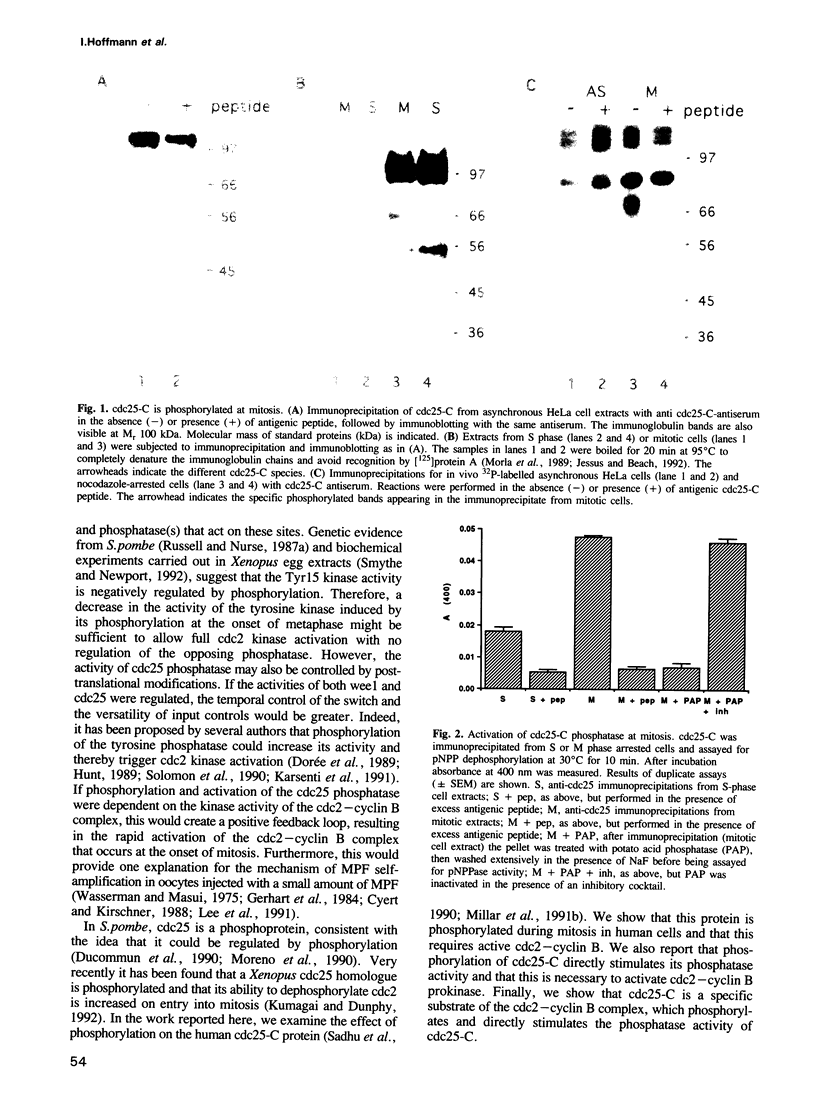
Abstract
We have investigated the mechanisms responsible for the sudden activation of the cdc2-cyclin B protein kinase before mitosis. It has been found previously that cdc25 is the tyrosine phosphatase responsible for dephosphorylating and activating cdc2-cyclin B. In Xenopus eggs and early embryos a cdc25 homologue undergoes periodic phosphorylation and activation. Here we show that the catalytic activity of human cdc25-C phosphatase is also activated directly by phosphorylation in mitotic cells. Phosphorylation of cdc25-C in mitotic HeLa extracts or by cdc2-cyclin B increases its catalytic activity. cdc25-C is not a substrate of the cyclin A-associated kinases. cdc25-C is able to activate cdc2-cyclin B1 in Xenopus egg extracts and to induce Xenopus oocyte maturation, but only after stable thiophosphorylation. This demonstrates that phosphorylation of cdc25-C is required for the activation of cdc2-cyclin B and entry into M-phase. Together, these studies offer a plausible explanation for the rapid activation of cdc2-cyclin B at the onset of mitosis and the self-amplification of MPF observed in vivo.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amon A., Surana U., Muroff I., Nasmyth K. Regulation of p34CDC28 tyrosine phosphorylation is not required for entry into mitosis in S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):368–371. doi: 10.1038/355368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arion D., Meijer L., Brizuela L., Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase-specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R. N., Alfa C. E., Hyams J. S., Beach D. H. The fission yeast cdc2/cdc13/suc1 protein kinase: regulation of catalytic activity and nuclear localization. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):485–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. R., Karsenti E. Regulation of p34cdc2 protein kinase: new insights into protein phosphorylation and the cell cycle. J Cell Sci. 1991 Nov;100(Pt 3):409–414. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.3.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. R., Leiss D., Pagano M., Karsenti E. Cyclin A- and cyclin B-dependent protein kinases are regulated by different mechanisms in Xenopus egg extracts. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1751–1761. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05227.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyert M. S., Kirschner M. W. Regulation of MPF activity in vitro. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90380-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M., Newport J. W. Completion of DNA replication is monitored by a feedback system that controls the initiation of mitosis in vitro: studies in Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):811–823. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90191-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorée M., Labbé J. C., Picard A. M phase-promoting factor: its identification as the M phase-specific H1 histone kinase and its activation by dephosphorylation. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;12:39–51. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_12.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Piwnica-Worms H., Morrison D., Druker B., Roberts T., Beach D. Human cdc2 protein kinase is a major cell-cycle regulated tyrosine kinase substrate. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):738–744. doi: 10.1038/336738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Félix M. A., Franza B. R., Jr, Karsenti E., Draetta G. cdc2 phosphorylation is required for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Draetta G., Young P., Beach D. Fission yeast cdc25 is a cell-cycle regulated protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 28;167(1):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91765-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Kumagai A. The cdc25 protein contains an intrinsic phosphatase activity. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90582-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:367–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., O'Farrell P. H. Genetic control of cell division patterns in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):177–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90183-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Nurse P. Mutation of fission yeast cell cycle control genes abolishes dependence of mitosis on DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):665–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90669-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantes P. A. Control of timing of cell cycle events in fission yeast by the wee 1+ gene. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):153–155. doi: 10.1038/302153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix M. A., Pines J., Hunt T., Karsenti E. A post-ribosomal supernatant from activated Xenopus eggs that displays post-translationally regulated oscillation of its cdc2+ mitotic kinase activity. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3059–3069. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galaktionov K., Beach D. Specific activation of cdc25 tyrosine phosphatases by B-type cyclins: evidence for multiple roles of mitotic cyclins. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1181–1194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Matsukawa T., Nurse P., Maller J. Dephosphorylation and activation of Xenopus p34cdc2 protein kinase during the cell cycle. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):626–629. doi: 10.1038/339626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Solomon M. J., Booher R. N., Bazan J. F., Kirschner M. W. cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90583-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J., Wu M., Kirschner M. Cell cycle dynamics of an M-phase-specific cytoplasmic factor in Xenopus laevis oocytes and eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1247–1255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., Whyte P., Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Beach D., Draetta G. A 60 kd cdc2-associated polypeptide complexes with the E1A proteins in adenovirus-infected cells. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):981–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90949-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity of an essential virulence determinant in Yersinia. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2166336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Embryology. Under arrest in the cell cycle. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):483–484. doi: 10.1038/342483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessus C., Beach D. Oscillation of MPF is accompanied by periodic association between cdc25 and cdc2-cyclin B. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90473-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsenti E., Newport J., Hubble R., Kirschner M. Interconversion of metaphase and interphase microtubule arrays, as studied by the injection of centrosomes and nuclei into Xenopus eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1730–1745. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Cell cycle regulation of vertebrate p34cdc2 activity: identification of Thr161 as an essential in vivo phosphorylation site. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Differential phosphorylation of vertebrate p34cdc2 kinase at the G1/S and G2/M transitions of the cell cycle: identification of major phosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):305–316. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07951.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. Regulation of the cdc25 protein during the cell cycle in Xenopus extracts. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90540-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. The cdc25 protein controls tyrosine dephosphorylation of the cdc2 protein in a cell-free system. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):903–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90315-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé J. C., Picard A., Karsenti E., Dorée M. An M-phase-specific protein kinase of Xenopus oocytes: partial purification and possible mechanism of its periodic activation. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Ogg S., Xu M., Parker L. L., Donoghue D. J., Maller J. L., Piwnica-Worms H. cdc25+ encodes a protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates p34cdc2. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):73–84. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Solomon M. J., Mumby M. C., Kirschner M. W. INH, a negative regulator of MPF, is a form of protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90649-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Walworth N., Booher R., Dembski M., Kirschner M., Beach D. mik1 and wee1 cooperate in the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1111–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K. X., Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Cyanogen bromide cleavage and proteolytic peptide mapping of proteins immobilized to membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:149–152. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01014-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKintosh C., Beattie K. A., Klumpp S., Cohen P., Codd G. A. Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 21;264(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80245-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin O., Meggio F., Draetta G., Pinna L. A. The consensus sequences for cdc2 kinase and for casein kinase-2 are mutually incompatible. A study with peptides derived from the beta-subunit of casein kinase-2. FEBS Lett. 1992 Apr 13;301(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. B., Blevitt J., Gerace L., Sadhu K., Featherstone C., Russell P. p55CDC25 is a nuclear protein required for the initiation of mitosis in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10500–10504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. B., McGowan C. H., Lenaers G., Jones R., Russell P. p80cdc25 mitotic inducer is the tyrosine phosphatase that activates p34cdc2 kinase in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4301–4309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. B., Russell P. The cdc25 M-phase inducer: an unconventional protein phosphatase. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):407–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90177-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Nurse P., Russell P. Regulation of mitosis by cyclic accumulation of p80cdc25 mitotic inducer in fission yeast. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):549–552. doi: 10.1038/344549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Draetta G., Beach D., Wang J. Y. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2: dephosphorylation accompanies activation during entry into mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Blow J., Nurse P. Regulatory phosphorylation of the p34cdc2 protein kinase in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3321–3329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. Cell cycle control: many ways to skin a cat. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;2(6):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90034-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavassiliou A. G., Bohmann K., Bohmann D. Determining the effect of inducible protein phosphorylation on the DNA-binding activity of transcription factors. Anal Biochem. 1992 Jun;203(2):302–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90317-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Piwnica-Worms H. Inactivation of the p34cdc2-cyclin B complex by the human WEE1 tyrosine kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1955–1957. doi: 10.1126/science.1384126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Cyclin-dependent kinases: a new cell cycle motif? Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;1(5):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90116-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. The mitotic inducer nim1+ functions in a regulatory network of protein kinase homologs controlling the initiation of mitosis. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu K., Reed S. I., Richardson H., Russell P. Human homolog of fission yeast cdc25 mitotic inducer is predominantly expressed in G2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5139–5143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe C., Newport J. W. Coupling of mitosis to the completion of S phase in Xenopus occurs via modulation of the tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Lee T., Kirschner M. W. Role of phosphorylation in p34cdc2 activation: identification of an activating kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):13–27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Murray A. W. S-phase feedback control in budding yeast independent of tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc28. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):365–368. doi: 10.1038/355365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausfeld U., Labbé J. C., Fesquet D., Cavadore J. C., Picard A., Sadhu K., Russell P., Dorée M. Dephosphorylation and activation of a p34cdc2/cyclin B complex in vitro by human CDC25 protein. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):242–245. doi: 10.1038/351242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. CD45, an integral membrane protein tyrosine phosphatase. Characterization of enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10674–10680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman W. J., Masui Y. Effects of cyclohexamide on a cytoplasmic factor initiating meiotic naturation in Xenopus oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Mar 15;91(2):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Gerhart J. C. Partial purification and characterization of the maturation-promoting factor from eggs of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]