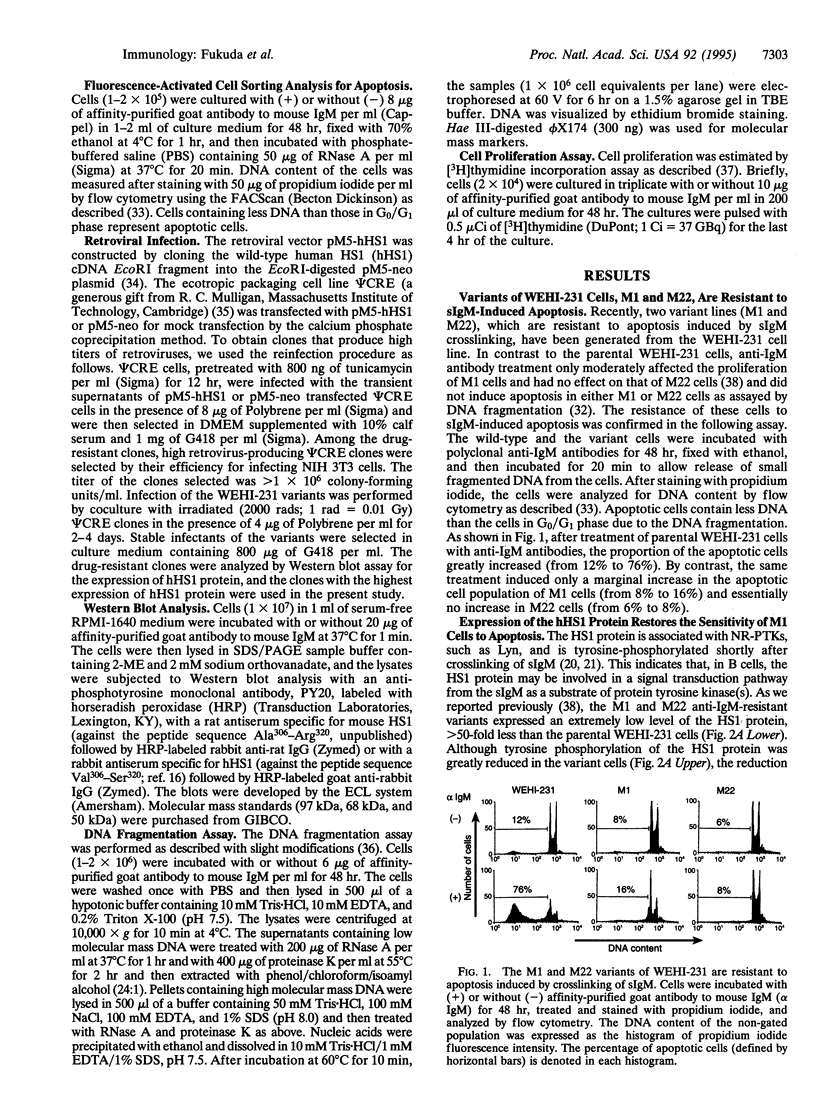
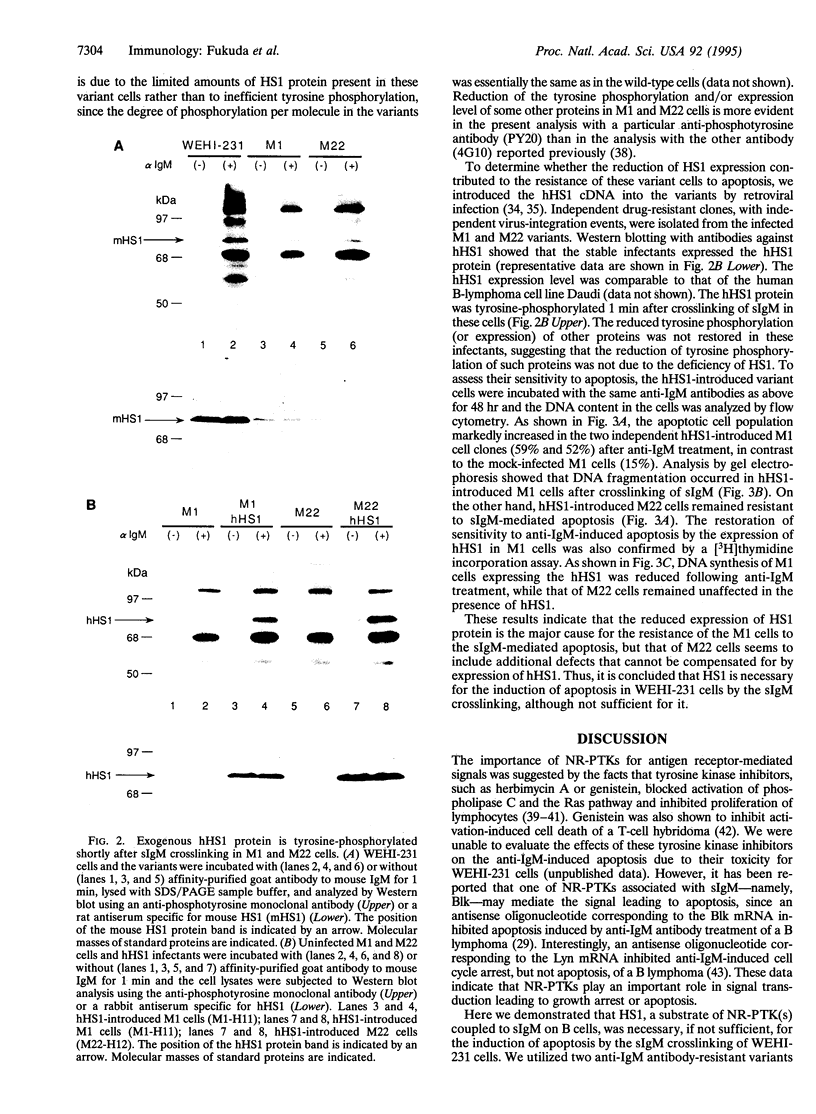
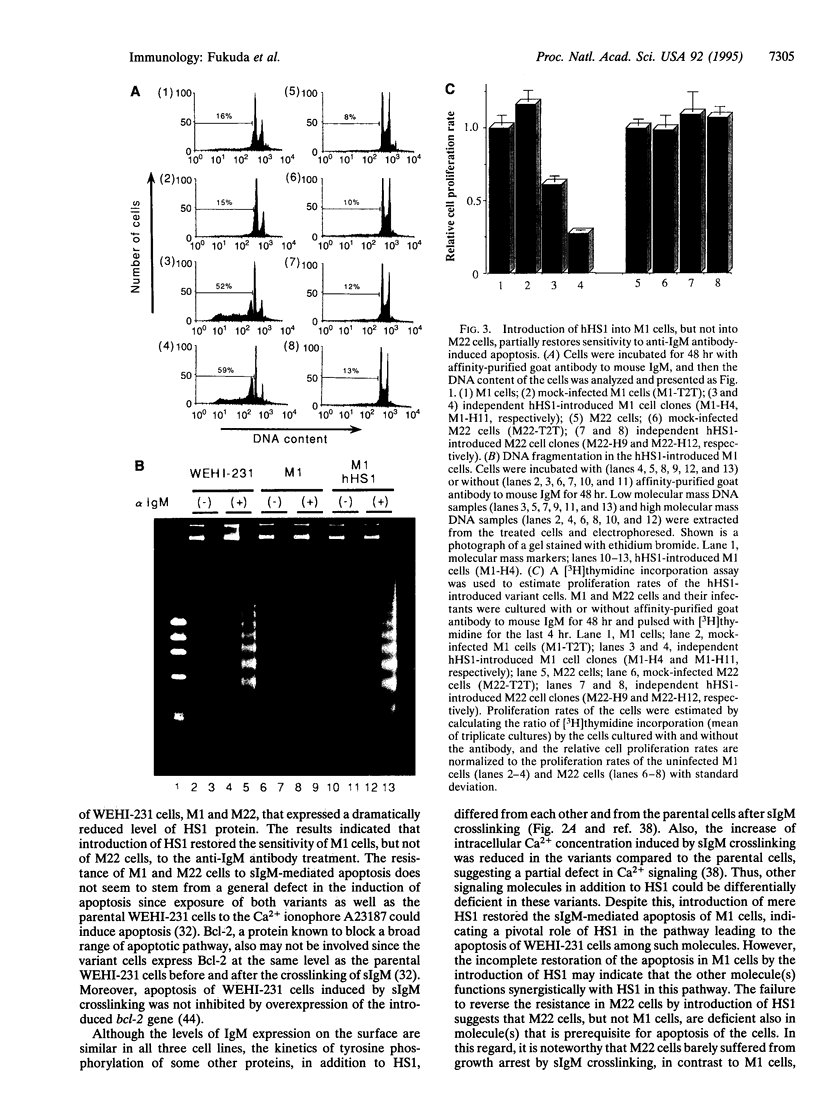
Abstract
The HS1 protein is one of the major substrates of non-receptor-type protein-tyrosine kinases and is phosphorylated immediately after crosslinking of the surface IgM on B cells. The mouse B-lymphoma cell line WEHI-231 is known to undergo apoptosis upon crosslinking of surface IgM by anti-IgM antibodies. Variants of WEHI-231 that were resistant to anti-IgM-induced apoptosis expressed dramatically reduced levels of HS1 protein. Expression of the human HS1 protein from an expression vector introduced into one of the variant cell lines restored the sensitivity of the cells to apoptosis induced by surface IgM crosslinking. These results suggest that HS1 protein plays a crucial role in the B-cell antigen receptor-mediated signal transduction pathway that leads to apoptosis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baixeras E., Kroemer G., Cuende E., Márquez C., Boscá L., Alés Martínez J. E., Martínez C. Signal transduction pathways involved in B-cell induction. Immunol Rev. 1993 Apr;132:5–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1993.tb00836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann G., Maier D., Freuler F., Tschopp C., Baudisch K., Wienands J. In vitro characterization of major ligands for Src homology 2 domains derived from protein tyrosine kinases, from the adaptor protein SHC and from GTPase-activating protein in Ramos B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Aug;24(8):1799–1807. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benhamou L. E., Cazenave P. A., Sarthou P. Anti-immunoglobulins induce death by apoptosis in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1405–1407. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benhamou L. E., Watanabe T., Kitamura D., Cazenave P. A., Sarthou P. Signaling properties of anti-immunoglobulin--resistant variants of WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Sep;24(9):1993–1999. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A. L., Brunswick M., Bolen J. B., Mond J. J. Anti-immunoglobulin stimulation of B lymphocytes activates src-related protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustelo X. R., Barbacid M. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the vav proto-oncogene product in activated B cells. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1196–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. H., Park D. J., Rhee S. G., Fearon D. T. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C induced by membrane immunoglobulin in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2745–2749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuende E., Alés-Martínez J. E., Ding L., Gónzalez-García M., Martínez C., Nunez G. Programmed cell death by bcl-2-dependent and independent mechanisms in B lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1555–1560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Mulligan R. C. Safe and efficient generation of recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz Z., Bruno S., Del Bino G., Gorczyca W., Hotz M. A., Lassota P., Traganos F. Features of apoptotic cells measured by flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1992;13(8):795–808. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990130802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Crowley M. T., Martin G. A., McCormick F., DeFranco A. L. Targets of B lymphocyte antigen receptor signal transduction include the p21ras GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and two GAP-associated proteins. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):377–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley S. B., Cooke M. P., Fulcher D. A., Harris A. W., Cory S., Basten A., Goodnow C. C. Elimination of self-reactive B lymphocytes proceeds in two stages: arrested development and cell death. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):325–335. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley S. B., Crosbie J., Brink R., Kantor A. B., Basten A., Goodnow C. C. Elimination from peripheral lymphoid tissues of self-reactive B lymphocytes recognizing membrane-bound antigens. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):765–769. doi: 10.1038/353765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasbold J., Klaus G. G. Anti-immunoglobulin antibodies induce apoptosis in immature B cell lymphomas. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1685–1690. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel W. M., Schatzman R. C., DeFranco A. L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 2 upon cross-linking of membrane Ig on murine B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3021–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibner U., Benhamou L. E., Haury M., Cazenave P. A., Sarthou P. Signaling of programmed cell death induction in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Nov;23(11):2821–2825. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchcroft J. E., Harrison M. L., Geahlen R. L. Association of the 72-kDa protein-tyrosine kinase PTK72 with the B cell antigen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8613–8619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida Y., Agata Y., Shibahara K., Honjo T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3887–3895. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05481.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin L. W., Inaba K., Saitoh T. The involvement of protein kinase C in activation-induced cell death in T-cell hybridoma. Cell Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;144(1):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90238-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Schieven G. L., Siegel J. N., Phillips A. F., Samelson L. E. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents T-cell receptor-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7722–7726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawauchi K., Lazarus A. H., Rapoport M. J., Harwood A., Cambier J. C., Delovitch T. L. Tyrosine kinase and CD45 tyrosine phosphatase activity mediate p21ras activation in B cells stimulated through the antigen receptor. J Immunol. 1994 Apr 1;152(7):3306–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura D., Kaneko H., Miyagoe Y., Ariyasu T., Watanabe T. Isolation and characterization of a novel human gene expressed specifically in the cells of hematopoietic lineage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9367–9379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Scott M. P. Sequence of a Drosophila segmentation gene: protein structure homology with DNA-binding proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):25–31. doi: 10.1038/310025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. E., Pepe V. H., Kent R. B., Dean M., Marshak-Rothstein A., Sonenshein G. E. Specific regulation of c-myc oncogene expression in a murine B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5546–5550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. G. Up-regulation of c-fos expression is a component of the mIg signal transduction mechanism but is not indicative of competence for proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1454–1460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Tsubata T., Okamoto M., Shimizu A., Kumagai S., Imura H., Honjo T. Antigen-induced apoptotic death of Ly-1 B cells responsible for autoimmune disease in transgenic mice. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):77–80. doi: 10.1038/357077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Isakov N., Altman A. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C requires tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2138816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemazee D. A., Bürki K. Clonal deletion of B lymphocytes in a transgenic mouse bearing anti-MHC class I antibody genes. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):562–566. doi: 10.1038/337562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Cellular mechanisms of immunologic tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:33–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Negative selection of lymphocytes. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):392–392. doi: 10.1038/341392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Mayer B. J., Cicchetti P., Baltimore D. Identification of a ten-amino acid proline-rich SH3 binding site. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.8438166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarthou P., Henry-Toulmé N., Cazenave P. A. Membrane IgM cross-linking is not coupled to protein kinase C translocation in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1247–1252. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuermann R. H., Racila E., Tucker T., Yefenof E., Street N. E., Vitetta E. S., Picker L. J., Uhr J. W. Lyn tyrosine kinase signals cell cycle arrest but not apoptosis in B-lineage lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):4048–4052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.4048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfert V. L., Sukhatme V. P., Monroe J. G. Differential expression of a zinc finger-encoding gene in response to positive versus negative signaling through receptor immunoglobulin in murine B lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2083–2088. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocking C., Kollek R., Bergholz U., Ostertag W. Long terminal repeat sequences impart hematopoietic transformation properties to the myeloproliferative sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5746–5750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilzey J. F., Chiles T. C., Rothstein T. L. Jun-B gene expression mediated by the surface immunoglobulin receptor of primary B lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 28;175(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Fukui Y., Wongsasant B., Kinoshita Y., Ichimori Y., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. Activation of Src-like protein-tyrosine kinase Lyn and its association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase upon B-cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1118–1122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Kakiuchi T., Mizuguchi J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1702903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Okada M., Semba T., Yamori T., Umemori H., Tsunasawa S., Toyoshima K., Kitamura D., Watanabe T., Yamamoto T. Identification of HS1 protein as a major substrate of protein-tyrosine kinase(s) upon B-cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3631–3635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao X. R., Scott D. W. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to the blk tyrosine kinase prevent anti-mu-chain-mediated growth inhibition and apoptosis in a B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):7946–7950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.7946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




