Abstract
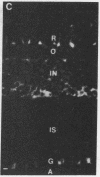
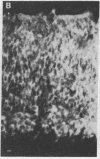
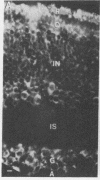
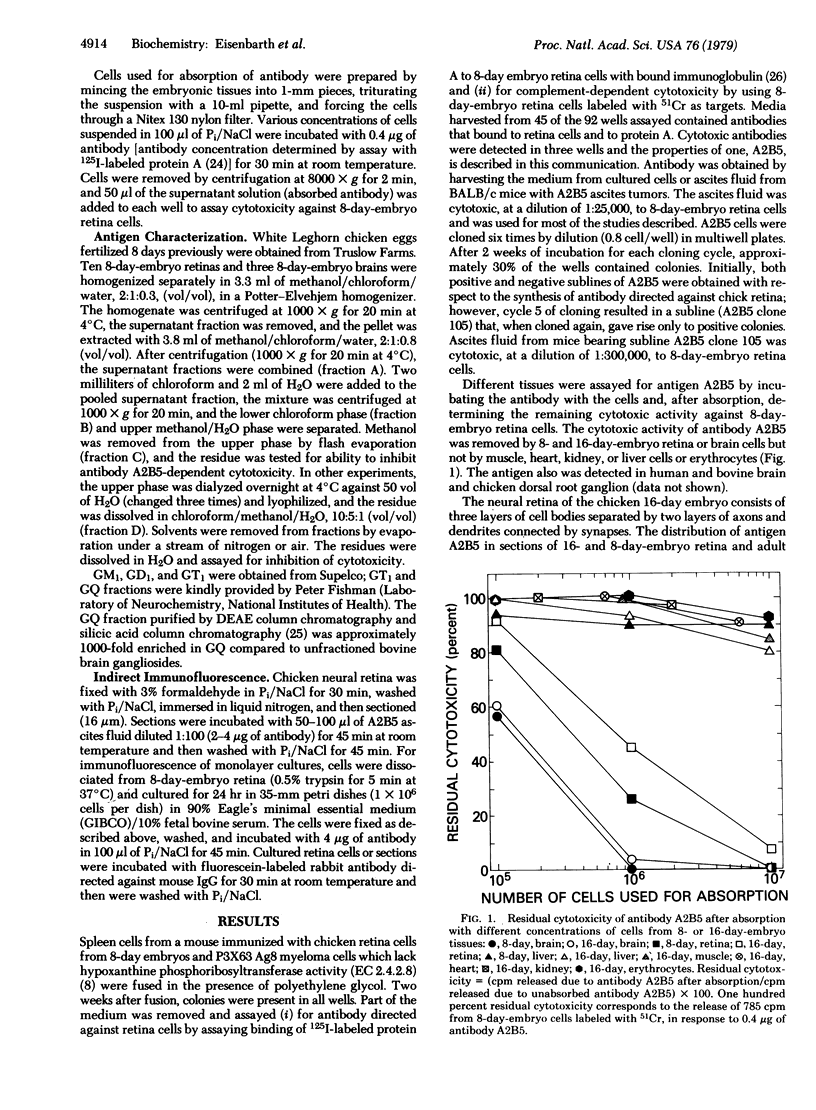
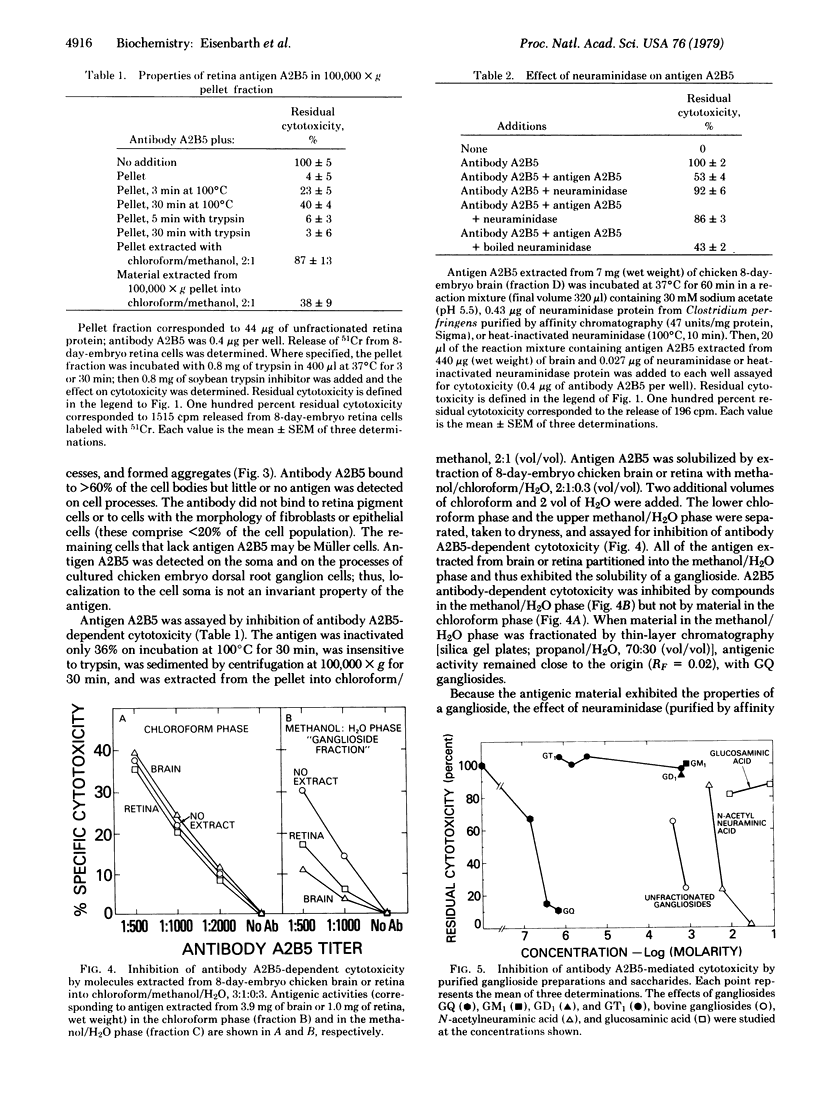
Fusion of spleen cells from a mouse immunized with chicken embryo retina cells with clonal mouse myeloma cells yielded a lymphocyte hybrid cell line that produced antibody that bound to neural tissue such as retina, brain, spinal cord, and dorsal root ganglia but not to other tissues tested. The antigen was shown by indirect immunofluorescence to be associated with plasma membranes of most, or all, neuron cell bodies in chicken retina, but little or no antigen was detected on axons or dendrites, Müller cells, or retina pigment cells. The activity of antigen A2B5 is relatively stable at 100 degrees C, is insensitive to trypsin, exhibits the solubility properties of a ganglioside, and is destroyed by neuraminidase. Antibody A2B5 cytotoxicity against retina cells is inhibited by a GQ ganglioside fraction from bovine brain (estimated half-maximal inhibition at 0.2 microM) or by N-acetylneuraminic acid (half-maximal inhibition at 5000 microM) but not by other purified gangliosides tested. These results suggest that the antigen is a complex ganglioside in plasma membranes of retina neuron cell bodies but not axons or dendrites.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akeson R., Herschman H. R. Modulation of cell-surface antigens of a murine neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):187–191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock E., Jorgensen O. S., Morris S. J. Antigen-antibody crossed electrophoresis of rat brain synaptosomes and synaptic vesicles: correlation to water-soluble antigens from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1974 Jun;22(6):1013–1017. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Gosling C., Megson M., Stern P. L. New cell surface antigens in rat defined by tumors of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1296–1300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Moscona A. A. Tissue-specific cell-surface antigens in embryonic cells. J Cell Biol. 1972 May;53(2):435–449. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman R. E., Moscona A. A. Isolation of retina-specific cell-aggregating factor from membranes of embryonic neural retina tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett R. H., Gilbert F. Hybrid myelomas producing antibodies against a human neuroblastoma antigen present on fetal brain. Science. 1979 Mar 16;203(4385):1120–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.424740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Steplewski Z., Herlyn D., Herlyn M. Study of antibodies against human melanoma produced by somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3405–3409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Levy R., Grumet F. C., Ness D., Pious D. Production in vitro of murine antibody to a human histocompatibility alloantigen. Nature. 1978 Feb 2;271(5644):461–462. doi: 10.1038/271461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J., Boyle M. D., Borsos T. 125I protein A: applications to the quantitative determination of fluid phase and cell-bound IgG. J Immunol Methods. 1977;18(3-4):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. E. Mouse brain antigen detected by rat anti-C1300 antiserum. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):71–73. doi: 10.1038/249071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T., Galfrè G., Ziegler A., Milstein C. A myeloma hybrid producing antibody specific for an allotypic determinant on "IgD-like" molecules of the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Oct;7(10):684–690. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puro D. G., De Mello F. G., Nirenberg M. Synapse turnover: the formation and termination of transient synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4977–4981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Eisenbarth G. S., Thompson J. M., Nirenberg M. Synapse turnover: a mechanism for acquiring synaptic specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2281–2285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Thiery J. P., Brackenbury R., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. III. Relationship of the surface molecule CAM to cell adhesion and the development of histotypic patterns. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):371–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEN S. C., GREENFIELD P., BOELL E. J. Localization of acetylcholinesterase in chick retina during histogenesis. J Comp Neurol. 1956 Dec;106(2):433–461. doi: 10.1002/cne.901060211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachner M., Wortham K. A., Kincade P. W. Detection of nervous-system specific cell surface antigen(s) by heterologous anti-mouse brain antiserum. Cell Immunol. 1976 Mar 15;22(2):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield J. B., Moscona A. A. Electron microscopic analysis of aggregation of embryonic cells: the structure and differentiation of aggregates of neural retina cells. Dev Biol. 1970 Sep;23(1):36–61. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(70)80006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanelli A., Zacchei A. M., Caravita S., Cataldi A., Ieradi L. A. New-forming retinal synapses in vitro. Experientia. 1967 Mar 15;23(3):199–200. doi: 10.1007/BF02136284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern P. L., Willison K. R., Lennox E., Galfrè G., Milstein C., Secher D., Ziegler A. Monoclonal antibodies as probes for differentiation and tumor-associated antigens: a Forssman specificity on teratocarcinoma stem cells. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90333-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Daniels M. P., Nirenberg M. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors of the developing retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5524–5528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Brackenbury R., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. II. Purification and characterization of a cell adhesion molecule from neural retina. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6841–6845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Daniels M. P., Nirenberg M. Synapse and acetylcholine receptor synthesis by neurons dissociated from retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2370–2374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Nirenberg M. Localization of acetylcholine receptors during synaptogenesis in retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1806–1810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Galfrè G., Milstein C. Analysis of cell surfaces by xenogeneic myeloma-hybrid antibodies: differentiation antigens of rat lymphocytes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]