Abstract
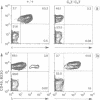
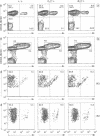
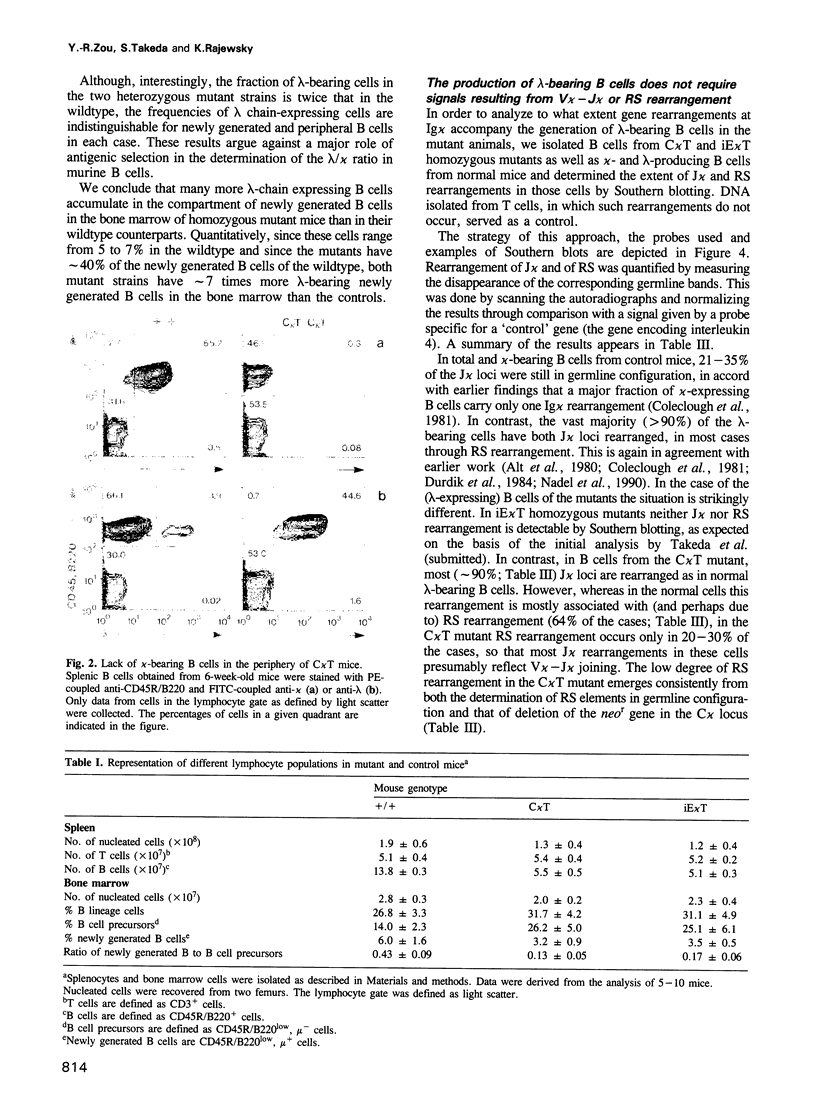
The production of lambda chain-expressing B cells was studied in mice in which either the gene encoding the constant region of the kappa chain (C kappa) or the intron enhancer in the Ig kappa locus was inactivated by insertion of a neomycin resistance gene. The two mutants have similar phenotypes: in heterozygous mutant mice the fraction of lambda chain-bearing B cells is twice that in the wildtype. Homozygous mutants produce approximately 7 times more lambda-expressing B cells (and about 2.3 times fewer total B cells) in the bone marrow than their normal counterparts, suggesting that B cell progenitors can differentiate into either kappa- or lambda-producing cells and do the latter in the mutants. Whereas gene rearrangements in the Ig kappa locus are blocked in the case of enhancer inactivation, they still occur in that of the C kappa mutant, although in this mutant RS rearrangement is lower than in the wildtype. This indicates that gene rearrangements in the Ig lambda locus can occur in the absence of a putative positive signal resulting from gene rearrangements in Ig kappa, including RS recombination. Complementing these results, we also present data indicating that in normal B cell development kappa chain rearrangement can be preceded by lambda chain rearrangement and that the frequency of kappa/lambda double producers is small and insufficient to explain the massive production of lambda chain-expressing B cells in the mutants.
Full text
PDF


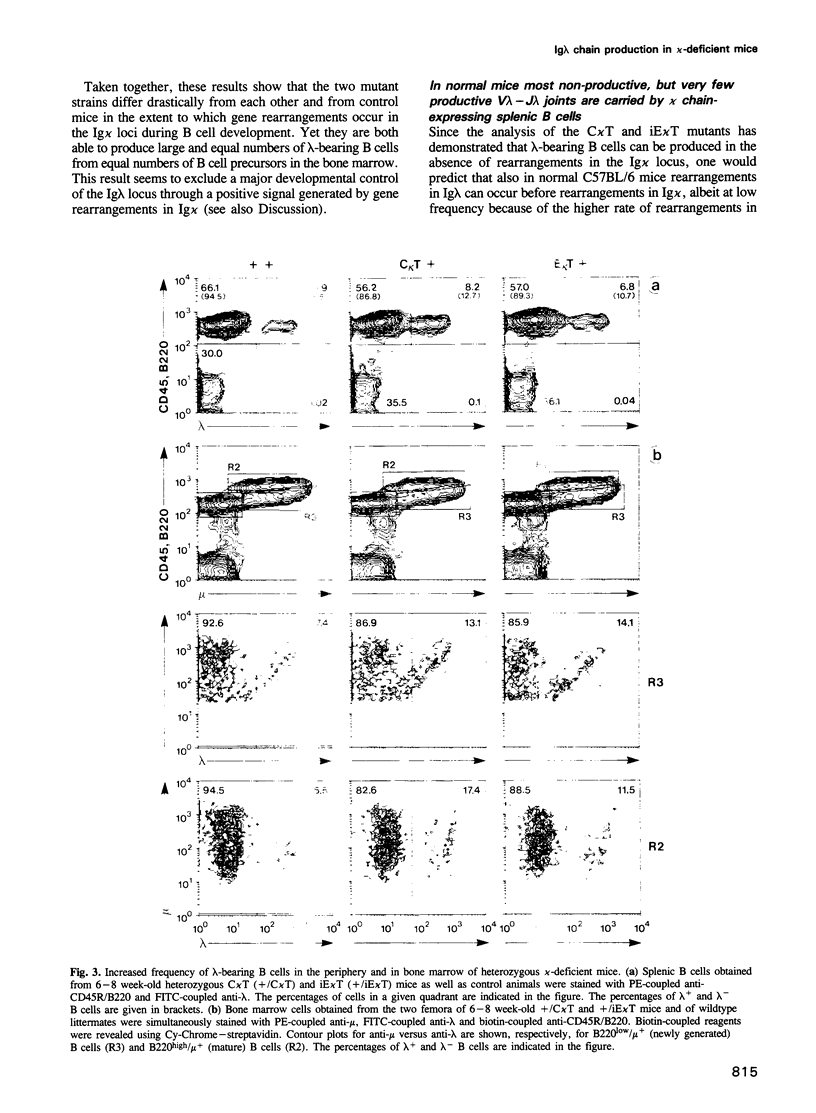
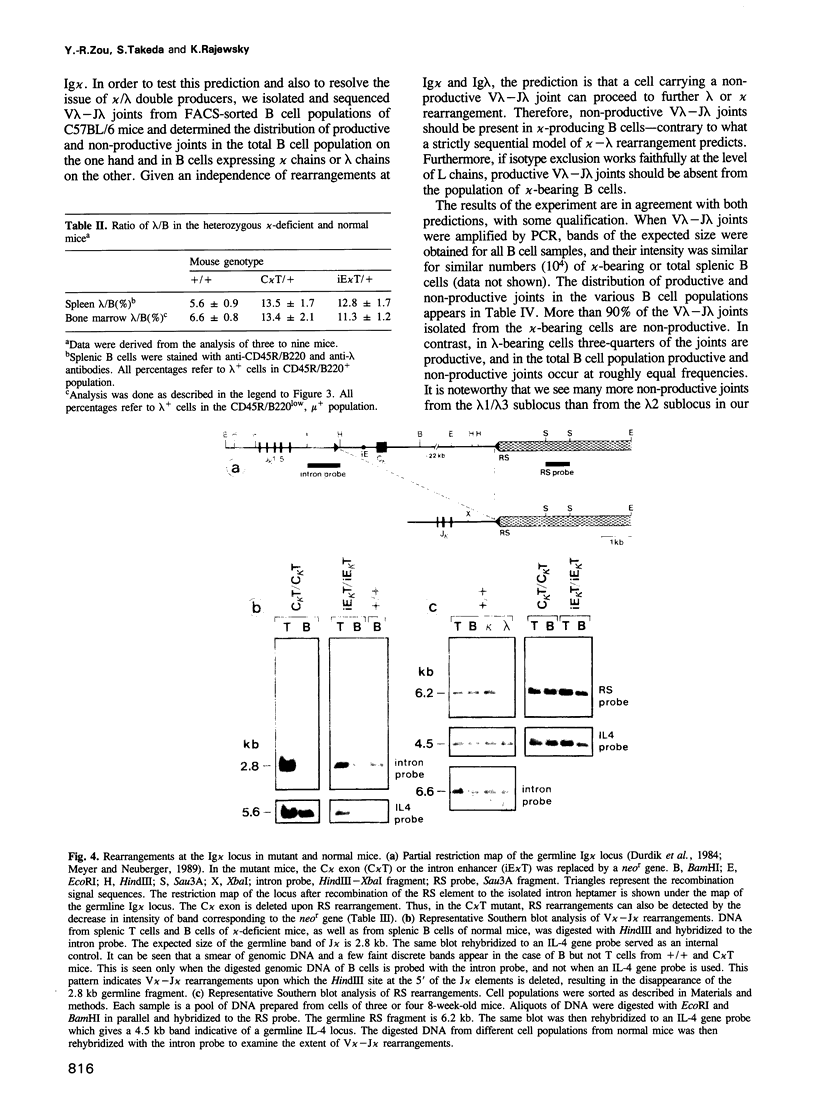




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., DePinho R. A., Reth M. G., Yancopoulos G. D. Regulation of genome rearrangement events during lymphocyte differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1986 Feb;89:5–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Enea V., Bothwell A. L., Baltimore D. Activity of multiple light chain genes in murine myeloma cells producing a single, functional light chain. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J., McDowell M., Jäck H. M., Wabl M. Immunoglobulin lambda gene rearrangement can precede kappa gene rearrangement. Dev Immunol. 1990;1(1):53–57. doi: 10.1155/1990/56014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Malynn B. A., Pollock R. R., Ferrier P., Covey L. R., Fulop G. M., Phillips R. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. Isolation of scid pre-B cells that rearrange kappa light chain genes: formation of normal signal and abnormal coding joins. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):735–742. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03433.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg B., Traunecker A., Eisen H., Tonegawa S. Organization of four mouse lambda light chain immunoglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3765–3769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Trounstine M., Kurahara C., Young F., Kuo C. C., Xu Y., Loring J. F., Alt F. W., Huszar D. B cell development in mice that lack one or both immunoglobulin kappa light chain genes. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):821–830. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05722.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L. Surface antigen expression and immunoglobulin gene rearrangement during mouse pre-B cell development. Immunol Rev. 1982;69:5–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb00446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn M., Langman R. E. The protecton: the unit of humoral immunity selected by evolution. Immunol Rev. 1990 Jun;115:11–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleclough C. A critique of the Cohn-Langman protection theory. Immunol Rev. 1990 Jun;115:173–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleclough C., Perry R. P., Karjalainen K., Weigert M. Aberrant rearrangements contribute significantly to the allelic exclusion of immunoglobulin gene expression. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):372–378. doi: 10.1038/290372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Tyler B. M., Adams J. M. Sets of immunoglobulin V kappa genes homologous to ten cloned V kappa sequences: implications for the number of germline V kappa genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(2):103–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Rosales R., Staub A., Chambon P. The HeLa cell protein TEF-1 binds specifically and cooperatively to two SV40 enhancer motifs of unrelated sequence. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):931–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildrop R., Gause A., Müller W., Rajewsky K. A new V gene expressed in lambda-2 light chains of the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1987 May;17(5):731–734. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durdik J., Moore M. W., Selsing E. Novel kappa light-chain gene rearrangements in mouse lambda light chain-producing B lymphocytes. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):749–752. doi: 10.1038/307749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feddersen R. M., Martin D. J., Van Ness B. G. The frequency of multiple recombination events occurring at the human Ig kappa L chain locus. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):1088–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsher D. W., Ando D. T., Braun J. Independent rearrangement of Ig lambda genes in tissue culture-derived murine B cell lines. Int Immunol. 1991 Jul;3(7):711–718. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.7.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förster I., Vieira P., Rajewsky K. Flow cytometric analysis of cell proliferation dynamics in the B cell compartment of the mouse. Int Immunol. 1989;1(4):321–331. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.4.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollahon K. A., Hagman J., Brinster R. L., Storb U. Ig lambda-producing B cells do not show feedback inhibition of gene rearrangement. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2771–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu H., Förster I., Rajewsky K. Sequence homologies, N sequence insertion and JH gene utilization in VHDJH joining: implications for the joining mechanism and the ontogenetic timing of Ly1 B cell and B-CLL progenitor generation. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2133–2140. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07382.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu H., Kitamura D., Rajewsky K. B cell development regulated by gene rearrangement: arrest of maturation by membrane-bound D mu protein and selection of DH element reading frames. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90406-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu H., Tarlinton D., Müller W., Rajewsky K., Förster I. Most peripheral B cells in mice are ligand selected. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1357–1371. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada K., Yamagishi H. Lack of feedback inhibition of V kappa gene rearrangement by productively rearranged alleles. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):409–415. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Carmack C. E., Shinton S. A., Kemp J. D., Hayakawa K. Resolution and characterization of pro-B and pre-pro-B cell stages in normal mouse bone marrow. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1213–1225. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Dangl J. L., Hayakawa K., Jager G., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Frequent lambda light chain gene rearrangement and expression in a Ly-1 B lymphoma with a productive kappa chain allele. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1438–1442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haughton G., Lanier L. L., Babcock G. F. The murine kappa light chain shift. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):154–157. doi: 10.1038/275154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin kappa light-chain genes are deleted or rearranged in lambda-producing B cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):368–372. doi: 10.1038/290368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg D., Lundkvist I., Forni L., Ivars F., Coutinho A. Absence of immunoglobulin heavy chain expression results in altered kappa/lambda light chain ratios. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1985;2(1):51–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber C., Klobeck H. G., Zachau H. G. Ongoing V kappa-J kappa recombination after formation of a productive V kappa-J kappa coding joint. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1561–1565. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S., Kim K. J., Scher I. Surface membrane kappa and lambda light chain expression on spleen cells of neonatal and maturing normal and immune-defective CBA/NB mice: the kappa:lambda ratio is constant. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1674–1678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura D., Rajewsky K. Targeted disruption of mu chain membrane exon causes loss of heavy-chain allelic exclusion. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):154–156. doi: 10.1038/356154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobeck H. G., Zachau H. G. The human CK gene segment and the kappa deleting element are closely linked. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4591–4603. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Smithies O. Inactivating the beta 2-microglobulin locus in mouse embryonic stem cells by homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8932–8935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubagawa H., Cooper M. D., Carroll A. J., Burrows P. D. Light-chain gene expression before heavy-chain gene rearrangement in pre-B cells transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2356–2360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeJeune J. M., Briles D. E., Lawton A. R., Kearney J. F. Estimate of the light chain repertoire size of fetal and adult BALB/cJ and CBA/J mice. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):673–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledermann B., Bürki K. Establishment of a germ-line competent C57BL/6 embryonic stem cell line. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Dec;197(2):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Sachs D. H., Samelson L. E., Bluestone J. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a murine T3 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Rosenberg N., Alt F., Baltimore D. Continuing kappa-gene rearrangement in a cell line transformed by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire K. L., Vitetta E. S. kappa/lambda Shifts do not occur during maturation of murine B cells. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1670–1673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K. B., Neuberger M. S. The immunoglobulin kappa locus contains a second, stronger B-cell-specific enhancer which is located downstream of the constant region. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1959–1964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Reth M. Ordered activation of the Ig lambda locus in Abelson B cell lines. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2131–2137. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel B., Cazenave P. A., Sanchez P. Murine lambda gene rearrangements: the stochastic model prevails over the ordered model. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):435–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08128.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa S. I., Kina T., Gyotoku J. I., Katsura Y. High frequency of lambda gene activation in bone marrow pre-B cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):617–622. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Gorman S., Fox D. T., Wahl G. M. Recombinase-mediated gene activation and site-specific integration in mammalian cells. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.1900642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmond D. G. Proliferation kinetics and the lifespan of B cells in central and peripheral lymphoid organs. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Apr;3(2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persiani D. M., Durdik J., Selsing E. Active lambda and kappa antibody gene rearrangement in Abelson murine leukemia virus-transformed pre-B cell lines. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1655–1674. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primi D., Levi-Strauss M., Cazenave P. A. The level of lambda 1 light chain expression in the mouse reflects the probability of rearrangement of the relevant gene. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jan;16(1):53–59. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsden D. A., Wu G. E. Mouse kappa light-chain recombination signal sequences mediate recombination more frequently than do those of lambda light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10721–10725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A., Streb M., Melchers F. The kappa/lambda ratio in surface immunoglobulin molecules on B lymphocytes differentiating from DHJH-rearranged murine pre-B cell clones in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Nov;21(11):2895–2898. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez P., Cazenave P. A. A new variable region in mouse immunoglobulin lambda light chains. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):265–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez P., Marche P. N., Le Guern C., Cazenave P. A. Structure of a third murine immunoglobulin lambda light chain variable region that is expressed in laboratory mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9185–9188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauter H., Paige C. J. Detection of normal B-cell precursors that give rise to colonies producing both kappa and lambda light immunoglobulin chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4989–4993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Baltimore D. Activation of immunoglobulin kappa gene rearrangement correlates with induction of germline kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):1001–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90951-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch K. A., Bakhshi A., Goldman P., Korsmeyer S. J. A uniform deleting element mediates the loss of kappa genes in human B cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):260–262. doi: 10.1038/316260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch K. A., Moore M. W., Durdik J., Selsing E. The human kappa deleting element and the mouse recombining segment share DNA sequence homology. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2699–2705. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori T., Rajewsky K. Lambda chain expression at different stages of ontogeny in C57BL/6, BALB/c and SJL mice. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Aug;11(8):618–625. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]