar Z., Rothman J. E. Stepwise assembly of functionally active transport vesicles. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):1015–1025. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90545-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. J., Helms J. B., Beckers C. J., Orci L., Rothman J. E. Binding of coatomer to Golgi membranes requires ADP-ribosylation factor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):12083–12089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):55–63. doi: 10.1038/372055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Warren G. Implications of the SNARE hypothesis for intracellular membrane topology and dynamics. Curr Biol. 1994 Mar 1;4(3):220–233. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmöller F., Singer-Krüger B., Schröder S., Krüger U., Barlowe C., Riezman H. The absence of Emp24p, a component of ER-derived COPII-coated vesicles, causes a defect in transport of selected proteins to the Golgi. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 3;14(7):1329–1339. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini T., Orci L., Amherdt M., Brunner M., Kahn R. A., Rothman J. E. ADP-ribosylation factor is a subunit of the coat of Golgi-derived COP-coated vesicles: a novel role for a GTP-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):239–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90176-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini T., Stenbeck G., Brecht A., Lottspeich F., Orci L., Rothman J. E., Wieland F. T. A coat subunit of Golgi-derived non-clathrin-coated vesicles with homology to the clathrin-coated vesicle coat protein beta-adaptin. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):215–220. doi: 10.1038/349215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer-Krüger B., Frank R., Crausaz F., Riezman H. Partial purification and characterization of early and late endosomes from yeast. Identification of four novel proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14376–14386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamnes M. A., Rothman J. E. The binding of AP-1 clathrin adaptor particles to Golgi membranes requires ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding protein. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90277-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Rothman J. E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawa G., Orci L., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Helms J. B., Rothman J. E. Hydrolysis of bound GTP by ARF protein triggers uncoating of Golgi-derived COP-coated vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 1):1365–1371. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempst P., Link A. J., Riviere L. R., Fleming M., Elicone C. Internal sequence analysis of proteins separated on polyacrylamide gels at the submicrogram level: improved methods, applications and gene cloning strategies. Electrophoresis. 1990 Jul;11(7):537–553. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada I., Rindress D., Cameron P. H., Ou W. J., Doherty J. J., 2nd, Louvard D., Bell A. W., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Bergeron J. J. SSR alpha and associated calnexin are major calcium binding proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19599–19610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Beckers C. J., Rothman J. E. Purification of coat protomers. Methods Enzymol. 1992;219:331–337. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)19033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss O., Holden J., Rulka C., Kahn R. A. Nucleotide binding and cofactor activities of purified bovine brain and bacterially expressed ADP-ribosylation factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21066–21072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




