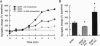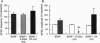Abstract
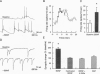
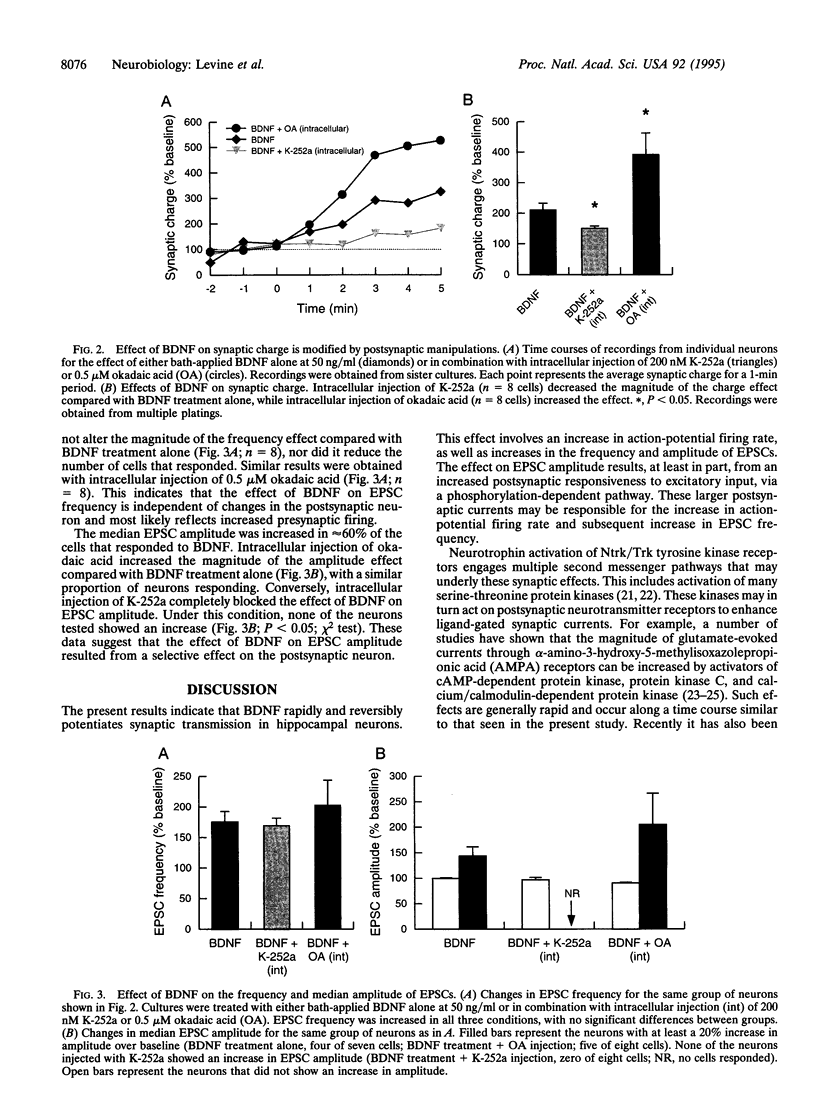
Although neurotrophins are primarily associated with long-term effects on neuronal survival and differentiation, recent studies have shown that acute changes in synaptic transmission can also be produced. In the hippocampus, an area critically involved in learning and memory, we have found that brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) rapidly enhanced synaptic efficacy through a previously unreported mechanism--increased postsynaptic responsiveness via a phosphorylation-dependent pathway. Within minutes of BDNF application to cultured hippocampal neurons, spontaneous firing rate was dramatically increased, as were the frequency and amplitude of excitatory postsynaptic currents. The increased frequency of postsynaptic currents resulted from the change in presynaptic firing. However, the increased amplitude was postsynaptic in origin because it was selectively blocked by intracellular injection of the tyrosine kinase receptor (Ntrk2/TrkB) inhibitor K-252a and potentiated by injection of the phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid. These results suggest a role for BDNF in the modulation of synaptic transmission in the hippocampus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg M. M., Sternberg D. W., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. K-252a inhibits nerve growth factor-induced trk proto-oncogene tyrosine phosphorylation and kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berninger B., García D. E., Inagaki N., Hahnel C., Lindholm D. BDNF and NT-3 induce intracellular Ca2+ elevation in hippocampal neurones. Neuroreport. 1993 Sep 30;4(12):1303–1306. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199309150-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackstone C., Murphy T. H., Moss S. J., Baraban J. M., Huganir R. L. Cyclic AMP and synaptic activity-dependent phosphorylation of AMPA-preferring glutamate receptors. J Neurosci. 1994 Dec;14(12):7585–7593. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-12-07585.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrén E., Pitkänen M., Sirviö J., Parsadanian A., Lindholm D., Thoenen H., Riekkinen P. J. The induction of LTP increases BDNF and NGF mRNA but decreases NT-3 mRNA in the dentate gyrus. Neuroreport. 1993 Jul;4(7):895–898. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199307000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. M. The role of neurotrophins in the developing nervous system. J Neurobiol. 1994 Nov;25(11):1334–1348. doi: 10.1002/neu.480251103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P., Jen J., Nairn A. C., Stevens C. F. Enhancement of the glutamate response by cAMP-dependent protein kinase in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1135–1138. doi: 10.1126/science.1716001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang H., Schuman E. M. Long-lasting neurotrophin-induced enhancement of synaptic transmission in the adult hippocampus. Science. 1995 Mar 17;267(5204):1658–1662. doi: 10.1126/science.7886457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Stephens R. M. Neurotrophin signal transduction by the Trk receptor. J Neurobiol. 1994 Nov;25(11):1404–1417. doi: 10.1002/neu.480251108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan K., Halegoua S. Signal transduction pathways in neuronal differentiation. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Feb;3(1):14–19. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller B. U., Hollmann M., Heinemann S., Konnerth A. Calcium influx through subunits GluR1/GluR3 of kainate/AMPA receptor channels is regulated by cAMP dependent protein kinase. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):891–896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05127.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. G., Wang T., Olafsson P., Lu B. Neurotrophin 3 potentiates neuronal activity and inhibits gamma-aminobutyratergic synaptic transmission in cortical neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12341–12345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M., Parada L. F. Expression of the tyrosine kinase receptor gene trkB is confined to the murine embryonic and adult nervous system. Development. 1990 Aug;109(4):845–850. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.4.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Nanduri V., Jing S. A., Lamballe F., Tapley P., Bryant S., Cordon-Cardo C., Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F., Barbacid M. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase is a receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90628-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipper M., Leung L. S., Zhao D., Rylett R. J. Short-term modulation of glutamatergic synapses in adult rat hippocampus by NGF. Neuroreport. 1994 Dec 20;5(18):2433–2436. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199412000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipper M., da Penha Berzaghi M., Blöchl A., Breer H., Thoenen H., Lindholm D. Positive feedback between acetylcholine and the neurotrophins nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1994 Apr 1;6(4):668–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1994.tb00312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knüsel B., Hefti F. K-252 compounds: modulators of neurotrophin signal transduction. J Neurochem. 1992 Dec;59(6):1987–1996. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knüsel B., Kaplan D. R., Winslow J. W., Rosenthal A., Burton L. E., Beck K. D., Rabin S., Nikolics K., Hefti F. K-252b selectively potentiates cellular actions and trk tyrosine phosphorylation mediated by neurotrophin-3. J Neurochem. 1992 Aug;59(2):715–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindefors N., Ernfors P., Falkenberg T., Persson H. Septal cholinergic afferents regulate expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and beta-nerve growth factor mRNA in rat hippocampus. Exp Brain Res. 1992;88(1):78–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02259130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohof A. M., Ip N. Y., Poo M. M. Potentiation of developing neuromuscular synapses by the neurotrophins NT-3 and BDNF. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):350–353. doi: 10.1038/363350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B., Yokoyama M., Dreyfus C. F., Black I. B. Depolarizing stimuli regulate nerve growth factor gene expression in cultured hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6289–6292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B., Yokoyama M., Dreyfus C. F., Black I. B. NGF gene expression in actively growing brain glia. J Neurosci. 1991 Feb;11(2):318–326. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-02-00318.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlio J. P., Ernfors P., Jaber M., Persson H. Molecular cloning of rat trkC and distribution of cells expressing messenger RNAs for members of the trk family in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1992 Dec;51(3):513–532. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90292-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye S. H., Squinto S. P., Glass D. J., Stitt T. N., Hantzopoulos P., Macchi M. J., Lindsay N. S., Ip N. Y., Yancopoulos G. D. K-252a and staurosporine selectively block autophosphorylation of neurotrophin receptors and neurotrophin-mediated responses. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jun;3(6):677–686. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.6.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S. L., Grover L. M., Schwartzkroin P. A., Bothwell M. Neurotrophin expression in rat hippocampal slices: a stimulus paradigm inducing LTP in CA1 evokes increases in BDNF and NT-3 mRNAs. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1081–1088. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90067-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringstedt T., Lagercrantz H., Persson H. Expression of members of the trk family in the developing postnatal rat brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1993 Mar 19;72(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(93)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. E., Wenthold R. J., Soderling T. R. Phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and protein kinase C in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1994 Mar;14(3 Pt 1):1123–1129. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-03-01123.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapley P., Lamballe F., Barbacid M. K252a is a selective inhibitor of the tyrosine protein kinase activity of the trk family of oncogenes and neurotrophin receptors. Oncogene. 1992 Feb;7(2):371–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H. The changing scene of neurotrophic factors. Trends Neurosci. 1991 May;14(5):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90097-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafra F., Castrén E., Thoenen H., Lindholm D. Interplay between glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid transmitter systems in the physiological regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10037–10041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafra F., Hengerer B., Leibrock J., Thoenen H., Lindholm D. Activity dependent regulation of BDNF and NGF mRNAs in the rat hippocampus is mediated by non-NMDA glutamate receptors. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3545–3550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafra F., Lindholm D., Castrén E., Hartikka J., Thoenen H. Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor mRNA in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons and astrocytes. J Neurosci. 1992 Dec;12(12):4793–4799. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-12-04793.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]