Abstract
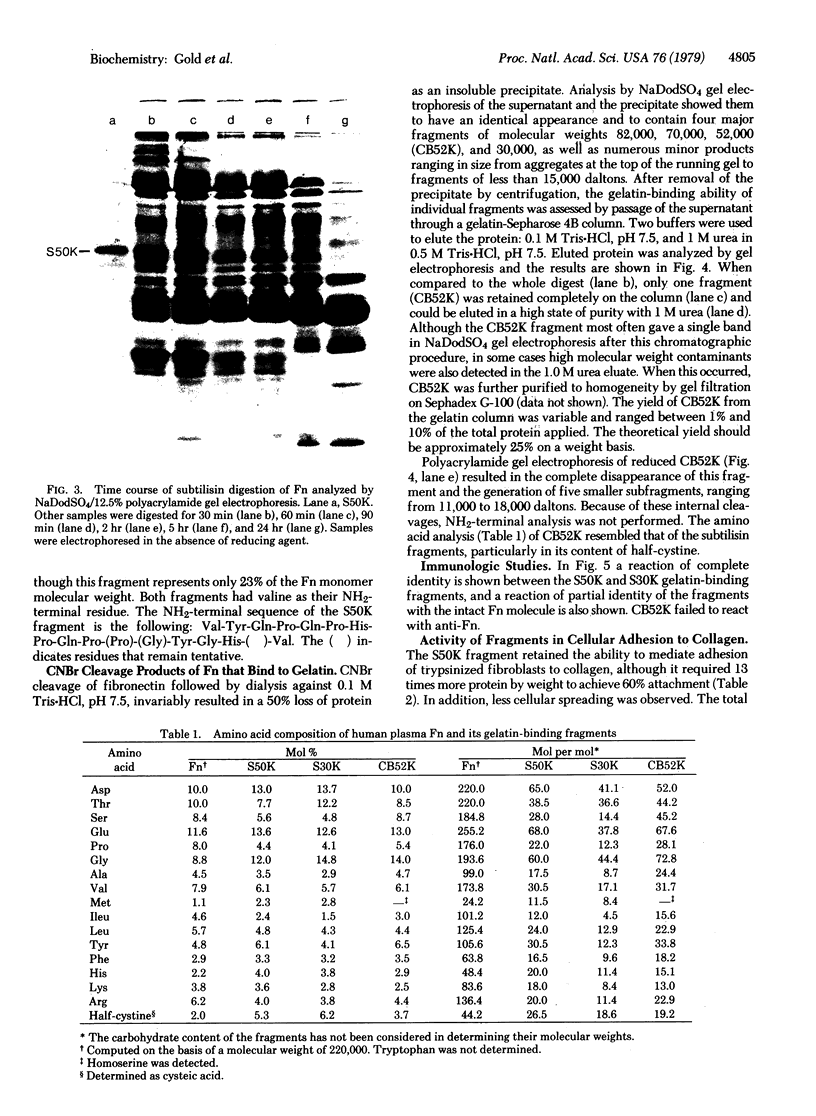
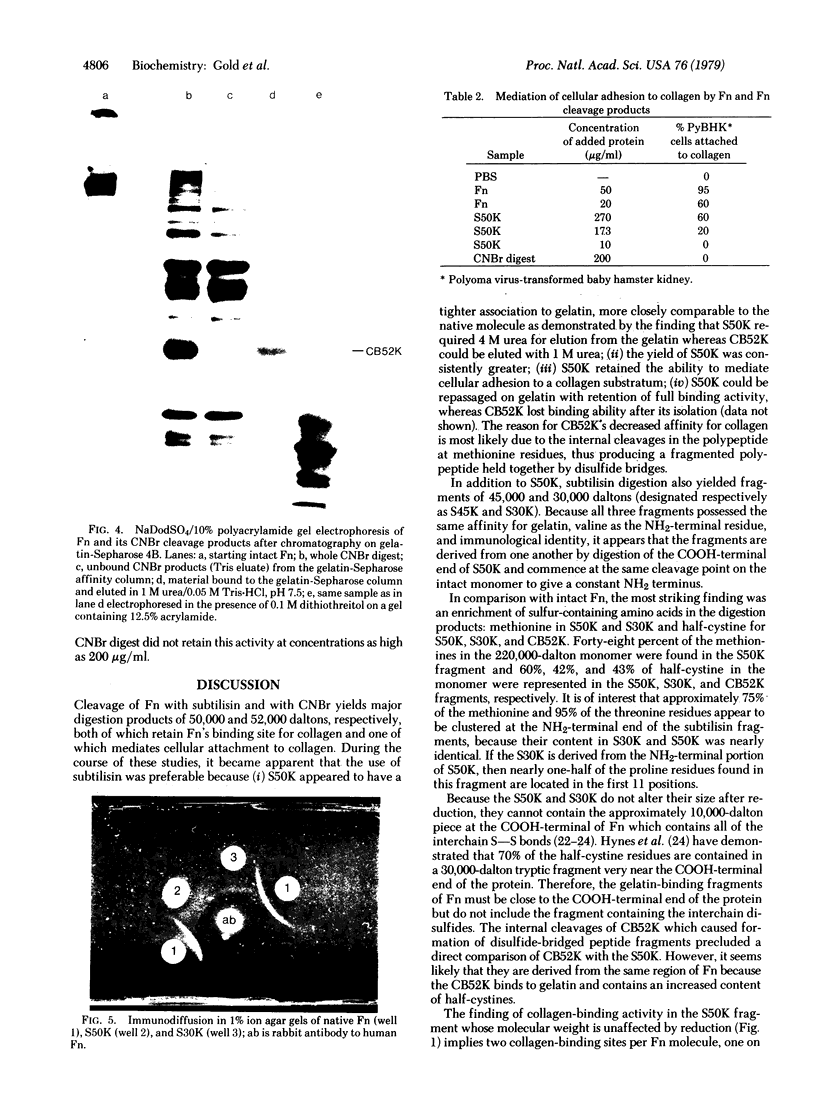
The gelatin-binding region of fibronectin has been obtained by subtilisin digestion and cyanogen bromide cleavage of the molecule. Enzymatic digestion yielded two fragments of molecular weights 50,000 (S50K) and 30,000 (S30K) which were isolated by elution from gelatin-Sepharose affinity columns. Because the S50K fragment also mediated the adhesion of fibroblasts to collagen, it contains both the collagen and cell binding sites on the fibronectin molecule. Both fragments had valine as the NH2-terminal residue, were enriched in half-cystine and methionine residues compared to the whole molecule, and were identical by immunodiffusion. The S50K fragment begins with the sequence Val-Tyr-Gln-Pro-Gln-Pro-His-Pro-Gln-Pro-(Pro)-(Gly)-Tyr-Gly-His-( )-Val, a region with an extended conformation which is susceptible to proteolysis and connects this domain to the remainder of the fibronectin molecule. The S50K fragment appears to be located in the COOH-terminal one-third of the fibronectin molecule but does not contain the interchain disulfide bridge(s); the S30K fragment is probably derived from the NH2-terminal region of S50K.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. L., Sobel M. E., Howard B. H., Olden K., Yamada K. M., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Levels of translatable mRNAs for cell surface protein, collagen precursors, and two membrane proteins are altered in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3399–3403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander S. S., Jr, Colonna G., Yamada K. M., Pastan I., Edelhoch H. Molecular properties of a major cell surface protein from chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5820–5824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balian G., Click E. M., Crouch E., Davidson J. M., Bornstein P. Isolation of a collagen-binding fragment from fibronectin and cold-insoluble globulin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1429–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray B. A. Cold-insoluble globulin (fibronectin) in connective tissues of adult human lung and in trophoblast basement membrane. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):745–752. doi: 10.1172/JCI109185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessau W., Adelmann B. C., Timpl R. Identification of the sites in collagen alpha-chains that bind serum anti-gelatin factor (cold-insoluble globulin). Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):55–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1690055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Binding of soluble form of fibroblast surface protein, fibronectin, to collagen. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jul 15;20(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Franklin E. C. Split immunoglobulin genes and human heavy chain deletion-mutants. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1177–1179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F., Milam M., Srere P. A. Studies on cell adhesion. II. Adhesion of cells to surfaces of diverse chemical composition and inhibition of adhesion by sulfhydryl binding reagents. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Nov;153(1):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90436-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F., Minter D. Cell adhesion and spreading factor: chemical modification studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 5;550(1):92–99. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F., Shere P. A. Inhibition of cellular adhesiveness by sulfhydryl blocking agents. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Aug;78(1):153–158. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F. Studies on the mechanism of cell attachment to a substratum with serum in the medium: further evidence supporting a requirement for two biochemically distinct processes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Dec;165(2):524–530. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn L. H., Yamada K. M. Identification and isolation of a collagen-binding fragment of the adhesive glycoprotein fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1160–1163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S. Strategy and tactics in protein chemistry. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):805–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1190805f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Ali I. U., Destree A. T., Mautner V., Perkins M. E., Senger D. R., Wagner D. D., Smith K. K. A large glycoprotein lost from the surfaces of transformed cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:317–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga S., Suzuki K., Hashimoto S. Bovine plasma cold-insoluble globulin: gross structure and function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:56–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jilek F., Hörmann H. Cold-insoluble globulin (fibronectin), IV[1-35 affinity to soluble collagen of various types. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Feb;359(2):247–250. doi: 10.1515/bchm.1978.359.1.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jilek F., Hörmann H. Cold-insoluble globulin, II. Plasminolysis of cold-insoluble globulin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Jan;358(1):133–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jilek F., Hörmann H. Cold-insoluble globulin, II[1,2]. Cyanogen bromide and plasminolysis fragments containing a label introduced by transamidation. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Sep;358(9):1165–1168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebe R. J. Isolation of a collagen-dependent cell attachment factor. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):248–251. doi: 10.1038/250248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Klebe R. J. Binding of cell attachment protein to collagen: effect of chemical modifications. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:436–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Klebe R. J., Fietzek P. P., Woolley D. E. Localization of the binding site for cell attachment in the alpha1(I) chain of collagen. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5642–5646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Murray J. C., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R. Connective tissue structure: cell binding to collagen. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Jul;71(1):9–11. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12543641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Ruoslahti E., Vaheri A. Polypeptides of a glycoprotein antigen (SF) present in serum and surface of normal but not of transformed chicken fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 30;379(1):295–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelsen T. E., Frangione B., Franklin E. C. Primary structure of the "hinge" region of human IgG3. Probable quadruplication of a 15-amino acid residue basic unit. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):883–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Umfleet R. A. The cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma. I. Purification, primary characterization, and relationship to fibrinogen and other cold-insoluble fraction components. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5728–5736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein E., Gold L. I. High-molecular-weight glycorprotein as a mediator of cellular adhesion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:278–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein E. Plasma membrane glycoprotein which mediates adhesion of fibroblasts to collagen. Nature. 1976 Aug 5;262(5568):497–500. doi: 10.1038/262497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E. Immunochemical and collagen-binding properties of fibronectin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:178–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Hayman E. G. Two active sites with different characteristics in fibronectin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 15;97(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Rogers J. H., Hüppi K., Brack C., Traunecker A., Maki R., Wall R., Tonegawa S. Domains and the hinge region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain are encoded in separate DNA segments. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):627–633. doi: 10.1038/277627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder P. The arrangement and rearrangement of antibody genes. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):790–795. doi: 10.1038/276790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenman S., Vaheri A. Distribution of a major connective tissue protein, fibronectin, in normal human tissues. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1054–1064. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Kurkinen M., Lehto V. P., Linder E., Timpl R. Codistribution of pericellular matrix proteins in cultured fibroblasts and loss in transformation: fibronectin and procollagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4944–4948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Mosher D. F. High molecular weight, cell surface-associated glycoprotein (fibronectin) lost in malignant transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 18;516(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Olden K. Fibronectins--adhesive glycoproteins of cell surface and blood. Nature. 1978 Sep 21;275(5677):179–184. doi: 10.1038/275179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







