Abstract
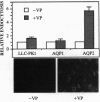
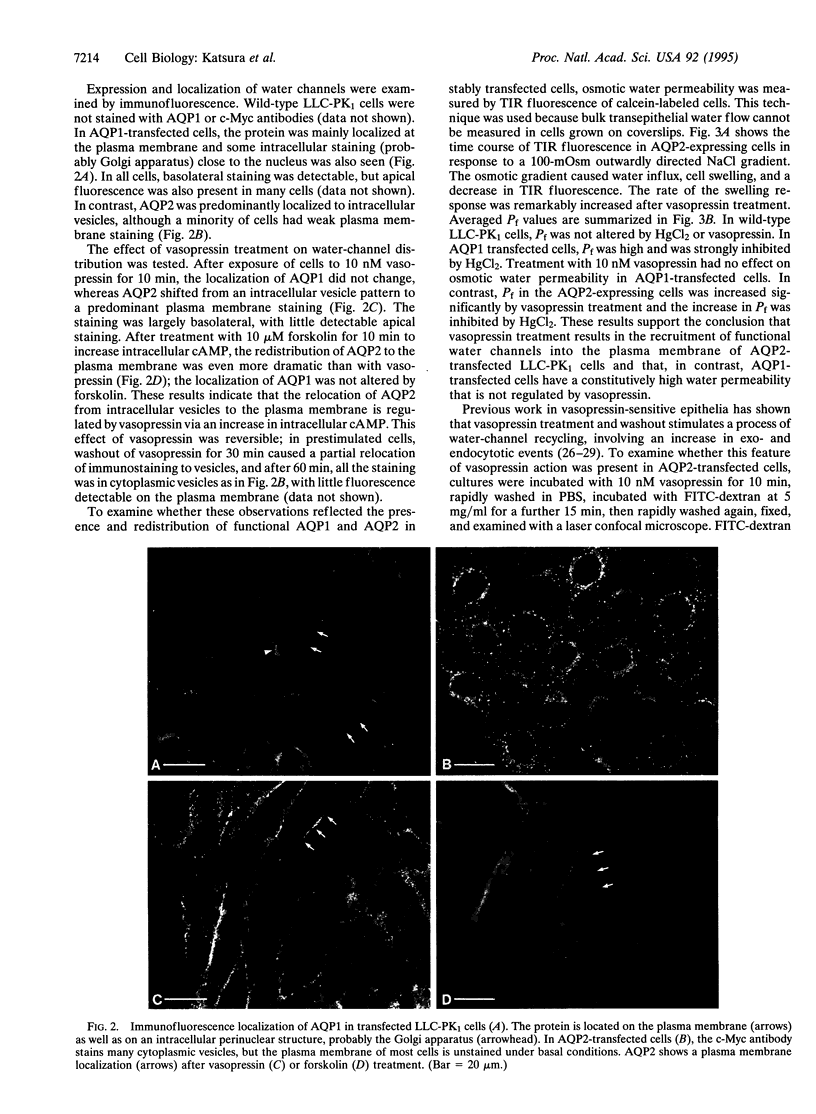
The aquaporins (AQPs) are a family of homologous water-channel proteins that can be inserted into epithelial cell plasma membranes either constitutively (AQP1) or by regulated exocytosis following vasopressin stimulation (AQP2). LLC-PK1 porcine renal epithelial cells were stably transfected with cDNA encoding AQP2 (tagged with a C-terminal c-Myc epitope) or rat kidney AQP1 cDNA in an expression vector containing a cytomegalovirus promoter. Immunofluorescence staining revealed that AQP1 was mainly localized to the plasma membrane, whereas AQP2 was predominantly located on intracellular vesicles. After treatment with vasopressin or forskolin for 10 min, AQP2 was relocated to the plasma membrane, indicating that this relocation was induced by cAMP. The location of AQP1 did not change. The basal water permeability of AQP1-transfected cells was 2-fold greater than that of nontransfected cells, whereas the permeability of AQP2-transfected cells increased significantly only after vasopressin treatment. Endocytotic uptake of fluorescein isothiocyanate-coupled dextran was stimulated 6-fold by vasopressin in AQP2-transfected cells but was only slightly increased in wild-type or AQP1-transfected cells. This vasopressin-induced endocytosis was inhibited in low-K+ medium, which selectively affects clathrin-mediated endocytosis. These water channel-transfected cells represent an in vitro system that will allow the detailed dissection of mechanisms involved in the processing, targeting, and trafficking of proteins via constitutive versus regulated intracellular transport pathways.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agre P., Preston G. M., Smith B. L., Jung J. S., Raina S., Moon C., Guggino W. B., Nielsen S. Aquaporin CHIP: the archetypal molecular water channel. Am J Physiol. 1993 Oct;265(4 Pt 2):F463–F476. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.4.F463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Orci L. Vasopressin stimulates formation of coated pits in rat kidney collecting ducts. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):253–255. doi: 10.1038/302253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. Structural-functional features of antidiuretic hormone-induced water transport in the collecting duct. Semin Nephrol. 1991 Jul;11(4):478–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Weyer P., Orci L. Vasopressin stimulates endocytosis in kidney collecting duct principal cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;46(2):336–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvera S., Chawla A., Chakrabarti R., Joly M., Buxton J., Czech M. P. A double leucine within the GLUT4 glucose transporter COOH-terminal domain functions as an endocytosis signal. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(4):979–989. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.4.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen P. M., Dempster J. A., Wieringa B., Van Os C. H. Isolation of a cDNA for rat CHIP28 water channel: high mRNA expression in kidney cortex and inner medulla. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 16;188(3):1267–1273. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91368-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen P. M., Verdijk M. A., Knoers N. V., Wieringa B., Monnens L. A., van Os C. H., van Oost B. A. Requirement of human renal water channel aquaporin-2 for vasopressin-dependent concentration of urine. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8140421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farinas J., Simanek V., Verkman A. S. Cell volume measured by total internal reflection microfluorimetry: application to water and solute transport in cells transfected with water channel homologs. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4):1613–1620. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80335-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fushimi K., Uchida S., Hara Y., Hirata Y., Marumo F., Sasaki S. Cloning and expression of apical membrane water channel of rat kidney collecting tubule. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):549–552. doi: 10.1038/361549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottardi C. J., Pietrini G., Roush D. L., Caplan M. J. Sorting of ion transport proteins in polarized cells. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:13–20. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes M., Kelly R. B. Intermediates in the constitutive and regulated secretory pathways released in vitro from semi-intact cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):539–549. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S. H., Sandvig K., van Deurs B. Molecules internalized by clathrin-independent endocytosis are delivered to endosomes containing transferrin receptors. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(1):89–97. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. W., Jr, Strange K., Zeidel M. L. Current understanding of the cellular biology and molecular structure of the antidiuretic hormone-stimulated water transport pathway. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):1–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI115263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa H., Zhang R., Dohrman A., Verkman A. S. Tissue-specific expression of mRNA encoding rat kidney water channel CHIP28k by in situ hybridization. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 1):C237–C245. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.1.C237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Pathways of protein secretion in eukaryotes. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):25–32. doi: 10.1126/science.2994224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin J. M., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G. Depletion of intracellular potassium arrests coated pit formation and receptor-mediated endocytosis in fibroblasts. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma T., Frigeri A., Tsai S. T., Verbavatz J. M., Verkman A. S. Localization and functional analysis of CHIP28k water channels in stably transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22756–22764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma T., Hasegawa H., Skach W. R., Frigeri A., Verkman A. S. Expression, functional analysis, and in situ hybridization of a cloned rat kidney collecting duct water channel. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jan;266(1 Pt 1):C189–C197. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.1.C189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Chou C. L., Marples D., Christensen E. I., Kishore B. K., Knepper M. A. Vasopressin increases water permeability of kidney collecting duct by inducing translocation of aquaporin-CD water channels to plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1013–1017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., DiGiovanni S. R., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Harris H. W. Cellular and subcellular immunolocalization of vasopressin-regulated water channel in rat kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11663–11667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Smith B. L., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Agre P. CHIP28 water channels are localized in constitutively water-permeable segments of the nephron. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):371–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Agre P. Isolation of the cDNA for erythrocyte integral membrane protein of 28 kilodaltons: member of an ancient channel family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11110–11114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Carroll T. P., Guggino W. B., Agre P. Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red cell CHIP28 protein. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):385–387. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., Pang S., Harris D. S., Heuser J., James D. E. Translocation of the glucose transporter (GLUT4) to the cell surface in permeabilized 3T3-L1 adipocytes: effects of ATP insulin, and GTP gamma S and localization of GLUT4 to clathrin lattices. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1181–1196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić I., Katsura T., Verbavatz J. M., Brown D. The AQP2 water channel: effect of vasopressin treatment, microtubule disruption, and distribution in neonatal rats. J Membr Biol. 1995 Feb;143(3):165–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00233445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić I., Valenti G., Verbavatz J. M., Van Hoek A. N., Verkman A. S., Ausiello D. A., Brown D. Localization of the CHIP28 water channel in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 1):C1225–C1233. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.6.C1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange K., Willingham M. C., Handler J. S., Harris H. W., Jr Apical membrane endocytosis via coated pits is stimulated by removal of antidiuretic hormone from isolated, perfused rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jul;103(1):17–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01871929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhey K. J., Birnbaum M. J. A Leu-Leu sequence is essential for COOH-terminal targeting signal of GLUT4 glucose transporter in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2353–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkman A. S., Lencer W. I., Brown D., Ausiello D. A. Endosomes from kidney collecting tubule cells contain the vasopressin-sensitive water channel. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):268–269. doi: 10.1038/333268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkman A. S. Water channels in cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:97–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. B., Stetson D. L., Lewis S. A. ADH action: evidence for a membrane shuttle mechanism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;372:106–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang R., Skach W., Hasegawa H., van Hoek A. N., Verkman A. S. Cloning, functional analysis and cell localization of a kidney proximal tubule water transporter homologous to CHIP28. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):359–369. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]