Abstract
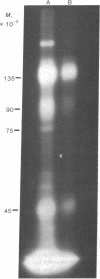
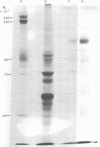
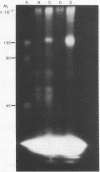
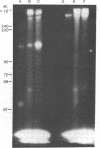
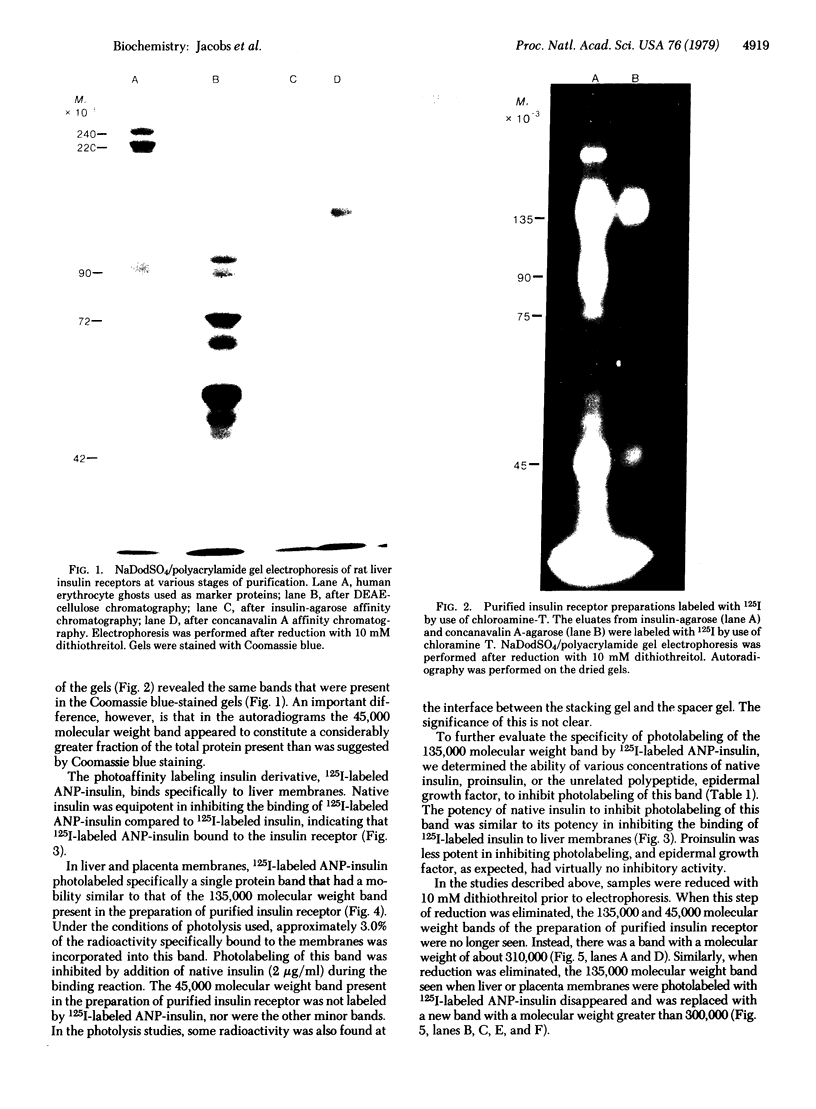
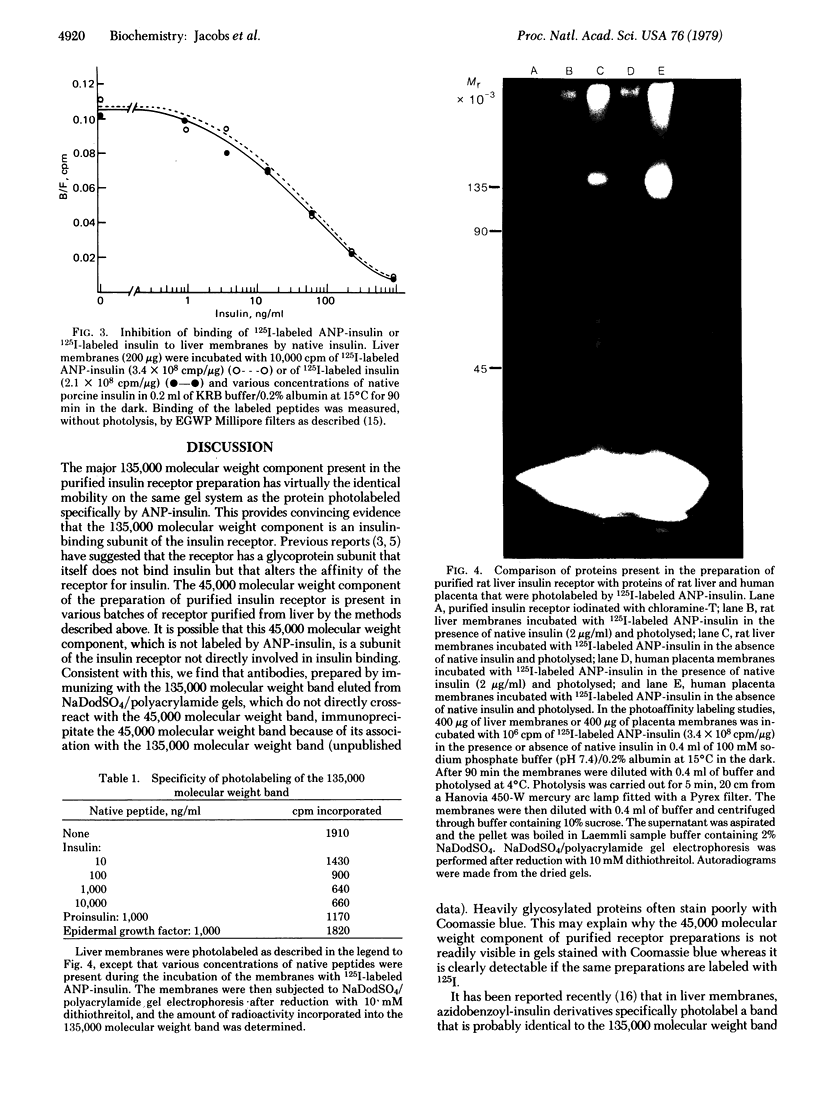
Two methods were used to label insulin receptors covalently with 125I. In the first, an aryl azide derivative of insulin, 125I-labeled 4-azido-2-nitrophenyl-insulin, was synthesized and used to photolabel the binding region of the insulin receptor in rat liver membranes and human placenta membranes. In the second, insulin receptors were purified from rat liver membranes and labeled with 125I by use of chloramine-T; this method presumably has no specificity for the binding region of the receptor. The proteins labeled by both methods were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis after or without reduction by dithiothreitol. The photoaffinity label specifically labeled a single band in both liver and placenta that had an apparent molecular weight of 135,000 after reduction. A band with similar mobility was present in the chloramine-T-labeled preparation, which also contained a second major band with an apparent molecular weight of 45,000. Without reduction, both methods resulted in a single labeled band with an apparent molecular weight of about 310,000. These results indicate that the insulin receptor of both liver and placenta has a subunit of molecular weight 135,000 that binds insulin and that the receptor may be composed of at least two different subunits that are linked together or greatly stabilized by disulfide bonds.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang H. W., Bock E. Molecular forms of acetylcholine receptor. Effects of calcium ions and a sulfhydryl reagent on the occurrence of oligomers. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4513–4520. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W. Purification and characterization of acetylcholine receptor-I from Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2113–2117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor isolated from liver and fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):1980–1991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor of isolated fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7265–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg B. H., Kahn C. R., Roth J., De Meyts P. Insulin-induced dissociation of its receptor into subunits: possible molecular concomitant of negative cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 20;73(4):1068–1074. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. L., McLaughlin M., Karlin A. Disulfide bond cross-linked dimer in acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):692–699. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Billington T., East I. J., Nichols R. J., Clark S. The effect of solubilization on the properties of the insulin receptor of human placental membranes. Endocrinology. 1978 May;102(5):1485–1495. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-5-1485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Shechter Y., Bissell K., Cuatrecasas P. Purification and properties of insulin receptors from rat liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):981–988. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M. N., Livingston J. N. Effects of insulin on insulin-binding components extracted from rat fat cell membranes. Nature. 1979 Mar 1;278(5699):61–62. doi: 10.1038/278061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M. N., Livingston J. N. Insulin binding to solubilized material from fat cell membranes: evidence for two binding species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. Preparation of photo-affinity probes for the insulin receptor site in adipose and liver cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 18;322(2):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maturo J. M., 3rd, Hollenberg M. D. Insulin receptor: interaction with nonreceptor glycoprotein from liver cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3070–3074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maturo J. M., 3rd, Shackelford W. H., Hollenberg M. D. Characteristics of the solubilized insulin receptor of human placenta. Life Sci. 1978 Nov 13;23(20):2063–2071. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe E., Hollenberg M. D., Cuatrecasas P. Epidermal growth factor. Characteristics of specific binding in membranes from liver, placenta, and other target tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):518–526. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parikh I., Sica V., Nola E., Puca G. A., Cuatrecasas P. Affinity chromatography of estrogen receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:670–688. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Interaction of cross-linking agents with the insulin effector system of isolated fat cells. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a plasma membrane receptor protein of 140,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Robb R. J., Terhorst C., Strominger J. L. Submit and disulfide structure of monomeric and dimeric forms of detergent-soluble HLA antigens. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4694–4700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzemann V., Raftery M. Specific molecular aggregates or Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 14;81(3):1025–1031. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Yeung C. W., Moule M. L. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor of rat adiopocyte plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1743–1745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]