Abstract
Irradiation of cells with ultraviolet light (UV) leads to modifications of c-Jun resembling those elicited by phorbol esters or oncogenes, and to enhanced transcription of AP-1-dependent genes. The UV-induced signal also triggers activation of Raf-1 and MAP-2 kinases. A dominant-negative Raf-1 kinase mutant strongly interferes with both phorbol ester and UV-induced AP-1 activation, indicating obligatory involvement of identical components in cytoplasmic signal transduction. Thus, from a presumably nuclear site of energy absorption, a signal needs to be transmitted to the cytoplasm in order to achieve activation of a nuclear transcription factor. Further, signals elicited from different primary sites merge prior to or at the level of activation of Raf-1 kinase.
Full text
PDF

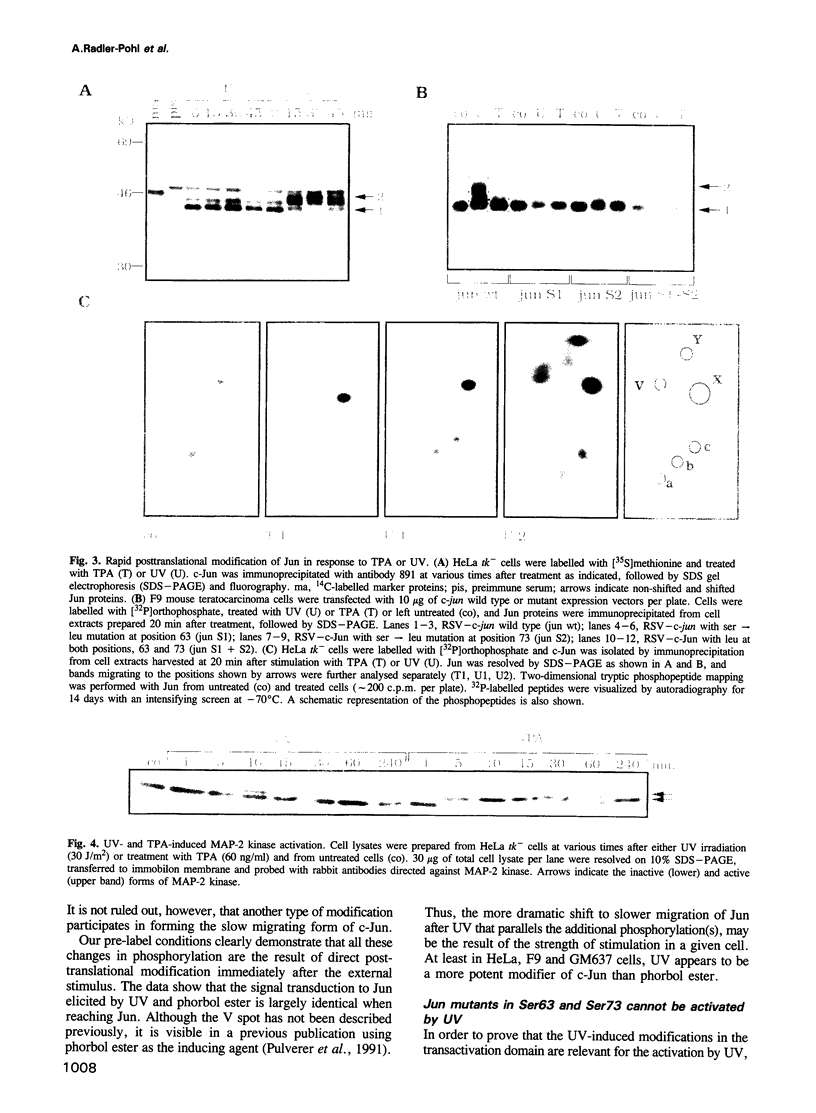
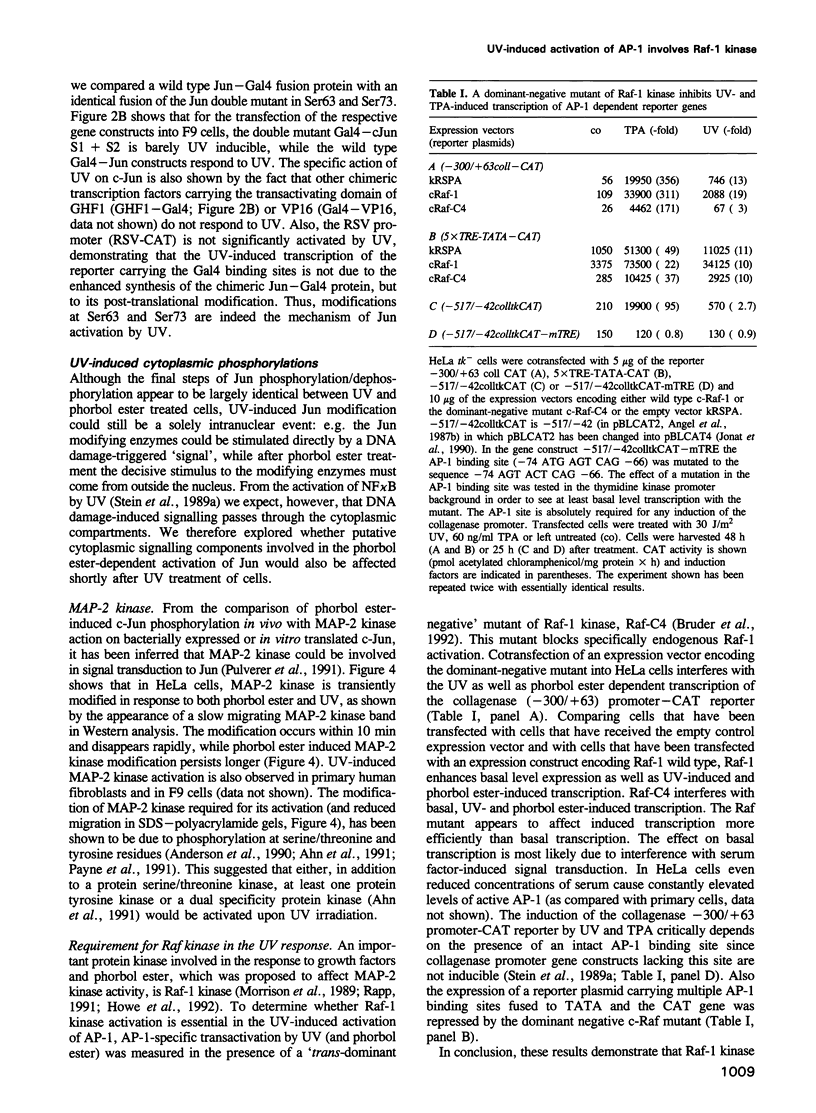
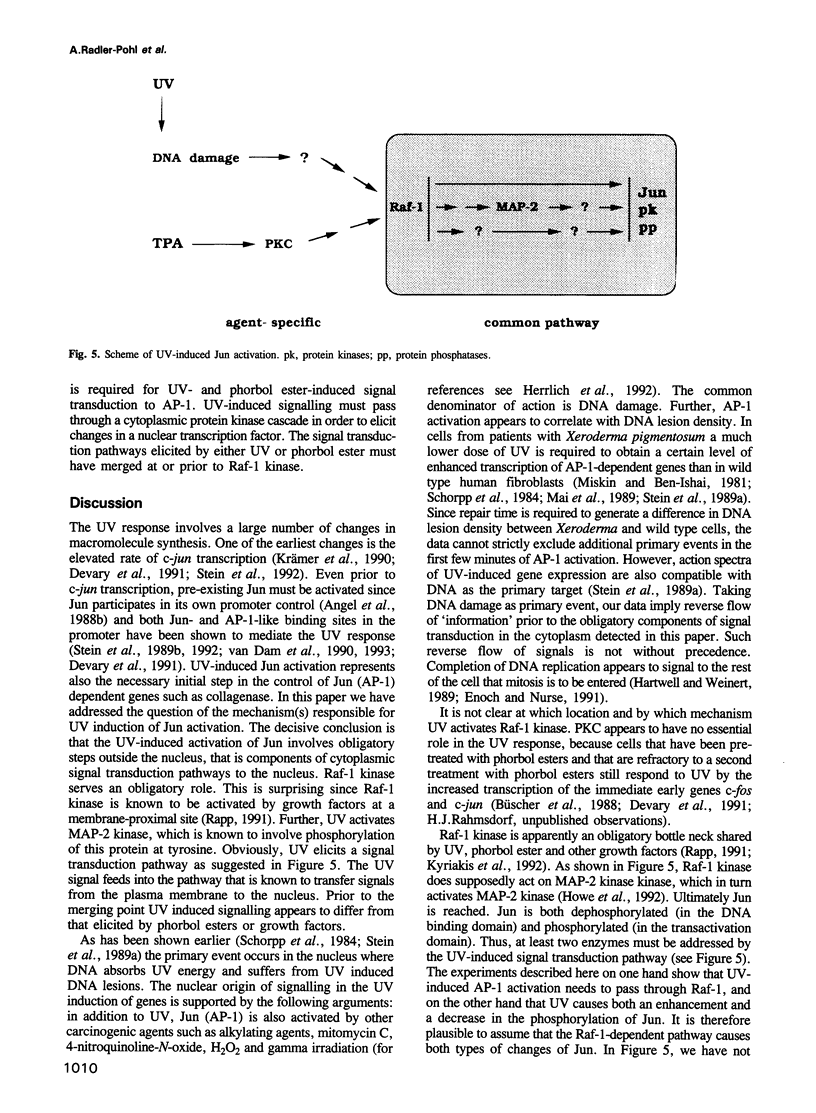


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler V., Polotskaya A., Wagner F., Kraft A. S. Affinity-purified c-Jun amino-terminal protein kinase requires serine/threonine phosphorylation for activity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17001–17005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Bratlien R. L., Diltz C. D., Tonks N. K., Krebs E. G. Multiple components in an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade. In vitro activation of a myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4220–4227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez E., Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Latour D. A., Seth A., Abate C., Curran T., Davis R. J. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15277–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Smeal T., Meek J., Karin M. Jun and v-jun contain multiple regions that participate in transcriptional activation in an interdependent manner. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Kerppola T. K., Luk D., Vandenberg M. T., Marshak D. R., Curran T., Abate C. Jun is phosphorylated by several protein kinases at the same sites that are modified in serum-stimulated fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4694–4705. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binétruy B., Smeal T., Karin M. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):122–127. doi: 10.1038/351122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruder J. T., Heidecker G., Rapp U. R. Serum-, TPA-, and Ras-induced expression from Ap-1/Ets-driven promoters requires Raf-1 kinase. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):545–556. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher M., Rahmsdorf H. J., Litfin M., Karin M., Herrlich P. Activation of the c-fos gene by UV and phorbol ester: different signal transduction pathways converge to the same enhancer element. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):301–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Gordon M. B., Rubino K. L., Sambucetti L. C. Isolation and characterization of the c-fos(rat) cDNA and analysis of post-translational modification in vitro. Oncogene. 1987;2(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Teich N. M. Candidate product of the FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus oncogene: characterization of a 55,000-dalton phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Lau L. F., Karin M. Rapid and preferential activation of the c-jun gene during the mammalian UV response. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2804–2811. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Nurse P. Coupling M phase and S phase: controls maintaining the dependence of mitosis on chromosome replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):921–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90542-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin C. C., Sanchez V., Wagner F., Woodgett J. R., Kraft A. S. Phorbol ester-induced amino-terminal phosphorylation of human JUN but not JUNB regulates transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7247–7251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Weinert T. A. Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):629–634. doi: 10.1126/science.2683079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlich P., Ponta H., Rahmsdorf H. J. DNA damage-induced gene expression: signal transduction and relation to growth factor signaling. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1992;119:187–223. doi: 10.1007/3540551921_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook N. J., Fornace A. J., Jr Response to adversity: molecular control of gene activation following genotoxic stress. New Biol. 1991 Sep;3(9):825–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Tjian R. O-glycosylation of eukaryotic transcription factors: implications for mechanisms of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer M., Stein B., Mai S., Kunz E., König H., Loferer H., Grunicke H. H., Ponta H., Herrlich P., Rahmsdorf H. J. Radiation-induced activation of transcription factors in mammalian cells. Radiat Environ Biophys. 1990;29(4):303–313. doi: 10.1007/BF01210410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H., Ponta H., Rahmsdorf U., Büscher M., Schönthal A., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. Autoregulation of fos: the dyad symmetry element as the major target of repression. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2559–2566. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK2, by p21ras oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):569–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Frost J., Deng T., Smeal T., al-Alawi N., Kikkawa U., Hunter T., Brenner D., Karin M. Casein kinase II is a negative regulator of c-Jun DNA binding and AP-1 activity. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90311-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mai S., Stein B., van den Berg S., Kaina B., Lücke-Huhle C., Ponta H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Kraemer M., Gebel S., Herrlich P. Mechanisms of the ultraviolet light response in mammalian cells. J Cell Sci. 1989 Dec;94(Pt 4):609–615. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.4.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskin R., Ben-Ishai R. Induction of plasminogen activator by UV light in normal and xeroderma pigmentosum fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6236–6240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Müller D., Kurz C., Renz M. Different types of modification in c-fos and its associated protein p39: modulation of DNA binding by phosphorylation. Oncogene Res. 1987;2(1):19–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler T., Angel P. A common intermediary factor (p52/54) recognizing "acidic blob"-type domains is required for transcriptional activation by the Jun proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5508–5515. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Schönthal A., Angel P., Litfin M., Rüther U., Herrlich P. Posttranscriptional regulation of c-fos mRNA expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1643–1659. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R. Role of Raf-1 serine/threonine protein kinase in growth factor signal transduction. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):495–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Baeuerle P. A. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3805–3817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorpp M., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. UV-induced extracellular factor from human fibroblasts communicates the UV response to nonirradiated cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):861–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90421-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D., Grover-Bardwick A., Heidecker G., Rapp U. R., Karin M. Oncoprotein-mediated signalling cascade stimulates c-Jun activity by phosphorylation of serines 63 and 73. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3507–3513. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Angel P., van Dam H., Ponta H., Herrlich P., van der Eb A., Rahmsdorf H. J. Ultraviolet-radiation induced c-jun gene transcription: two AP-1 like binding sites mediate the response. Photochem Photobiol. 1992 Mar;55(3):409–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1992.tb04255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Rahmsdorf H. J., Steffen A., Litfin M., Herrlich P. UV-induced DNA damage is an intermediate step in UV-induced expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, collagenase, c-fos, and metallothionein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5169–5181. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theill L. E., Castrillo J. L., Wu D., Karin M. Dissection of functional domains of the pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):945–948. doi: 10.1038/342945a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N., Jin J. R., Green S., Hollis M., Chambon P. The yeast UASG is a transcriptional enhancer in human HeLa cells in the presence of the GAL4 trans-activator. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90505-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Duyndam M., Rottier R., Bosch A., de Vries-Smits L., Herrlich P., Zantema A., Angel P., van der Eb A. J. Heterodimer formation of cJun and ATF-2 is responsible for induction of c-jun by the 243 amino acid adenovirus E1A protein. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):479–487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05680.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Offringa R., Meijer I., Stein B., Smits A. M., Herrlich P., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J. Differential effects of the adenovirus E1A oncogene on members of the AP-1 transcription factor family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5857–5864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]