Abstract
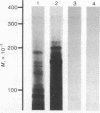
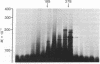
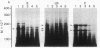
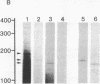
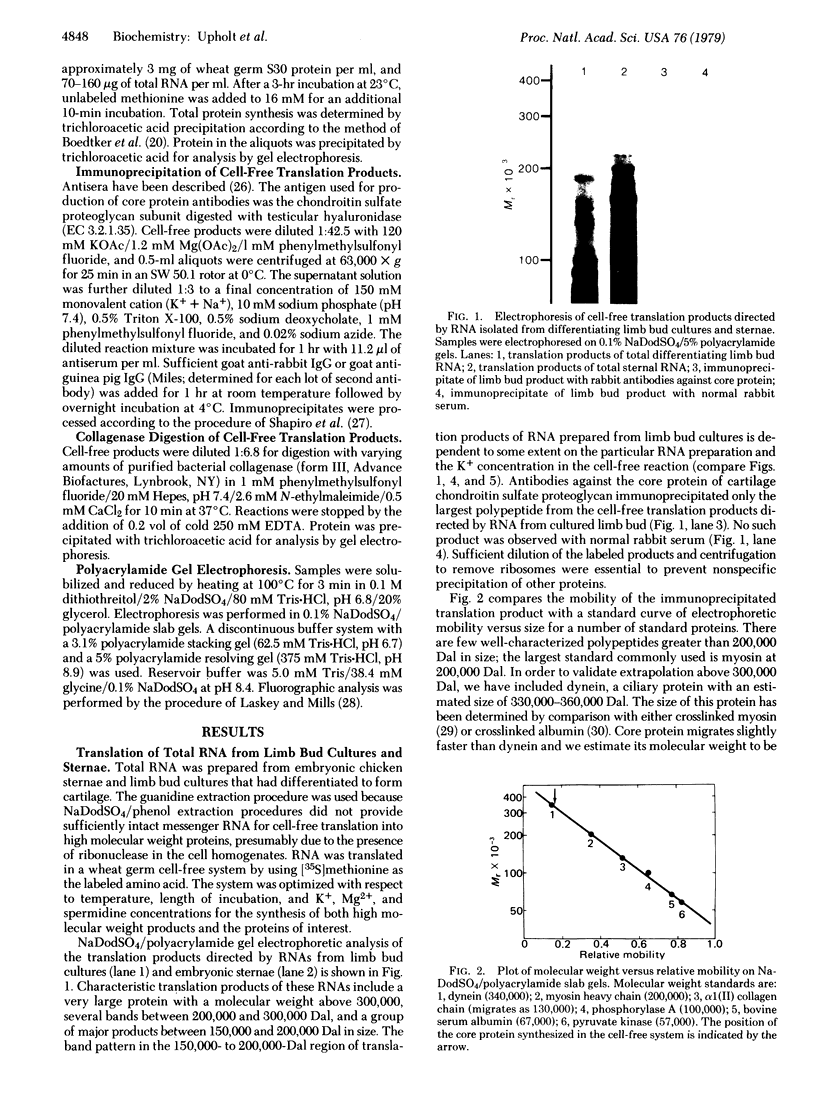
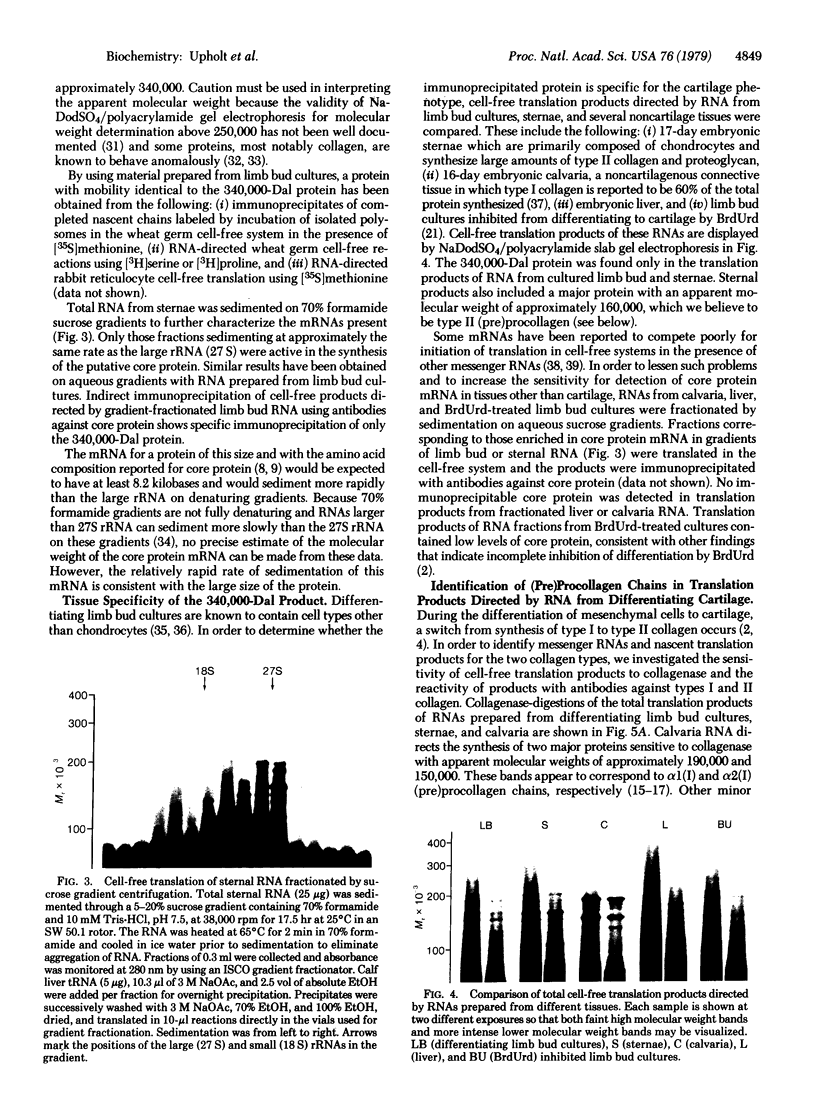
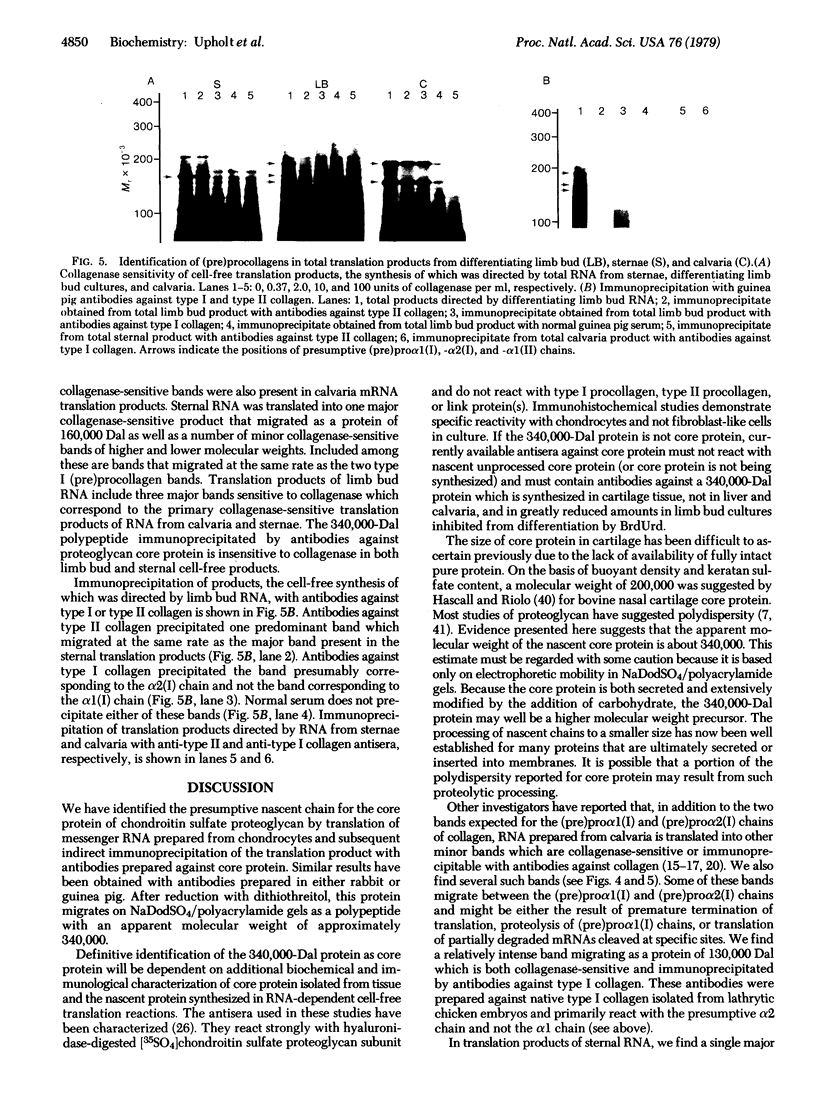
Total RNA, prepared from chicken limb bud cultures undergoing differentiation to cartilage, has been translated in a wheat germ cell-free protein-synthesizing system. Antibodies against chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan core protein immunoprecipitate a single component which migrates as a protein of 340,000 daltons in sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels. The messenger RNA for this protein sediments at approximately 27 S in 70% formamide or aqueous sucrose gradients. The 340,000-dalton protein is present in cell-free translation products directed by RNA prepared from limb bud cultures and sternae and is absent in cell-free translation directed by RNA prepared from embryonic calvaria or liver. The level of synthesis of this protein is greatly reduced when RNA prepared from limb bud cultures inhibited from differentiation by BrdUrd is used. (Pre)pro alpha 1(I), -alpha 2(I), and -alpha 1(II) collagen bands have been identified on gels by electrophoresis of collagenase-digested or immunoprecipitated cell-free translation products directed by RNA from differentiating limb bud cultures, embryonic sternae, and embryonic calvaria.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. L., Sobel M. E., Howard B. H., Olden K., Yamada K. M., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Levels of translatable mRNAs for cell surface protein, collagen precursors, and two membrane proteins are altered in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3399–3403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boedtker H., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Isolation and translation of calvaria procollagen messenger ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4765–4770. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. I., Zwilling E., Kaplan N. O. 3-acetylpyridine: effects in vitro related to teratogenic activity in chicken embryos. Science. 1968 May 31;160(3831):1009–1010. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3831.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diegelmann R. F., Peterkofsky B. Collagen biosynthesis during connective tissue development in chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1972 Jul;28(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Characterization of collagen peptides by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):510–516. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood R., Grant M. E., Jackson D. S. Translation of type I and type II procollagen messengers in a cell-free system derived from wheat germ. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Oegema T. R., Brown M., Caplan A. I. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from chick limb bud chondrocytes grown in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3511–3519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Riolo R. L. Characteristics of the protein-keratan sulfate core and of keratan sulfate prepared from bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4529–4538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Physical properties and polydispersity of proteoglycan from bovine nasal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):4920–4930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Axelsson I. Distribution of keratan sulfate in cartilage proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1971–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. H., Adams S. L., Sobel M. E., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Decreased levels of collagen mRNA in rous sarcoma virus-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5869–5874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat D., Chappell M. R. Competition between globin messenger ribonucleic acids for a discriminating initiation factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2684–2690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Osdoby P., Caplan A. I., Hascall V. C. Electron microscopic and biochemical studies of proteoglycan polydispersity in chick limb bud chondrocyte cultures. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4721–4729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Frischauf A. M., Hanahan D., Wozney J., Fuller F., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Construction and characterization of a 2.5-kilobase procollagen clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5417–5421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Dorfman A. Concepts and mechanisms of cartilage differentiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1974;8:103–149. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60607-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Dorfman A. The irreversible inhibition of differentiation of limb-bud mesenchyme by bromodeoxyuridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1253–1257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson J. M., Goodman H. M. Translation of chick calvarial procollagen messenger RNA'S by a messenger RNA dependent reticulocyte lysate. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5122–5128. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevo Z., Horwitz A. L., Dorfmann A. Synthesis of chondromucoprotein by chondrocytes in suspension culture. Dev Biol. 1972 May;28(1):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K., Gibbons I. R. Dynein 2. A new adenosine triphosphatase from sea urchin sperm flagella. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5793–5801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osdoby P., Caplan A. I. The possible differentiation of osteogenic elements in vitro from chick limb mesodermal cells. I. Morphological evidence. Dev Biol. 1976 Sep;52(2):283–299. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90246-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Davidson J. M., Gagnon J., Rowe D. W., Bornstein P. NH2-terminal sequence of the chick proalpha1(I) chain synthesized in the reticulocyte lysate system. Evidence for a transient hydrophobic leader sequence. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1433–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack S. G., Veis A., Breen M. Solvent-dependent changes in proteoglycan subunit conformation in aqueous guanidine hydrochloride solutions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2206–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quittner S., Watts L. A., Roxby R. Molecular properties of the Busycon hemocyanin--SDS complex with reference to its usefulness as a high molecular weight standard. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):187–195. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90740-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Hellmann W., Kleinschmidt A. K. Electron microscopic studies of proteoglycan aggregates from bovine articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1877–1883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., Moen R. C., Davidson J. M., Byers P. H., Bornstein P., Palmiter R. D. Correlation of procollagen mRNA levels in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts with different rates of procollagen synthesis. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1581–1590. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Taylor J. M., McKnight G. S., Palacios R., Gonzalez C., Kiely M. L., Schimke R. T. Isolation of hen oviduct ovalbumin and rat live albumin polysomes by indirect immunoprecipitation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3665–3671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Kaesberg P. Translation of brome mosaic viral ribonucleic acid in a cell-free system derived from wheat embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1799–1803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel M. E., Yamamoto T., Adams S. L., DiLauro R., Avvedimento V. E., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Construction of a recombinant bacterial plasmid containing a chick pro-alpha2 collagen gene sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5846–5850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasan N. S., Lash J. W. Heterogeneity of proteoglycans in developing chick limb cartilage. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):179–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1640179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vertel B. M., Dorfman A. Simultaneous localization of type II collagen and core protein of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan in individual chondrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1261–1264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner F. D., Mitchell D. R., Perkins C. R. Structural conformation of the ciliary ATPase dynein. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 15;114(3):367–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., von der Mark H. Immunological and biochemical studies of collagen type transition during in vitro chrondrogenesis of chick limb mesodermal cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jun;73(3):736–747. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]