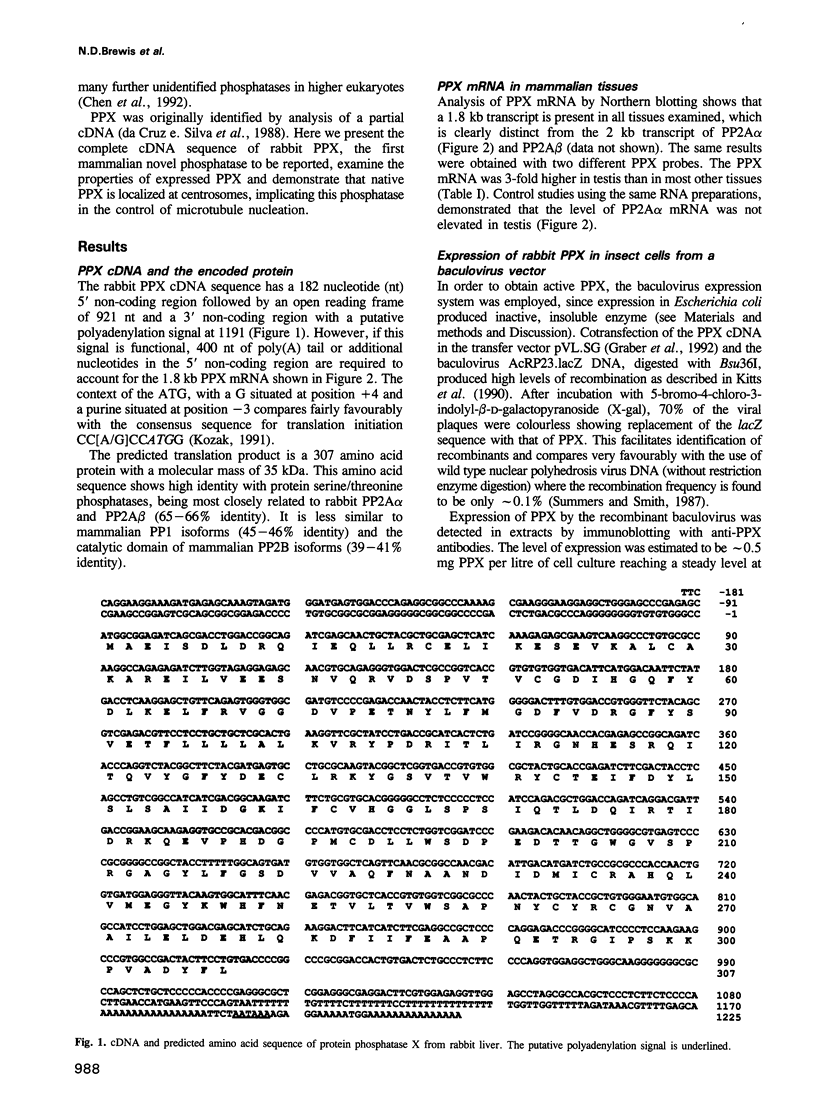
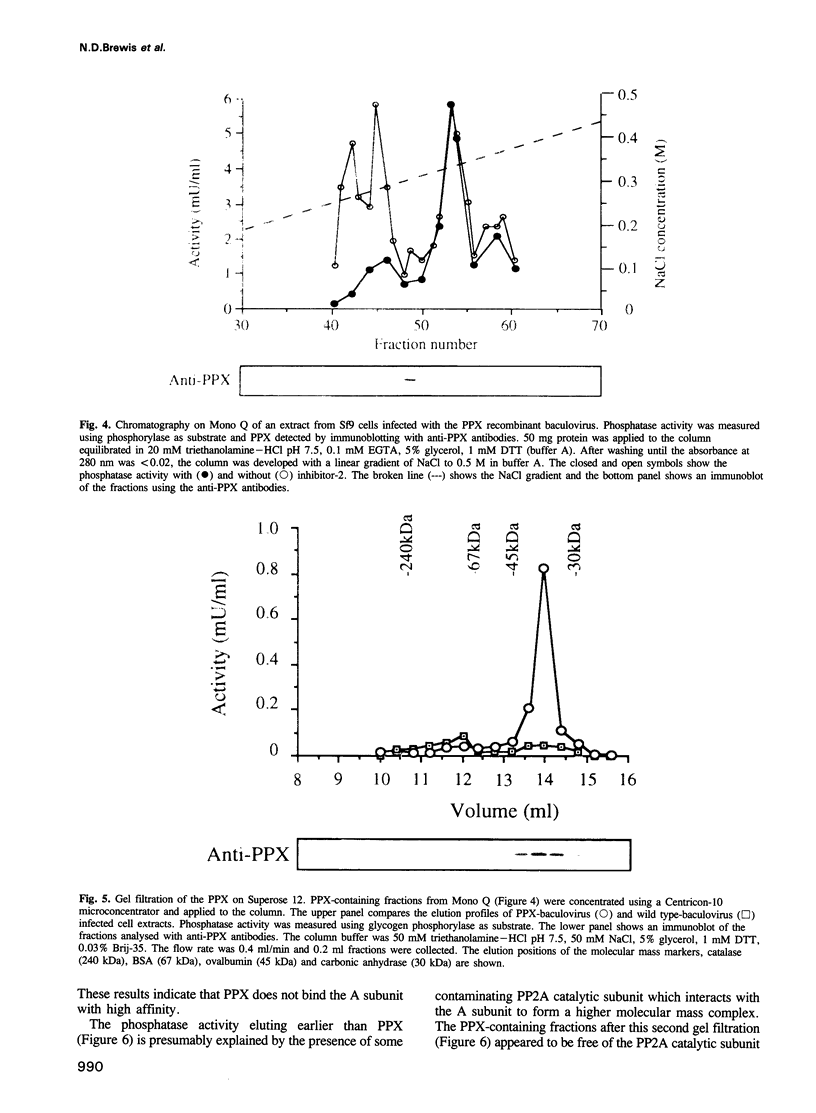
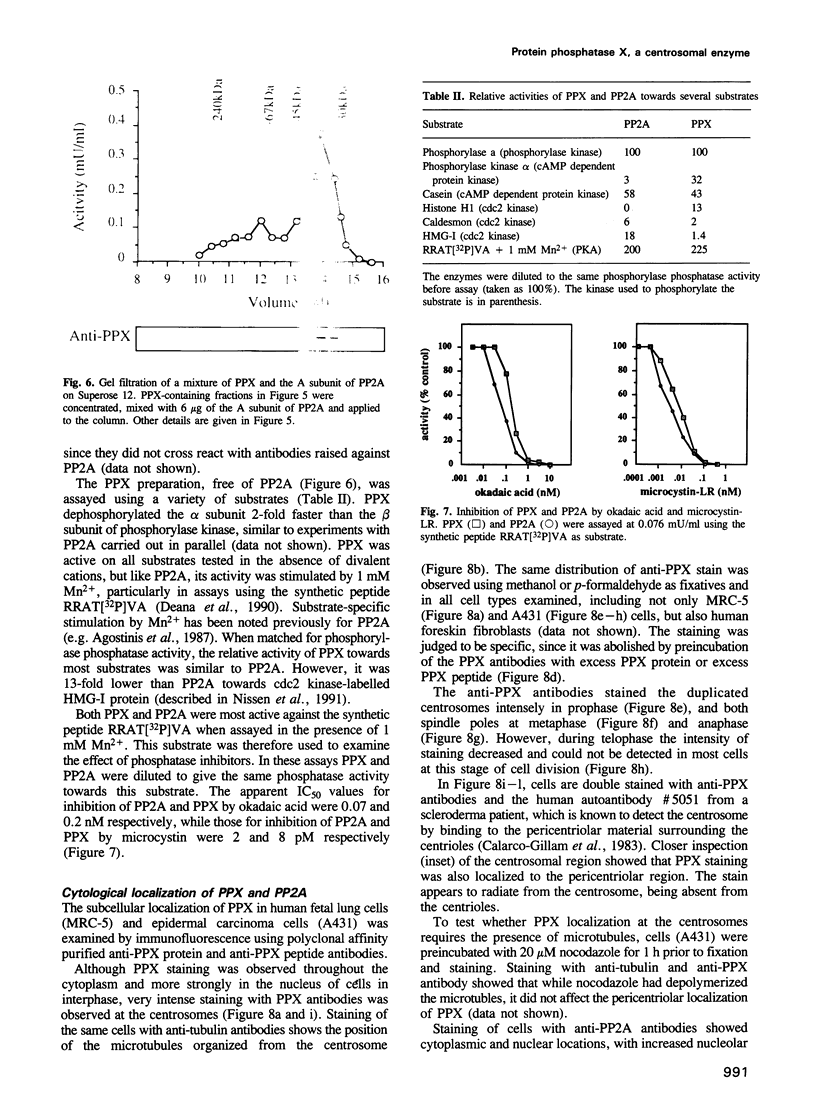
Abstract
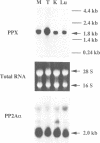
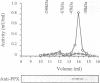
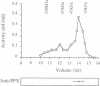
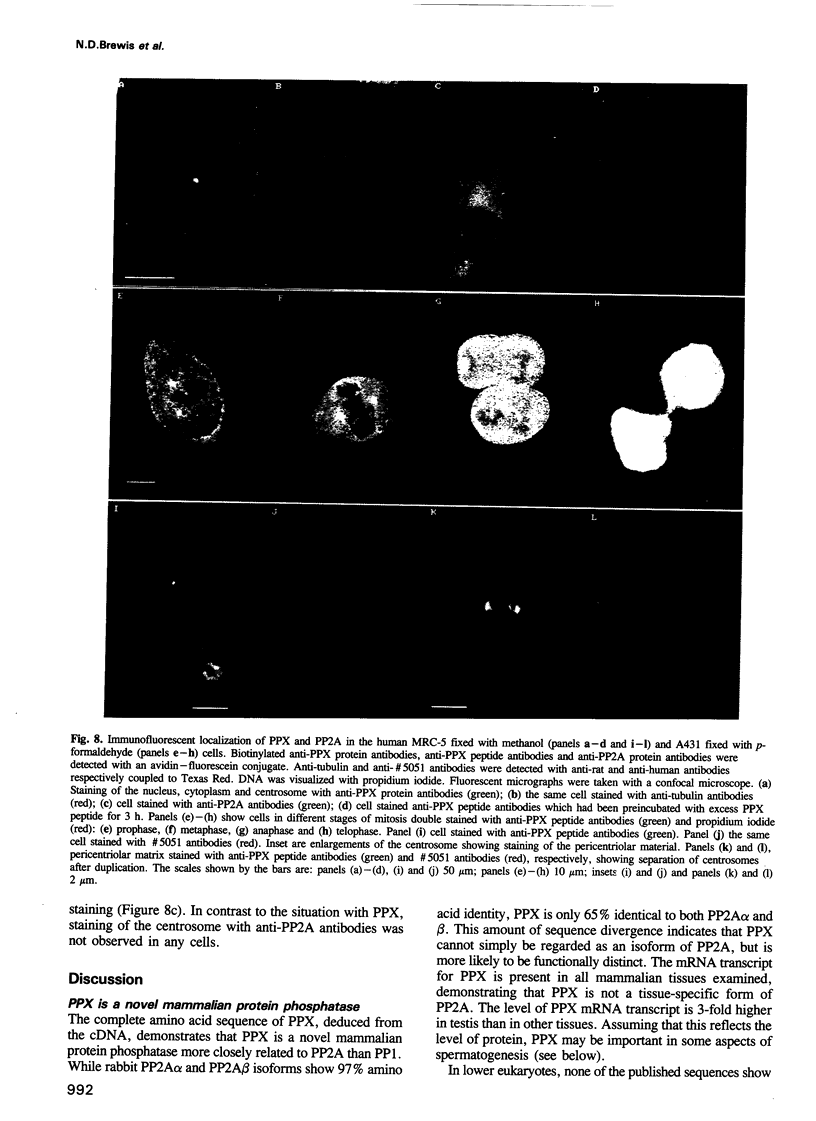
The amino acid sequence of a novel mammalian protein phosphatase, termed PPX (and designated PPP4 in the human genome nomenclature), has been deduced from the cDNA and shown to be 65% identical to PP2A alpha and PP2A beta and 45% identical to PPI isoforms, the predicted molecular mass being 35 kDa. PPX was expressed in the baculovirus system. Its substrate specificity and sensitivity to the inhibitors, okadaic acid and microcystin, were similar (but not identical) to the catalytic subunit of PP2A. However, PPX did not bind the 65 kDa regulatory subunit of PP2A. The intracellular localization of PPX was investigated by immunofluorescence using two different antibodies raised against bacterially expressed PPX and a PPX-specific peptide. These showed that although PPX was distributed throughout the cytoplasm and the nucleus, intense staining occurred at centrosomes. The centrosomal staining was apparent in interphase and at all stages of mitosis, except telophase. In contrast, antibodies directed against bacterially expressed PP2A were not specifically localized to centrosomes. The human autoantibody #5051, which stains the pericentriolar material, colocalizes with PPX antibodies, suggesting that PPX may play a role in microtubule nucleation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agostinis P., Goris J., Waelkens E., Pinna L. A., Marchiori F., Merlevede W. Dephosphorylation of phosphoproteins and synthetic phosphopeptides. Study of the specificity of the polycation-stimulated and MgATP-dependent phosphorylase phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1060–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandre H., Van Cauwenberge A., Tsukitani Y., Mulnard J. Pleiotropic effect of okadaic acid on maturing mouse oocytes. Development. 1991 Aug;112(4):971–980. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.4.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. T., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. A suppressor of a HIS4 transcriptional defect encodes a protein with homology to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90576-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axton J. M., Dombrádi V., Cohen P. T., Glover D. M. One of the protein phosphatase 1 isoenzymes in Drosophila is essential for mitosis. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90286-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly E., Dorée M., Nurse P., Bornens M. p34cdc2 is located in both nucleus and cytoplasm; part is centrosomally associated at G2/M and enters vesicles at anaphase. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3985–3995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berndt N., Cohen P. T. Renaturation of protein phosphatase 1 expressed at high levels in insect cells using a baculovirus vector. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jun 20;190(2):291–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewis N. D., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatase X has been highly conserved during mammalian evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 29;1171(2):231–233. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90129-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browner M. F., Rasor P., Tugendreich S., Fletterick R. J. Temperature-sensitive production of rabbit muscle glycogen phosphorylase in Escherichia coli. Protein Eng. 1991 Feb;4(3):351–357. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.3.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buendia B., Draetta G., Karsenti E. Regulation of the microtubule nucleating activity of centrosomes in Xenopus egg extracts: role of cyclin A-associated protein kinase. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1431–1442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
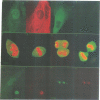
- Calarco-Gillam P. D., Siebert M. C., Hubble R., Mitchison T., Kirschner M. Centrosome development in early mouse embryos as defined by an autoantibody against pericentriolar material. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):621–629. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centonze V. E., Borisy G. G. Nucleation of microtubules from mitotic centrosomes is modulated by a phosphorylated epitope. J Cell Sci. 1990 Mar;95(Pt 3):405–411. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.3.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. X., Chen Y. H., Cohen P. T. Polymerase chain reactions using Saccharomyces, Drosophila and human DNA predict a large family of protein serine/threonine phosphatases. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 13;306(1):54–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. T., Brewis N. D., Hughes V., Mann D. J. Protein serine/threonine phosphatases; an expanding family. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81285-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. T. Cloning of protein-serine/threonine phosphatases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:398–408. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Alemany S., Hemmings B. A., Resink T. J., Strålfors P., Tung H. Y. Protein phosphatase-1 and protein phosphatase-2A from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:390–408. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatases come of age. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21435–21438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Foulkes J. G., Holmes C. F., Nimmo G. A., Tonks N. K. Protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 and inhibitor-2 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:427–437. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Cruz e Silva E. F., Hughes V., McDonald P., Stark M. J., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatase 2Bw and protein phosphatase Z are Saccharomyces cerevisiae enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 13;1089(2):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90023-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V., Axton J. M., Barker H. M., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatase 1 activity in Drosophila mutants with abnormalities in mitosis and chromosome condensation. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81434-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V., Axton J. M., Glover D. M., Cohen P. T. Molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of a novel Drosophila protein phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):391–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donella Deana A., Mac Gowan C. H., Cohen P., Marchiori F., Meyer H. E., Pinna L. A. An investigation of the substrate specificity of protein phosphatase 2C using synthetic peptide substrates; comparison with protein phosphatase 2A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Feb 19;1051(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90194-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doonan J. H., Morris N. R. The bimG gene of Aspergillus nidulans, required for completion of anaphase, encodes a homolog of mammalian phosphoprotein phosphatase 1. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):987–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giard D. J., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J., Arnstein P., Kersey J. H., Dosik H., Parks W. P. In vitro cultivation of human tumors: establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1417–1423. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber S. G., Figler R. A., Garrison J. C. Expression and purification of functional G protein alpha subunits using a baculovirus expression system. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1271–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Adams-Pearson C., Maurer F., Müller P., Goris J., Merlevede W., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. alpha- and beta-forms of the 65-kDa subunit of protein phosphatase 2A have a similar 39 amino acid repeating structure. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3166–3173. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. P., Jones C. M., Baille J. P. Characteristics of a human diploid cell designated MRC-5. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):168–170. doi: 10.1038/227168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita N., Ohkura H., Yanagida M. Distinct, essential roles of type 1 and 2A protein phosphatases in the control of the fission yeast cell division cycle. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90173-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Ayres M. D., Possee R. D. Linearization of baculovirus DNA enhances the recovery of recombinant virus expression vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5667–5672. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Structural features in eukaryotic mRNAs that modulate the initiation of translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19867–19870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroczek R. A., Siebert E. Optimization of northern analysis by vacuum-blotting, RNA-transfer visualization, and ultraviolet fixation. Anal Biochem. 1990 Jan;184(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama R., Kanatani H. The centriolar complex isolated from starfish spermatozoa. J Cell Sci. 1981 Jun;49:33–49. doi: 10.1242/jcs.49.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Solomon M. J., Mumby M. C., Kirschner M. W. INH, a negative regulator of MPF, is a form of protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90649-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougall L. K., Campbell D. G., Hubbard M. J., Cohen P. Partial structure and hormonal regulation of rabbit liver inhibitor-1; distribution of inhibitor-1 and inhibitor-2 in rabbit and rat tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 9;1010(2):218–226. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKintosh C., Beattie K. A., Klumpp S., Cohen P., Codd G. A. Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 21;264(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80245-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan C. H., Cohen P. Identification of two isoenzymes of protein phosphatase 2C in both rabbit skeletal muscle and liver. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 3;166(3):713–721. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K. Insect baculoviruses: powerful gene expression vectors. Bioessays. 1989 Oct;11(4):91–95. doi: 10.1002/bies.950110404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T., Giri P. R., Higuchi S., Kincaid R. L. Molecular cloning of a calmodulin-dependent phosphatase from murine testis: identification of a developmentally expressed nonneural isoenzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):529–533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen M. S., Langan T. A., Reeves R. Phosphorylation by cdc2 kinase modulates DNA binding activity of high mobility group I nonhistone chromatin protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19945–19952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura H., Kinoshita N., Miyatani S., Toda T., Yanagida M. The fission yeast dis2+ gene required for chromosome disjoining encodes one of two putative type 1 protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):997–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard A., Capony J. P., Brautigan D. L., Dorée M. Involvement of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A in the control of M phase-promoting factor activity in starfish. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3347–3354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rime H., Huchon D., Jessus C., Goris J., Merlevede W., Ozon R. Characterization of MPF activation by okadaic acid in Xenopus oocyte. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Jan;29(1):47–58. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90023-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronne H., Carlberg M., Hu G. Z., Nehlin J. O. Protein phosphatase 2A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects on cell growth and bud morphogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4876–4884. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Kitagawa Y., Shima H., Irino S., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Production of shorter mRNA for protein phosphatase 2A beta by alternative poly(A) addition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91255-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Nairn A. C. Protein phosphatases: recent progress. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:1–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. D., Walker J. C. Isolation and expression of a maize type 1 protein phosphatase. Plant Physiol. 1991 Oct;97(2):677–683. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.2.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon A. A., Cohen P. T., Stark M. J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein phosphatase 2A performs an essential cellular function and is encoded by two genes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4339–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele F. R., Washburn T., Rieger R., O'Tousa J. E. Drosophila retinal degeneration C (rdgC) encodes a novel serine/threonine protein phosphatase. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):669–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90230-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. A., Hemmings B. A., Cohen P., Goris J., Merlevede W. The MgATP-dependent protein phosphatase and protein phosphatase 1 have identical substrate specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):197–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Immanuel D., Arndt K. T. The SIT4 protein phosphatase functions in late G1 for progression into S phase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2133–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandré D. D., Wills V. L. Inhibition of mitosis by okadaic acid: possible involvement of a protein phosphatase 2A in the transition from metaphase to anaphase. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):79–91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A. J., Bai G., Deans-Zirattu S., Browner M. F., Lee E. Y. Expression of the catalytic subunit of phosphorylase phosphatase (protein phosphatase-1) in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1484–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Cruz e Silva O. B., Cohen P. T. A second catalytic subunit of type-2A protein phosphatase from rabbit skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 21;226(1):176–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80574-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Cruz e Silva O. B., da Cruz e Silva E. F., Cohen P. T. Identification of a novel protein phosphatase catalytic subunit by cDNA cloning. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):106–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80995-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]