Abstract
A psoralen crosslinking assay was utilized to detect localized, unrestrained DNA supercoiling (torsional tension) in vivo in Drosophila chromosomal regions subject to differential transcriptional activity. By comparing rates of crosslinking in intact cells with those in cells where potential tension in chromosomal domains was relaxed by DNA strand nicking, the contribution to psoralen accessibility caused by altered DNA-protein interactions (e.g. nucleosomal perturbations) was distinguished from that due to the presence of unrestrained supercoiling in a region of interest. The heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) genes were wound with a significant level of superhelical tension that remained virtually unaltered whether or not the genes were transcriptionally activated by thermal elevation. Constitutively expressed 18S ribosomal RNA genes also exhibited unrestrained superhelical tension at a level comparable with that across hsp70. In contrast, flanking regions downstream of each of the divergent hsp70 genes at locus 87A7 exhibited substantially less tension. Thus the results point to the existence of stable, torsionally stressed topological domains within eukaryotic chromosomal DNA, suggesting that the relaxing action of topoisomerases is not ubiquitous throughout the nucleus but, in fact, is likely to be tightly regulated.
Full text
PDF

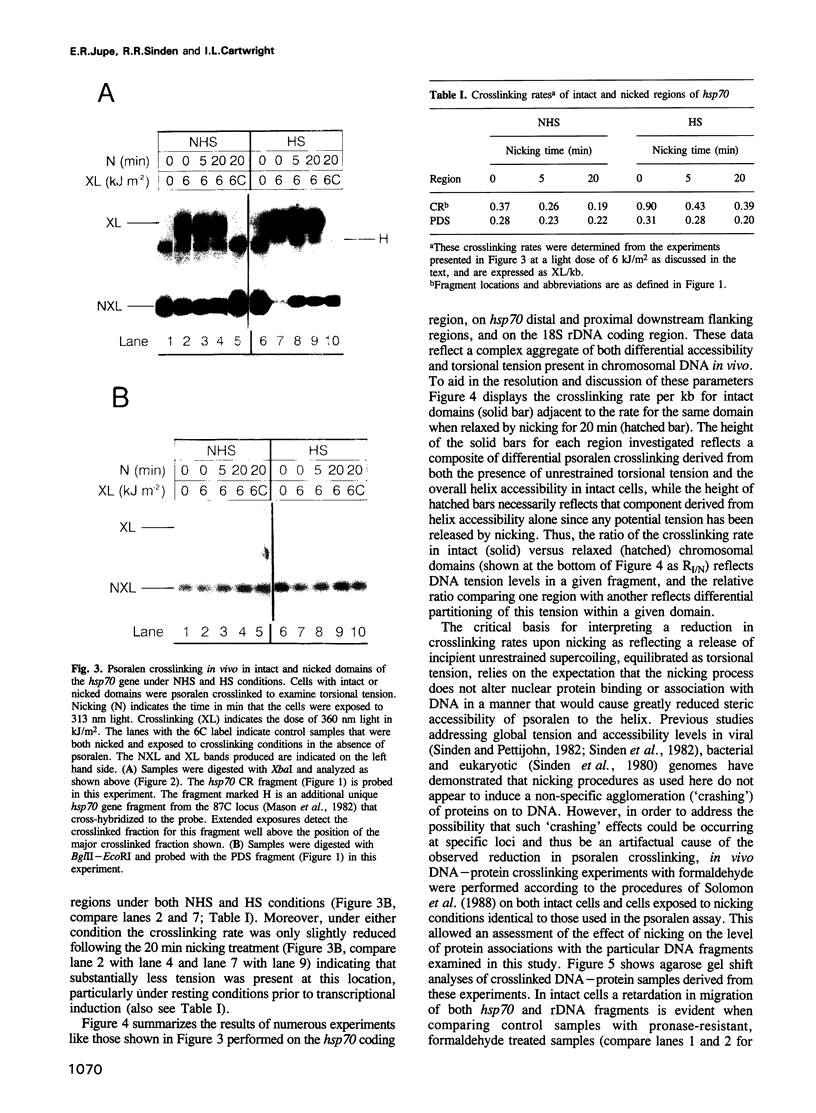
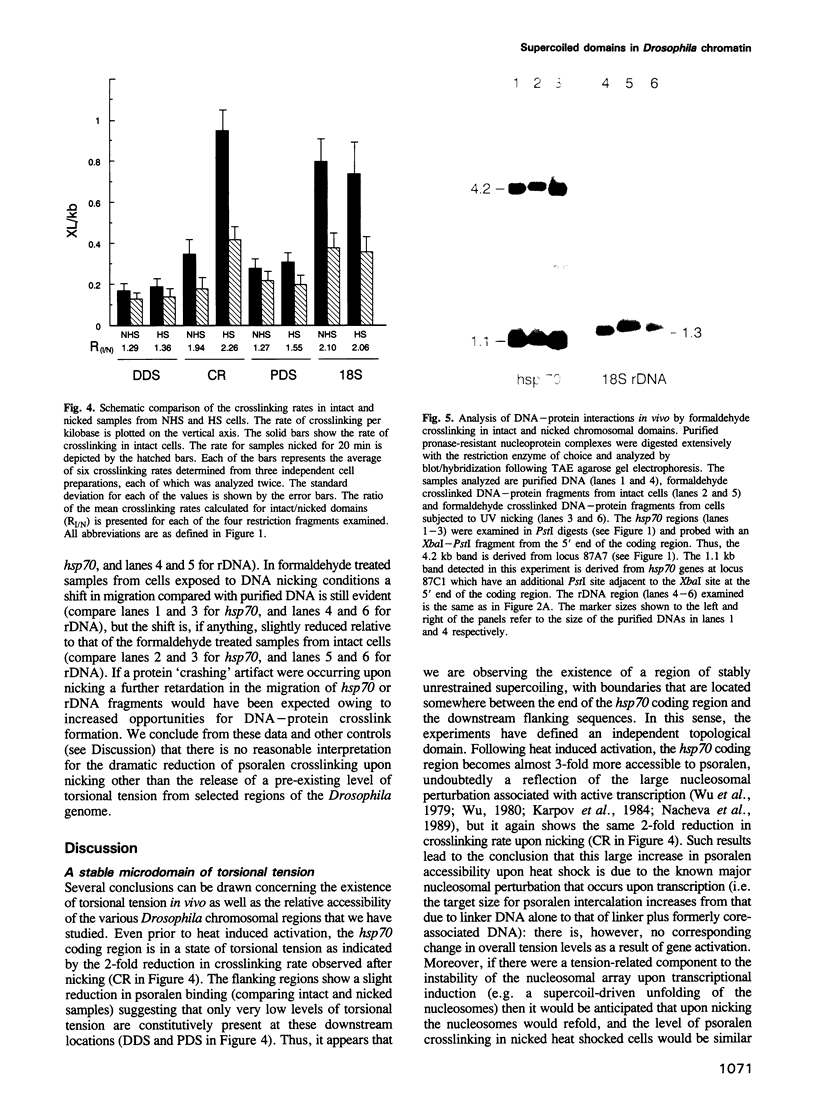




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J., Neilson L., Pellegrini M. Effect of heat shock on ribosome synthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):91–95. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Worcel A. Isolation, characterization, and structure of the folded interphase genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Sternglanz R. Transcription-dependent DNA supercoiling in yeast DNA topoisomerase mutants. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Elgin S. C. Nucleosomal instability and induction of new upstream protein-DNA associations accompany activation of four small heat shock protein genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):779–791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T., Pardue M. L. Cross-linking of DNA with trimethylpsoralen is a probe for chromatin structure. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):631–640. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champlin D. T., Frasch M., Saumweber H., Lis J. T. Characterization of a Drosophila protein associated with boundaries of transcriptionally active chromatin. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1611–1621. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimino G. D., Gamper H. B., Isaacs S. T., Hearst J. E. Psoralens as photoactive probes of nucleic acid structure and function: organic chemistry, photochemistry, and biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1151–1193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Wolffe A. P. Superhelical stress and nucleosome-mediated repression of 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3419–3428. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04906.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. N., Armstrong G. A., Hearst J. E. Induction of anaerobic gene expression in Rhodobacter capsulatus is not accompanied by a local change in chromosomal supercoiling as measured by a novel assay. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4836–4843. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4836-4843.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Conformational constraints in nuclear DNA. J Cell Sci. 1976 Nov;22(2):287–302. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. P., Thompson R. J., Mosig G. Intercalation of psoralen into DNA of plastid chromosomes decreases late during barley chloroplast development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5219–5225. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B., Wellauer P. K., Long E. O. Ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. I. Isolation and characterization of cloned fragments. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):749–768. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Biology of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerases. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):273–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.273-289.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge P., Nordheim A. Transcription-induced conformational change in a topologically closed DNA domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2941–2946. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg J. C., Cartwright I. L., Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Selected topics in chromatin structure. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:485–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito F., Sinden R. R. DNA supercoiling and eukaryotic gene expression. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1988;5:1–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann G., Pflugfelder G., Steiner E. K., Javaherian K., Howard G. C., Wang J. C., Elgin S. C. Drosophila DNA topoisomerase I is associated with transcriptionally active regions of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6958–6962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman L. A., Garrard W. T. DNA supercoiling in chromatin structure and gene expression. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1992;2(2):165–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel A., Axel R. Selective digestion of transcriptionally active ovalbumin genes from oviduct nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Pflugfelder G., Wang J. C., Lis J. T. Topoisomerase I interacts with transcribed regions in Drosophila cells. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M. Two genes for the major heat-shock protein of Drosophila melanogaster arranged as an inverted repeat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):235–252. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Drlica K. Regulation of bacterial DNA supercoiling: plasmid linking numbers vary with growth temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4046–4050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbes T. R., Thorne A. W., Crane-Robinson C. A direct link between core histone acetylation and transcriptionally active chromatin. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1395–1402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igó-Kemenes T., Zachau H. G. Domains in chromatin structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):109–118. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpov V. L., Preobrazhenskaya O. V., Mirzabekov A. D. Chromatin structure of hsp 70 genes, activated by heat shock: selective removal of histones from the coding region and their absence from the 5' region. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellum R., Schedl P. A group of scs elements function as domain boundaries in an enhancer-blocking assay. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2424–2431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellum R., Schedl P. A position-effect assay for boundaries of higher order chromosomal domains. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):941–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90318-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Lutter L. C. The helical periodicity of DNA on the nucleosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4267–4283. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochel T. J., Sinden R. R. Analysis of trimethylpsoralen photoreactivity to Z-DNA provides a general in vivo assay for Z-DNA: analysis of the hypersensitivity of (GT)n B-Z junctions. Biotechniques. 1988 Jun;6(6):532–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger P. E., Rowe T. C. Analysis of topoisomerase I and II cleavage sites on the Drosophila actin and Hsp70 heat shock genes. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 10;31(9):2492–2501. doi: 10.1021/bi00124a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger P. E., Rowe T. C. Interaction of topoisomerase 1 with the transcribed region of the Drosophila HSP 70 heat shock gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8495–8509. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Axel R. Analysis of DNA of isolated chromatin subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard M. W., Patient R. K. Evidence for torsional stress in transcriptionally activated chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6128–6138. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungman M., Hanawalt P. C. Efficient protection against oxidative DNA damage in chromatin. Mol Carcinog. 1992;5(4):264–269. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940050406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungman M., Hanawalt P. C. Localized torsional tension in the DNA of human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6055–6059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Rebbert M. L., Dawid I. B. Nucleotide sequence of the initiation site for ribosomal RNA transcription in Drosophila melanogaster: comparison of genes with and without insertions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1513–1517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. J., Török I., Kiss I., Karch F., Udvardy A. Evolutionary implications of a complex pattern of DNA sequence homology extending far upstream of the hsp70 genes at loci 87A7 and 87C1 in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 25;156(1):21–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani M., Ohta T., Watanabe H., Handa H., Hirose S. Negative supercoiling of DNA facilitates an interaction between transcription factor IID and the fibroin gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):718–722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse R. H., Cantor C. R. Nucleosome core particles suppress the thermal untwisting of core DNA and adjacent linker DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4653–4657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacheva G. A., Guschin D. Y., Preobrazhenskaya O. V., Karpov V. L., Ebralidse K. K., Mirzabekov A. D. Change in the pattern of histone binding to DNA upon transcriptional activation. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90399-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton V. G., Imai B. S., Yau P., Bradbury E. M. Histone acetylation reduces nucleosome core particle linking number change. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90920-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton V. G., Marvin K. W., Yau P., Bradbury E. M. Nucleosome linking number change controlled by acetylation of histones H3 and H4. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19848–19852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T., Lis J. T. RNA polymerase II pauses at the 5' end of the transcriptionally induced Drosophila hsp70 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5285–5290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patient R. K., Allan J. Active chromatin. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;1(3):454–459. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Drlica K. DNA supercoiling and prokaryotic transcription. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90574-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridsdale J. A., Hendzel M. J., Delcuve G. P., Davie J. R. Histone acetylation alters the capacity of the H1 histones to condense transcriptionally active/competent chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5150–5156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougvie A. E., Lis J. T. Postinitiation transcriptional control in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6041–6045. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougvie A. E., Lis J. T. The RNA polymerase II molecule at the 5' end of the uninduced hsp70 gene of D. melanogaster is transcriptionally engaged. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):795–804. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe T. C., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. In vivo localization of DNA topoisomerase II cleavage sites on Drosophila heat shock chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):985–992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz M. C., Brill S. J., Ju Q., Sternglanz R., Reeder R. H. Topoisomerases and yeast rRNA transcription: negative supercoiling stimulates initiation and topoisomerase activity is required for elongation. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1332–1341. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuey D. J., Parker C. S. Bending of promoter DNA on binding of heat shock transcription factor. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):459–461. doi: 10.1038/323459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Carlson J. O., Pettijohn D. E. Torsional tension in the DNA double helix measured with trimethylpsoralen in living E. coli cells: analogous measurements in insect and human cells. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):773–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Pettijohn D. E., Francke B. Organization of herpes simplex virus type 1 deoxyribonucleic acid during replication probed in living cells with 4,5',8-trimethylpsoralen. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4484–4490. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Pettijohn D. E. Torsional tension in intracellular bacteriophage T4 DNA. Evidence that a linear DNA duplex can be supercoiled in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):659–677. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90394-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
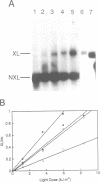
- Sinden R. R., Ussery D. W. Analysis of DNA structure in vivo using psoralen photobinding: measurement of supercoiling, topological domains, and DNA-protein interactions. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:319–335. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12020-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
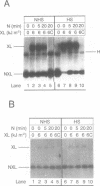
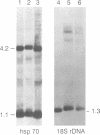
- Sogo J. M., Ness P. J., Widmer R. M., Parish R. W., Koller T. Psoralen-crosslinking of DNA as a probe for the structure of active nucleolar chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):897–919. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Larsen P. L., Varshavsky A. Mapping protein-DNA interactions in vivo with formaldehyde: evidence that histone H4 is retained on a highly transcribed gene. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):937–947. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Groudine M. Transcription elongation and eukaryotic gene regulation. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):777–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. F., Herrera R. E., Nordheim A. Rapid induction of c-fos transcription reveals quantitative linkage of RNA polymerase II and DNA topoisomerase I enzyme activities. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90724-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabuchi H., Hirose S. DNA supercoiling facilitates formation of the transcription initiation complex on the fibroin gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15282–15287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Bird A. Alternative chromatin structure at CpG islands. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90339-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J., Mosig G. Light affects the structure of Chlamydomonas chloroplast chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2625–2631. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., Birley A. J., Lavender J. Histone H4 isoforms acetylated at specific lysine residues define individual chromosomes and chromatin domains in Drosophila polytene nuclei. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90417-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Maine E., Schedl P. The 87A7 chromomere. Identification of novel chromatin structures flanking the heat shock locus that may define the boundaries of higher order domains. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):341–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90408-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Schedl P. Chromatin organization of the 87A7 heat shock locus of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 5;172(4):385–403. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Schedl P. Chromatin structure, not DNA sequence specificity, is the primary determinant of topoisomerase II sites of action in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4973–4984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Giaever G. N. Action at a distance along a DNA. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):300–304. doi: 10.1126/science.3281259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wong Y. C., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: II. Disruption of chromatin structure during gene activity. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. Y., Shyy S. H., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. Transcription generates positively and negatively supercoiled domains in the template. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng G. X., Kochel T., Hoepfner R. W., Timmons S. E., Sinden R. R. Torsionally tuned cruciform and Z-DNA probes for measuring unrestrained supercoiling at specific sites in DNA of living cells. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):107–122. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80208-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]