Abstract
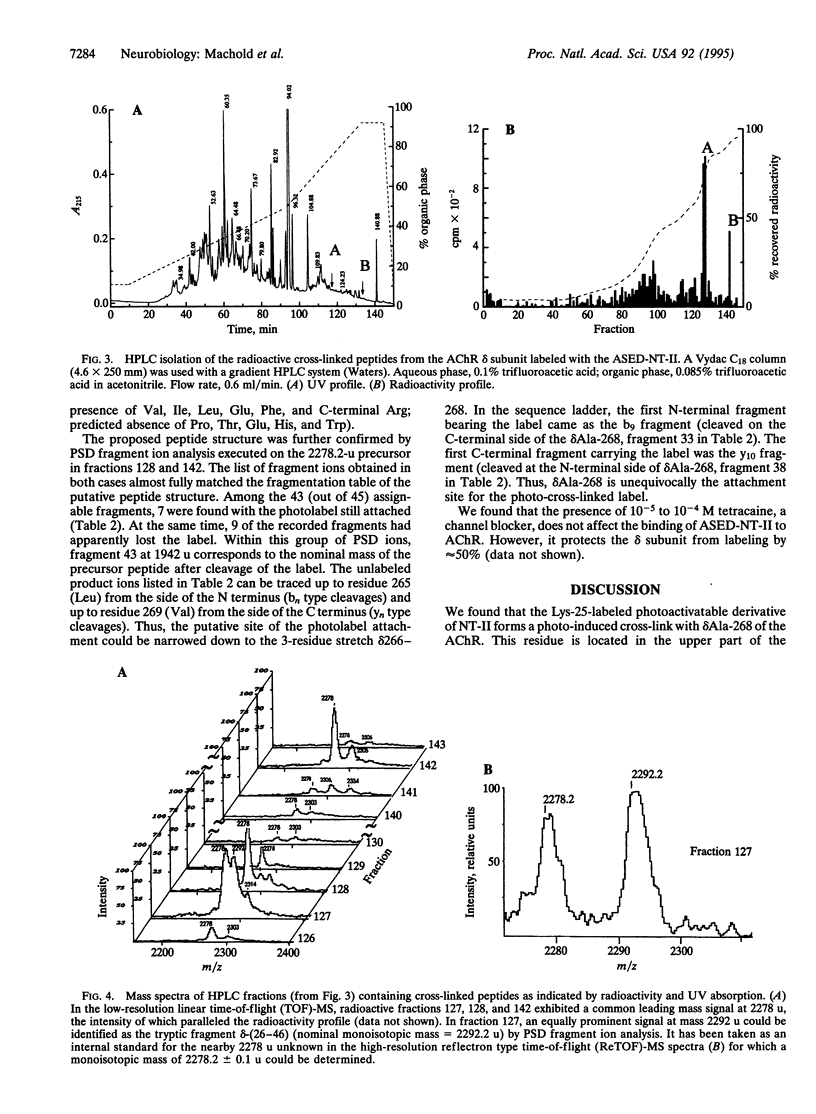
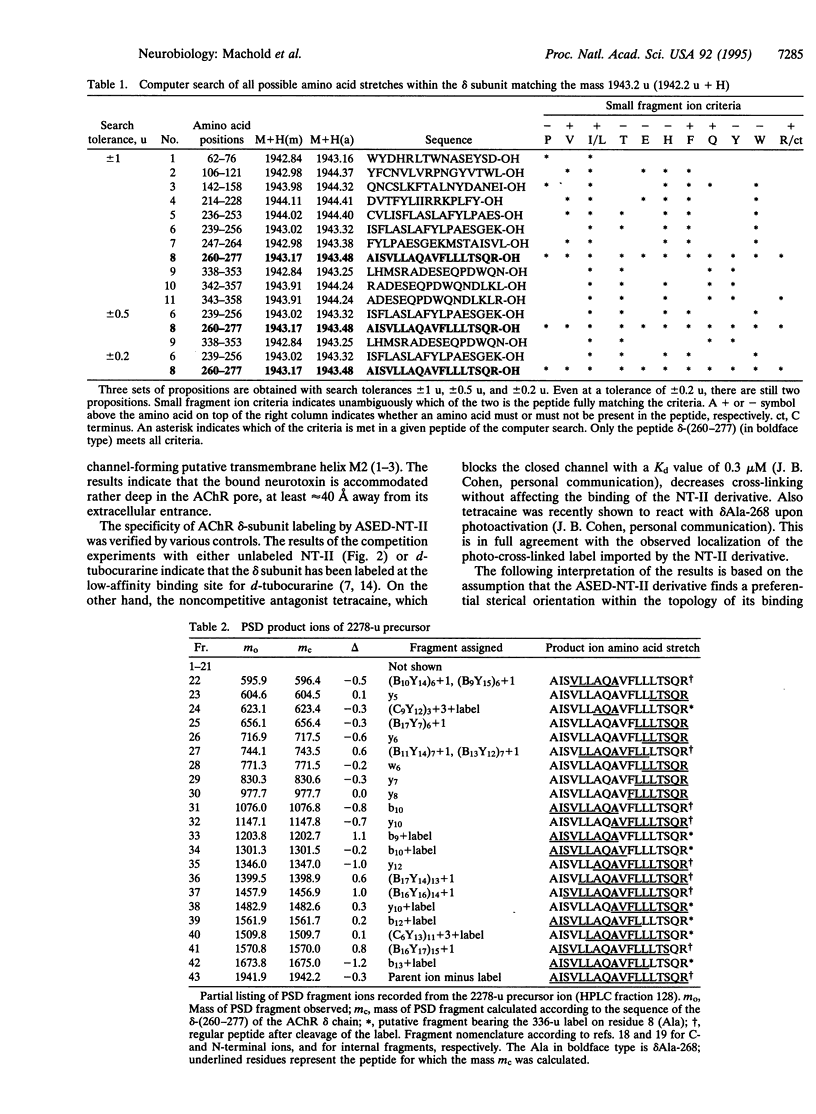
A photoactivatable derivative of neurotoxin II from Naja naja oxiana containing a 125I-labeled p-azidosalicylamidoethyl-1,3'-dithiopropyl label at Lys-25 forms a photo-induced cross-link with the delta subunit of the membrane-bound Torpedo californica nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR). The cross-linked radioactive receptor peptide was isolated by reverse-phase HPLC after tryptic digestion of the labeled delta subunit. The sequence of this peptide, delta-(260-277), and the position of the label at Ala-268 were established by matrix-assisted laser-desorption-ionization mass spectrometry based on the molecular mass and on post-source decay fragment analysis. With the known dimensions of the AChR molecule, of the photolabel, and of alpha-neurotoxin, finding the cross-link at delta Ala-268 (located in the upper part of the channel-forming transmembrane helix M2) means that the center of the alpha-neurotoxin binding site is situated at least approximately 40 A from the extracellular surface of the AChR, proximal to the channel axis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betz H. Ligand-gated ion channels in the brain: the amino acid receptor superfamily. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90077-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betzel C., Lange G., Pal G. P., Wilson K. S., Maelicke A., Saenger W. The refined crystal structure of alpha-cobratoxin from Naja naja siamensis at 2.4-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21530–21536. doi: 10.2210/pdb2ctx/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blount P., Merlie J. P. Molecular basis of the two nonequivalent ligand binding sites of the muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Devillers-Thiéry A., Galzi J. L., Bertrand D. New mutants to explore nicotinic receptor functions. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Aug;13(8):299–301. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90094-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski C., Karlin A. Agonist binding site of Torpedo electric tissue nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. A negatively charged region of the delta subunit within 0.9 nm of the alpha subunit binding site disulfide. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22603–22612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraudat J., Dennis M., Heidmann T., Chang J. Y., Changeux J. P. Structure of the high-affinity binding site for noncompetitive blockers of the acetylcholine receptor: serine-262 of the delta subunit is labeled by [3H]chlorpromazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2719–2723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golovanov A. P., Lomize A. L., Arseniev A. S., Utkin Y. N., Tsetlin V. I. Two-dimensional 1H-NMR study of the spatial structure of neurotoxin II from Naja naja oxiana. Eur J Biochem. 1993 May 1;213(3):1213–1223. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J. M., Johnson D. A., Taylor P. Distance between the agonist and noncompetitive inhibitor sites on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12439–12448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman E., Wise D., Wall J., Karlin A. Electron microscopy of complexes of isolated acetylcholine receptor, biotinyl-toxin, and avidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):310–314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F., Oberthür W., Lottspeich F. The ion channel of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is formed by the homologous helices M II of the receptor subunits. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80881-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Cushman R., Malekzadeh R. Orientation of cobra alpha-toxin on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Fluorescence studies. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7360–7368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Nuss J. M. The histrionicotoxin-sensitive ethidium binding site is located outside of the transmembrane domain of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: a fluorescence study. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 9;33(31):9070–9077. doi: 10.1021/bi00197a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A. Explorations of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Harvey Lect. 1989;85:71–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A. Structure of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Jun;3(3):299–309. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90121-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreienkamp H. J., Utkin Y. N., Weise C., Machold J., Tsetlin V. I., Hucho F. Investigation of ligand-binding sites of the acetylcholine receptor using photoactivatable derivatives of neurotoxin II from Naja naja oxiana. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 8;31(35):8239–8244. doi: 10.1021/bi00150a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. W., Corfield P. W. Erabutoxin b. Structure/function relationships following initial protein refinement at 0.140-nm resolution. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 15;161(3):579–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machold J., Weise C., Utkin Y. N., Franke P., Tsetlin V. I., Hucho F. A new class of photoactivatable and cleavable derivatives of neurotoxin II from Naja naja oxiana. Synthesis, characterisation, and application for affinity labelling of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Mar 15;228(3):947–954. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. E., Cohen J. B. d-Tubocurarine binding sites are located at alpha-gamma and alpha-delta subunit interfaces of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepstorff P., Fohlman J. Proposal for a common nomenclature for sequence ions in mass spectra of peptides. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1984 Nov;11(11):601–601. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200111109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebler W., Lauffer L., Hucho F. Acetylcholine receptor enriched membranes: acetylcholine binding and excitability after reduction in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 1;81(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80923-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrattenholz A., Godovac-Zimmermann J., Schäfer H. J., Albuquerque E. X., Maelicke A. Photoaffinity labeling of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor by physostigmine. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Sep 1;216(2):671–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M. Molecular dissection of subunit interfaces in the acetylcholine receptor: identification of residues that determine curare selectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9436–9440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Isla B. A., Hucho F. Acetylcholine receptor: SH group reactivity as indicator of conformational changes and functional states. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin N. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at 9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1993 Feb 20;229(4):1101–1124. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]