Abstract
The secretion of the Klebsiella oxytoca cell surface lipoprotein pullulanase involves translocation across the cytoplasmic and outer membranes of the Gram-negative bacterial cell envelope. A variant of pullulanase was created by fusing the signal peptide-encoding 5' region of the Escherichia coli gene for periplasmic MalE protein to the 3' end of the pulA gene encoding almost the entire mature part of pullulanase. When produced in E. coli carrying the malE-pulA gene fusion on a high copy number plasmid and the complete set of genes specifically required for pullulanase secretion on a second plasmid, the hybrid protein differed from wild-type pullulanase as follows: (i) it was not fatty-acylated; (ii) it was apparently processed by LepB signal peptidase rather than by LspA lipoprotein signal peptidase; (iii) it was released into the periplasm and was only slowly transported across the outer membrane, and (iv) it was released directly into the medium rather than via the usual surface-anchored intermediate. The hybrid protein was secreted more rapidly when malE-pulA was expressed from a low copy number plasmid. The two steps in the secretion pathway could be totally uncoupled by expressing first the malE-pulA gene fusion and then the cognate secretion genes. These results show that fatty-acylation of wild-type PulA is not essential for secretion but may improve its efficiency when large amounts of the protein are produced, that the two steps in secretion can occur quite independently and that the periplasmic intermediate can persist for long periods under certain circumstances.
Full text
PDF

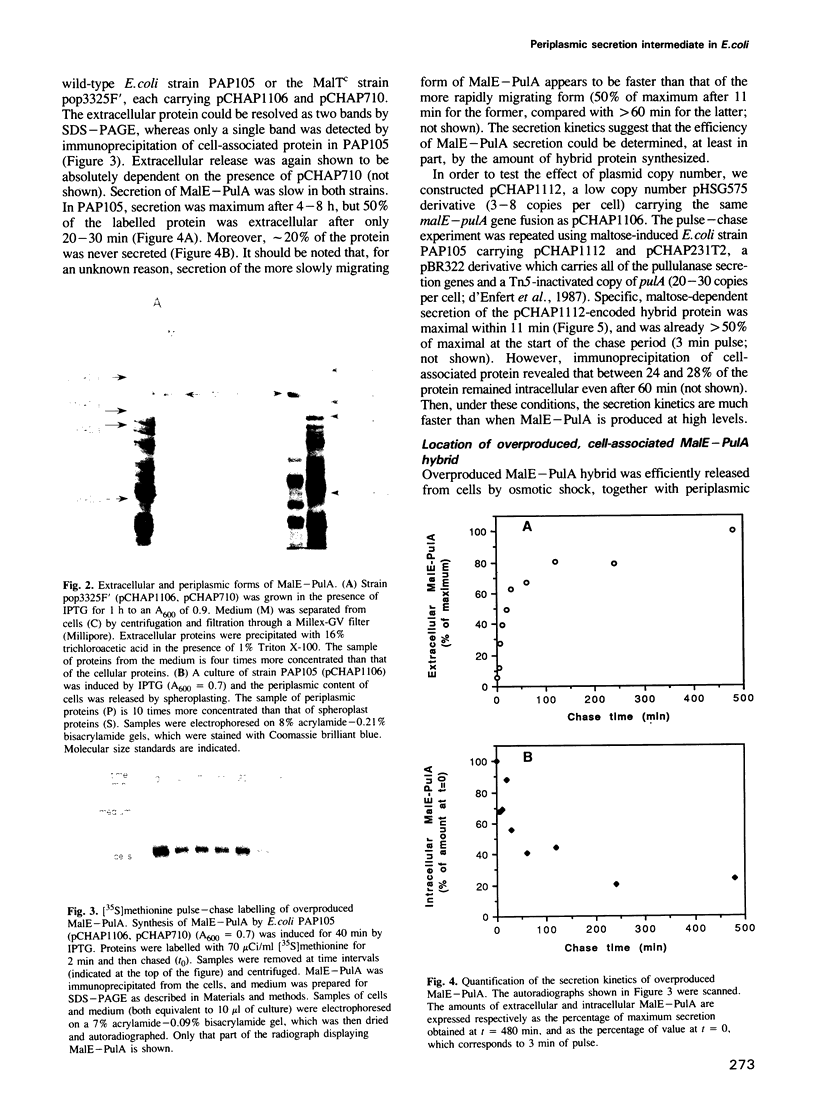
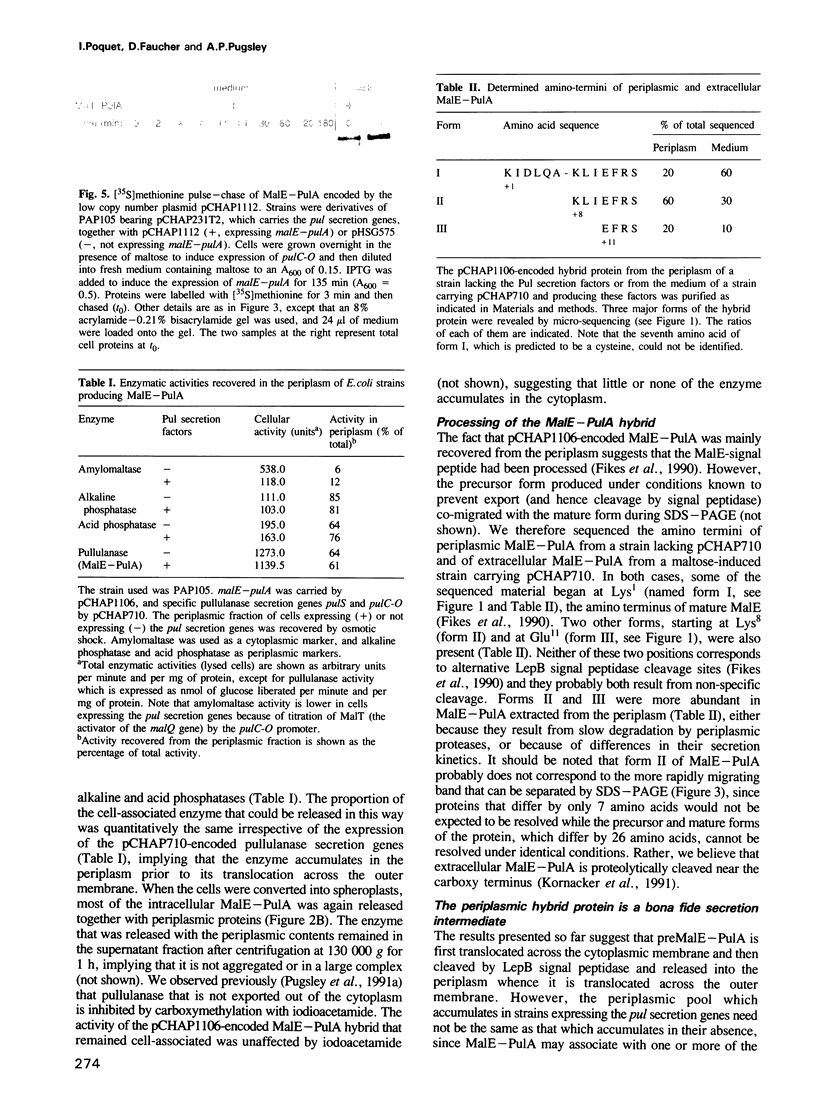




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andro T., Chambost J. P., Kotoujansky A., Cattaneo J., Bertheau Y., Barras F., Van Gijsegem F., Coleno A. Mutants of Erwinia chrysanthemi defective in secretion of pectinase and cellulase. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1199–1203. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1199-1203.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bally M., Filloux A., Akrim M., Ball G., Lazdunski A., Tommassen J. Protein secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: characterization of seven xcp genes and processing of secretory apparatus components by prepilin peptidase. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(9):1121–1131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., McGovern K., Beckwith J. Identification of a protein required for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):581–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman R. W., Heppel L. A. On the localization of alkaline phosphatase and cyclic phosphodiesterase in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jul;7(7):2554–2562. doi: 10.1021/bi00847a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Enfert C., Pugsley A. P. Klebsiella pneumoniae pulS gene encodes an outer membrane lipoprotein required for pullulanase secretion. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3673–3679. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3673-3679.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dums F., Dow J. M., Daniels M. J. Structural characterization of protein secretion genes of the bacterial phytopathogen Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris: relatedness to secretion systems of other gram-negative bacteria. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Oct;229(3):357–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00267456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Débarbouillé M., Shuman H. A., Silhavy T. J., Schwartz M. Dominant constitutive mutations in malT, the positive regulator gene of the maltose regulon in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):359–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90304-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikes J. D., Barkocy-Gallagher G. A., Klapper D. G., Bassford P. J., Jr Maturation of Escherichia coli maltose-binding protein by signal peptidase I in vivo. Sequence requirements for efficient processing and demonstration of an alternate cleavage site. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3417–3423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filloux A., Bally M., Ball G., Akrim M., Tommassen J., Lazdunski A. Protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria: transport across the outer membrane involves common mechanisms in different bacteria. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4323–4329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07881.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamood A. N., Olson J. C., Vincent T. S., Iglewski B. H. Regions of toxin A involved in toxin A excretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1817–1824. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1817-1824.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He S. Y., Lindeberg M., Chatterjee A. K., Collmer A. Cloned Erwinia chrysanthemi out genes enable Escherichia coli to selectively secrete a diverse family of heterologous proteins to its milieu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1079–1083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He S. Y., Schoedel C., Chatterjee A. K., Collmer A. Extracellular secretion of pectate lyase by the Erwinia chrysanthemi out pathway is dependent upon Sec-mediated export across the inner membrane. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4310–4317. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4310-4317.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard S. P., Buckley J. T. Protein export by a gram-negative bacterium: production of aerolysin by Aeromonas hydrophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1118–1124. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1118-1124.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N. T., Hung M. N., Chiou S. J., Tang F., Chiang D. C., Huang H. Y., Wu C. Y. Cloning and characterization of a gene required for the secretion of extracellular enzymes across the outer membrane by Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2679–2687. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2679-2687.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultgren S. J., Normark S., Abraham S. N. Chaperone-assisted assembly and molecular architecture of adhesive pili. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:383–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.002123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang B., Howard S. P. The Aeromonas hydrophila exeE gene, required both for protein secretion and normal outer membrane biogenesis, is a member of a general secretion pathway. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(10):1351–1361. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamitani S., Akiyama Y., Ito K. Identification and characterization of an Escherichia coli gene required for the formation of correctly folded alkaline phosphatase, a periplasmic enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):57–62. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornacker M. G., Boyd A., Pugsley A. P., Plastow G. S. A new regulatory locus of the maltose regulon in Klebsiella pneumoniae strain K21 identified by the study of pullulanase secretion mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Feb;135(Pt 2):397–408. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-2-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornacker M. G., Boyd A., Pugsley A. P., Plastow G. S. Klebsiella pneumoniae strain K21: evidence for the rapid secretion of an unacylated form of pullulanase. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):497–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornacker M. G., Faucher D., Pugsley A. P. Outer membrane translocation of the extracellular enzyme pullulanase in Escherichia coli K12 does not require a fatty acylated N-terminal cysteine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13842–13848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornacker M. G., Pugsley A. P. Molecular characterization of pulA and its product, pullulanase, a secreted enzyme of Klebsiella pneumoniae UNF5023. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):73–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornacker M. G., Pugsley A. P. The normally periplasmic enzyme beta-lactamase is specifically and efficiently translocated through the Escherichia coli outer membrane when it is fused to the cell-surface enzyme pullulanase. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1101–1109. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Chapon C., D'Enfert C., Pugsley A. P., Schwartz M. Characterization and expression of the structural gene for pullulanase, a maltose-inducible secreted protein of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):633–638. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.633-638.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murooka Y., Ikeda R. Biosynthesis and secretion of pullulanase, a lipoprotein from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17524–17531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Porins and specific channels of bacterial outer membranes. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):435–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possot O., d'Enfert C., Reyss I., Pugsley A. P. Pullulanase secretion in Escherichia coli K-12 requires a cytoplasmic protein and a putative polytopic cytoplasmic membrane protein. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(1):95–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Chapon C., Schwartz M. Extracellular pullulanase of Klebsiella pneumoniae is a lipoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1083–1088. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1083-1088.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Dubreuil C. Molecular characterization of malQ, the structural gene for the Escherichia coli enzyme amylomaltase. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jul;2(4):473–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Dupuy B. An enzyme with type IV prepilin peptidase activity is required to process components of the general extracellular protein secretion pathway of Klebsiella oxytoca. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(6):751–760. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Kornacker M. G., Poquet I. The general protein-export pathway is directly required for extracellular pullulanase secretion in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):343–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Kornacker M. G., Ryter A. Analysis of the subcellular location of pullulanase produced by Escherichia coli carrying the pulA gene from Klebsiella pneumoniae strain UNF5023. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):59–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Kornacker M. G. Secretion of the cell surface lipoprotein pullulanase in Escherichia coli. Cooperation or competition between the specific secretion pathway and the lipoprotein sorting pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13640–13645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Poquet I., Kornacker M. G. Two distinct steps in pullulanase secretion by Escherichia coli K12. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):865–873. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00760.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., d'Enfert C., Reyss I., Kornacker M. G. Genetics of extracellular protein secretion by gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:67–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Vidal-Ingigliardi D., Richet E. A complex nucleoprotein structure involved in activation of transcription of two divergent Escherichia coli promoters. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 5;205(3):471–485. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Hedge P. J., te Heesen S., Edelman A., Broome-Smith J. K. Kanamycin-resistant vectors that are analogues of plasmids pUC8, pUC9, pEMBL8 and pEMBL9. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita S., Sato M., Toba M., Masahashi W., Hashimoto-Gotoh T. High-copy-number and low-copy-number plasmid vectors for lacZ alpha-complementation and chloramphenicol- or kanamycin-resistance selection. Gene. 1987;61(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Enfert C., Ryter A., Pugsley A. P. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Klebsiella pneumoniae genes for production, surface localization and secretion of the lipoprotein pullulanase. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3531–3538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02679.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]